Abstract
BACKGROUND & AIMS
Some patients with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) have intestinal hyperpermeability, which contributes to their diarrhea and abdominal pain. MicroRNA 29 (MIR29) regulates intestinal permeability in patients with IBS-D. We investigated and searched for targets of MIR29 and investigated the effects of disrupting Mir29 in mice.
METHODS
We investigated expression MIR29A and B in intestinal biopsies collected during endoscopy from patients with IBS (n = 183) and without IBS (controls) (n = 36). Levels were correlated with disease phenotype. We also generated and studied Mir29−/− mice, in which expression of Mir29a and b, but not c, is lost. Colitis was induced by administration of 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid; intestinal tissues were collected and permeability was assessed. Microarray analysis was performed using tissues from Mir29−/− mice. Changes in levels of target genes were measured in human colonic epithelial cells and small intestinal epithelial cells after knockdown of MIR29 with anti-MIRs.
RESULTS
Intestinal tissues from patients with IBS-D (but not IBS with constipation or controls) had increased levels of MIR29A and B, but reduced levels of Claudin-1 (CLDN1) and nuclear factor-κB–repressing factor (NKRF). Induction of colitis and water avoidance stress increased levels of Mir29a and Mir29b and intestinal permeability in wild-type mice; these increased intestinal permeability in colons of far fewer Mir29−/− mice. In microarray and knockdown experiments, MIR29A and B were found to reduce levels of NKRF and CLDN1 messenger RNA, and alter levels of other messenger RNAs that regulate intestinal permeability.
CONCLUSIONS
Based on experiments in knockout mice and analyses of intestinal tissue samples from patients with IBS-D, MIR29 targets and reduces expression of CLDN1 and NKRF to increase intestinal permeability. Strategies to block MIR29 might be developed to restore intestinal permeability in patients with IBS-D.
Keywords: Gene Regulation, mRNA Processing, Intestinal Barrier Function, Mouse Model
Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) is a common gastrointestinal disorder in which patients suffer from chronic abdominal pain associated with diarrhea/constipation, urgency, and/or bloating.1 Recent evidence has shown that some IBS-associated symptoms, such as abdominal pain and diarrhea, may result from increased intestinal permeability.2–7 An intact intestinal barrier is key to preventing paracellular penetration of toxic macromolecules, bacteria, and cytokines from the gut lumen into the systemic circulation. Disruption of intestinal tight junctions may be a critical underlying pathophysiologic factor in patients with allergic (food) disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, chronic dermatologic conditions, and alcoholic cirrhosis.8,9 Our current understanding of the in vivo molecular mechanisms of increased intestinal permeability in patients with gastrointestinal disorders is still limited.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are a class of 21–23 nucleotides, endogenously expressed RNAs that are small, noncoding RNA molecules that bind through partial sequence homology to the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) of target messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and block translation. miRNAs have emerged as regulators involved in gene expression of critical biologic processes, such as differentiation, apoptosis, and proliferation. miR-29a is an important miRNA that regulates intestinal barrier integrity in diarrhea-predominant IBS (IBS-D) patients through interaction with 2 seed sequence binding sites located at the 3′-end of the GLUL gene.10 Indeed, miR-29 is critical for homeostasis of the intestinal barrier through gene regulation in terminally differentiated intestinal epithelial cells. Predicted targets of miR-29 are significantly enriched for key signaling pathway-related networks and genes involved in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity. Upregulated genes highly represented in these networks include nuclear factor-κB–repressing factor (NKRF) and Claudin-1 (CLDN1), both critical signaling molecules involved in the regulation of intestinal permeability.
We investigated the functions of miR-29 in IBS patients and in an miRNA knockout mouse model (miR-29a/b−/−) to determine the effects of the miR-29 family on intestinal permeability. A total of 219 subjects completed the study and underwent intestinal permeability testing and evaluation of gut miRNA to determine if enhanced expression of miR-29 regulates intestinal permeability. miR-29a/b−/− mice were used to study how silencing of the miR-29 family alters intestinal permeability. Subsequent microarray analysis was performed to detect the specific target gene changes after in vivo knockout of miR-29a/b. We report here that silencing miR-29 by generating knockout mice or by inhibiting cluster expression using anti-miRNAs prevents or reverses intestinal hyperpermeability. Thus, miR-29 may have important therapeutic implications for selected IBS patients with symptoms arising from increased intestinal permeability.
Materials and Methods
miR-29a/b−/− Mice
To determine the essential role of miR-29 in vivo, we generated miR-29a/b knockout mice. Homozygous floxed miR-29ab1 mice (C57BL/6 strain) were generated by 2 homologous recombination arms that were amplified by polymerase chain reaction on 129 SvJ/X1 genomic DNA, a 5′ sequence of 4171 bp, and a 3′ sequence of 3857 bp. The genomic fragment to be deleted, which had 600 bp, and which contained the miR-29a and miR-29b1 regions, was amplified and cloned in between 2 loxP sites, in a pFlox vector (Supplementary Figure 1A). Genotyping was performed by polymerase chain reaction in DNA extracted by tail clippings to identify the genotype of the first generation of recombinant mice with floxed miR-29a/b (Supplementary Figure 1B).
Animal Experiments
All animal experiments were reviewed and approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees at the Ohio State University and the University of Texas Medical Branch. Male miR-29a/b−/− and wild-type (WT) mice (10–13 weeks) were used. Intracolonic 2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid (TNBS) in 50% ethanol was used to produce colitis as described previously.11 The water avoidance stress (WAS) model was also used to induce visceral hyperalgesia.12 Testing for visceral hypersensitivity to nociceptive colonic distension was performed as described previously.13
Human
All human studies were approved by the Institutional Review Boards at the Ohio State University and the University of Texas Medical Branch. All IBS patients met the Rome III criteria and had IBS symptoms for >5 years. All participants underwent a hydrogen breath test for bacterial overgrowth and had an antiendomysial antibody titer drawn. All participants underwent a 24-hour urine collection for intestinal permeability testing after ingestion of a solution of lactulose and mannitol.7,10 Increased intestinal permeability was defined as an elevated urinary lactulose/mannitol ratio (≥0.07). Within 1 week of permeability testing, all subjects underwent endoscopy with small intestinal/colonic biopsies that were stained with H&E and processed for measurement of miR-29a/b, CLDN1, and NKRF.
Subjects were excluded from participation if they had history of inflammatory bowel disease or microscopic colitis, lactose intolerance, bacterial overgrowth, or celiac sprue; positive hydrogen breath test or antiendomysial antibody titer; used nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and/or alcohol for a period of 21 days before the study; history of diabetes, pancreatitis, cirrhosis, food allergies, rheumatoid arthritis, collagen vascular disease, kidney disease, or chronic dermatologic condition.
Cell Culture
Human colonic epithelial cells (FHC) and small intestinal epithelial cells (ATCC CCL-241; FHs74Int) (CRL-1831, ATCC, Manassas, VA) were cultured as described previously.10
Microarray Analysis
Microarray analysis for gene and microRNA profiling was performed in SeqWright and LC Sciences (Houston, TX) as described previously.10
miRNA Target Prediction
Target mRNAs of the miR-29 family were determined using the miRGen web tool for the algorithms TargetScanS (release 3.1) and PicTar (4-species conservation). Targets predicted by 2-way intersection of these algorithms were further analyzed. Ensembl gene identification numbers of putative targets retrieved from miRGen were referenced to Ensembl builder. The convergence of these miRNA targets with mRNAs that were differentially expressed in a microarray study of miR-29a/b−/− vs WT mouse colon tissue was determined. mRNA probe sets were considered differentially expressed if the fold change was ≥ +1.5 or ≤ −1.5 at cyberT P ≤. 05.
Additional Methods
Detailed methodology is described in the Supplementary Methods.
Statistical Analysis
All statistical analyses were done using GeneSpring GX software version 7.3 (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA), Prism version 6 (GraphPad Inc, San Diego, CA), and ASA software Version 9.1.3. One-way analysis of variance was done, followed by Tukey’s comparison or by the Benjamini and Hochberg correction for false-positive reduction. T tests were also used. Values are expressed as mean ± SD. Human tissue samples were paired for comparisons based on matching for age and sex. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to explore the association between intestinal permeability and miR-29a and miR-29b expression.
Results
Intestinal Hyperpermeability and miR-29 Expression in Humans
We enrolled 233 subjects; 219 (94%) of which completed the study; 14 dropped out, including 12 IBS patients and 2 controls. Of the 219, there were 109 IBS-D patients (28.6 ± 2.9 years old, 34 male and 75 female); 74 constipation-predominant IBS (IBS-C) patients (30.4 ± 4.3 years, 20 male and 54 female); and 36 healthy controls (mean age 31.5 ± 3.6 years; 10 male and 26 female). There was no significant difference in age or sex between the groups (controls, IBS).
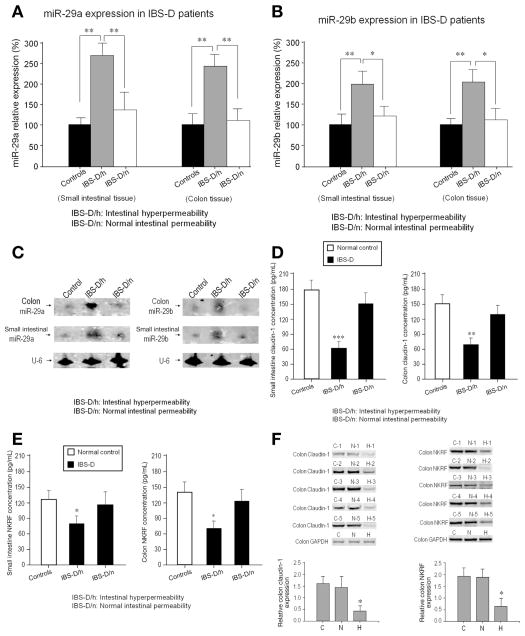
Increased intestinal permeability was found in 37% (40 of 109) of IBS-D patients and in approximately 4% (3 of 74) of IBS-C patients. Enhanced expressions of miR-29a and miR-29b, but not miR-29c, were found in small bowel and colon biopsies from only the IBS-D patients who had increased intestinal permeability compared with IBS-D patients with normal intestinal permeability (Figure 1A and B). Northern blots (Figure 1C) confirmed the polymerase chain reaction data in Figure 1A and B. There were not increased levels of miR-29a and miR-29b in IBS-C patients (Supplementary Figures 2A and B). There was no significant variability in miR-29 levels across patients with IBS-D and increased intestinal permeability. The distribution of increased miR-29a/b expression was similar in the small intestine and colon without regional differences noted. There was a positive correlation between the L/M ratio and miR-29a and miR-29b expression (Supplementary Table 1) in IBS-D patients with increased intestinal permeability. Interestingly, decreased CLDN1 and NKRF expression was present in the small intestine and colon in IBS-D patients with increased intestinal permeability, but not, IBS-D patients with normal intestinal permeability (Figures 1D, E, and F).
Figure 1.
Increased intestinal permeability and miR-29 expression in humans: (A) Real-time polymerase chain reaction assay of miR-29a expression in human small intestine and colon from IBS-D patients. Significant upregulation of miR-29a expression in IBS-D/h patients (n = 40) compared with both controls (n = 36) and IBS-D/n patients (n = 69) (**P < .01) was present in both colon and small intestine. There were no significant differences in miR-29a expression between IBS-D/n patients and controls. (B) Analysis of miR-29b expression in small intestinal and colon tissue showed similar changes as miR-29a. Significant changes in IBS-D/h patients compared to normal controls (**P < .01) and to IBS-D/n patients (*P < .05) were present. (C) Northern blots: Left panel shows miR-29a expression from 3 subjects (control, IBS-D/h, IBS-D/n); right panel shows corresponding blots for miR-29b. These results further confirm the PCR data in (A) and (B). (D) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for CLDN1 expression in small intestine and colon that was significantly decreased in IBS-D/h patients (n = 40) compared with IBS-D/n patients (n = 69) and controls (n = 36) (**P < .01; ***P < .001). (E) NKRF expression was decreased in small intestine and colon in IBS-D/h patients compared with IBS-D/n patients and controls (*P < .05). (F) Western blots from 5 controls, 5 IBS-D patients with normal intestinal permeability, and 5 IBS-D patients with intestinal hyper-permeability. There was a decrease in CLDN1 (left) and NKRF (right) expression in IBS-D patients with intestinal hyper-permeability (H) compared with controls (C) and IBS-D with normal intestinal permeability (N) (*P < .05).
In Vivo Deletion of miR-29 (miR-29a/b−/−) Prevents Intestinal Hyperpermeability
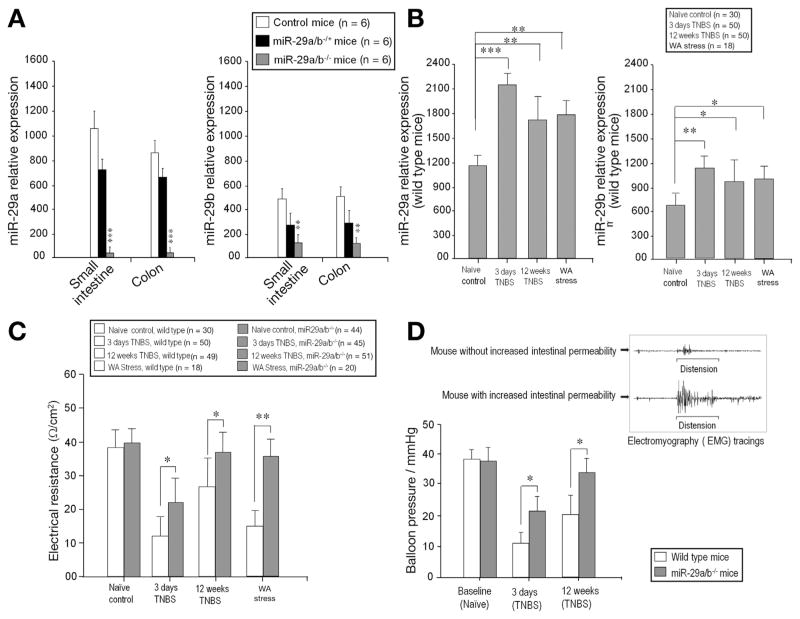
Validations of miR-29 expression in miR-29a/b−/− mice were performed. miR-29a and miR-29b expression were decreased in colon and small intestine (Figure 2A), and the major organs of miR-29a/b−/− mice (Supplementary Figures 3A and B), however, miR-29c was not altered (data not shown).
Figure 2.
In vivo deletion of miR-29 prevents intestinal hyperpermeability. Real-time PCR generated from 6 WT, 6 miR-29a/b−/+ (heterozygous) mice, and 6 miR-29a/b−/− (homozygous) mice. (A) There was significantly diminished miR-29a expression (left panel) in the small intestine and colon of miR-29a/b−/− mice compared with control and miR-29a/b−/+ mice (***P < .0001). There was significantly diminished miR-29b expression (right panel) in miR-29a/b−/− mice compared with control and miR-29a/b−/+ mice (**P < .001). (B) TNBS colitis (3 days, 12 weeks) and WAS resulted in up-regulation of miR-29a and miR-29b expression in WT mouse colon tissue. (C) There was increased intestinal permeability (decreased intestinal electrical resistance) after TNBS colitis or WAS. (D) Left: Depicts decreased visceral hypersensitivity in miR-29a/b−/− mice compared with WT after TNBS. Right: Electromyographic (EMG) tracing of mouse abdominal wall muscles shows increased in EMG activity after colonic distension in mice with increased intestinal permeability (lower tracing) compared with mice with normal intestinal permeability (upper tracing) after TNBS.
We then investigated whether silencing miR-29 expression could augment intestinal barrier integrity. TNBS colitis resulted in up-regulation of miR-29a and miR-29b expression in WT mouse colon tissue at both 3 days and 12 weeks after TNBS administration compared with naïve control WT mice (Figure 2B). We performed a parallel study to the TNBS experiments using WAS in which there was enhanced miR-29a and miR-29b expression after WAS (Figure 2B). There was increased intestinal permeability (decreased intestinal electrical resistance) after TNBS colitis or WAS in WT compared with miR-29a/b−/− mice (Figure 2C). Pearson correlation test showed that intestinal permeability tightly correlated with miR-29a, r = −0.44; P < .05, and r = −0.49; P < .05 with miR-29b expression at 3 days after TNBS colitis. Twelve weeks after TNBS, the correlation between intestinal permeability and miR-29a expression was r = −0.81; P < .001; and r = −0.79; P < .001 with miR-29b expression. Pearson correlation analysis also revealed a tight correlation between intestinal permeability (intestinal electrical resistance) and miR-29a/b expression after WAS, r = −0.71; P < .001 in miR-29a expression; and r = −0.65; P < .001 in miR-29b expression. There was significantly reduced visceral hypersensitivity in miR-29a/b knockout mice compared with WT mice at both 3 days and 12 weeks after TNBS (Figure 2D, left panel). Colonic distension resulted in a significant increase in electromyographic activity in mice with increased permeability compared with normal or recovered permeability (Figure 2D, right panel). Table 1 summarizes intestinal permeability (electrical resistance) in WT and miR-29a/b−/− mice 3 days and 12 weeks after TNBS. As is shown, in vivo knockout of miR-29a/b prevented increased intestinal permeability in both the acute and healed colitis group compared with WT mice.
Table 1.
Intestinal Permeability: Wild-type Mice vs miR-29a/b−/− Mice Following TNBS
| Total mice # of each group | Electrical resistance (Ω/cm2) | Normal intestinal permeability | Increased intestinal permeability | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Naïve control (wild-type mice) | 30 | 39.18 ± 5.0 | 100% | 0% |
| Naïve control (miR29a/b−/− mice) | 44 | 40.09 ± 4.2 | 100% | 0% |
| 3 days TNBS (wild-type mice) | 50 | 11.95 ± 6.1 | 0% | 100% |
| 3 days TNBS (miR-29a/b−/− mice) | 45 | 22.01 ± 7.8 | 36% (16/45) | 64% (29/45) |
| 12 weeks TNBS (wild-type mice) | 49 | 27.45 ± 8.6 | 29% (14/49) | 71% (35/49) |
| 12 weeks TNBS (miR-29a/b−/− mice) | 51 | 37.05 ± 5.5 | 94% (48/51) | 6% (3/51) |
Identification of New miR-29 Targets in miR-29a/b−/− Mice
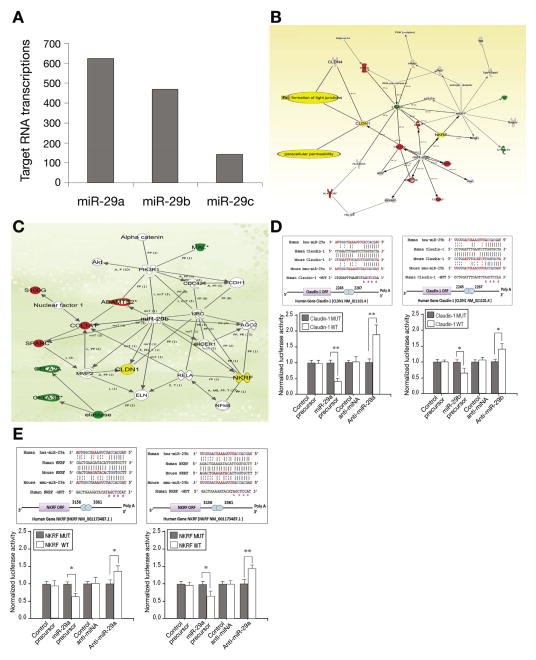
Microarray analysis was done on miR-29a/b−/− mice out using Affymetrix Expression Profiling (SeqWright, Houston, TX). The predicted target genes of miR-29 in miR-29a/b−/− mice were identified in silico. A conservative approach was undertaken, limiting the targets to those predicted by 2 algorithms, TargetScanS and 4-way PicTar, hereafter referred to as the 2-way intersection. At this intersection, 1238 target transcripts corresponding to 867 unique official gene symbols were present at this intersection for miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c (Figure 3A). The number of mRNA targets predicted for each of the differentially expressed miRNAs varied substantially. The existence of multiple miRNA targets on several different mRNA transcripts is explained by the various levels of complementarity between the target sequences and the miRNA sequence. This explains the different degrees of silencing efficiency exerted by miRNAs on targets in various organ types. Additionally, microRNA microarrays (LC Sciences, Houston, TX) were also carried out in colon tissues from miR-29a/b−/− mice. The miR-29 regulated miRNAs and their predicted targets are listed in Supplementary Table 2. The range of effects underscores the variety of roles miR-29 plays in control of transcription and other cellular processes by interacting with the 3′-UTR regions in these genes and miRNAs in different organs.
Figure 3.
Identification of new miR-29 targets in miR-29a/b−/− mice. (A) Microarray analysis on miR-29a/b−/− mice out using Affymetrix Expression Profiling. Targets were predicted by 2 algorithms, TargetScanS and 4-way PicTar (2-way intersection); 1238 target transcripts corresponding to 867 unique official gene symbols were present at this intersection for miR-29a, miR-29b and miR-29c. (B), (C) Genes identified as differentially expressed in miR-29a/b−/− mice were integrated into computationally generated networks on the basis of the evidence stored in the Ingenuity Pathway Analysis (IPA) knowledge memory indicating a relevance to this network. The node shapes in (B) denote miR-29 regulated tight junction proteins and paracellular permeability through CLDN1 and other signaling pathways such as NF-κB, PI3 kinase, collagen A1, and ubiquitin C are also involved. Networks in (C) further define NKRF and CLDN1 and their associated gene network in miR-29 knockout mice. (D, E) The upper panel shows dual-luciferase reporter assay with the vector containing the putative (mutant) CLDN1 and NKRF 3′ UTR target site downstream of a luciferase reporter gene. There was perfect complementarity between miR-29a and miR-29b and the 3′UTR of CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs (including the 2–7 seed), which is consistent with it being a bona fide miR-29a/b binding site with CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs (upper panels). CLDN1-WT and NKRF-WT (normal sequences) displayed increased luciferase activity compared with the activity of cells transfected with CLDN1 and NKRF-MUT (mutant) lower panels of Figure 3D and E. Relative luciferase reporter activity of FHC cells co-transfected with miR-29a/b precursor and with CLDN1 and NKRF-WT (normal sequences) was significantly lower than the activity of FHC cells transfected with CLDN1 and NKRF-MUT (mutant). FHC cells transfected with the anti-miR-29a/b inhibitor and with CLDN1 and NKRF-WT displayed increased luciferase activity when compared with the activity of cells transfected with CLDN1 and NKRF-MUT (D) and (E), lower panels (**P < .01 and *P < .05).
The functions of the 1238 predicted miRNA target transcripts and the molecular pathways they potentially constitute were then assessed using Ingenuity Pathway Analysis software for the microarray data. The predicted targets were significantly enriched for 5 key signaling pathway-related networks, including ones triggered by tumor necrosis factor; NR3C1 and dexamethasone; KITLG; GPD1, and erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor. Genes involved in maintaining intestinal barrier integrity and formation of tight junctions were highly represented within these networks (Figure 3B). Notable among the up-regulated genes were NKRF and CLDN1, which are both critical signaling molecules that regulate intestinal paracellular permeability (Figure 3B and C). Through a combined approach using both TargetScan and 4-way PicTar, these 2 genes were identified as functional intestinal integrity targets within the miR-29 family. Also, a further search for miR-29a/b target genes revealed that NKRF and CLDN1 carry putative miR-29a/b binding sites, as predicted by the Sanger miRNA data base target search program (miRBase http://micrna.sanger.ac.uk/sequences).
To confirm target specificity between miR-29a/b and CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs, we performed dual-luciferase reporter assay with the vector containing the putative (mutant) CLDN1 and NKRF 3′ UTR target site downstream of a luciferase reporter gene. The upper panel of Figure 3D and E shows the result of a dual-luciferase reporter assay with the vector containing the putative (mutant) CLDN1 and NKRF 3′ UTR target site downstream of a luciferase reporter gene. There was perfect complementarity between miR-29a/b and the 3′ UTR of CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs (including the 2–7 seed), which is consistent with it being a bonafide miR-29a/b binding site with CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs. CLDN1-WT and NKRF-WT (normal sequences) displayed increased luciferase activity compared with the activity of cells transfected with CLDN1 and NKRF-MUT (mutant) lower panels of Figure 3D and E. These data confirm that CLDN1 and NKRF mRNAs are targets of miR-29a/b, and that miR-29a/b can down-regulate expression of CLDN1 and NKRF proteins by translational repression. Therefore, we focused on these 2 target genes (CLDN1 and NKRF), however, there may be other genes also involved in the network of intestinal integrity function that we will investigate in future studies as shown in Figure 3B and C.
Eleven miR-29 target genes have been confirmed so far via in vitro studies, including CDC42, CDK6, COL1A1, DNMT3A, DNMT3B, GLUL, IGF1, MCL1, MMP2, PDGFC, and PIK3R1.14–28 We examined these 11 gene expressions in 3 major gastrointestinal organs from miR-29−/− mice, to investigate expression abnormalities after miR-29 (in vivo) knockout conditions (Supplementary Figures 3C, D, and E). These results illustrate that the same miRNA can target different genes in different organs and the expression of specific target genes is due to a balance between direct and indirect modulatory effects on gene expression by specific miRNAs.
Facilitation of Intestinal Barrier Integrity in miRNA-29a/b−/− Mice Via Claudin-1 and Nuclear Factor-κB–Repressing Factor Signaling
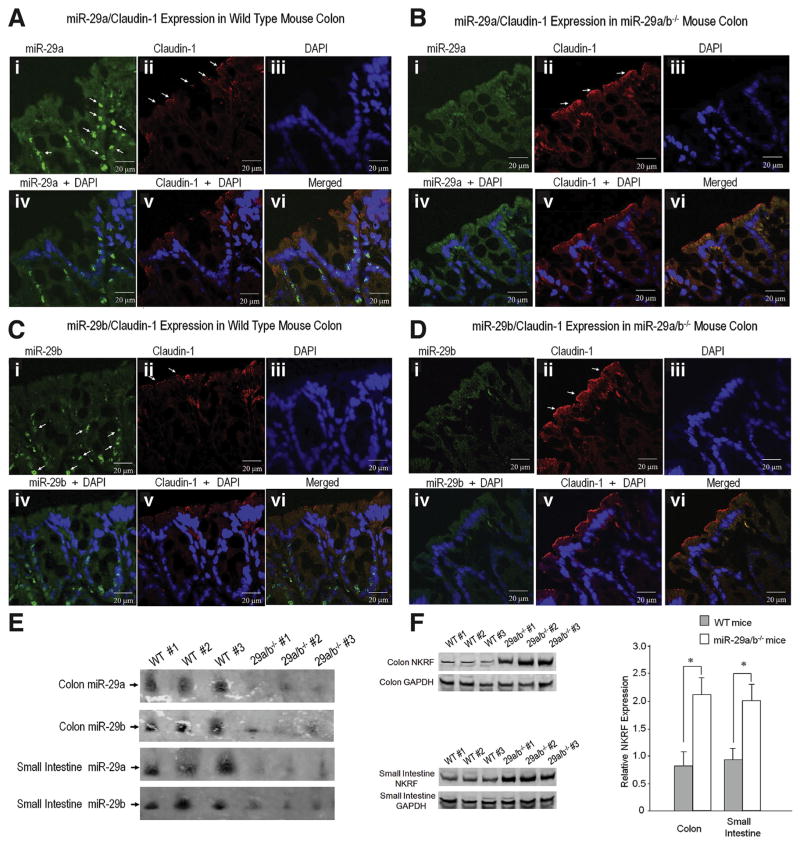
To confirm that CLDN1 and NKRF are target gene regulators of intestinal permeability in miR-29a/b−/− mice, we performed in situ hybridization on colon tissue sections from WT mice and miR-29a/b−/− mice labeled with a probe specific for mature miR-29a and miR-29b and its co-localization with CLDN1 (Figure 4A and B). The miR-29a expression was lower in miR-29a/b−/− mice (Figure 4Ba) than in controls (Figure 4Aa). There was an increase in CLDN1 expression in miR-29a/b−/− mouse colon (Figure 4Bb) compared with control mouse colon (Figure 4Ab). Figure 4C and D demonstrate that miR-29b expression is co-localized with CLDN1 in control mouse colon and miR-29a/b−/− mouse colon. In order to further confirm the co-localization of miR-29a and CLDN1 expression in the colon, additional time series experiments were done with 10-day-old mouse pups and 22-day-old mice. We found that miR-29 expression is translocated during aging. Supplementary Figure 4B demonstrates an infant mouse colon; the miR-29a and CLDN1 expression are very tightly co-localized compared with adult mouse colon (Figure 4). Supplementary Figure 4C shows double labeling using fluorescence in situ hybridization with the epithelial marker, E-cadherin and neural marker, PGP9.5.
Figure 4.
Facilitation of intestinal barrier integrity in miRNA-29a/b−/− mice via CLDN1 and NKRF signaling network: Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) was used to identify key target genes that regulate intestinal permeability in miR-29a/b−/− mice. (A) Shows FISH for miR-29a and its co-localization with CLDN1 expression in normal mouse colon (WT). (A-i) White arrows indicate miR-29a expression. (A-ii) shows immunohistochemical staining for CLDN1 in normal colon tissue. White arrows indicate CLDN1 expression. (A-vi) demonstrates co-localization of miR-29a expression and CLDN1 expression with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining. (B) Shows FISH analysis of miR-29a and its co-localization with CLDN1 expression in miR-29a/b−/− mouse colon. (B-i) shows a reduction in miR-29a expression in miR-29a/b−/− mouse colon compared with colon from WT mice (A-i). (B-ii) shows increased CLDN1 expression in miR-29a/b−/− mouse colon compared with WT mice (A-i). (B-vi) demonstrates co-localization of miR-29a expression and CLDN1 expression with DAPI in miR-29a/ b−/− mice. (C, D) show FISH for miR-29b and its co-localization with CLDN1 expression. (C-i) Shows miR-29b expression in WT mouse colon, the white arrows indicate miR-29b expression. There was an increase in CLDN1 expression (D-ii) in miR-29a/b−/− mice compared with WT mice (C-ii). (E) Northern blot that illustrates a decrease in miR-29a and miR-29b expression in miR-29a/b−/− mice compared to WT mice. (F) Illustrates Western blots of NKRF expression in colon and small intestine tissue. There was an increase in NKRF expression in miR-29a/b−/− mice (n = 3) compared with WT mice (n = 3) (*P < .05).
Northern blots show a diminution of miR-29a and miR-29b expression in miR-29a/b−/− mice (Figure 4E). Figure 4F shows a significant increase in NKRF expression in miR-29a/b−/− mice (small intestine and colon) compared with WT mice. CLDN1 was significantly up-regulated in miR-29a/b−/− mice vs WT mice after TNBS or WAS (Supplementary Figure 4A). Pearson correlation test showed that increased CLDN1 expression correlated with decreased miR-29a, r = −0.55; P < .01, and with decreased miR-29b expression r = −0.43; P < .05, 3 days after TNBS colitis. Twelve weeks after TNBS, the correlation between CLDN1 and miR-29a expression was r = −0.61; P < .001 and was r = −0.57; P < .01 with miR-29b expression. Pearson correlation analysis showed similar results in WAS mice between CLDN1 and miR-29a and miR-29b expression, r = −0.52; P < .01 and r = −0.53; P < .01, respectively.
Recruitment of Claudin-1 and Nuclear Factor-κB–Repressing Factor Prevents Epithelial Hyperpermeability Via In Vitro Modulation of miR-29
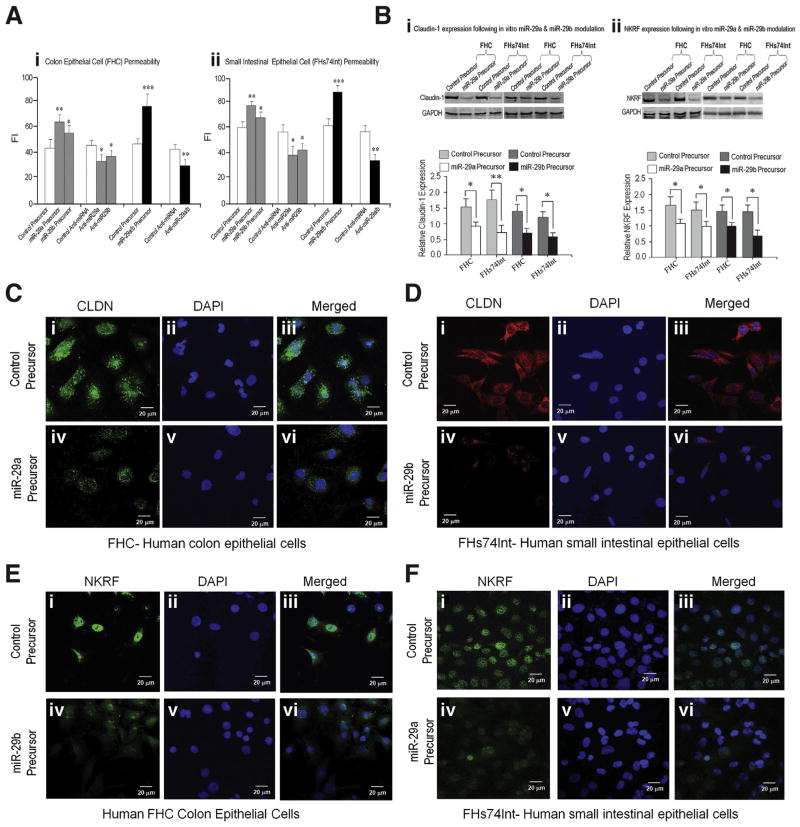
Overexpression of miR-29a or miR-29b enhanced epithelial permeability in both human colon (FHC) (Figure 5Aa) and small intestinal epithelial cells (FHs74Int) (Figure 5Ab); and anti–miR-29 (inhibitors) had the opposite effect and decreased epithelial permeability. Simultaneous overexpression or inhibition of both miR-29a and miR-29b showed even more pronounced effects confirming that the miR-29a/b cluster has synergy to regulate colon and small intestinal permeability. Transfection of miR-29a or miR-29b precursors down-regulated CLDN1 and NKRF expression in both FHC and FHs74Int cells (Figure 5Ba,b). Confocal immunofluorescent staining of these cells revealed that expression of CLDN1 and NKRF was reduced by miR-29a/b overexpression (Figure 5C, D, E, and F). Silencing CLDN1 and NKRF in vitro by RNA interference of CLDN1 and NKRF in FHC and FHs74Int cells induced increased epithelial cell permeability (Supplementary Figure 5A and B) that was associated with constitutive expression of miR-29a/b (Supplementary Figure 5C). Overexpression of miR-29a/b led to reductions in CLDN1 and NKRF, along with an increase in intestinal permeability.
Figure 5.
Recruitment of CLDN1 and NKRF prevents epithelia hyperpermeability via in vitro modulation of miR-29: Intestinal epithelial permeability was modulated by miR-29a and miR-29b as demonstrated in vitro by using fluorescence intensity (FI) to measure of epithelial cell permeability. Over-expression of miR-29a or miR-29b using precursors significantly enhanced epithelial permeability in both human FHC cells (A-i) and human FHs74Int cells (A-ii). Inhibiting miR-29a or miR-29b expression using anti-miRNAs had the opposite effect. Simultaneous over-expression or inhibition of both miR-29a and miR-29b showed even stronger effects (***P < .001; **P < .01; and *P < .05). Western blots (B-i) show a decrease in CLDN1 expression in human colon epithelial cells (FHC) and human small intestinal epithelial cells (FHs74Int) following transfection of miR-29a and miR-29b precursors compared with control precursor. (B-ii) Shows miR-29a and miR-29b regulation of NKRF expression in FHC and FHs74Int cells. There was a substantial decrease in NKRF expression after up-regulation of miR-29a and miR-29b using miR-29a or miR-29b precursors compared with control precursor (*P < .05; **P < .01). Confocal immunofluorescent staining of human FHC and human FHs-74Int cells for CLDN1 and NKRF expression is depicted in panels (C, D, E, and F). There were decreases in CLDN1 expression in FHC cells (C-iii) and in FHs74Int cells (D-iii) following overexpression of miR-29a or miR-29b (by using precursors of miR-29a or miR-29b) compared with control precursors (C-i and D-i). There were decreases in NKRF expression in FHC cells (E-iv) and FHs74Int cells (F-iv) after overexpression of miR-29a or miR-29b compared with control (E-i and F-i).
Discussion
The novel findings of our current study show that silencing miR-29 family in knockout mice (miR-29a/b−/−) restores intestinal permeability and the associated pathologic hallmarks of increased intestinal permeability. To our knowledge, our findings are the first translational datasets (in vitro, in vivo, and human ex vivo) to demonstrate that suppression of a cluster miRNA can reverse increased intestinal permeability; to identify miR-29 targets in miR-29a/b−/− mice and the function of 1238 predicted miRNA target transcripts and molecular pathways they potentially constitute; to show the miR-29a/b cluster has synergy to regulate intestinal epithelial permeability; and human study to identify that increased intestinal permeability may be caused by enhanced miR-29 expression in IBS-D patients, but not IBS-C patients.
Our findings add to the understanding of the regulation of intestinal permeability in the pathophysiology of gastrointestinal disorders. They suggest that silencing of miRNAs (miR-29) can reverse intestinal hyperpermeability via up-regulation of CLDN1 and NKRF and could lead to innovative targets and treatments for chronic gastrointestinal symptoms in patients with increased intestinal permeability, such as IBS-D. Our translational findings may also provide new treatments for other systemic diseases associated with increased intestinal permeability including food allergies, allergic disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, chronic dermatologic conditions, and alcoholic cirrhosis.8,9
miRNAs are involved in a number of chronic gastrointestinal disorders, such as IBS, ulcerative colitis, and Crohn’s disease.29 One study has shown increased expression of miR-510 that targets HTR3E in IBS patients.30 Recently, we found up-regulated gastrointestinal miR-29a expression increased intestinal permeability through down-regulation of glutamine synthetase in IBS-D patients.10 Glutamine synthetase mutations have been described in children with congenital deficiencies of glutamine.31 Our current study addresses the mechanisms by which miRNA-29 modulates intestinal permeability in vivo using a miRNA knockout mouse model.
CLDN1 is a key tight junction protein that interacts with intracellular signaling pathways that regulates and maintains intestinal permeability. Decreased CLDN1 leads to increased intestinal permeability in IBS patients.32 In contrast, overexpression of CLDN1 in epithelial MDCK cells strengthens barrier integrity and decreases paracellular permeability to macromolecules.33 The results here show enhanced expression of CLDN1 leads to restoration of normal intestinal permeability in vivo and in vitro by silencing the expression of miR-29a/b.
NKRF is a transcriptional silencer protein that is a suppression factor for NF-κB. In vitro, NF-κB proteins bind to purified NKRF by a direct protein–protein interaction and in a cellular assay NKRF inhibits NF-κB basal activity.34 This function has been linked to inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, septic shock, viral infection, and improper immune development.35,36 Our current study demonstrates that IBS-D patients with increased intestinal permeability have significantly decreased gut-NKRF expression. This mechanism is supported by the results that down-regulation of miR-29 expression enhances NKRF gene expression and leads to restoration of intestinal permeability both in vivo and in vitro.
Collectively, we have shown that in vivo miR-29a/b modulates CLDN1 and NKRF expression–that regulates intestinal permeability. Up-regulation of miR-29a/b and the consequent down-regulation of CLDN1 and NKRF expression may be key etiologic factors driving intestinal permeability and chronic gastrointestinal symptoms in a subset of patients with IBS-D. Silencing of the miR-29a/b cluster expression reverses intestinal hyperpermeability and represents an innovative approach to treating patients with increased intestinal permeability. Increased miR-29a causes decreased glutamine synthetase,10 which may potentially lead to decreased CLDN1 signaling, which directly or indirectly lead to increased intestinal permeability through several potential mechanistic pathways (Supplementary Figure 6). Enhanced feedback of increased intestinal permeability may occur due to cytokines.37–39 Increased intestinal permeability caused by tumor necrosis factor–α may be due to activation of NF-κB expression38 and disassembling of CLDN1. Aberrant NKRF and CLDN1 expression may be key pathological factors to induce and prolong the intestinal hyperpermeability. Our conclusions are supported by all of the approaches taken in our translational study—in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo. Taken together, these findings may lead to new therapeutic strategies and targets for the treatment of disorders with increased intestinal permeability via miR-29 regulation.40
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Institutes of Health from National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (DK099052); National Center for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (AT005291); and from the Department of Veteran Affairs.
Abbreviations used in this paper
- CLDN1
Claudin-1
- IBS
irritable bowel syndrome
- IBS-C
constipation-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
- IBS-D
diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome
- miRNA
micro-RNA
- mRNA
messenger RNA
- NKRF
nuclear factor-κB–repressing factor
- TNBS
2,4,6-trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid
- UTR
untranslated region
- WAS
water avoidance stress
- WT
wild-type
Footnotes
Conflicts of interest
The authors disclose no conflicts.
Note: To access the supplementary material accompanying this article, visit the online version of Gastroenterology at www.gastrojournal.org, and at http://dx.doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2014.09.037.
Author names in bold designate shared co-first authorship.
References
- 1.Mayer EA. Irritable bowel syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2008;358:1692–1699. doi: 10.1056/NEJMcp0801447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Simren M, Axelsson J, Gillberg H, et al. Quality of life in inflammatory bowel disease in remission: the impact of IBS-like symptoms and associated factors. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:389–396. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05475.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Camilleri M, Madsen K, Spiller R, et al. Intestinal barrier function in health and gastrointestinal disease. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2012;24:503–512. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2982.2012.01921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhou Q, Verne GN. New insights into visceral hypersensitivity-clinical implications in IBS. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011;8:349–355. doi: 10.1038/nrgastro.2011.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Spiller RC, Jenkins D, Thornley JP, et al. Increased rectal mucosal enteroendocrine cells, T lymphocytes, and increased gut permeability following acute Campylobacter enteritis and in post-dysenteric irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2000;47:804–811. doi: 10.1136/gut.47.6.804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dunlap SP, Hebden J, Campbell E, et al. Abnormal intestinal permeability in subgroups of diarrhea-predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Am J Gastroenterol. 2007;101:1288–1294. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2006.00672.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Zhou Q, Zhang B, Verne GN. Intestinal membrane permeability and hypersensitivity in the irritable bowel syndrome. Pain. 2009;146:41–46. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2009.06.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bjarnason I, MacPherson A, Hollander D. Intestinal permeability: an overview. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:1566–1581. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(95)90708-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Keshavarzian A, Holmes EW, Patel M, et al. Leaky gut in alcoholic cirrhosis: a possible mechanism for alcohol-inducedliverdamage. Am JGastroenterol. 1999;94:200–207. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.1999.00797.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Zhou Q, Souba WW, Croce C, et al. MicroRNA-29a regulates intestinal membrane permeability in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. Gut. 2010;59:775–784. doi: 10.1136/gut.2009.181834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhou Q, Price DD, Caudle RM, et al. Visceral and somatic hypersensitivity in a subset of rats following TNBS-induced colitis. Pain. 2008;134:9–15. doi: 10.1016/j.pain.2007.03.029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Bradesi S, Schwetz I, Ennes HS, et al. Repeated exposure to water avoidance stress in rats: a new model for sustained visceral hyperalgesia. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2005;289:G42–G53. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00500.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Zhou Q, Price DD, Dreher KL, et al. Localized colonic stem cell transplantation enhances tissue regeneration in murine colitis. J Cell Mol Med. 2012;16:1900–1915. doi: 10.1111/j.1582-4934.2011.01485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Park SY, Lee JH, Ha M, et al. miR-29 miRNAs activate p53 by targeting p85 alpha and CDC42. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2009;16:23–29. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.1533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Zhao JJ, Lin J, Lwin T, et al. MicroRNA expression profile and identification of miR-29 as a prognostic marker and pathogenetic factor by targeting CDK6 in mantle cell lymphoma. Blood. 2010;115:2630–2639. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-09-243147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Li Y, Wang F, Xu J, et al. Progressive miRNA expression profiles in cervical carcinogenesis and identification of HPV-related target genes for miR-29. J Pathol. 2011;224:484–495. doi: 10.1002/path.2873. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sekiya Y, Ogawa T, Yoshizato K, et al. Suppression of hepatic stellate cell activation by microRNA-29b. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2011;412:74–79. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2011.07.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, et al. Biological functions of miR-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. J Biol Chem. 2009;284:15676–15684. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M809787200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Meunier L, Siddeek B, Vega A, et al. Perinatal programming of adult rat germ cell death after exposure to xenoestrogens: role of microRNA miR-29 family in the down-regulation of DNA methyltransferases and Mcl-1. Endocrinology. 2012;153:1936–1947. doi: 10.1210/en.2011-1109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fabbri M, Garzon A, Cimmino Z, et al. MicroRNA-29 family reverts aberrant methylation in lung cancer by targeting DNA methyltranferases 3A and 3B. PNAS. 2007;104:15805–15810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0707628104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Koturbash I, Zemp F, Kolb B, et al. Sex-specific radiation-induced microRNAome responses in the hippocampus, cerebellum and frontal cortex in a mouse model. Mutat Res. 2011;722:114–118. doi: 10.1016/j.mrgentox.2010.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Creighton CJ, Hernandez-Herrera A, Jacobsen A, et al. Integrated analyses of microRNAs demonstrate their widespread influence on gene expression in high-grade serous ovarian carcinoma. PLOS ONE. 2012;7:e34546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nguyen T, Kuo C, Nicholl MB, et al. Downregulation of microRNA-29c is associated with hypermethylation of tumor-related genes and disease outcome in cutaneous melanoma. Epigenetics. 2011;6:388–394. doi: 10.4161/epi.6.3.14056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Hand NJ, Horner AM, Master ZR, et al. MicroRNA profiling identifies miR-29 as a regulator of disease-associated pathways in experimental biliary atresia. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2012;54:186–192. doi: 10.1097/MPG.0b013e318244148b. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Roggli E, Gattesco S, Caille D, et al. Changes in microRNA expression contribute to pancreatic β-cell dysfunction in prediabetic NOD mice. Diabetes. 2012;61:1742–1751. doi: 10.2337/db11-1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kovalchuk O, Zemp FJ, Filkowski JN, et al. micro-RNAome changes in bystander three-dimensional human tissue models suggest priming of apoptotic pathways. Carcinogenesis. 2010;31:1882–1888. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgq119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Ding Q, Chang CJ, Xie X, et al. APOBEC3G promotes liver metastasis in an orthotopic mouse model of colorectal cancer and predicts human hepatic metastasis. J Clin Invest. 2011;121:4526–4536. doi: 10.1172/JCI45008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Kwiecinski M, Elfimova N, Noetel A, et al. Expression of platelet-derived growth factor-C and insulin-like growth factor I in hepatic stellate cells is inhibited by miR-29. Lab Invest. 2012;92:978–987. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2012.70. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wu F, Zikusoka M, Trindale A, et al. MicroRNAs are differentially expressed in ulcerative colitis and alter expression of macrophage inflammatory peptide-2 alpha. Gastroenterology. 2008;135:1624–1635. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.07.068. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kapeller J, Houghton LA, Monnikes H, et al. First evidence for an association of a functional variant in the microRNA-510 target site of the serotonin receptor-type 3E gene with diarrhea predominant irritable bowel syndrome. Hum Mol Genet. 2008;17:2967–2977. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddn195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Haberle J, Gorg B, Rutsch F, et al. Congenital glutamine deficiency with glutamine synthetase mutations. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:1926–1933. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa050456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Bertiaux-Vandaele N, Youmba SB, Belmonte L, et al. The expression and cellular distribution of the tight junction proteins are altered in irritable bowel syndrome patients with differences according to the disease subtype. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:2165–2173. doi: 10.1038/ajg.2011.257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Inai T, Kobayashi J, Shibata Y. Claudin-1 contributes to the epithelial barrier function in MDCK cells. Eur J Cell Biol. 1999;78:849–855. doi: 10.1016/S0171-9335(99)80086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nourbakhsh M, Hauser H. Constitutive silencing of IBF-beta promoter is mediated by NRF (NF-kappaB-repressing factor), a nuclear inhibitor of NF-kappaB. EMBO J. 1999;18:6415–6425. doi: 10.1093/emboj/18.22.6415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Brasier AR. The nuclear factor-kappaB-interleukin-6 signaling pathway mediating vascular inflammation. Cardiovasc Res. 2010;86:211–218. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvq076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Sen R, Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a post-translational mechanism. Cell. 1986;47:921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Ma TY, Iwamoto GK, Hoa NT, et al. TNF-α-induced increase in intestinal epithelial tight junction permeability requires NF-κB activation. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2004;286:G367–G376. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00173.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bamias G, Corridoni D, Pizarro TT, et al. New insights into the dichotomous role of innate cytokines gut homeostasis and inflammation. Cytokine. 2012;59:451–459. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2012.06.014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Majewski PM, Thurston RD, Ramalingam R, et al. Cooperative role of NF-{kappa}B and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 (PARP-1) in the TNF-induced inhibition of PHEX expression in osteoblasts. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:34828–34838. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.152868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Zhou Q, Verne GN. miRNA-based therapies for ble Bowel Syndrome. Exp Opin Biol Ther. 2011;8:991–995. doi: 10.1517/14712598.2011.577060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.