Abstract
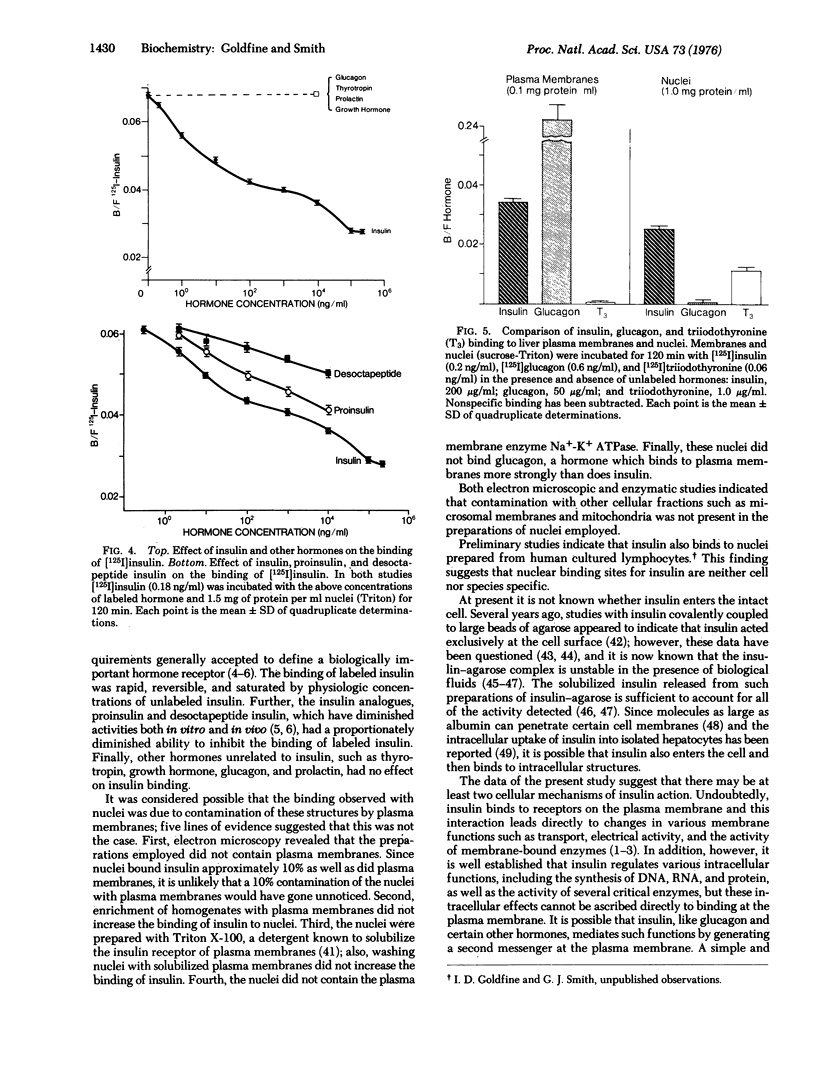
Specific binding sites for 125I-labeled insulin were detected in purified nuclei isolated from rat liver. Binding was rapid, reversible and directly proportional to the number of nuclei employed. Unlabeled native insulin, at concentrations as low as 1ng/ml, significantly inhibited the binding of labeled hormone, whereas unlabeled proinsulin and desoctapeptide insulin were less potent. In contrast, glucagon, thyrotropin, growth hormone (somatotropin), and prolactin were without effect. Under identical incubation conditions, 125I-labeled glucagon bound to liver plasma membranes 5- to 10-fold more strongly than did insulin; in contrast glucoagon did not bind to liver nuclei. These studies demonstrate the presence of specific binding sites for insulin in purified nuclei isolated from rat liver. In addition, they suggest that the nucleus may be an intracellular site of insulin action.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ARRIGONI O., SINGER T. P. Limitations of the phenazine methosulphate assay for succinic and related dehydrogenases. Nature. 1962 Mar 31;193:1256–1258. doi: 10.1038/1931256a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergeron J. J., Evans W. H., Geschwind I. I. Insulin binding to rat liver Golgi fractions. J Cell Biol. 1973 Dec;59(3):771–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.3.771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Dana S. E., Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase. Solubilization and purification of a cold-sensitive microsomal enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 10;248(13):4731–4738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Crofford O. B., Gammeltoff S., Gliemann J., Gavin J. R., 3rd, Goldfine I. D., Kahn C. R., Rodbell M., Roth J., Jarrett L. Letter: Insulin activity: the solid matrix. Science. 1973 Oct 26;182(4110):396–398. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4110.396-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
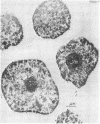
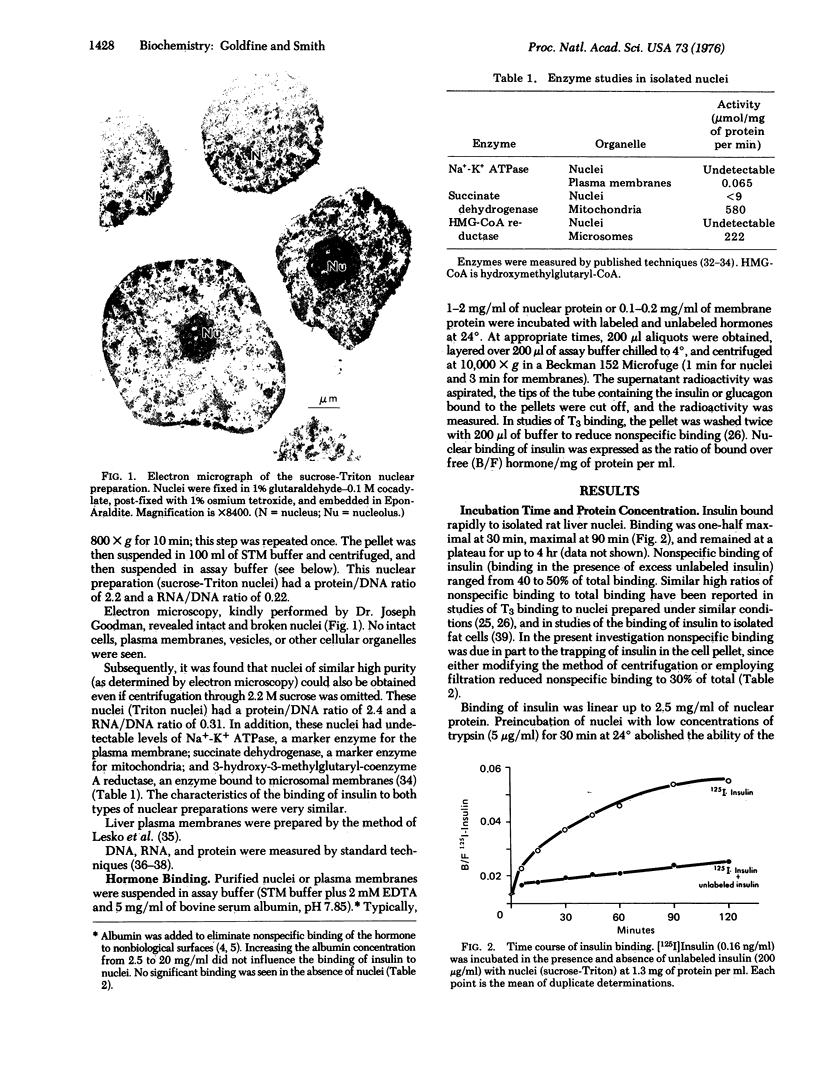
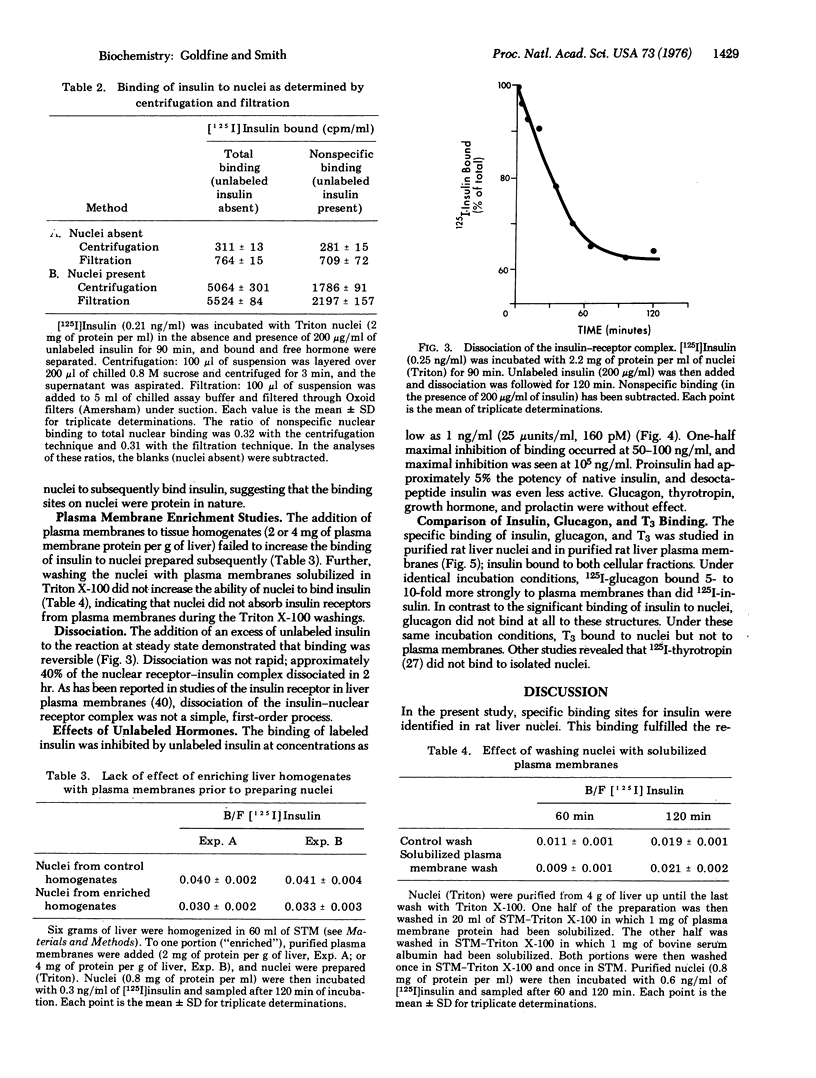
- CHAUVEAU J., MOULE Y., ROUILLER C. Isolation of pure and unaltered liver nuclei morphology and biochemical composition. Exp Cell Res. 1956 Aug;11(2):317–321. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(56)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang K. J., Bennett V., Cuatrecasas P. Membrane receptors as general markers for plasma membrane isolation procedures. The use of 125-I-labeled wheat germ agglutinin, insulin, and cholera toxin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):488–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Interaction of insulin with the cell membrane: the primary action of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):450–457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuatrecasas P. Isolation of the insulin receptor of liver and fat-cell membranes (detergent-solubilized-( 125 I)insulin-polyethylene glycol precipitation-sephadex). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson M. B., Van Herle A. J., Gerschenson L. E. Insulin and Sepharose-insulin effects on tyrosine transaminase levels in cultured rat liver cells. Endocrinology. 1973 May;92(5):1442–1446. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-5-1442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeGroot L. J., Torresani J. Triiodothyronine binding to isolated liver cell nuclei. Endocrinology. 1975 Feb;96(2):357–359. doi: 10.1210/endo-96-2-357. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake R. L., Morgan C. R. An in vivo insulin effect on hepatocyte chromatin determined by DNA-rna hybridization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jan 20;62(2):342–349. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue M. E., Freychet P. Insulin receptors in the heart muscle. Demonstration of specific binding sites and impairment of insulin binding in the plasma membrane of the obese hyperglycemic mouse. Diabetes. 1975 Aug;24(8):715–723. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.8.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gammeltoft S., Gliemann J. Binding and degradation of 125I-labelled insulin by isolated rat fat cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Aug 17;320(1):16–32. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90161-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garwin J. L., Gelehrter T. D. Induction of tyrosine aminotransferase by Sepharose-insulin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1974 Sep;164(1):52–59. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(74)90007-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Amir S. M., Petersen A. W., Ingbar S. H. Preparation of biologically active 125I-TSH. Endocrinology. 1974 Nov;95(5):1228–1233. doi: 10.1210/endo-95-5-1228. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Roth J., Birnbaumer L. Glucagon receptors in -cells. Binding of 125 I-glucagon and activation of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1972 Feb 25;247(4):1211–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYMER W. C., KUFF E. L. ISOLATION OF NUCLEI FROM MAMMALIAN TISSUES THROUGH THE USE OF TRITON X-100. J Histochem Cytochem. 1964 May;12:359–363. doi: 10.1177/12.5.359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvat A., Li E., Katsoyannis P. G. Cellular binding sites for insulin in rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Apr 8;382(4):609–620. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(75)90226-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Freychet P., Roth J., Neville D. M., Jr Quantitative aspects of the insulin-receptor interaction in liver plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2249–2257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen H. M., Vlahakes G. J. Biological activity of insulin-sepharose? Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1142–1144. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolb H. J., Renner R., Hepp K. D., Weiss L., Wieland O. H. Re-evaluation of Sepharose-insulin as a tool for the study of insulin action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):248–252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesko L., Donlon M., Marinetti G. V., Hare J. D. A rapid method for the isolation of rat liver plasma membranes using an aqueous two-phase polymer system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 22;311(2):173–179. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90264-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Permeability of membrane junctions. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1966 Jul 14;137(2):441–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1966.tb50175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan C. R., Bonner J. Template activity of liver chromatin increased by in vivo administration of insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Apr;65(4):1077–1080. doi: 10.1073/pnas.65.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olefsky J., Johnson J., Liu F., Edwards P., Baur S. Comparison of 125-I-insulin binding and degradation to isolated rat hepatocytes and liver membranes. Diabetes. 1975 Sep;24(9):801–810. doi: 10.2337/diab.24.9.801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oppenheimer J. H., Schwartz H. L., Koerner D., Surks M. I. Limited binding capacity sites for L-triiodothyronine in rat liver nuclei. Nuclear-cytoplasmic interrelation, binding constants, and cross-reactivity with L-thyroxine. J Clin Invest. 1974 Mar;53(3):768–777. doi: 10.1172/JCI107615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechler M. M., Podskalny J. M., Goldfine I. D., Wells C. A. DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts: stimulation by insulin and by nonsuppressible insulin-like activity (NSILA-S). J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1974 Sep;39(3):512–521. doi: 10.1210/jcem-39-3-512. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J. Peptide hormone binding to receptors: a review of direct studies in vitro. Metabolism. 1973 Aug;22(8):1059–1073. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(73)90225-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuels H. H., Tsai J. S. Thyroid hormone action. Demonstration of similar receptors in isolated nuclei of rat liver and cultured GH1 cells. J Clin Invest. 1974 Feb;53(2):656–659. doi: 10.1172/JCI107601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spindler B. J., MacLeod K. M., Ring J., Baxter J. D. Thyroid hormone receptors. Binding characteristics and lack of hormonal dependency for nuclear localization. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4113–4119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F. Insulin and the regulation of hepatic biosynthetic activity. Vitam Horm. 1966;24:1–61. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60202-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner D. F., King J. Insulin-stimulated ribonucleic acid synthesis and RNA polymerase activity in alloxan-diabetic rat liver. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Jun 22;119(3):510–516. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(66)90127-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E., Topper Y. J. The role of DNA synthesis and mitosis in hormone-dependent differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1283–1289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G., Singhal R. L., Stamm N. B., Lea M. A., Fisher E. A. Synchronous behavior pattern of key glycolytic enzymes: glucokinase, phosphofructokinase, and pyruvate kinase. Adv Enzyme Regul. 1966;4:59–81. doi: 10.1016/0065-2571(66)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widnell C. C., Tata J. R. A procedure for the isolation of enzymically active rat-liver nuclei. Biochem J. 1964 Aug;92(2):313–317. doi: 10.1042/bj0920313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]