Abstract
The yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, contains four types of histones resembling histones H3, H2b, H2a, and H4 of animal cells. These proteins are synthesized primarily, if not exclusively, in the S-phase of the cell cycle. This result is discussed with reference to the insensitivity of ongoing DNA replication in yeast to inhibitors of protein synthesis.
Full text
PDF
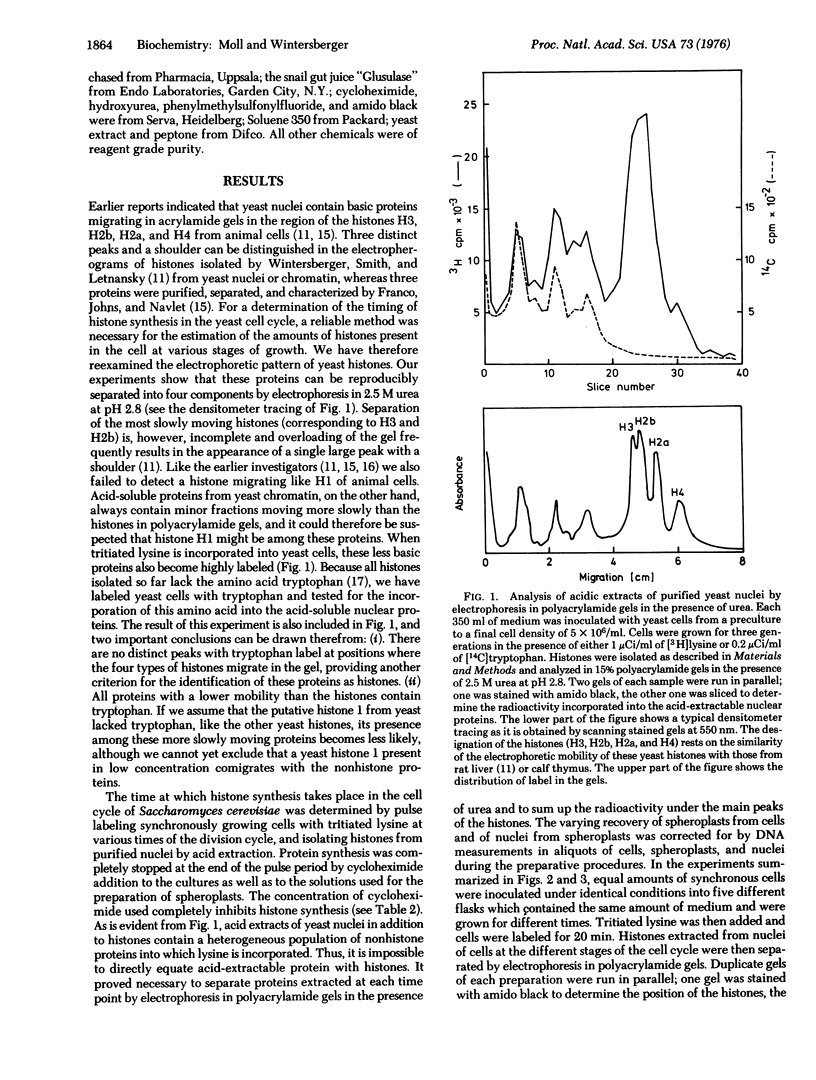
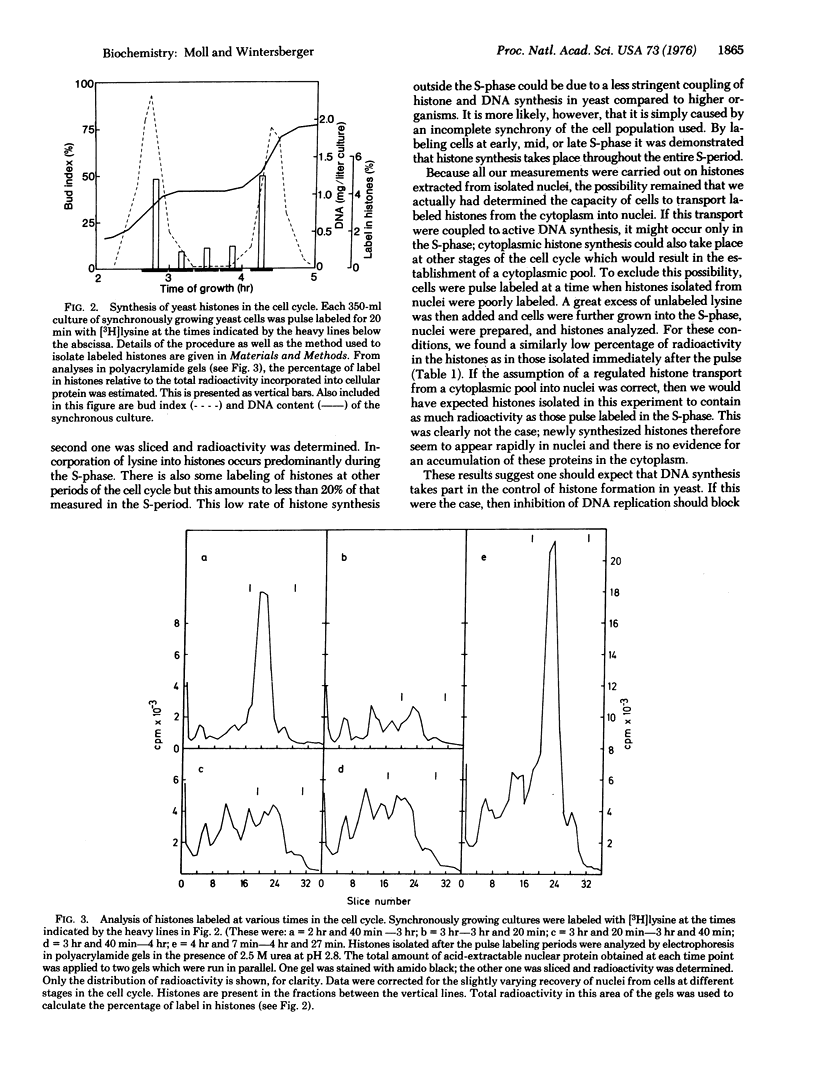


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamson E. D., Woodland H. R. Histone synthesis in early amphibian development: histone and DNA syntheses are not co-ordinated. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):263–285. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90481-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borun T. W., Scharff M. D., Robbins E. Rapidly labeled, polyribosome-associated RNA having the properties of histone messenger. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Nov;58(5):1977–1983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.5.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury E. M., Inglis R. J., Matthews H. R., Sarner N. Phosphorylation of very-lysine-rich histone in Physarum polycephalum. Correlation with chromosome condensation. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02664.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franco L., Johns E. W., Navlet J. M. Histones from baker's yeast. Isolation and fractionation. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jun 1;45(1):83–89. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03532.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golombek J., Wintersberger E. Glucose uptake in the cell cycle of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90673-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golombek J., Wolf W., Wintersberger E. DNA synthesis and DNA-polymerase activity in synchronized yeast cells. Mol Gen Genet. 1974;132(2):137–145. doi: 10.1007/BF00272179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorovsky M. A., Keevert J. B. Absence of histone F1 in a mitotically dividing, genetically inactive nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2672–2676. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2672. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Role of protein synthesis in the replication of yeast DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):129–131. doi: 10.1038/newbio244129a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lark K. G. Initiation and control of DNA synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1969;38:569–604. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.38.070169.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASTER R. W. POSSIBLE SYNTHESIS OF POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES OF KNOWN BASE-TRIPLET SEQUENCES. Nature. 1965 Apr 3;206:93–93. doi: 10.1038/206093b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newlon C. S., Petes T. D., Hereford L. M., Fangman W. L. Replication of yeast chromosomal DNA. Nature. 1974 Jan 4;247(5435):32–35. doi: 10.1038/247032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petes T. D., Williamson D. H. Fiber autoradiography of replicating yeast DNA. Exp Cell Res. 1975 Oct 1;95(1):103–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90614-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadgopal A., Bonner J. The relationship between histone and DNA synthesis in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Aug 20;186(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seale R. L., Simpson R. T. Effects of cycloheximide on chromatin biosynthesis. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):479–501. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90216-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonino G. J., Rozijn T. H. On the occurrence of histones in yeast. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Aug 24;124(2):427–429. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H. A possible role for histone in the synthesis of DNA. Nature. 1972 Dec 22;240(5382):449–453. doi: 10.1038/240449a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Holtzer H. Fine control of DNA synthesis in developing chick red blood cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Apr 28;66(1):13–35. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(72)80003-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson D. H. Replication of the nuclear genome in yeast does not require concomitant protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Jun 8;52(3):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90998-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Smith P., Letnansky K. Yeast chromatin. Preparation from isolated nuclei, histone composition and transcription capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



