Abstract
The role of latent membrane protein 2 (LMP2) in Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection was evaluated by using latently infected primary B lymphocytes that had been growth transformed by wild-type or specifically mutated EBV recombinants. LMP2 null mutant recombinant EBV-infected cells were similar to normal B lymphocytes in their rapid increase in intracellular free calcium after surface immunoglobulin crosslinking. These cells also became more permissive for lytic EBV replication. In sharp contrast, wild-type control infected cells had little or no increase in intracellular free calcium or in permissivity for EBV replication. The block to surface immunoglobulin crosslinking-induced permissivity in cells expressing wild-type LMP2 could be bypassed by raising intracellular free calcium levels with an ionophore and by activating protein kinase C with phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate. LMP2A, not LMP2B, mediates this effect on calcium mobilization. Genetic and biochemical data are consistent with these effects being due to the interaction of the LMP2A N-terminal cytoplasmic domain with B lymphocyte src family tyrosine kinases.
Full text
PDF
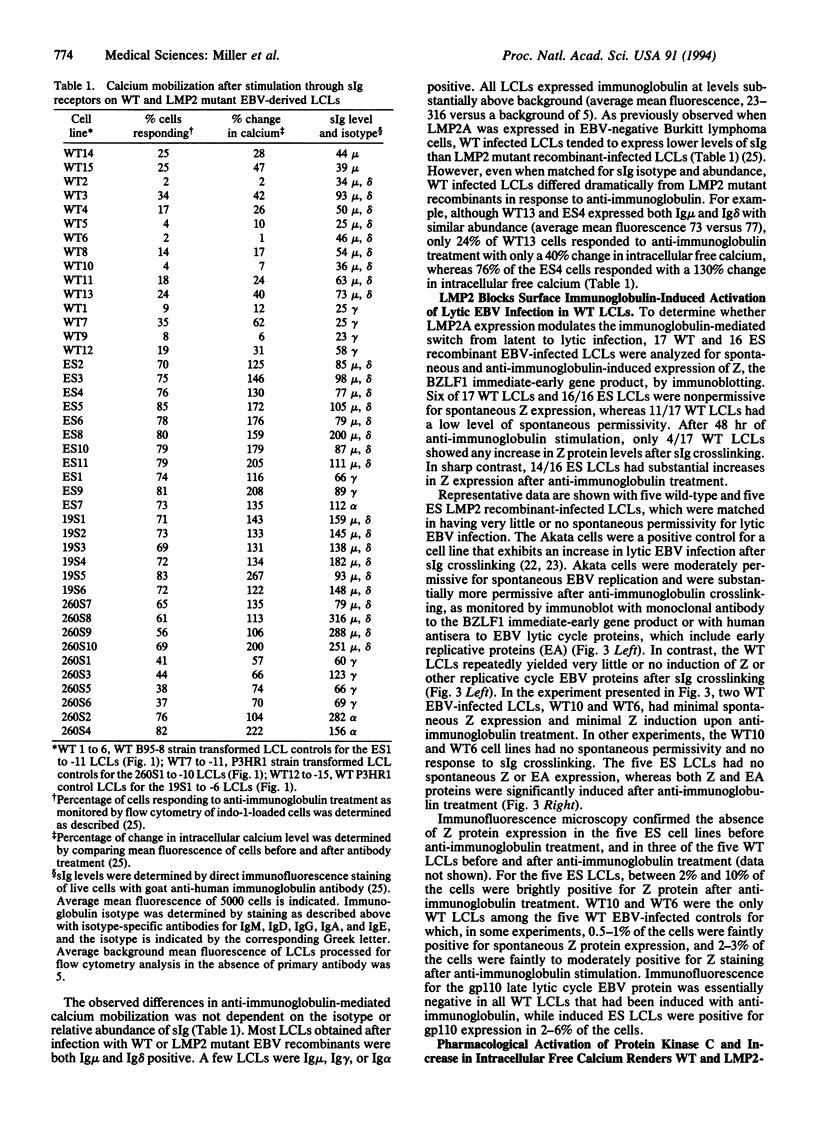
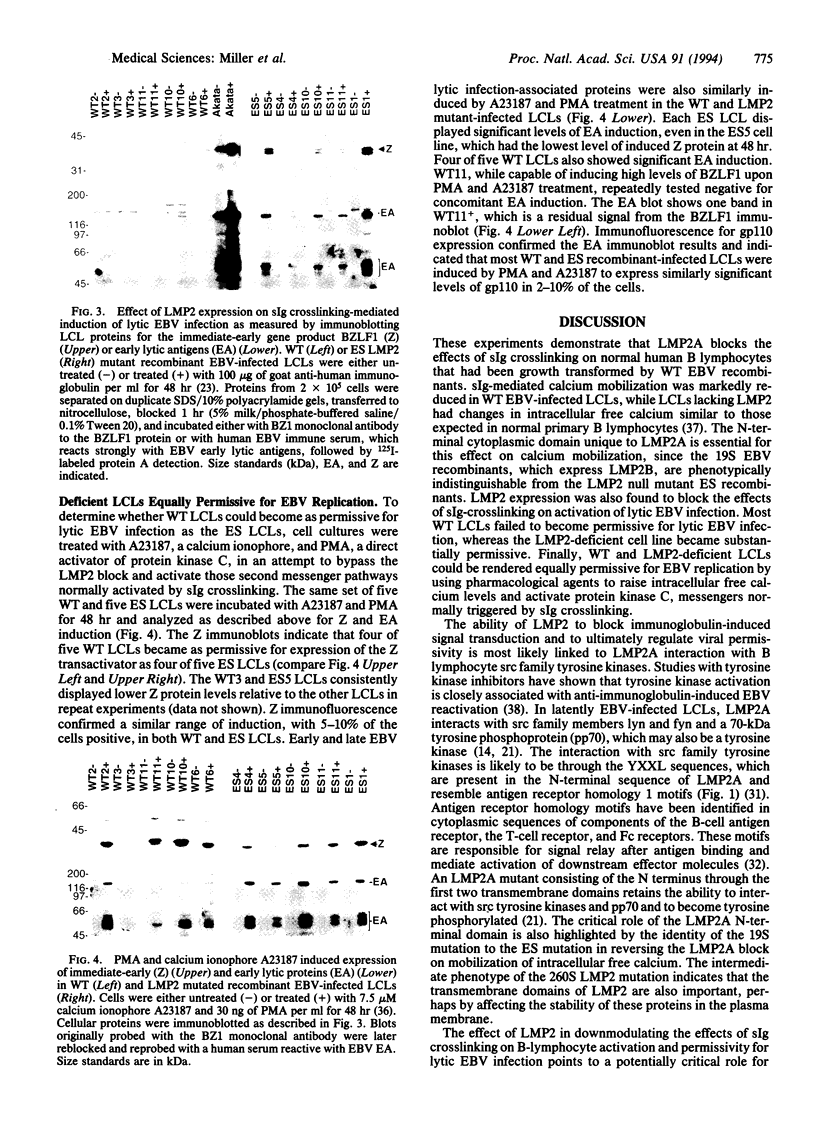

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baichwal V. R., Sugden B. Transformation of Balb 3T3 cells by the BNLF-1 gene of Epstein-Barr virus. Oncogene. 1988 May;2(5):461–467. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun J., Sha'afi R. I., Unanue E. R. Crosslinking by ligands to surface immunoglobulin triggers mobilization of intracellular 45Ca2+ in B lymphocytes. J Cell Biol. 1979 Sep;82(3):755–766. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt A. L., Bolen J. B., Kieff E., Longnecker R. An Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated membrane protein interacts with src family tyrosine kinases. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):5161–5167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5161-5167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cambier J. C., Campbell K. S. Membrane immunoglobulin and its accomplices: new lessons from an old receptor. FASEB J. 1992 Oct;6(13):3207–3217. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.13.1397843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleary M. L., Sklar J. Lymphoproliferative disorders in cardiac transplant recipients are multiclonal lymphomas. Lancet. 1984 Sep 1;2(8401):489–493. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92566-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daibata M., Humphreys R. E., Takada K., Sairenji T. Activation of latent EBV via anti-IgG-triggered, second messenger pathways in the Burkitt's lymphoma cell line Akata. J Immunol. 1990 Jun 15;144(12):4788–4793. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daibata M., Mellinghoff I., Takagi S., Humphreys R. E., Sairenji T. Effect of genistein, a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, on latent EBV activation induced by cross-linkage of membrane IgG in Akata B cells. J Immunol. 1991 Jul 1;147(1):292–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faggioni A., Zompetta C., Grimaldi S., Barile G., Frati L., Lazdins J. Calcium modulation activates Epstein-Barr virus genome in latently infected cells. Science. 1986 Jun 20;232(4757):1554–1556. doi: 10.1126/science.3012779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech B., Zimber-Strobl U., Suentzenich K. O., Pavlish O., Lenoir G. M., Bornkamm G. W., Mueller-Lantzsch N. Identification of Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein 1 (TP1) in extracts of four lymphoid cell lines, expression in insect cells, and detection of antibodies in human sera. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2759–2767. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2759-2767.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heston L., Rabson M., Brown N., Miller G. New Epstein-Barr virus variants from cellular subclones of P3J-HR-1 Burkitt lymphoma. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):160–163. doi: 10.1038/295160a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye K. M., Izumi K. M., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1 is essential for B-lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):9150–9154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.9150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishishita M., Luka J., Vroman B., Poduslo J. F., Pearson G. R. Production of monoclonal antibody to a late intracellular Epstein-Barr virus-induced antigen. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):363–375. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90402-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Economou A., Farrell P. J. The terminal protein gene 2 of Epstein-Barr virus is transcribed from a bidirectional latent promoter region. J Gen Virol. 1989 Nov;70(Pt 11):3079–3084. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-70-11-3079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laux G., Perricaudet M., Farrell P. J. A spliced Epstein-Barr virus gene expressed in immortalized lymphocytes is created by circularization of the linear viral genome. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):769–774. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02874.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazdins J., Zompetta C., Grimaldi S., Barile G., Venanzoni M., Frati L., Faggioni A. TPA induction of Epstein-Barr virus early antigens in Raji cells is blocked by selective protein kinase-C inhibitors. Int J Cancer. 1987 Dec 15;40(6):846–849. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Druker B., Roberts T. M., Kieff E. An Epstein-Barr virus protein associated with cell growth transformation interacts with a tyrosine kinase. J Virol. 1991 Jul;65(7):3681–3692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.7.3681-3692.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Kieff E. A second Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2319–2326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2319-2326.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Miller C. L., Miao X. Q., Marchini A., Kieff E. The only domain which distinguishes Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) from LMP2B is dispensable for lymphocyte infection and growth transformation in vitro; LMP2A is therefore nonessential. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6461–6469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6461-6469.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Miller C. L., Miao X. Q., Tomkinson B., Kieff E. The last seven transmembrane and carboxy-terminal cytoplasmic domains of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2 (LMP2) are dispensable for lymphocyte infection and growth transformation in vitro. J Virol. 1993 Apr;67(4):2006–2013. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.4.2006-2013.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Longnecker R., Miller C. L., Tomkinson B., Miao X. Q., Kieff E. Deletion of DNA encoding the first five transmembrane domains of Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane proteins 2A and 2B. J Virol. 1993 Aug;67(8):5068–5074. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.8.5068-5074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellinghoff I., Daibata M., Humphreys R. E., Mulder C., Takada K., Sairenji T. Early events in Epstein-Barr virus genome expression after activation: regulation by second messengers of B cell activation. Virology. 1991 Dec;185(2):922–928. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90574-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
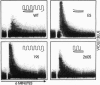
- Miller C. L., Longnecker R., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A blocks calcium mobilization in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Jun;67(6):3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3087-3094.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Shope T., Lisco H., Stitt D., Lipman M. Epstein-Barr virus: transformation, cytopathic changes, and viral antigens in squirrel monkey and marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu L., Rowe D. T. Epstein-Barr virus latent gene expression in uncultured peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3715–3724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3715-3724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. Antigen receptor tail clue. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):383–384. doi: 10.1038/338383b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe D. T., Hall L., Joab I., Laux G. Identification of the Epstein-Barr virus terminal protein gene products in latently infected lymphocytes. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2866–2875. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2866-2875.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sample J., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. Two related Epstein-Barr virus membrane proteins are encoded by separate genes. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):933–937. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.933-937.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K. Cross-linking of cell surface immunoglobulins induces Epstein-Barr virus in Burkitt lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1984 Jan 15;33(1):27–32. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takada K., Ono Y. Synchronous and sequential activation of latently infected Epstein-Barr virus genomes. J Virol. 1989 Jan;63(1):445–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.1.445-449.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. A., Hotchin N. A., Allday M. J., Amlot P., Rose M., Yacoub M., Crawford D. H. Immunohistology of Epstein-Barr virus-associated antigens in B cell disorders from immunocompromised individuals. Transplantation. 1990 May;49(5):944–953. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199005000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Kieff E. The truncated form of the Epstein-Barr virus latent-infection membrane protein expressed in virus replication does not transform rodent fibroblasts. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2337–2346. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2337-2346.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D., Liebowitz D., Wang F., Gregory C., Rickinson A., Larson R., Springer T., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang F., Gregory C., Sample C., Rowe M., Liebowitz D., Murray R., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein (LMP1) and nuclear proteins 2 and 3C are effectors of phenotypic changes in B lymphocytes: EBNA-2 and LMP1 cooperatively induce CD23. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2309–2318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2309-2318.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Lau R., Rowe M., Niedobitek G., Packham G., Shanahan F., Rowe D. T., Greenspan D., Greenspan J. S., Rickinson A. B. Differentiation-associated expression of the Epstein-Barr virus BZLF1 transactivator protein in oral hairy leukoplakia. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):2868–2874. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.2868-2874.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L., Alfieri C., Hennessy K., Evans H., O'Hara C., Anderson K. C., Ritz J., Shapiro R. S., Rickinson A., Kieff E. Expression of Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated genes in tissues of patients with EBV lymphoproliferative disease. N Engl J Med. 1989 Oct 19;321(16):1080–1085. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198910193211604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]