Abstract
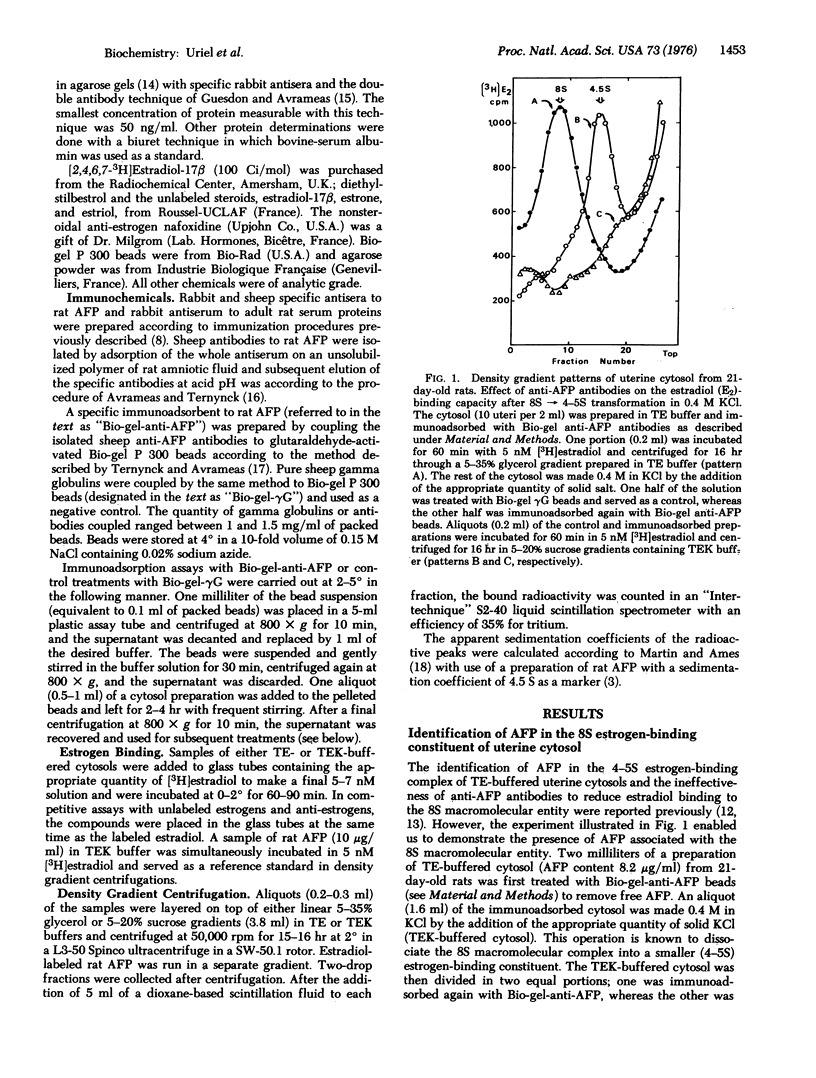
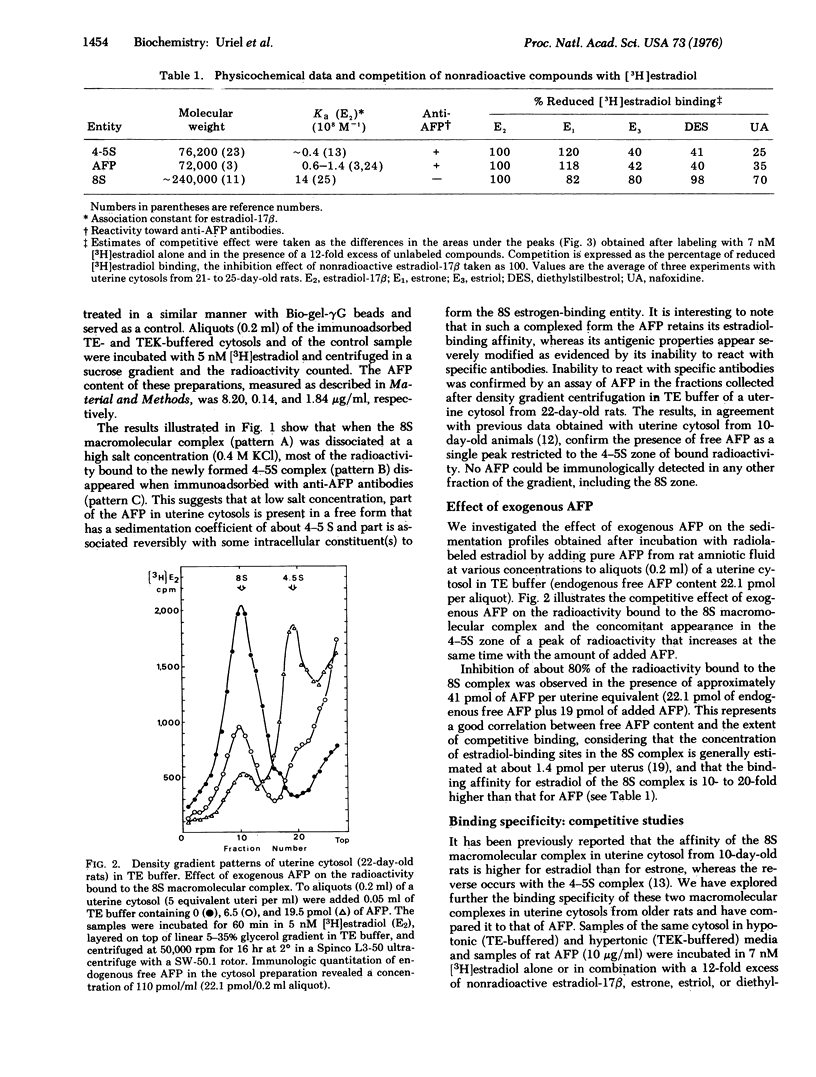
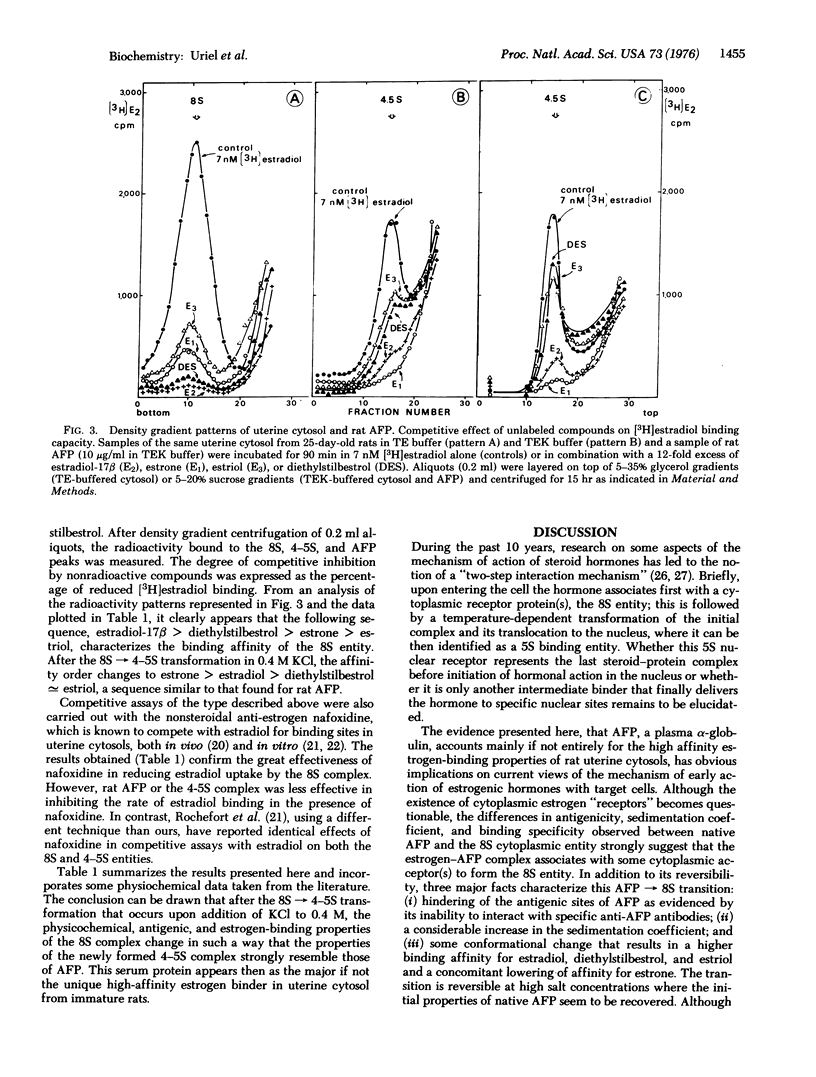
Evidence is present that alpha-fetoprotein (AFP), a serum globulin, accounts mainly, if not entirely, for the high estrogen-binding properties of uterine cytosols from immature rats. By the use of specific immunoadsorbents to AFP and by competitive assays with unlabeled steroids and pure AFP, it has been demonstrated that in hypotonic cytosols AFP is present partly as free protein with a sedimentation coefficient of about 4-5 S and partly in association with some intracellular constituent(s) to form an 8S estrogen-binding entity. The AFP leads to 8S transformation results in a loss of antigenic reactivity to antibodies against AFP and a significant change in binding specificity. This change in binding specificity is manifested by an increase in binding affinity for estradiol, estriol, diethylstillbestrol, and nafoxidine ( a non-steroidal anti-estrogen), and by a concomitant decrease in estrone binding. Both the antigenic and binding properties of native AFP are recovered after dissociation of the 8S complex in 0.4 M KC1. An AFP-mediated mechanism of early intracellular events associated with estrogen entry in target cells is suggested and discussed with regard to current views on steroid action.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aussel C., Uriel J., Mercier-Bodard C. Rat alpha-fetoprotein: isolation, characterization and estrogen-binding properties. Biochimie. 1973;55(11):1431–1437. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80550-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aussel C., Uriel J., Michel G., Baulieu E. E. Immunological demonstration of alpha-fetoprotein in uterine cytosol from immature rats. Biochimie. 1974;56(4):567–570. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(74)80075-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avrameas S., Ternynck T. The cross-linking of proteins with glutaraldehyde and its use for the preparation of immunoadsorbents. Immunochemistry. 1969 Jan;6(1):53–66. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(69)90178-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski J., Toft D., Shyamala G., Smith D., Notides A. Hormone receptors: studies on the interaction of estrogen with the uterus. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:45–80. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guesdon J. L., Avrameas S. An immunoenzymatic method for measuring low concentrations of antigens by single radial diffusion. Immunochemistry. 1974 Sep;11(9):595–598. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(74)90251-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., DeSombre E. R. Estrogen-receptor interaction. Science. 1973 Oct 12;182(4108):126–134. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4108.126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen E. V., Suzuki T., Kawashima T., Stumpf W. E., Jungblut P. W., DeSombre E. R. A two-step mechanism for the interaction of estradiol with rat uterus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Feb;59(2):632–638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.59.2.632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzenellenbogen B. S., Katzenellenbogen J. A. Antiestrogens: studies using an in vitro estrogen-responsive uterine system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Feb 20;50(4):1152–1159. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)91526-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel G., Jung I., Baulieu E. E., Aussel C., Uriel J. Two high affinity estrogen binding proteins of different specificity in the immature rat uterus cytosol. Steroids. 1974 Oct;24(4):437–449. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(74)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgrom E., Atger M., Baulieu E. E. Studies on estrogen entry into uterine cells and on estradiol-receptor complex attachment to the nucleus--is the entry of estrogen into uterine cells a protein-mediated process? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Sep 14;320(2):267–283. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(73)90307-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Notides A. C., Nielsen S. The molecular mechanism of the in vitro 4 S to 5 S transformation of the uterine estrogen receptor. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 25;249(6):1866–1873. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunez E., Engelmann F., Benassayag C., Jayle M. F. Identification et purification préliminaire de la faeto-protéine liant les aestrogènes dans le sérum de rats nouveau-nés. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1971 Aug 30;273(9):831–834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raynaud J. P., Mercier-Bodard C., Baulieu E. E. Rat estradiol binding plasma protein (EBP). Steroids. 1971 Dec;18(6):767–788. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(71)90035-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruh T. S., Katzenellenbogen B. S., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Gorski J. Estrone interaction with the rat uterus: in vitro response and nuclear uptake. Endocrinology. 1973 Jan;92(1):125–134. doi: 10.1210/endo-92-1-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sell S., Nichols M., Becker F. F., Leffert H. L. Hepatocyte proliferation and alpha 1-fetoprotein in pregnant, neonatal, and partially hepatectomized rats. Cancer Res. 1974 Apr;34(4):865–871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soloff M. S., Creange J. E., Potts G. O. Unique estrogen-binding properties of rat pregnancy plasma. Endocrinology. 1971 Feb;88(2):427–432. doi: 10.1210/endo-88-2-427. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanislawski-Birencwajg M. Specific antigens of rat embryonic serum. Cancer Res. 1967 Nov;27(11):1982–1989. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanislawski-Birencwajg M., Uriel J., Grabar P. Association of embryonic antigens with experimentally induced hepatic lesions in the rat. Cancer Res. 1967 Nov;27(11):1990–1997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szego C. M. Role of histamine in mediation of hormone action. Fed Proc. 1965 Nov-Dec;24(6):1343–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Structure-activity relationships of anti-oestrogens with regard to interaction with 17-beta-oestradiol in the mouse uterus and vagina. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1971 Mar;66(3):431–447. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0660431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ternynck T., Avrameas S. Polyacrylamide-protein immunoadsorbents prepared with glutaraldehyde. FEBS Lett. 1972 Jun 1;23(1):24–28. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toft D., Shyamala G., Gorski J. A receptor molecule for estrogens: studies using a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Jun;57(6):1740–1743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.57.6.1740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J., Bouillon D., Dupiers M. Affinity chromatography of human, rat and mouse alpha-fetoprotein on estradiol-sepharose adsorbents. FEBS Lett. 1975 May 15;53(3):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uriel J., de Nechaud B., Dupiers M. Estrogen-binding properties of rat, mouse and man fetospecific serum proteins. Demonstration by immuno-autoradiographic methods. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Feb 16;46(3):1175–1180. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Néchaud B., Uriel J. Antigènes cellulaires transitoires du foie de rat. I. Sécrétion et synthèse des protéines sériques foetospécifiques au cours du développement et de la régénération hépatiques. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jul 15;8(1):71–80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910080110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


