Abstract
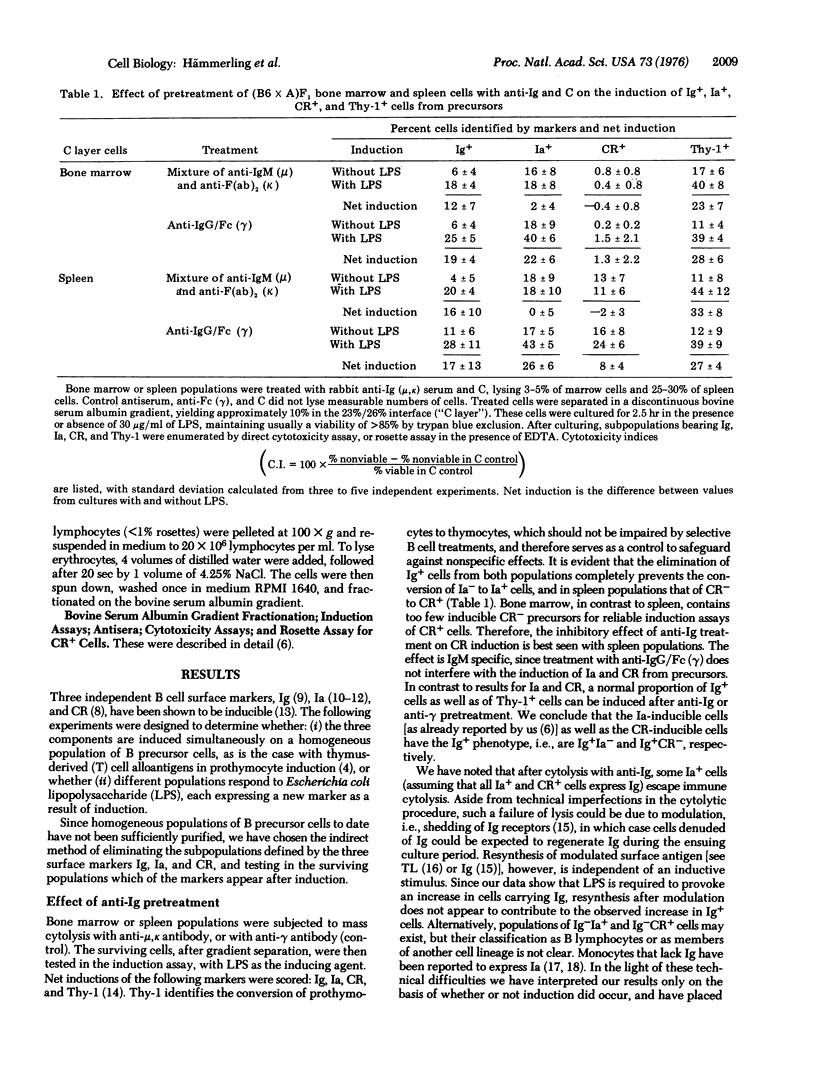
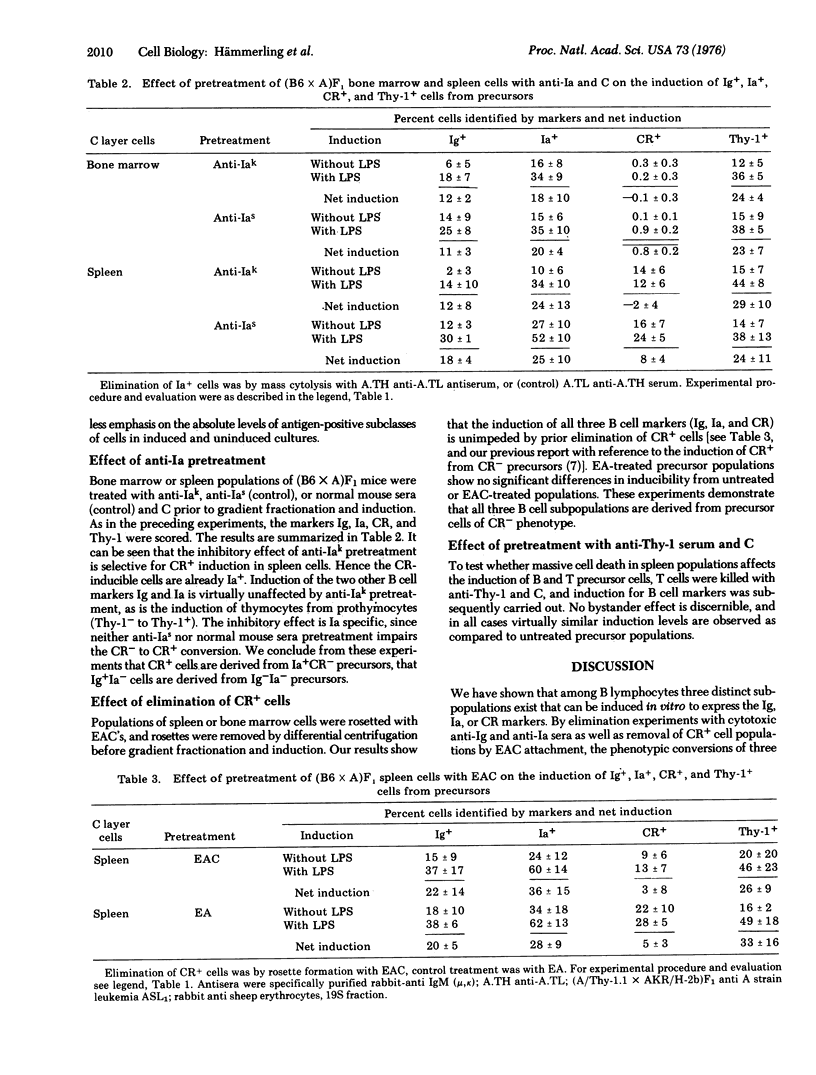
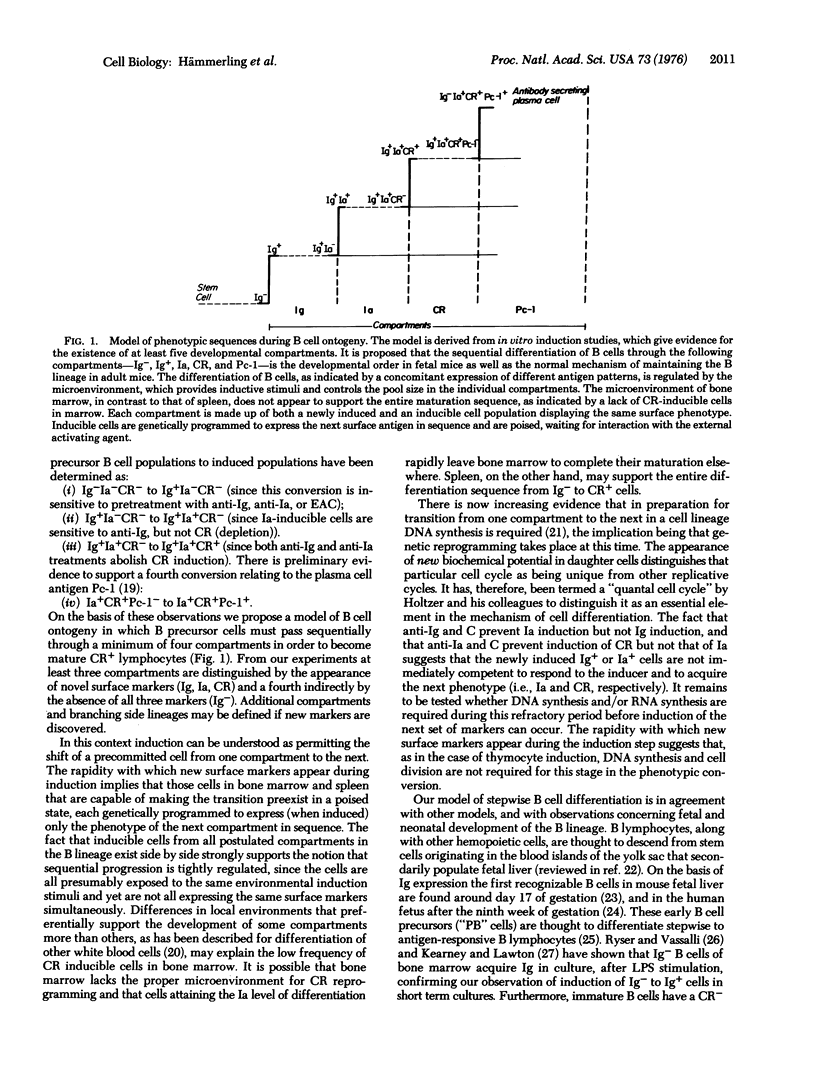
Among bone-marrow-derived (B) lymphocytes exist subpopulations of cells that can be induced to express the markers: surface immunoglobulin (Ig), the antigen associated with the immune response gene (Ia), and the receptor for the third complement component (CR). Inducible cells for the first two markers are found in bone marrow, and inducible cells for all three are in spleen. Experiments were designed to determine whether induction involves a single precursor cell population that on triggering with lipopolysaccharide expresses all three surface markers, or three separate precursor cell populations each of which expresses a single marker. Specific B cell subpopulations were eliminated by treatment with anti-Ig or anti-Ia and complement, or by rosette formation with erythrocytes-antibody-complement followed by differential centrifugation, and surviving cells were subsequently tested for inducibility of the three B cell markers. After anti-Ig cytolysis only Ig, but not Ia and CR, could be induced, implying that the Ia- and the CR-inducible cells are Ig+. Similarly, after anti-Ia cytolysis Ig and Ia but not CR could be induced. Thus, CR-inducible cells must have the Ig+Ia+ phenotype. Elimination of CR+ cells did not affect the induction of Ig, Ia, or CR from their precursors. None of the three elimination experiments affected the conversion of prothymocytes (Thy-1-) to thymocytes (Thy-1+). From these results we propose the hypothesis that the differentiation of B lymphocytes proceeds through at least four distinct stages characterized by the following phenotypes: Ig-Ia-CR- leads to Ig+Ia-CR- leads to Ig+Ia+CR- leads to Ig+Ia+CR+.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbott J., Schiltz J., Dienstman S., Holtzer H. The phenotypic complexity of myogenic clones. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1506–1510. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bianco C., Patrick R., Nussenzweig V. A population of lymphocytes bearing a membrane receptor for antigen-antibody-complement complexes. I. Separation and characterization. J Exp Med. 1970 Oct 1;132(4):702–720. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.4.702. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David C. S., Shreffler D. C., Frelinger J. A. New lymphocyte antigen system (Lna) controlled by the Ir region of the mouse H-2 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Sep;70(9):2509–2514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.9.2509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienstman S. R., Biehl J., Holtzer S., Holtzer H. Myogenic and chondrogenic lineages in developing limb buds grown in vitro. Dev Biol. 1974 Jul;39(1):83–95. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(74)80010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelfand M. C., Elfenbein G. J., Frank M. M., Paul W. E. Ontogeny of B lymphocytes. II. Relative rates of appearance of lymphocytes bearing surface immunoglobulin and complement receptors. J Exp Med. 1974 May 1;139(5):1125–1141. doi: 10.1084/jem.139.5.1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammerling U., Chin A. F., Abbott J., Scheid M. P. The ontogeny of murine B lymphocytes. I. Induction of phenotypic conversion of Ia-to Ia+ lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Nov;115(5):1425–1431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hauptfeld V., Klein D., Klein J. Serological identification of an Ir-region product. Science. 1973 Jul 13;181(4095):167–169. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4095.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kearney J. F., Lawton A. R. B lymphocyte differentiation induced by lipopolysaccharide. II. Response of fetal lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):677–681. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Komuro K., Boyse E. A. In-vitro demonstration of thymic hormone in the mouse by conversion of precursor cells into lymphocytes. Lancet. 1973 Apr 7;1(7806):740–743. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92127-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDERBERG J. Genes and antibodies. Science. 1959 Jun 19;129(3364):1649–1653. doi: 10.1126/science.129.3364.1649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafleur L., Miller R. G., Phillips R. A. Restriction of specificity in the precursors of bone marrow-associated lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Apr 1;137(4):954–966. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.4.954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J., Pike B. L. Evidence for the clonal abortion theory of B-lymphocyte tolerance. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):904–917. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Kim J. H. Antigenic modulation. Loss of TL antigen from cells exposed to TL antibody. Study of the phenomenon in vitro. J Exp Med. 1968 Mar 1;127(3):523–539. doi: 10.1084/jem.127.3.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen J. J., Cooper M. D., Raff M. C. In vitro generation of B lymphocytes in mouse foetal liver, a mammalian 'bursa equivalent'. Nature. 1974 May 24;249(455):361–363. doi: 10.1038/249361a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REIF A. E., ALLEN J. M. THE AKR THYMIC ANTIGEN AND ITS DISTRIBUTION IN LEUKEMIAS AND NERVOUS TISSUES. J Exp Med. 1964 Sep 1;120:413–433. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.3.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Two distinct populations of peripheral lymphocytes in mice distinguishable by immunofluorescence. Immunology. 1970 Oct;19(4):637–650. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryser J. E., Vassalli P. Mouse bone marrow lymphocytes and their differentiation. J Immunol. 1974 Sep;113(3):719–728. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid M. P., Goldstein G., Hammerling U., Boyse E. A. Lymphocyte differentiation from precursor cells in vitro. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Feb 28;249:531–540. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb29102.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheid M. P., Hoffmann M. K., Komuro K., Hämmerling U., Abbott J., Boyse E. A., Cohen G. H., Hooper J. A., Schulof R. S., Goldstein A. L. Differentiation of T cells induced by preparations from thymus and by nonthymic agents. J Exp Med. 1973 Oct 1;138(4):1027–1032. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.4.1027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidman C. L., Unanue E. R. Development of B lymphocytes. I. Cell populations and a critical event during ontogeny. J Immunol. 1975 Jun;114(6):1730–1735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. Surface alloantigens of plasma cells. J Exp Med. 1970 Jun 1;131(6):1325–1341. doi: 10.1084/jem.131.6.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dorf M. E., David C. S., Benacerraf B. The presence of I-region-associated antigens on B cells in molecules distinct from immunoglobulin and H-2K and H-2D. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):5014–5016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.5014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


