Abstract
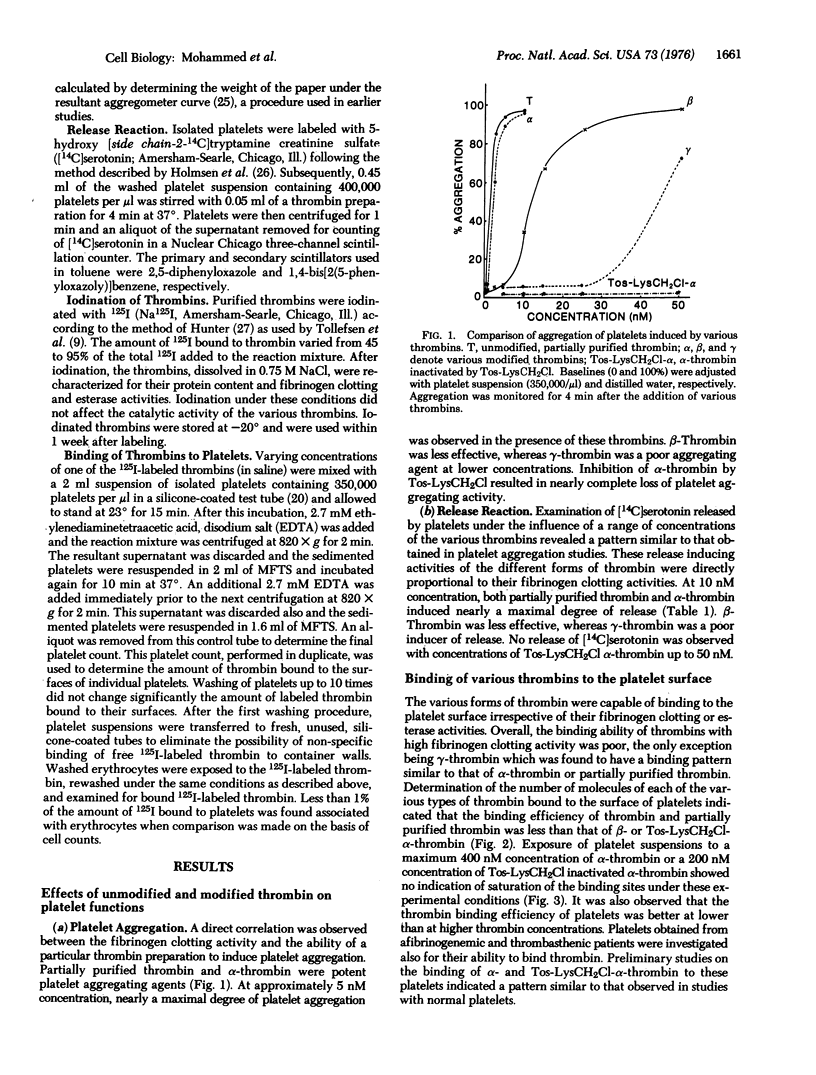
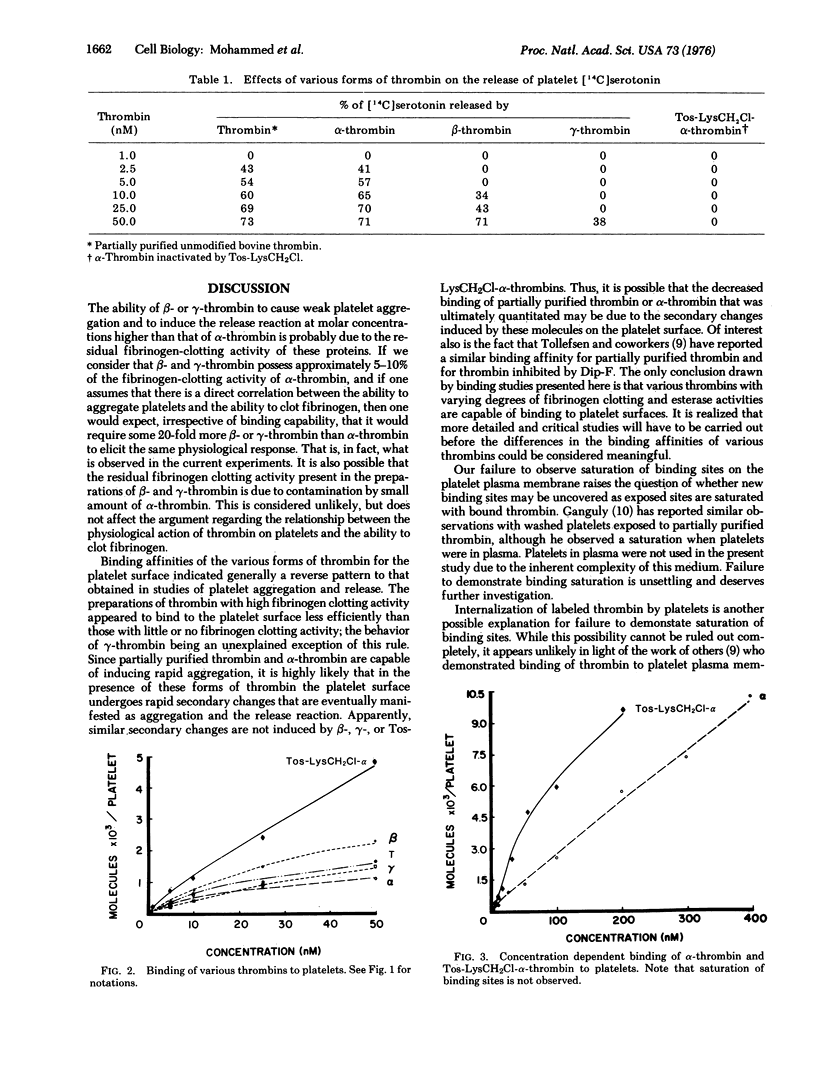
The effect of various forms of thrombin on certain platelet functions has been investigated. Partially purified bovine thrombin which is a mixture of multiple active forms of thrombin, was chromatographed to yield molecular species termed alpha-, beta-, and gamma-thrombin, each of which has varying degrees of fibrinogen clotting and esterase activities. A direct correlation was observed between the ability of the different forms of thrombin to clot fibrinogen and to influence platelet function. In general, thrombin with high fibrinogen clotting activity was also a potent inducer of platelet aggregation and the release reaction, while those species with low clotting ability were poor inducers of aggregation and release.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger N. L., Brodie G. N., Majerus P. W. A thrombin-sensitive protein of human platelet membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):240–243. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.240. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruchter R. G., Crestfield A. M. Preparation and properties of two active forms of ribonuclease dimer. J Biol Chem. 1965 Oct;240(10):3868–3874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRETTE K. Studies on the mechanism of thrombin-catalyzed hemostatic reactions in blood platelets. Acta Physiol Scand Suppl. 1962;195:1–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly P. Binding of thrombin to human platelets. Nature. 1974 Feb 1;247(5439):306–307. doi: 10.1038/247306a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly P. Human platelet proteins. Ser Haematol. 1971;4(1):135–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman J. J., Castaldi P. A. Isolation and characterization of multiple forms of human thrombin. Thromb Res. 1974 May;4(5):653–673. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90221-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASLAM R. J. ROLE OF ADENOSINE DIPHOSPHATE IN THE AGGREGATION OF HUMAN BLOOD-PLATELETS BY THROMBIN AND BY FATTY ACIDS. Nature. 1964 May 23;202:765–768. doi: 10.1038/202765a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmsen H., Ostvold A. C., Day H. J. Behaviour of endogenous and newly absorbed serotonin in the platelet release reaction. Biochem Pharmacol. 1973 Oct 15;22(20):2599–2608. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(73)90068-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LANCHANTIN G. F., FRIEDMANN J. A., HART D. W. THE CONVERSION OF HUMAN PROTHROMBIN TO THROMBIN BY SODIUM CITRATE. ANALYSIS BY SODIUM CITRATE. ANALYSIS OF THE ACTIVATION MIXTURE. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3276–3282. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanchantin G. F., Friedmann J. A., Hart D. W. Two forms of human thrombin. Isolation and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):5956–5966. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L. A rapid method for the purification of bovine thrombin and the inhibition of the purified enzyme wtih phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2501–2506. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundblad R. L., Uhteg L. C., Vogel C. N., Kingdon H. S., Mann K. G. Preparation and partial characterization of two forms of bovine thrombin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Sep 16;66(2):482–489. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90536-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Heldebrant C. M., Fass D. N. Multiple active forms of thrombin. II. Mechanism of production from prothrombin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 10;246(19):6106–6114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammad S. F., Reddick R. L., Mason R. G. Characterization of human platelets separated from blood by ADP-induced aggregation. Am J Pathol. 1975 Apr;79(1):81–94. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. Amino acid analysis: aqueous dimethyl sulfoxide as solvent for the ninhydrin reaction. J Biol Chem. 1968 Dec 10;243(23):6281–6283. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mustard J. F., Packham M. A. Factors influencing platelet function: adhesion, release, and aggregation. Pharmacol Rev. 1970 Jun;22(2):97–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saba S. R., Mason R. G. Studies of an activity from endothelial cells that inhibits platelet aggregation, serotonin release, and clot retraction. Thromb Res. 1974 Dec;5(6):747–757. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90118-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., McCoy L., Kipfer R. K., Murano G. Preparation and properties of thrombin. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Oct;128(1):194–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90022-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seegers W. H., Walz D. A., Reuterby J., McCoy L. E. Isolation and some properties of thrombin-E and other prothrombin derivatives. Thromb Res. 1974 Jun;4(6):829–860. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(74)90026-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tangen O., Berman H. J., Marfey P. Gel filtration. A new technique for separation of blood platelets from plasma. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1971 Jun 30;25(2):268–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tollefsen D. M., Feagler J. R., Majerus P. W. The binding of thrombin to the surface of human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 25;249(8):2646–2651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waugh D. F., Rosenberg R. D. Specific activities of bovine thrombin and thrombin components. Thromb Diath Haemorrh. 1972 Apr 30;27(2):183–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


