Abstract
Background
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) in infants is a rare but increasingly reported autoimmune blistering skin disease. Autoantibody reactivity is usually poorly characterized. Current guidelines do not address specific aspects of the infantile form of BP. The objectives of this study are to define clinical and diagnostic characteristics of infantile BP and develop a treatment algorithm.
Methods
Detailed characterization of a current case series of five infants with BP from our departments. Comprehensive analysis of all reported cases (1–12 months) with respect to clinical and laboratory characteristics, treatment and outcome.
Results
In total 81 cases were identified (including our own). The mean age was 4.5 months. Moderately severe and severe disease was seen in 84% of cases. Involvement of hands and feet was present in all cases. Immunofluorescence microscopy was comparable with BP in adults. Where analyzed, the NC16A domain of bullous pemphigoid 180 kDa antigen/collagen XVII (BP180) was identified as the major target antigen. BP180 NC16A ELISA values in our cohort were significantly higher than in a control cohort of 28 newly diagnosed adult patients.
50% of patients were treated with systemic corticosteroids, 20% with a combination of systemic corticosteroids and dapsone or sulfapyridine and 10% with topical corticosteroids alone. 14% of patients needed a combination of multiple immunosuppressants. All but one patient reached remission. Relapses were rare.
Conclusions
Presentation of infantile BP is often severe with blistering of hands and feet present in all cases. Pathogenesis and diagnostic criteria are comparable to adult BP, yet BP180 NC16A ELISA levels seem to be significantly higher in infants. The overall disease outcome is favorable. Based on the results of this study we propose a treatment algorithm for infantile BP.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s13023-014-0185-6) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Bullous skin disease, Skin blistering, Vaccination
Background
Bullous pemphigoid (BP, ORPHA703) is an acquired autoimmune disorder presenting with subepidermal blistering, eosinophilia, and severe itch [1-5]. Its incidence is increasing [6,7] and it mostly affects the elderly; it is considered rare in children [8,9]. The first case of BP in a child was described in 1970 based on immunofluorescence diagnosis [10]; the first case of BP in an infant was described in 1977 [11]. Since then, the number of reported pediatric cases has steadily increased, prompting Nemeth et al. to propose diagnostic criteria for childhood BP [12] which included children and adolescents up to 18 years of age. In 2008, Waisbourd-Zinman et al. noticed different clinical presentations depending on the age of affected children [13]. In a literature review, they showed that the majority of cases of childhood BP occurred in small children under the age of 12 months and that these infants presented with a particular clinical picture. All affected infants had acral involvement with or without generalized blistering. The distribution in later childhood was far less uniform and included a subgroup of children with localized genital BP, a presentation not described in infants. These clinical differences led to the distinction of infantile versus childhood BP [13].
Diagnostic results in infantile and adult BP are similar, but serological tests were not performed systematically in many of the reported cases [13]. The gold standard for diagnosis is direct immunofluorescence microscopy (DIF). However, little information is available on the interpretation of ELISA levels [14], inflammatory markers or blood cell counts in infants. Further knowledge, especially about the relevance of ELISA levels might help to assess disease severity and thus influence the choice of medication or duration of treatment.
Concerning the treatment of infantile BP, first line treatment usually consists of topical or systemic corticosteroids. However, there are no stringent therapeutic criteria and there has been very little discussion on the different options for second line treatment. Furthermore, in clinical consensus guidelines on treatment of BP, there is very little, if any, information on treatment in infants [15-18].
Here, we report the diagnostic results and disease course of five children with infantile BP in our care and a comprehensive analysis of all cases reported in the literature. Based on these data – and taking into account the published guidelines for adults as well as special circumstances of treating small infants – we propose a first treatment algorithm for infantile BP.
Methods
Infantile BP cohort and adult BP control cohort
Five infantile BP patients presented at or were referred to our departments. They were included in this study after we obtained parental informed consent for participation and took blood and skin samples for diagnostic and research purposes. As a control, BP180 NC16A ELISA levels of a cohort of 28 adult BP patients that were newly diagnosed in the same time period were determined after informed consent was provided. All investigations were conducted according to the declaration of Helsinki criteria.
Histopathology, immunofluorescence microscopy, immunoblotting and ELISA
Hematoxylin eosin staining of formalin fixed, paraffin embedded tissue sections was performed using standard methods. DIF and indirect immunofluorescence microscopy (IIF) were performed as previously described [19-21]. FITC labeled antibodies used for DIF were anti human IgG, IgA, IgM and C3c (Dako, Hamburg, Germany) at a dilution of 1:200, 1:50, 1:50 and 1:500 respectively. For IIF on salt-split skin, patient sera were diluted 1:10, secondary antibodies used were FITC labeled anti human IgG and IgA (Dako, Hamburg, Germany) at a dilution of 1:100 and 1:25 respectively. Immunoblotting of normal human keratinocyte extracts with patient sera at a 1:20 dilution and alkaline phosphatase anti human IgG (Sigma-Aldrich, Taufkirchen, Germany) secondary antibody was performed as previously described [20,21]. ELISA kits for the detection of BP180- and bullous pemphigoid 230 kDa antigen (BP230)-specific antibodies (MBL, Nagoya, Japan) were used according to the manufacturer’s protocol with the cut-off at 9 U/ml.
Statistical analysis
Boxplot descriptive statistics of BP180 NC16A ELISA values were performed using GraphPad Prism software (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA).
Literature search
We searched all retrievable English- and foreign-language medical literature using PubMed, PubMed Central, EMBASE, and Google Scholar databases as well as literature cited in the obtained reports. Relevant information was extracted and reviewed to avoid duplications of reports. We included only infants up to 12 months in our review and excluded cases of neonatal BP.
Results
Patient cohort/index case
The clinical and laboratory findings of the five patients in our cohort are presented in Table 1. Patient 1 (index case) showed characteristic infantile BP and was the most severely affected; his treatment proved to be the most challenging. He is therefore presented in more detail. The previously healthy three-month-old boy of Algerian descent presented with a one-week history of small blisters on hands and feet and urticarial plaques on the trunk. Impetigo had been ruled out at a nearby hospital but no diagnosis had been made. He had received one oral vaccination against Rotavirus one month prior. No other vaccinations had been given. Apart from mild eczema, there was no family history of skin disease. Over the course of one week the lesions increased in number and size. The patient was irritable and not feeding well.
Table 1.
Clinical and laboratory findings of the patient cohort
| Age (months)/Gender | Extent of Disease/Hands/Feet (HF) | OM | DIF/IIF/Immunoblot | ELISA | WBC (Eos in%) Thrombocytes | Treatment | Time Until Remission/Relapse/Duration of Treatment | Special aspects | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1) | 3/M | Generalized | + | DIF: IgG, C3 (BM) | Anti BP180 | 10.4 × 109/l (10) | a) Prednisolone | Initially rapid response with disease control | Family history of atopy |
| HF+ | IIF: IgG (BR) | 136 U/ml | At relapse: | 2 mg/kg/d → 1 mg/kg/d | Relapse within 2 weeks after diagnosis on systemic prednisolone (2 mg/kg) and during respiratory tract infection | Rotavirus vaccine | |||
| IB: 180kD pos. | (norm < 9) | 54 × 109/l (52) | b) Dapsone 2 mg/kg/d | Slow response after relapse, need for multiple medications | 4 weeks prior | ||||
| At relapse: | Tc >1000 × 109/l | c) IVIG 1 g/kg × 3 | Response to dapsone after 2.5 weeks | ||||||
| Anti BP180 | d) MMF (2× 600 mg/m2/ d) | Duration of treatment: 8 months | |||||||
| 189 U/ml | |||||||||
| Anti BP230 neg. | |||||||||
| 2) | 3/M | Localized with few disseminated lesions HF+ | - | DIF: IgG, C3 (BM) | Anti BP180 | 16.1 × 109/l (23) | a) Topical Prednicarbate | Good response to topical treatment within days | |
| IIF: IgG (BR) | 90 U/ml | (mid-potency corticosteroid) | No relapse | ||||||
| IB: 180kD pos. | (norm < 9) | Duration of treatment: 4 weeks | |||||||
| Anti BP230 neg. | |||||||||
| 3) | 4/M | Generalized | - | DIF: IgG, C3 (BM) | Anti BP180 | 23.4 × 109/l (20) | a) Prednisolone | Complete remission within 1 week | Vaccination 4 weeks prior |
| HF+ | IIF: IgG (BR) | 156 U/ml | 2 mg/kg/d → 1 mg/kg/d | Weaning of steroids within 3 months | (DPTP, HiB, HepB, Rotavirus) | ||||
| IB: 180kD pos. | (norm < 9) | b) Dapsone 1.5 mg/kg/d | No relapse | ||||||
| Anti BP230 neg. | Duration of treatment: 6 months | ||||||||
| 4) | 3/F | Generalized | - | DIF: IgG, C3 (BM) | Anti BP180 | 25.1 × 109/l (13) | a) Prednisolone | Slow response to prednisolone 1 mg/kg | Rotavirus vaccine |
| HF+ | IIF: IgG (BR) | 125U/ml | Tc 860 × 109/l | 2 mg/kg/d → 1 mg/kg/d | Rapid response to oral betamethasone 0.3 mg/kg/d | 4 weeks prior | |||
| IB: 180kD pos. | (norm < 9) | b) Systemic betamethasone | No relapse upon glucocorticoid tapering | Arterial hypertension | |||||
| Anti BP230 neg. | 0.3 mg/kg/d | Complete remission under dapsone 0.5 mg/kg/d | Myocardial hypertrophy | ||||||
| c) Dapsone | Treatment ongoing | → Propranolol | |||||||
| 1 mg/kg/d → 0.5 mg/kg/d | |||||||||
| 5) | 7/M | Generalized | - | DIF: IgG, C3 (BM) | Anti BP180 | 27.3 × 109/l (9) | a) Prednisolone 1 → 0.5 mg/kg/d | Rapid response to oral betamethasone | |
| HF+ | IIF: IgG (BR) | 154 U/ml | Tc 599 × 109/l | b) Systemic betamethasone | Full remission after 2 months | ||||
| IB: 180kD pos. | (norm < 9) | 0.4 mg/kg/d → 0.2 mg/kg/d | No relapse | ||||||
| Anti BP230 neg. | c) Dapsone 0.5 mg/kg/d | Treatment ongoing |
HF: Hands/Feet + present, − not present; OM: Involvement of oral mucosa; + present, − not present; DIF: Direct immunofluorescence microscopy; IIF: Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy; IB: Immunoblot; BM: basement membrane; BR: Blister roof; WBC White blood cell count; Eos: eosinophil granulocytes; Tc: thrombocytes; DPTP: Diphteria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Poliovirus; HiB: Haemophilus influenzae type b; HepB: Hepatitis B.
Generalized disease = Moderately severe and severe disease.
On clinical examination, he had firm blisters and bullae predominantly on the hands and feet, as well as urticarial plaques with an elevated rim and a dusky center. These plaques were predominantly located on the trunk but also present on all other areas of the body (Figure 1A, B). The Nikolsky sign was negative; there were no mucosal lesions.
Figure 1.
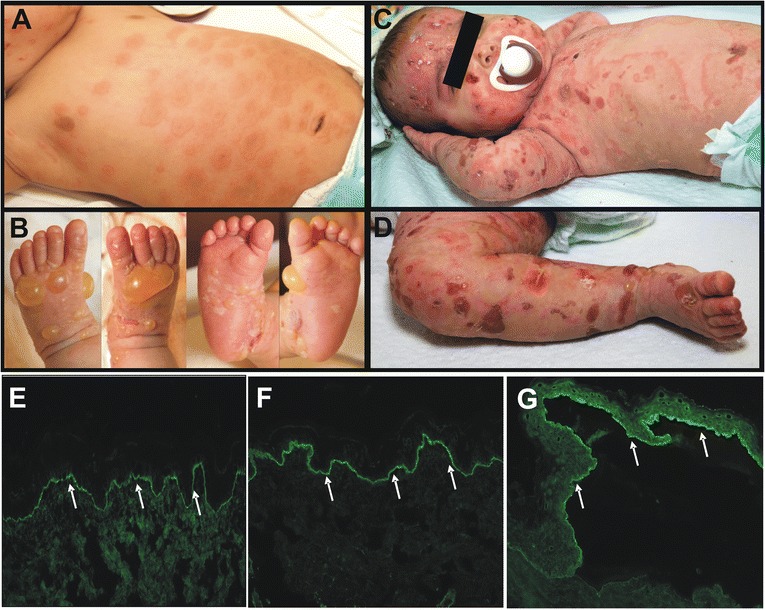
Clinical and diagnostic hallmarks of infantile BP. Patient 1 at initial presentation: A, urticarial plaques on the trunk. B, firm blisters and bullae on the hands and feet. C, D, Patient 1 after relapse with severe blistering on 2 mg/kg prednisolone daily. Direct immunofluorescence microscopy: E, linear IgG and F, linear C3c depositions along the basement membrane zone (white arrows, 200× original magnification). G, indirect immunofluorescence on salt-split skin reveals circulating IgG antibodies that bind to the blister roof, which is diagnostic for BP (white arrows, 200× original magnification).
Blister fluid microscopy demonstrated mainly eosinophil granulocytes; cultures from blister fluid remained sterile. Blood testing, including a full blood count, showed normal values with the exception of a peripheral eosinophilia of 10%. Punch biopsies were performed for histologic and immunofluorescence analyses. Histology showed dermal edema and eosinophil inflammatory infiltrate (not shown). DIF revealed linear staining of IgG (Figure 1E) and complement component C3 (Figure 1F) along the basement membrane zone. IIF microscopy showed circulating IgG autoantibodies binding to the epidermal side of the salt-split skin (Figure 1G). ELISA testing with recombinant NC16A domain of BP180 was strongly positive (136 U/ml, norm <9 U/ml). The findings were diagnostic for BP.
Initially, we treated with potent topical corticosteroids and oral antihistamines, which did not lead to significant improvement. After confirmation of the diagnosis, a treatment with prednisolone up to 2 mg/kg/day was initiated. After a brief period of clinical improvement and disease control, the patient had a respiratory tract infection in the course of which he developed severe blistering. At this time he was still on 2 mg/kg prednisolone daily (Figure 1C, D). Peripheral blood count showed leucocytosis with a maximum of 54 G/l (52% eosinophils) and significant reactive thrombocytosis (>1000 G/l) with signs of increased coagulation activity necessitating treatment with acetylsalicylic acid. The ELISA value for BP180-specific antibodies at this point was 189 U/ml. After confirming normal glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase levels, we added dapsone at a maximum dose of 2 mg/kg daily, controlling for the development of methemoglobinemia. As the blistering continued to progress, we added intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) 1 g/kg three times. Yet the patient developed more cutaneous and additionally intraoral blisters causing refusal of oral intake. He also developed persistent hoarseness, but laryngeal involvement of the BP could be excluded.
After two weeks of worsening, we added oral mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) at a dose of 625 mg/m2 twice daily (MMF local dosing regimen, note that recommended standard dose in children is 600 mg/m2 twice daily). Within days, the patient’s skin improved and the number of new lesions decreased. We interpreted this improvement as delayed response to dapsone rather than response to MMF, which usually takes several weeks to set in. Over the following weeks, we slowly weaned the patient off systemic corticosteroids and then reduced the MMF dose in two steps over two months. After another two months of clinical remission, we also stopped treatment with dapsone. After 12 months the patient was off all medication. Anti-BP180 antibody values significantly decreased over the course of three months, parallel to clinical improvement. Also, the number of leukocytes (including eosinophils) and thrombocytes decreased and normalized. At the time of submission, the patient had been free of symptoms for two years. Due to parental fear of relapse, the patient had not received any further vaccinations.
Analysis of all reported infantile BP cases, including own patient cohort
Clinical characteristics
The literature review of all obtainable reports between the years 1977 and 2013 including our own cases revealed 53 reports [8,11-14,22-68] with a total of 81 cases of BP occurring in children within the first year of life but beyond the neonatal period (Additional file 1: Table S1). While very few cases were reported before the year 2000, there has been a significant increase since then (Additional file 2: Figure S1). The mean and median age was approximately four months with 64% of cases between three to five months. The gender ratio male to female was 39 to 38. In four cases gender was not stated. Moderately severe and severe (generalized) disease (>10% body surface area – BSA) was seen in 83.9% of cases (n = 68 of 81). All children showed at least some involvement of the hands and feet. Mucosal blistering was present in 14.8% of cases (n = 12 of 81); four of these patients had severe disease (Table 2).
Table 2.
Clinical characteristics of all reported infantile BP cases, including own patient cohort
| No of cases | N = 81 | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Mean (median) age/age range | 4.5 (4) months/1–12 months | |
| Gender M/F | 39/38 (4 unknown) | |
| Extent of skin in involvement | ||
| • Localized/mild disease (+/− few disseminated plaques) | N = 10 (12.3%) | |
| • Generalized/moderately severe and severe disease | N = 68 (83.9%) | |
| • N/A | N = 3 (3.7%) | |
| • Involvement of hands and feet | N = 81 (100%) | |
| Involvement of oral mucosa (with generalized disease) | N = 12 (14.8%) | All children with oral lesions had generalized skin involvement |
| Severe disease N = 5 | ||
| No of children vaccinated prior to onset | N = 25 (30.8%) | Latency between vaccination and onset of disease: 1 day - 4 weeks |
| • DPTP +/− others, | N = 22 | |
| • Rotavirus, | N = 2 | |
| • DPTP plus Rotavirus | N = 1 | |
| No of patients with a relapse | N = 12 (14.8%) | |
| Outcome | ||
| • Cured | N = 76 (93.8%) | Patient had congenital immune deficiency |
| • In remission under treatment at time of report | N = 3 (3.7%) | |
| • Still symptomatic at time of report | N = 1 (1.2%) | |
| • Death | N = 1 (1.2%) |
N/A: Not Available; DPTP: Diphteria, Pertussis, Tetanus, Poliovirus.
98% (n = 79 of 81) of children affected had previously been healthy. One patient had a congenital T-cell lymphocytopenia and one child had been diagnosed with Hyper IgE-syndrome. The general condition at the time of presentation was good in the majority of cases; some patients were irritable, likely due to pruritus. However, one child with a very delayed initiation of appropriate treatment presented with significant morbidity, including severe weight loss, dehydration and failure to thrive, as well as developmental delay [41]. One of our own patients was also severely affected during a relapse where he refused oral intake and lost weight (see index case above). Both children improved quickly once sufficient treatment was established.
Twenty five children (30.8%) had been vaccinated within days or weeks prior to the onset of disease, the majority with the standard mix of passive vaccines recommended in this age group. Two of our five own cases had received a newly recommended oral vaccine against Rotavirus prior to the onset of disease. This has not been reported before. In two children a febrile infection was reported prior to the onset of disease [37] or prior to a relapse [27], this report.
Pathophysiology and diagnostic features
Histology, if reported, showed dermal edema, an inflammatory infiltrate dominated by eosinophils and subepidermal blistering. DIF showed IgG and/or C3 along the basement membrane in 72 cases (90%), in 12 cases (15%) there were additional IgA deposits, in four cases there were IgM- and in one case IgE-deposits. In immunoblot analyses reported in 20 patients, 15 sera recognized a 180 kDa protein, five sera recognized a 230 kDa protein, and one serum both.
ELISA values were reported in only 21 (25.9%) cases. All of these patients had antibodies against the NC16A-domain of BP180; two also had additional anti-BP 230 antibodies. Comparison of ELISA values of reported cases from different centers is not fully possible because of different commercial and non-commercial ELISA systems used. In our own cohort, BP180 NC16A ELISA values in infantile patients were significantly higher than in a control group of 28 adults newly diagnosed with BP in our center in the same time period (Figure 2). Extremely high values in our cohort and in reported patients seemed to be associated with more extensive disease and the need for systemic treatment.
Figure 2.
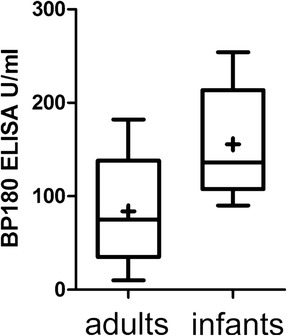
ELISA values in infantile and adult BP. Anti-BP180 ELISA values in our infantile BP cohort were significantly higher, compared to a control group of newly diagnosed adult BP patients (normal value <9 U/ml; boxplot analysis; whiskers: minimum and maximum values; bottom and top of boxes: first and third quartiles; band inside box: median; cross: mean).
A blood cell count was reported in 37 patients, the mean white blood cell count was 23.9 G/l (range <10-120G/l, median 19.4). The percentage of eosinophils had a mean of 23% (range 7-66%, median 19%).
Treatment modalities
The majority of patients were treated with systemic corticosteroids (50.6%) with or without additional erythromycin or other antibiotics. 19.8% of patients were treated with a combination of systemic corticosteroids and dapsone or sulfapyridine, and 9.9% were treated with topical corticosteroids alone. 13.7% of patients (n = 11) needed a combination of multiple agents (Table 3). All but one patient reached remission eventually. However, the patient with concomitant congenital T-cell lymphocytopenia died from unknown cause three months after having received two doses of rituximab for severe disease. Relapses were not common (14.8%, n = 12) (Table 3 and Additional file 3: Table S2).
Table 3.
Treatment Modalities of Infantile BP Patients
| Treatment | No of cases (% of total N = 81) | Comments |
|---|---|---|
| Topical corticosteroids alone | N = 8 (9.9%) | Good response |
| Topical corticosteroids + IVIG | N = 1 (1.2%) | Several relapses for one year |
| Topical corticosteroids + erythromycin | N = 1 (1.2%) | Good response |
| Systemic +/− topical corticosteroids (+/− antibiotics) | N = 41 (50.6%) | Good response |
| Systemic corticosteroids + dapsone/ sulphapyridin (+/− antibiotics) | N = 16 (19.8%) | Good response |
| Dapsone/ sulphapyridin alone | N = 2 (2.5%) | One relapse under treatment. Same treatment was attempted in one other patient without success, so steroids were added. |
| No treatment | N = 1 | |
| N/A | N = 1 | |
| Corticosteroids +/− dapsone plus other medications due to poor response | N = 11 (13.7%) | |
| • Azathioprine | N = 1 | No response |
| • Cyclosporine | N = 2 | Good response in N = 1 Partial response in N = 1 |
| • Mycophenolate mofetil | N = 7 | Moderate response in N = 7 |
| • Erythromycin and nicotinamide | N = 8 | Good response in N = 3 Partial / uncertain response in N = 5 |
| • IVIG | N = 8 | Good response in N = 2 Partial/ uncertain response in N = 6 |
| • Rituximab | N = 3 | Good response N = 2. Partial response N = 1. One sudden death in one of those two patients after three months (child had congenital immune deficiency). |
| • Omalizumab | N = 1 | Good response |
IVIG: Intravenous immunoglobulins.
Discussion
Infantile BP is considered very rare. Prospective studies are therefore difficult to perform. Incidence in Israel was estimated to be 2.36:100,000 per year [13]; however, in most countries no central registry exists and the disease might be under-recognized. We present a detailed characterization of a current cohort of five infants with BP from our departments. Furthermore we performed a comprehensive analysis of all cases reported in the literature (age 1–12 months) with respect to clinical and laboratory characteristics and treatment modalities. Taken together the results allow for the following conclusions.
Diagnostic features
Laboratory test results in infantile BP generally resemble those in adult BP. Linear IgG and/or C3 depositions at the basement membrane in DIF are the diagnostic hallmark. Autoantibody profiles, as detected by various methods, are comparable to those in adults with BP [69]: autoantibodies against the NC16A domain of BP180 are more frequent than anti-BP230 antibodies.
We propose the following minimal diagnostic criteria for infantile BP: typical clinical picture (urticarial plaques and blisters, acral distribution) and linear IgG and/or C3 deposition at the basement membrane in DIF. Further diagnostic pointers are the presence of serum autoantibodies against BP180 and/or BP230. and – even though less specific – subepidermal blistering with an eosinophil rich inflammatory infiltrate in conventional histology.
Even though ELISA results were only reported in a minority of cases, and different test systems used do not allow for direct comparison, the reported autoantibody levels in infants seem fairly high. Comparing ELISA values of our five infants with a control group of 28 adults newly diagnosed with BP in our center in the same time period, we found that the mean and median levels of anti-BP180 NC16A antibody levels in infants were significantly higher. These ELISA values had been measured with the same test system (see Methods).
The clinical relevance of antibody testing in infantile BP has been contested [14]. Nevertheless – when tested – patients with a more recalcitrant disease course demonstrated high autoantibody levels. In our cohort, higher values at presentation correlated with the need for more aggressive and longer-term treatment, and values increased before relapses. Therefore, it appears reasonable to take into account the levels of BP180-specific autoantibodies in infantile BP when making treatment decisions.
Patient characteristics/clinical features
At disease onset, the mean age of children was around four months. As opposed to previous reports [13], there was no significant female predominance.
No common trigger was identified. A large number of patients had either been vaccinated or suffered an infection prior to the onset or relapse of disease (Table 2, Additional file 1: Table S1 and Additional file 3: Table S2). The type of infection or vaccine varied. It can be speculated that a modulation of the immune system might play a role in triggering or unmasking an underlying subclinical BP. Nevertheless, especially due to the high number of infants receiving vaccination, this association might be purely coincidental and we believe that the term postvaccination infantile BP should be used with caution.
Cases of adult BP associated with malignancy exist, even though the causal relation remains unclear. In contrast, no case of infantile BP in relation with a malignant neoplasm has been reported. Furthermore, unlike in adult BP [70,71], drugs do not seem to play a major role in triggering infantile BP.
Within the age group of four weeks to 12 months, the clinical picture was moderately severe to severe (generalized) in over 80% of cases. Acral blistering was present in all children, while mucosal involvement was uncommon. In localized disease, hands and feet were usually affected. There was no case of isolated genital infantile BP. Taken together, involvement of the hands and feet can be considered as a clinical hallmark and diagnostic clue of infantile BP. This is in contrast to childhood and adult BP [1,4,69]. Important differential diagnoses of infantile BP are listed in Table 4.
Table 4.
Important Differential Diagnoses of Infantile BP
| Autoimmune blistering skin diseases | • Linear IgA dermatosis |
| • Epidermolysis bullosa acquisita | |
| Hereditary | • Epidermolysis bullosa |
| • Porphyria | |
| Infectious | • Bullous impetigo |
| Others | • Pompholyx |
| • Bullous mastocytosis | |
| • Insect bites | |
| • Insect bite like reaction of hematologic malignancy |
Most infants were doing well at the time of presentation despite some irritability, likely due to pruritus. However, individual children with significant morbidity including difficulty breathing and feeding, and weight loss, have been reported.
Even though initial presentation is often severe, the prognosis of infantile BP is excellent, with all but one patient reaching complete remission. That child had only been followed up short-term at the time of publication [8] and subsequent remission is possible. One infant passed away shortly after having been discharged from hospital. This child had received several doses of rituximab and had an underlying immune deficiency, which might have played a role.
The number of relapses was low. It seems that relapses can be triggered by infections or that they occurred in patients where tapering of corticosteroids was started early. Also, relapses were more frequent in patients who did not receive systemic corticosteroids (Additional file 3: Table S2). Once the disease has been controlled for several months, the likelihood of a relapse is extremely small.
Treatment algorithm
In contrast to adult BP, no treatment guidelines for infantile BP exist [15-18,72], and there has been little discussion on possible criteria for choosing the right treatment. After a comprehensive analysis of reported treatments in all published cases of infantile BP – together with lessons learned from our own cohort – we propose a first treatment algorithm. This step-by-step diagnostic and treatment algorithm takes into account disease severity, response to initial treatment and specific practical aspects of steroid sparing agents. It is based on general experience with the different medications in infants and the treatment recommendations published for adult BP (Figure 3).
Figure 3.
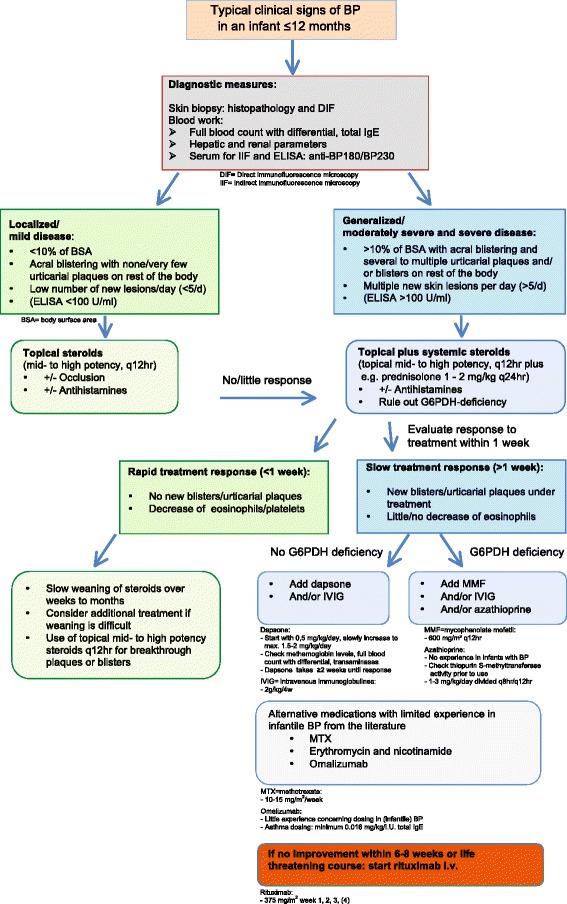
Step-by-step diagnostic and treatment algorithm. The algorithm was developed taking into account disease severity, response to initial treatment and specific aspects of steroid sparing agents.
After the diagnosis is established, all patients should receive treatment with mid- to high-potency topical corticosteroids. Children with moderately severe or severe disease (generalized, >10% BSA) usually require additional treatment with systemic corticosteroids. If the treatment response is slow or high doses of corticosteroids are needed for disease control, additional steroid sparing agents should be considered. Dapsone seems to be the agent of choice as it is usually well tolerated, effective, and is frequently used for other autoimmune blistering diseases of infancy and childhood, such as linear IgA dermatosis. Other steroid sparing agents used are IVIGs and MMF. Little or no experience exists for erythromycin-, methotrexate-, cyclophosphamide or azathioprine treatment in infants with BP. Rituximab is to be reserved as rescue treatment for the most severe cases [49,67]. The full potential and dosing of omalizumab in infantile BP warrant further investigation [56,73].
After clinical remission for several months, treatment discontinuation can be considered. In our experience ELISA autoantibody values can take a long time to normalize and are therefore not always helpful for deciding when to end treatment.
Conclusions
Infantile BP is considered a rare disorder; however an increasing number of reports during the last years show that it might have been under-recognized. As the disorder is not well known to general pediatricians and dermatologists, most infants are not promptly diagnosed and undergo multiple examinations before establishment of the correct diagnosis.
Infantile BP presents with urticarial plaques and blisters. Involvement of hands and feet is present in all cases. The clinical picture of infantile BP is characteristic. It is therefore a realistic aim to make the diagnosis early, avoid unnecessary diagnostic measures, and treat appropriately to avoid severe morbidity.
Pathogenesis and diagnostic criteria are comparable to adult BP, yet ELISA levels seem to be higher in infants. The overall disease outcome is favorable. Based on the results of this study we have established a first step-by-step diagnostic and treatment algorithm, taking into account disease severity, response to initial treatment and specific aspects of steroid sparing agents.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patients and their families for participating in this study. We would further like to thank A. Bedorf and K. Thoma for expert technical assistance. The article processing charge was funded by the German Research Foundation (DFG) and the Albert Ludwigs University Freiburg in the funding program Open Access Publishing.
Abbreviations
- BP
Bullous pemphigoid
- BP180
Bullous pemphigoid 180 kDa antigen/collagen XVII
- BP230
Bullous pemphigoid 230 kDa antigen
- BSA
Body surface area
- DIF
Direct immunofluorescence microscopy
- IIF
Indirect immunofluorescence microscopy
- IVIG
Intravenous immunoglobulins
- MMF
Mycophenolate mofetil
Additional files
All cases of infantile BP in the literature and this study.
The number of published infantile BP cases has significantly increased since 2000.
Relapses of infantile BP.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
ASB and JSK conceptualized and designed the study, collected and analyzed the entire data, drafted the manuscript and approved the final manuscript as submitted. CM, HO, BM, FS and DK contributed clinical data, helped with data analysis and approved the final manuscript as submitted. ES and CS contributed diagnostic data, helped with data analysis and approved the final manuscript as submitted. All the authors revised and accepted the final version of the manuscript.
Contributor Information
Agnes Schwieger-Briel, Email: agnes.schwieger@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Cornelia Moellmann, Email: cornelia.moellmann@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Birgit Mattulat, Email: Birgit.Mattulat@af-k.de.
Franziska Schauer, Email: franziska.schauer@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Dimitra Kiritsi, Email: dimitra.kiritsi@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Enno Schmidt, Email: Enno.Schmidt@uk-sh.de.
Cassian Sitaru, Email: cassian.sitaru@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
Hagen Ott, Email: h.ott@KKH-Wilhelmstift.de.
Johannes S Kern, Email: johannes.steffen.kern@uniklinik-freiburg.de.
References
- 1.Schmidt E, Zillikens D. Pemphigoid diseases. Lancet. 2013;381:320–332. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(12)61140-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di Zenzo G, Della Torre R, Zambruno G, Borradori L. Bullous pemphigoid: from the clinic to the bench. Clin Dermatol. 2012;30:3–16. doi: 10.1016/j.clindermatol.2011.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Murrell DF, Daniel BS, Joly P, Borradori L, Amagai M, Hashimoto T, Caux F, Marinovic B, Sinha AA, Hertl M, Bernard P, Sirois D, Cianchini G, Fairley JA, Jonkman MF, Pandya AG, Rubenstein D, Zillikens D, Payne AS, Woodley D, Zambruno G, Aoki V, Pincelli C, Diaz L, Hall RP, Meurer M, Mascaro JM, Jr, Schmidt E, Shimizu H, Zone J, et al. Definitions and outcome measures for bullous pemphigoid: recommendations by an international panel of experts. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2012;66:479–485. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2011.06.032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kneisel A, Hertl M. Autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Part 1: clinical manifestations. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:844–856. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07793.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Yeh SW, Ahmed B, Sami N, Razzaque Ahmed A. Blistering disorders: diagnosis and treatment. Dermatol Ther. 2003;16:214–223. doi: 10.1046/j.1529-8019.2003.01631.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Langan SM, Smeeth L, Hubbard R, Fleming KM, Smith CJP, West J. Bullous pemphigoid and pemphigus vulgaris–incidence and mortality in the UK: population based cohort study. BMJ. 2008;337:a180. doi: 10.1136/bmj.a180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Joly P, Baricault S, Sparsa A, Bernard P, Bédane C, Duvert-Lehembre S, Courville P, Bravard P, Rémond B, Doffoel-Hantz V, Bénichou J. Incidence and mortality of bullous pemphigoid in France. J Invest Dermatol. 2012;132:1998–2004. doi: 10.1038/jid.2012.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Fisler RE, Saeb M, Liang MG, Howard RM, McKee PH. Childhood bullous pemphigoid: a clinicopathologic study and review of the literature. Am J Dermatopathol. 2003;25:183–189. doi: 10.1097/00000372-200306000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lara-Corrales I, Pope E. Autoimmune blistering diseases in children. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2010;29:85–91. doi: 10.1016/j.sder.2010.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bean SF, Good RA, Windhorst DB. Bullous pemphigoid in an 11-year-old boy. Arch Dermatol. 1970;102:205–208. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1970.04000080077015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gould WM, Zlotnick DA. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy: a case report. Pediatrics. 1977;59:942–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Nemeth AJ, Klein AD, Gould EW, Schachner LA. Childhood bullous pemphigoid. Clinical and immunologic features, treatment, and prognosis. Arch Dermatol. 1991;127:378–386. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1991.01680030098014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Waisbourd-Zinman O, Ben-Amitai D, Cohen AD, Feinmesser M, Mimouni D, Adir-Shani A, Zlotkin M, Zvulunov A. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy: clinical and epidemiologic characteristics. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2008;58:41–48. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Brazzelli V, Grasso V, Bossi G, Borroni G: Is there a role for the detection of autoantibodies in the clinical practice of treating infants with bullous pemphigoid? A case report.Pediatr Dermatol 2013. [Epub ahead of print]. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 15.Wojnarowska F, Kirtschig G, Highet AS, Venning VA, Khumalo NP, British Association of Dermatologists Guidelines for the management of bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 2002;147:214–221. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2133.2002.04835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Bernard P, Bedane C, Prost C, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Joly P, Centres de référence des maladies bulleuses auto-immunes. Société Française de Dermatologie [Bullous pemphigoid. Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment]. Centres de référence des maladies bulleuses auto-immunes. Société Française de Dermatologie] Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2011;138:247–251. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2011.01.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Kirtschig G, Middleton P, Bennett C, Murrell DF, Wojnarowska F, Khumalo NP. Interventions for bullous pemphigoid. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;6(10):CD002292. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD002292.pub3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Fuertes De Vega I, Iranzo-Fernández P, Mascaró-Galy JM. Bullous pemphigoid: clinical practice guidelines. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2014;105:328–346. doi: 10.1016/j.ad.2012.10.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Sitaru C, Schmidt E, Petermann S, Munteanu LS, Bröcker E-B, Zillikens D. Autoantibodies to bullous pemphigoid antigen 180 induce dermal-epidermal separation in cryosections of human skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2002;118:664–671. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.2002.01720.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Kern JS, Gehring W, Kreisel W, Hertl M, Technau-Hafsi K, Bruckner-Tuderman L, Hofmann SC. Overlap of IgA pemphigus and linear IgA dermatosis in a patient with ulcerative colitis: a mere coincidence? Acta Derm Venereol. 2014;94(2):228–230. doi: 10.2340/00015555-1658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Hofmann SC, Voith U, Sasaki T, Trüeb RM, Nischt R, Bruckner-Tuderman L. The autoantigen in anti-p200 pemphigoid is synthesized by keratinocytes and fibroblasts and is distinct from nidogen-2. J Invest Dermatol. 2008;128:87–95. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700952. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Marsden RA, McKee PH, Bhogal B, Black MM, Kennedy LA. A study of benign chronic bullous dermatosis of childhood and comparison with dermatitis herpetiformis and bullous pemphigoid occurring in childhood. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1980;5:159–176. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1980.tb01684.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Hernández-Aguado I, Sánchez-Pedreño-Guillén P, Moreno-Giménez JC, Camacho-Martínez F. [Bullous pemphigoid in a 5-month-old infant] Med Cutan Ibero Lat Am. 1982;10:391–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Marsden RA. Bullous pemphigoid in a child. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1983;8:329–332. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1983.tb01788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Tani M, Tani M, Komura A, Murata Y. Bullous pemphigoid of childhood: report of a case and immunoelectron microscopic studies. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1988;19(2 Pt 1):366–367. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(88)80259-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Oranje AP, Vuzevski VD, van Joost T, ten Kate F, Naafs B. Bullous pemphigoid in children. Report of three cases with special emphasis on therapy. Int J Dermatol. 1991;30:339–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-4362.1991.tb03871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ostlere LS, Stevens H, Black MM, Rustin MH, Hashimoto T, Nishikawa T. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy–a case report including new immunoblotting observations. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1993;18:483–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1993.tb02259.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kirtschig G, Wojnarowska F, Marsden RA, Edwards S, Bhogal B, Black MM. Acquired bullous diseases of childhood: re-evaluation of diagnosis by indirect immunofluorescence examination on 1 M NaCl split skin and immunoblotting. Br J Dermatol. 1994;130:610–616. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb13108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Cambazard F, Thivolet J, Mironneau P. Bullous pemphigoid in a 4-month-old boy. Br J Dermatol. 1994;131:449–451. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1994.tb08540.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Nagano T, Tani M, Adachi A, Takanaga T, Sakamoto S, Kodama S, Fujiwara S. Childhood bullous pemphigoid: immunohistochemical, immunoelectron microscopic, and western blot analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1994;30(5 Pt 2):884–888. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(94)70106-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Wisuthsarewong W, Viravan S, Kulthanan K. Bullous pemphigoid in an infant: a case report and literature review. J Med Assoc Thai. 1997;80:270–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Edwards S, Wakelin SH, Wojnarowska F, Marsden RA, Kirtschig G, Bhogal B, Black MM. Bullous pemphigoid and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita: presentation, prognosis, and immunopathology in 11 children. Pediatr Dermatol. 1998;15:184–190. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1470.1998.1998015184.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Cunha PR, Thomazeski PV, Hipólito E, Michalany NS, Bystryn JC. Bullous pemphigoid in a 2-month-old infant. Int J Dermatol. 1998;37:935–938. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.1998.00615.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Amos B, Deng JS, Flynn K, Suarez S. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy: case report and literature review. Pediatr Dermatol. 1998;15:108–111. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1470.1998.1998015108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Trüeb RM, Didierjean L, Fellas A, Elias A, Borradori L. Childhood bullous pemphigoid: report of a case with characterization of the targeted antigens. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999;40(2 Pt 2):338–344. doi: 10.1016/S0190-9622(99)70481-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Chimanovitch I, Hamm H, Georgi M, Kroiss M, Stolz W, Apitz C, Bröcker EB, Zillikens D. Bullous pemphigoid of childhood: autoantibodies target the same epitopes within the NC16A domain of BP180 as autoantibodies in bullous pemphigoid of adulthood. Arch Dermatol. 2000;136:527–532. doi: 10.1001/archderm.136.4.527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Segurado Rodriguez M, Guerra Tapia A, Sanchez Gomez E, Rodriguez Peralto J, Vanaclocha Sebastian F, Iglesia Diez I. Penfigoide ampolloso infantil: a propósito de dos casos. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2000;91:149–152. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Baykal C, Okan G, Sarica R. Childhood bullous pemphigoid developed after the first vaccination. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2001;44(2 Suppl):348–350. doi: 10.1067/mjd.2001.103034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Petronius D, Bergman R. Bullous pemphigoid in two young infants. Pediatr Dermatol. 2002;19:119–121. doi: 10.1046/j.1525-1470.2002.00054.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Singalavanija S, Limpongsanurak W. Immunobullous diseases in Thai children: report of 24 cases. J Med Assoc Thai. 2003;86(Suppl 3):S681–S688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Kuenzli S, Grimaître M, Krischer J, Saurat J-H, Calza A-M, Borradori L. Childhood bullous pemphigoid: report of a case with life-threatening course during homeopathy treatment. Pediatr Dermatol. 2004;21:160–163. doi: 10.1111/j.0736-8046.2004.21215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sousa B, Mota A, Morgado H, Lopes JM, Dias JA. [Bullous pemphigoid in an infant] Acta Med Port. 2005;18:159–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Mérida C, Martínez-Escribano JA, Frías JF, Sánchez-Pedreño P, Corbalán R. [Bullous pemphigoid in an infant after vaccination] Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2005;96:255–257. doi: 10.1016/S0001-7310(05)73081-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Voltan E, Maeda JY, Muniz Silva MA, Maruta CW, Santi CG, de Almeida Zimbres S, Aoki V. Childhood bullous pemphigoid: report of three cases. J Dermatol. 2005;32:387–392. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2005.tb00912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Chiavérini C, Hamel-Teillac D, Gilbert D, Prost Y. Absence of anti-BP180 antibodies in mothers of infants with bullous pemphigoid. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:839–843. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2005.07061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Xiao T, Li B, Wang Y-K, He C-D, Chen H-D. Childhood bullous pemphigoid treated by i.v. immunoglobulin. J Dermatol. 2007;34:650–653. doi: 10.1111/j.1346-8138.2007.00348.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sugawara N, Nagai Y, Matsushima Y, Aoyama K, Ishikawa O. Infantile bullous pemphigoid treated with intravenous immunoglobulin therapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2007;57:1084–1089. doi: 10.1016/j.jaad.2007.08.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Martinez-De Pablo MI, González-Enseñat MA, Vicente A, Gilaberte M, Mascaró JM., Jr Childhood bullous pemphigoid: clinical and immunological findings in a series of 4 cases. Arch Dermatol. 2007;143:215–220. doi: 10.1001/archderm.143.2.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Schulze J, Bader P, Henke U, Rose MA, Zielen S. Severe bullous pemphigoid in an infant–successful treatment with rituximab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:462–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2008.00751.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Belhadjali H, Youssef M, Njim L, Chaabane S, Sriha B, Chakroun M, Zakhama A, Zili J. Childhood vesicular pemphigoid mimicking severe atopic dermatitis: a case report. Cutis. 2009;83:182–184. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Toyama T, Nakamura K, Kuramochi A, Ohyama B, Hashimoto T, Tsuchida T. Two cases of childhood bullous pemphigoid. Eur J Dermatol. 2009;19:368–371. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2009.0694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Majmudar V, Herath D, O’Toole EA, Harrison A. Bullous pemphigoid of childhood: a rare disease with diagnostic and management challenges. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:213–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.03091.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Khaled A, Kharfi M, Fazaa B, Kamoun MR. Bullous eruption in a five-month-old girl. CMAJ. 2010;182:1325–1327. doi: 10.1503/cmaj.090867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hafiji J, Bhogal B, Rytina E, Burrows NP. Bullous pemphigoid in infancy developing after the first vaccination. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2010;35:940–941. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2010.03839.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Valdivielso-Ramos M, Velázquez D, Tortoledo A, Hernanz JM. [Infantile bullous pemphigoid developing after hexavalent, meningococcal and pneumococcal vaccinations] An Pediatr (Barc) 2011;75:199–202. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2011.04.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Dufour C, Souillet AL, Chaneliere C, Jouen F, Bodemer C, Jullien D, Cambazard F, Joly P, Reix P. Successful management of severe infant bullous pemphigoid with omalizumab. Br J Dermatol. 2012;166:1140–1142. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2011.10748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Fuertes I, Luelmo J, Leal L, Romaní J, Sánchez S, Mascaró JM., Jr Refractory childhood pemphigoid successfully treated with rituximab. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:e96–e97. doi: 10.1111/pde.12057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Barreau M, Stefan A, Brouard J, Leconte C, Morice C, Comoz F, Verneuil L. Infantile bullous pemphigoid. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 2012;139:555–558. doi: 10.1016/j.annder.2012.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Lynch M, Devaney D, Khaw Y, O’Donnell B. Bullae of the hands, feet, and perioral area in a 3-month-old infant. Bullous Pemphigoid. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:135–136. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2012.01731.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Pai VV, Sori T, Kikkeri NN, Athanikar SB, Dinesh US, Rai V. Childhood bullous pemphigoid in a four-month-old child. Eur J Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;23:15–18. [Google Scholar]
- 61.De la Fuente S, Hernández-Martín Á, de Lucas R, González-Enseñat MA, Vicente A, Colmenero I, González-Beato M, Suñol M, Torrelo A. Postvaccination bullous pemphigoid in infancy: report of three new cases and literature review. Pediatr Dermatol. 2013;30:741–744. doi: 10.1111/pde.12231. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Marsden RA, Skeete MV, Black MM. The chronic acquired bullous diseases of childhood. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1979;4:227–240. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.1979.tb01623.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Zebede MS, Anhalt GJ, Nsouli TM, Nsouli SM, Bellanti JA. Diffuse bullous eruption in a 3-month-old infant. Ann Allergy. 1987;58(12–13):63–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Wang P, Chen X, Li R, Zhu X. A case of infantile bullous pemphigoid. Chin J Dermatovenereol. 2010;7:026. [Google Scholar]
- 65.Purvis DJ, Bhogal BS, Harper JI. Bullous pemphigoid in an infant using complementary medicine. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2009;34:195–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2230.2008.02815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Erbagci Z. Childhood bullous pemphigoid in association with hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome. Pediatr Dermatol. 2008;25:28–33. doi: 10.1111/j.1525-1470.2007.00577.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Schmidt E, Seitz CS, Benoit S, Bröcker EB, Goebeler M. Rituximab in autoimmune bullous diseases: mixed responses and adverse effects. Br J Dermatol. 2007;156:352–356. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07646.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Santos AL, Mota AV, Ramon J, Lopes JM, Azevedo F. An infant with bullous pemphigoid. Dermatol Online J. 2007;13:17. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Nishie W. Update on the pathogenesis of bullous pemphigoid: an autoantibody-mediated blistering disease targeting collagen XVII. J Dermatol Sci. 2014;73:179–186. doi: 10.1016/j.jdermsci.2013.12.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Bastuji-Garin S, Joly P, Lemordant P, Sparsa A, Bedane C, Delaporte E, Roujeau J-C, Bernard P, Guillaume J-C, Ingen-Housz-Oro S, Maillard H, Pauwels C, Picard-Dahan C, Dutronc Y, Richard M-A, French Study Group for Bullous Diseases Risk factors for bullous pemphigoid in the elderly: a prospective case–control study. J Invest Dermatol. 2011;131:637–643. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Lloyd-Lavery A, Chi C-C, Wojnarowska F, Taghipour K. The associations between bullous pemphigoid and drug use: a UK case–control study. JAMA Dermatol. 2013;149:58–62. doi: 10.1001/2013.jamadermatol.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Kneisel A, Hertl M. Autoimmune bullous skin diseases. Part 2: diagnosis and therapy. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2011;9:927–947. doi: 10.1111/j.1610-0387.2011.07809.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Busse WW, Morgan WJ, Gergen PJ, Mitchell HE, Gern JE, Liu AH, Gruchalla RS, Kattan M, Teach SJ, Pongracic JA, Chmiel JF, Steinbach SF, Calatroni A, Togias A, Thompson KM, Szefler SJ, Sorkness CA. Randomized trial of omalizumab (anti-IgE) for asthma in inner-city children. N Engl J Med. 2011;364:1005–1015. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1009705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


