Abstract
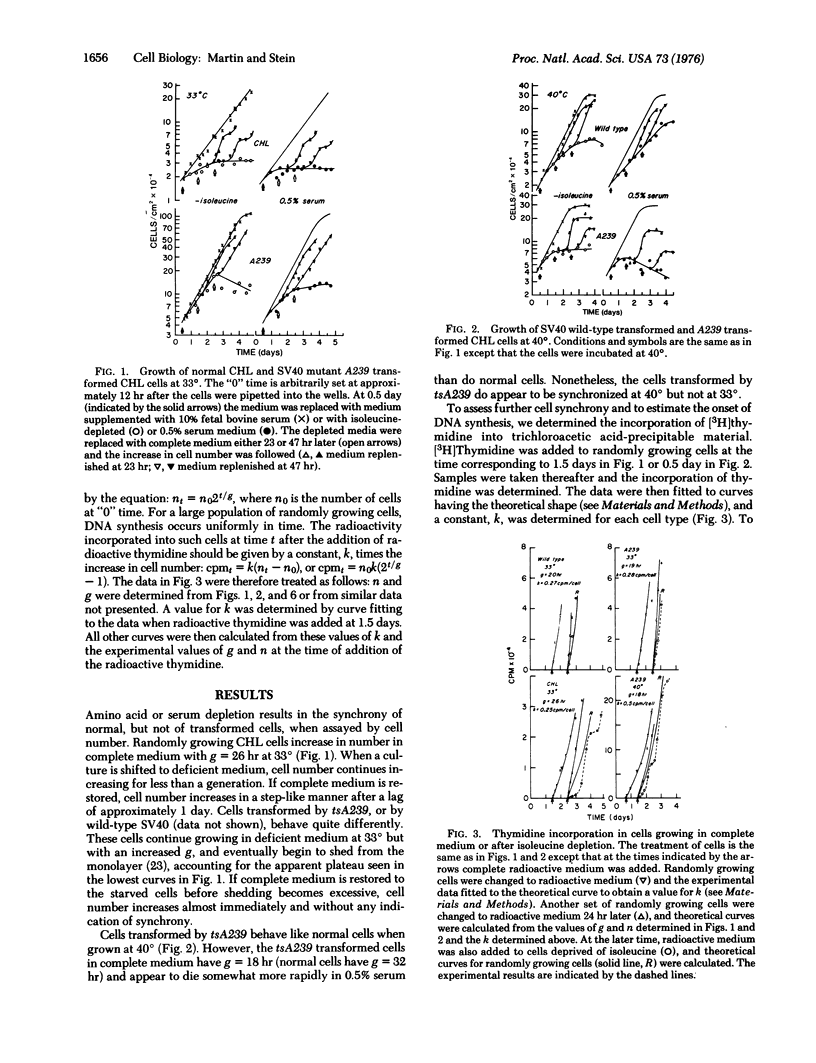
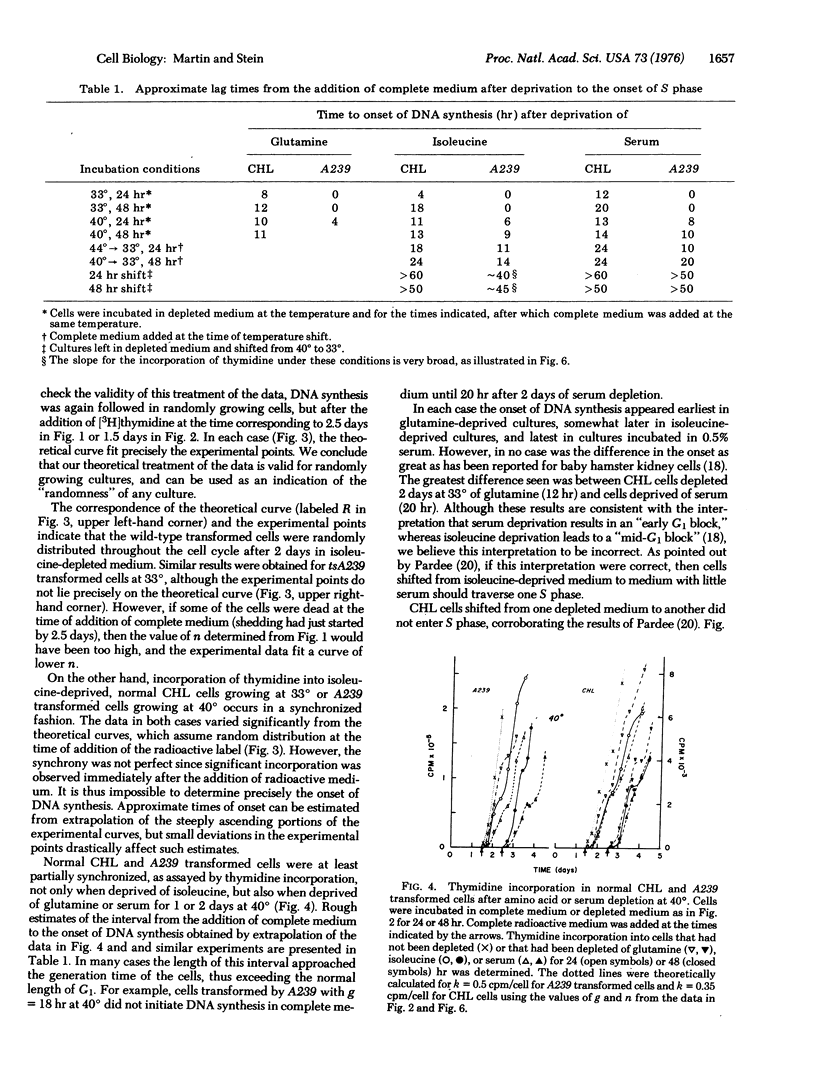
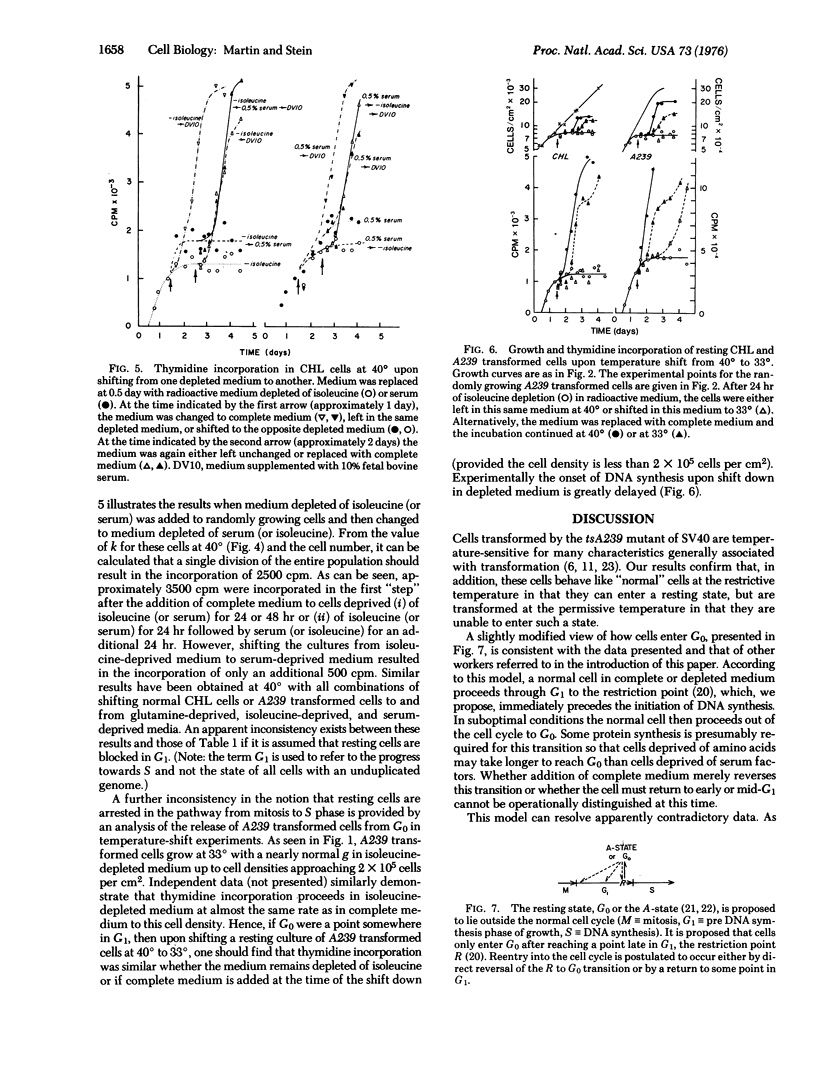
Normal cell deprived of amino acids or serum factors enter a resting state, whereas cells transformed by wild-type simian virus 40 do not. The ability to enter a resting state is temperature-sensitive (ts) in cells transformed by a tsA mutant of simian virus 40. We shown further: (i) that when complete medium is added to resting cells, the length of time until the onset of DNA synthesis often exceeds the length of G1 in growing cells; (ii) that the length of this interval depends upon the conditions used to arrest cell growth; but (iii) that transferring cultures from medium depleted for one factor to medium depleted in a second factor never leads to a round of DNA synthesis; and (iv) that DNA synthesis does not resume rapidly when a resting culture of cells transformed by the tsA mutant is transferred to the permissive temperature in suboptimal medium. A model proposing that in suboptimal conditions cells leave the cell cycle and traverse a branch pathway to enter the resting state is consistent with these findings.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baltimore D. Tumor viruses: 1974. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1187–1200. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baserga R., Costlow M., Rovera G. Changes in membrane function and chromatin template activity in diploid and transformed cells in culture. Fed Proc. 1973 Nov;32(11):2115–2118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Butel J. S. Role of simian virus 40 gene A function in maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):619–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.619-635.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstin S. J., Meiss H. K., Basilico C. A temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutant of the BHK cell line. J Cell Physiol. 1974 Dec;84(3):397–408. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040840308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butel J. S., Brugge J. S., Noonan C. A. Transformation of primate and rodent cells by temperature-sensitive mutants of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):25–36. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Avila J., Martin R. G. Viral DNA synthesis in cells infected by temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):116–124. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.116-124.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou J. Y., Martin R. G. DNA infectivity and the induction of host DNA synthesis with temperature-sensitive mutants of simian virus 40. J Virol. 1975 Jan;15(1):145–150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.1.145-150.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R., Elkington J. Conditions limiting multiplication of fibroblastic and epithelial cells in dense cultures. Nature. 1973 Nov 23;246(5430):197–199. doi: 10.1038/246197a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura G., Itagaki A. Initiation and maintenance of cell transformation by simian virus 40: a viral genetic property. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):673–677. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.673. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y., Avila J., Saral R. The semiautonomous replicon: a molecular model for the oncogenicity of SV40. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):17–24. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin R. G., Chou J. Y. Simian virus 40 functions required for the establishment and maintenance of malignant transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):599–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.599-612.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Simian virus 40 gene A function and maintenance of transformation. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):636–644. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.636-644.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardee A. B. A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1286. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sander G., Pardee A. B. Transport changes in synchronously growing CHO and L cells. J Cell Physiol. 1972 Oct;80(2):267–271. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040800214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. A., Martin L. Do cells cycle? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1263–1267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Function of simian virus 40 gene A in transforming infection. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):613–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.613-618.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P. Simian virus 40 deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis: the viral replicon. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):591–598. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.591-598.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tenen D. G., Baygell P., Livingston D. M. Thermolabile T (tumor) antigen from cells transformed by a temperature-sensitive mutant of simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4351–4355. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4351. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



