Abstract
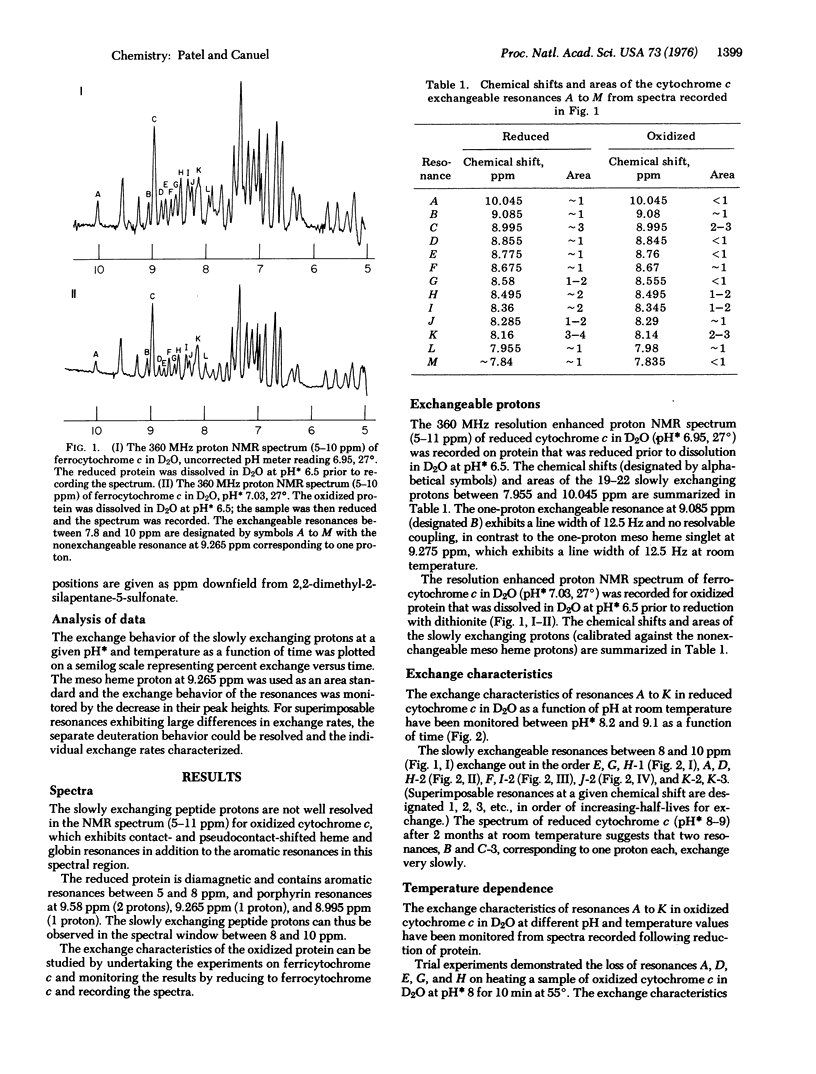
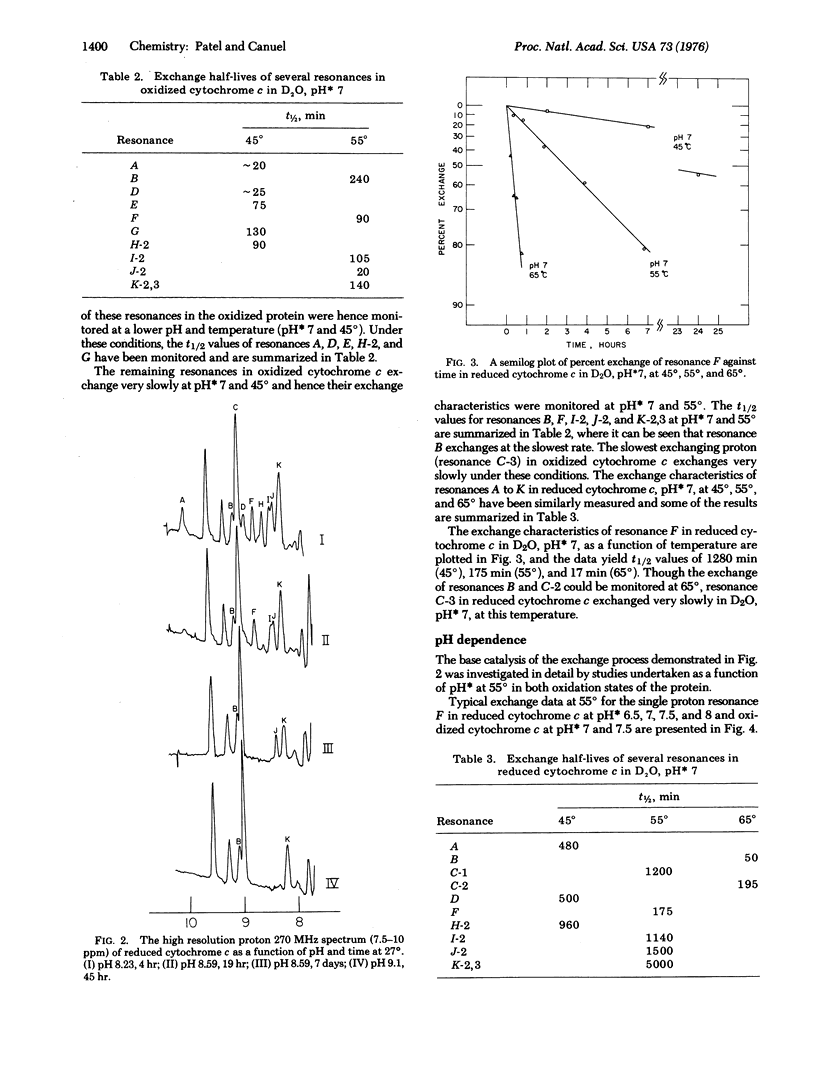
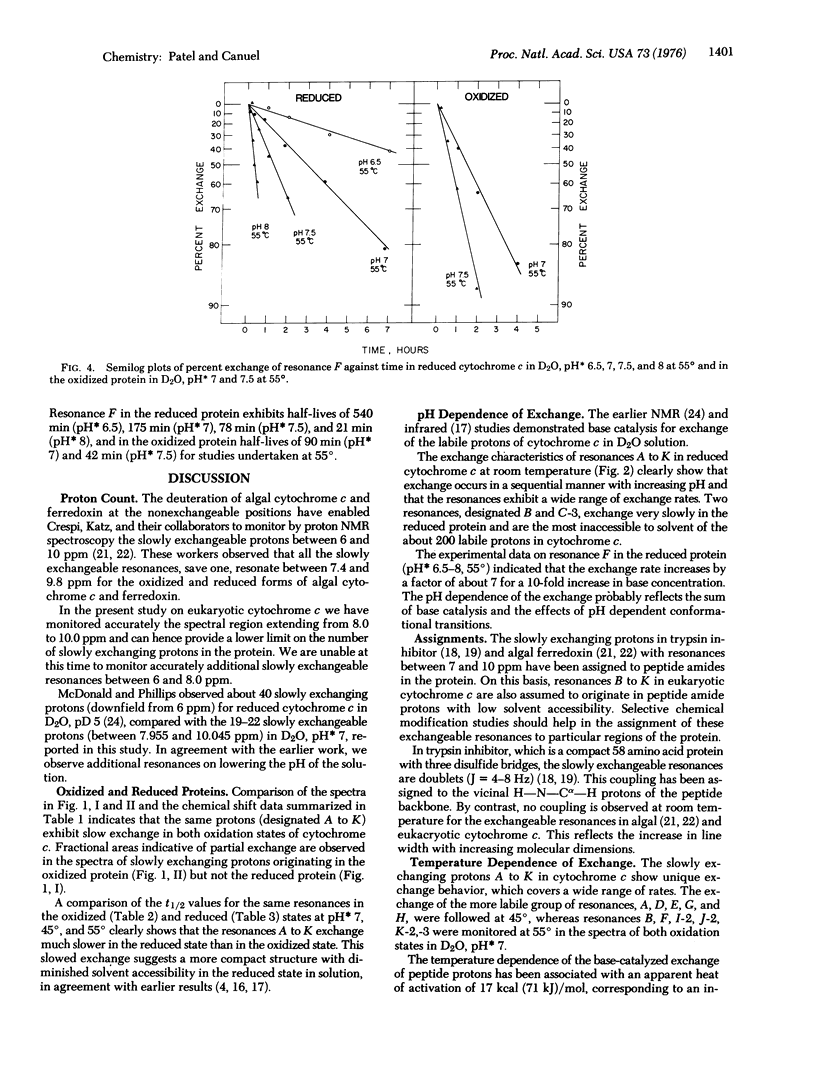
The slowly exchanging protons in oxidized and reduced horse heart cytochrome c (D20, uncorrected pH meter reading 6.5 room temperature) have been monitored by recording the 270 and 360 MHz proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra of the reduced protein between 5 and 11 parts per million downfield from 2,2-dimethyl-2-silapentane-5-sulfonate.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Campbell I. D., Dobson C. M., Jeminet G., Williams R. J. Pulsed NMR methods for the observation and assignment of exchangeable hydrogens: application to bacitracin. FEBS Lett. 1974 Dec 1;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80645-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell I. D., Dobson C. M., Williams J. P. Studies of exchangeable hydrogens in lysozyme by means of Fourier transform proton magnetic resonance. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 17;189(1097):485–502. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1975.0069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crespi H. L., Kostka A. G., Smith U. H. Proton Magnetic resonance observations of hydrogen exchange rates and secondary structure in algal ferredoxin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Dec 23;61(4):1407–1414. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80440-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E., Takano T., Eisenberg D., Kallai O. B., Samson L., Cooper A., Margoliash E. Ferricytochrome c. I. General features of the horse and bonito proteins at 2.8 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 10;246(5):1511–1535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickerson R. E. The structure and history of an ancient protein. Sci Am. 1972 Apr;226(4):58–passim. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0472-58. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson C. M., Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Assignment of aromatic amino acid PMR resonances of horse ferricytochrome c. FEBS Lett. 1975 Mar 1;51(1):60–65. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80854-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Englander S. W., Downer N. W., Teitelbaum H. Hydrogen exchange. Annu Rev Biochem. 1972;41:903–924. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.41.070172.004351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huber R., Kukla D., Rühlmann A., Steigemann W. Pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz). I. Structure and function. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:141–148. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karplus S., Snyder G. H., Sykes B. D. A nuclear magnetic resonance study of bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. Tyrosine titrations and backbone NH groups. Biochemistry. 1973 Mar 27;12(7):1323–1329. doi: 10.1021/bi00731a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz J. J., Crespi H. L. Biologically important isotope hybrid compounds in NMR: 1 H fourier transform NMR at unnatural abundance. Pure Appl Chem. 1972;32(1):221–250. doi: 10.1351/pac197232010221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kägi J. H., Ulmer D. D. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange of cytochrome c. II. Effect of pH. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2718–2723. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margoliash E., Schejter A. Cytochrome c. Adv Protein Chem. 1966;21:113–286. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60128-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masson A., Wüthrich K. Proton magnetic resonance investigation of the conformational properties of the basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. FEBS Lett. 1973 Apr 1;31(1):114–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80086-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonald C. C., Phillips W. D. Proton magnetic resonance studies of horse cytochrome c. Biochemistry. 1973 Aug 14;12(17):3170–3186. doi: 10.1021/bi00741a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore G. R., Williams R. J. Assignment of aromatic amino acid PMR resonances of horse ferrocytochrome C. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 15;53(3):334–338. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redfield A. G., Gupta R. K. Pulsed NMR study of the structure of cytochrome c. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:405–411. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.052. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salemme F. R., Kraut J., Kamen M. D. Structural bases for function in cytochromes c. An interpretation of comparative x-ray and biochemical data. J Biol Chem. 1973 Nov 25;248(22):7701–7716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheard B., Yamane T., Shulman R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of cyanoferrimyoglobin; identification of pseudocontact shifts. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):35–48. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90044-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stellwagen E., Shulman R. G. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of exchangeable protons in ferrocytochrome c. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 25;75(4):683–698. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90301-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Kallai O. B., Swanson R., Dickerson R. E. The structure of ferrocytochrome c at 2.45 A resolution. J Biol Chem. 1973 Aug 10;248(15):5234–5255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano T., Swanson R., Kallai O. B., Dickerson R. E. Conformational changes upon reduction of cytochrome c. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1972;36:397–404. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1972.036.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulmer D. D., Kägi J. H. Hydrogen-deuterium exchange of cytochrome c. I. Effect of oxidation state. Biochemistry. 1968 Aug;7(8):2710–2717. doi: 10.1021/bi00848a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch W. H., Jr, Fasman G. D. Hydrogen-tritium exchange in polypeptides. Models of alpha-helical and beta conformations. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2455–2466. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



