Abstract
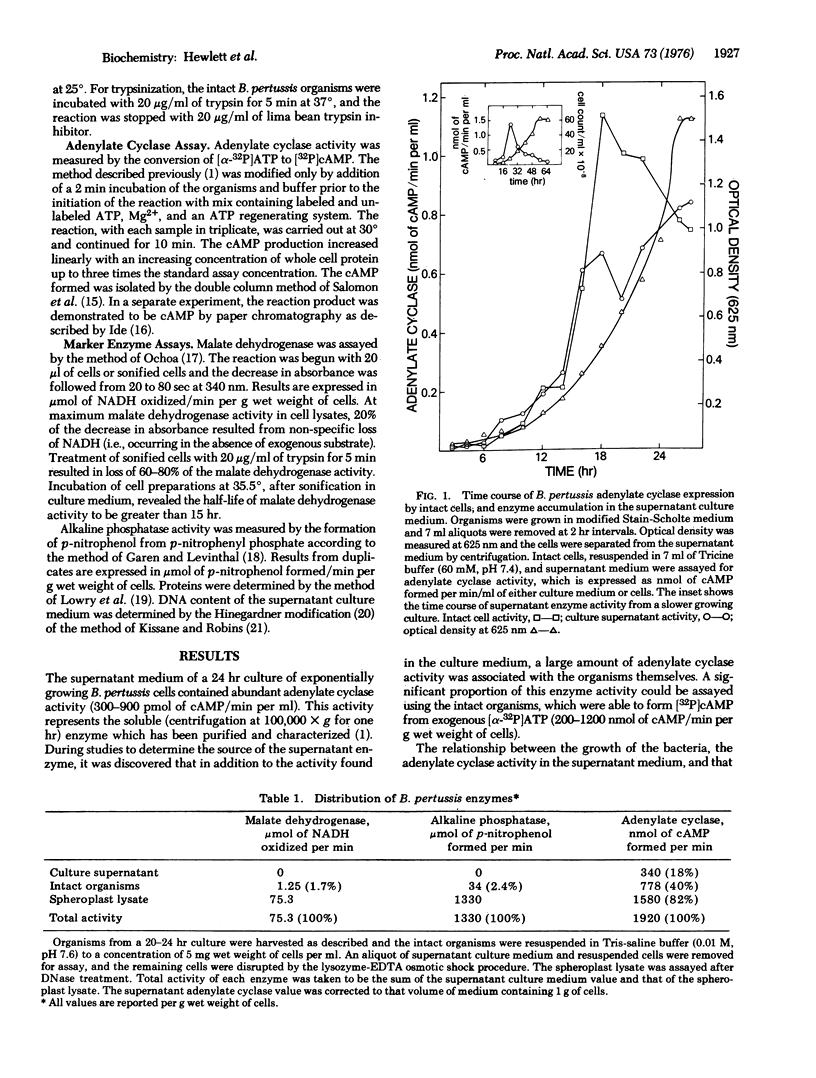
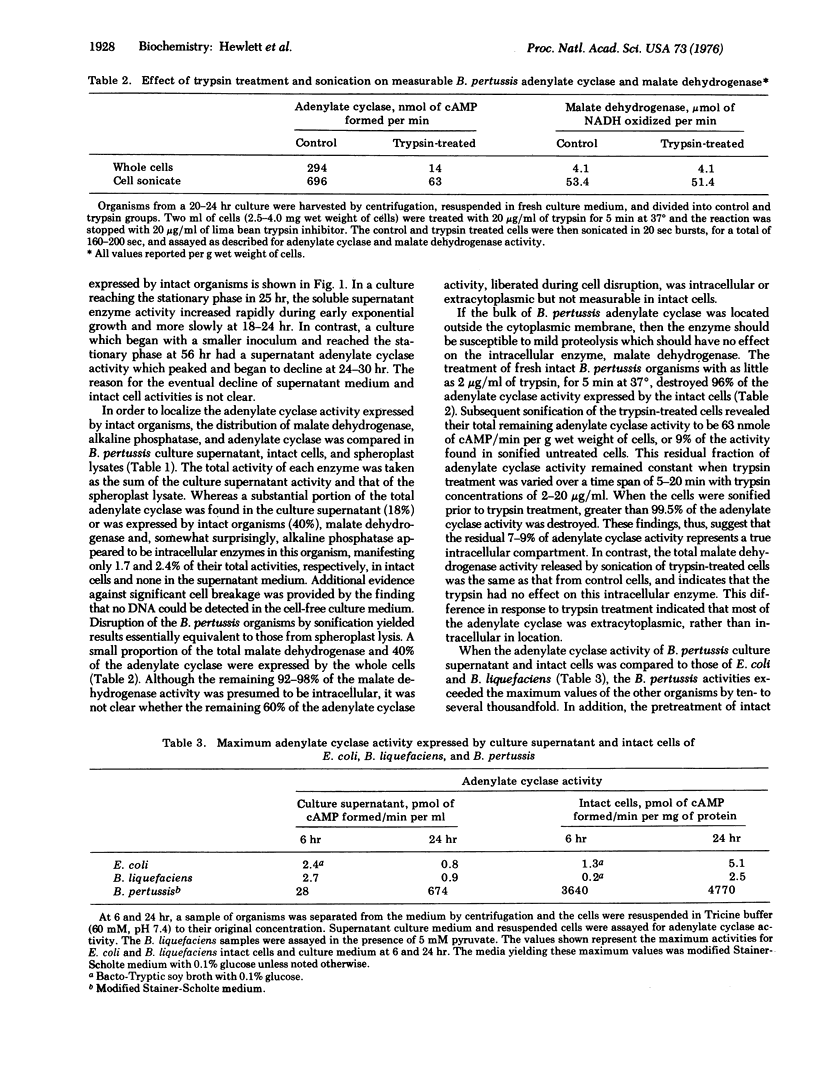
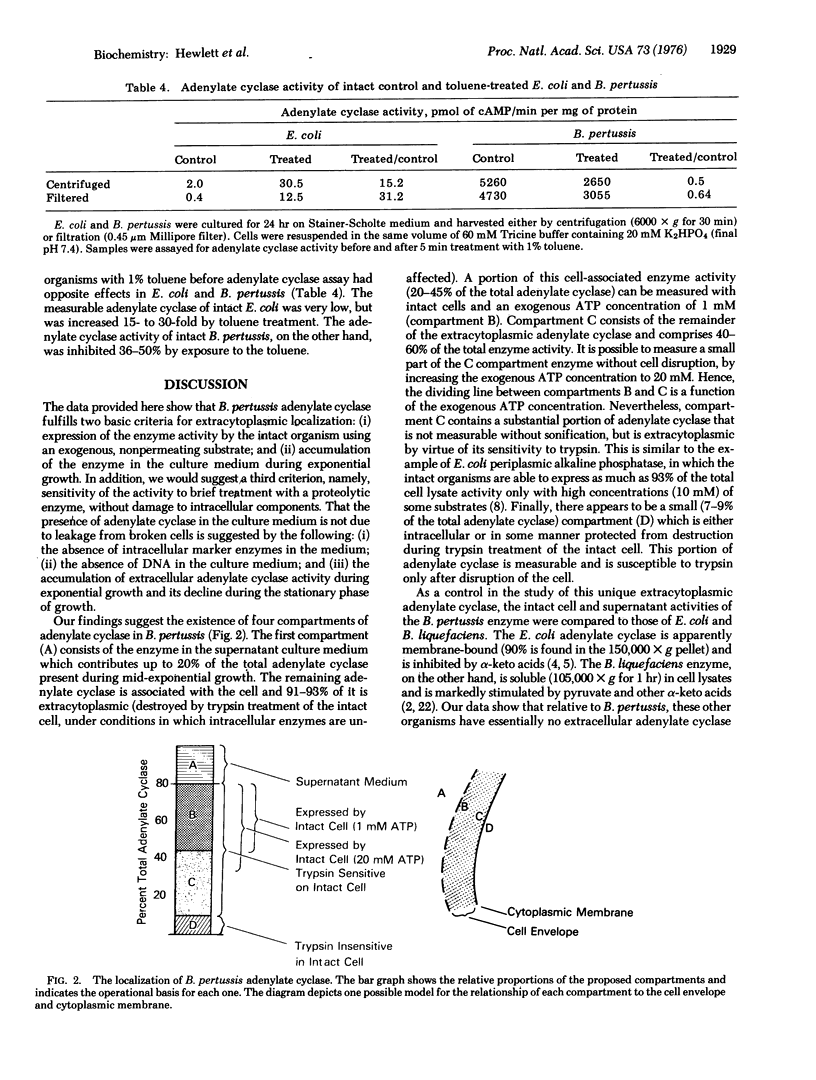
Soluble adenylate cyclase [EC 4.6.1.1] accumulates in the culture medium of exponentially growing Bordetella pertussis (300-900 pmol of cAMP formed/min per ml of 24 hr culture supernatant). In addition, there is an extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase which enables the intact organisms to form [32P] cAMP (adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate) from exogenous [alpha-32P] ATP (200-1200 nmol of cAMP formed/min per g wet weight of cells) and which comprises 20-45% of the total adenylate cyclase activity. In contrast, only 1.7 and 2.4% of the total cell malate dehydrogenase [EC 1.1.1.37] and alkaline phosphatase [EC 3.1.3.1], respectively, are detectable in the intact cell. Trypsin treatment of intact organisms destroys 96% of the extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase, but does not reduce the total cell malate dehydrogenase or a small pool of intracellular adenylate cyclase. Four compartments of adenylate cyclase in B. pertussis are proposed; (A) soluble enzyme in the culture supernatant (up to 20% of the total activity); (B) enzyme associated with intact cells and measurable without cell disruption (20-45%); (C) extracytoplasmic enzyme sensitive to trypsin, but not measurable in intact cells at standard substrate concentrations (40-60%); and (D) intracellular enzyme (7-9%). In comparison with previously studied bacterial adenylate cyclases, the extracytoplasmic location appears to be unique to the B. pertussis enzyme.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brockman R. W., Heppel L. A. On the localization of alkaline phosphatase and cyclic phosphodiesterase in Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1968 Jul;7(7):2554–2562. doi: 10.1021/bi00847a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. J., Day D. F., Costerton J. W., Ingram J. M. Alkaline phosphatase subunits in the culture filtrate of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Can J Biochem. 1972 Mar;50(3):268–276. doi: 10.1139/o72-038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Crombrugghe B., Perlman R. L., Varmus H. E., Pastan I. Regulation of inducible enzyme synthesis in Escherichia coli by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 10;244(21):5828–5835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAREN A., LEVINTHAL C. A fine-structure genetic and chemical study of the enzyme alkaline phosphatase of E. coli. I. Purification and characterization of alkaline phosphatase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:470–483. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganguly U., Greenough W. B., 3rd Adenosine 3',5'-cyclic monophosphate in Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1975 Feb;11(2):343–349. doi: 10.1128/iai.11.2.343-349.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glew R. H., Heath E. C. Studies on the extracellular alkaline phosphatase of Micrococcus sodonensis. II. Factors affecting secretion. J Biol Chem. 1971 Mar 25;246(6):1566–1574. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harwood J. P., Peterkofsky A. Glucose-sensitive adenylate cyclase in toluene-treated cells of Escherichia coli B. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4656–4662. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinegardner R. T. An improved fluorometric assay for DNA. Anal Biochem. 1971 Jan;39(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90476-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayaishi O. Adenyl cyclase of Brevibacterium liquefaciens. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 Nov 21;149(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(67)90685-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata M., Hayaishi O. Pyruvate dependent adenyl cyclase activity of Brevibacterium liquefaciens. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1965 Nov 22;21(4):361–365. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(65)90202-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ide M. Adenyl cyclase of Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Jul 7;36(1):42–46. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90646-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KISSANE J. M., ROBINS E. The fluorometric measurement of deoxyribonucleic acid in animal tissues with special reference to the central nervous system. J Biol Chem. 1958 Jul;233(1):184–188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khandelwal R. L., Hamilton I. R. Purification and properties of adenyl cyclase from Streptococcus salivarius. J Biol Chem. 1971 May 25;246(10):3297–3304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LICHTENSTEIN J., BARNER H. D., COHEN S. S. The metabolism of exogenously supplied nucleotides by Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1960 Feb;235:457–465. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane A. G. Appearance of mouse-lethal toxin in liquid cultures of Bordetella pertussis. Appl Microbiol. 1968 Sep;16(9):1400–1405. doi: 10.1128/am.16.9.1400-1405.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal N. G., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes by osmotic shock from Escherichia coli in exponential phase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jul 10;241(13):3055–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterkofsky A., Gazdar C. Interaction of enzyme I of the phosphoenolpyruvate:sugar phosphotransferase system with adenylate cyclase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):2920–2924. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.2920. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stainer D. W., Scholte M. J. A simple chemically defined medium for the production of phase I Bordetella pertussis. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Oct;63(2):211–220. doi: 10.1099/00221287-63-2-211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tao M., Huberman A. Some properties of Escherichia coli adenyl cyclase. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1970 Nov;141(1):236–240. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(70)90127-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota T., Gots J. S. Requirement of adenosine 3', 5'-cyclic phosphate for flagella formation in Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1970 Aug;103(2):513–516. doi: 10.1128/jb.103.2.513-516.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]