Abstract
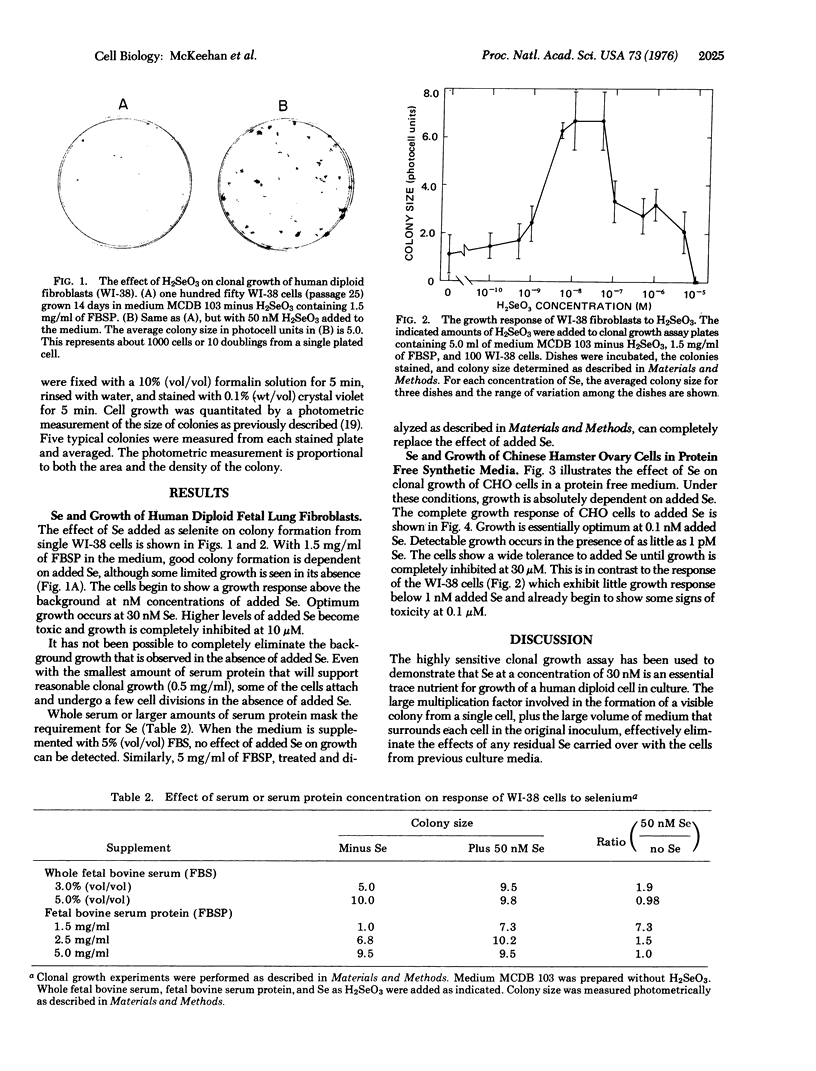
The trace element selenium is essential for clonal growth of diploid fibroblasts from human fetal lung (WI-38) in media containing small amounts of serum protein. Maximum growth stimulation is obtained when 30 nM neutralized selenious acid is added to a synthetic medium containing 1.5 mg/ml of dialyzed fetal bovine serum protein (equivalent to a 3% serum concentration). Serum appears to be a source of selenium in most culture media, since higher concentrations of serum protein or whole serum mask the selenium requirement of WI-38 cells. Selenium is also required by a Chinese hamster cell line that can be grown in a protein-free synthetic culture medium.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Deaven L. L., Petersen D. F. The chromosomes of CHO, an aneuploid Chinese hamster cell line: G-band, C-band, and autoradiographic analyses. Chromosoma. 1973;41(2):129–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00319690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flohe L., Günzler W. A., Schock H. H. Glutathione peroxidase: a selenoenzyme. FEBS Lett. 1973 May 15;32(1):132–134. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80755-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost D. V., Lish P. M. Selenium in biology. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1975;15:259–284. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.15.040175.001355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. An improved nutrient solution for diploid Chinese hamster and human cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Feb;29:515–526. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(63)80014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. CLONAL GROWTH OF MAMMALIAN CELLS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:288–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. Clonal growth of diploid Chinese hamster cells in a synthetic medium supplemented with purified protein fractions. Exp Cell Res. 1962 Dec;28:489–500. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(62)90253-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAYFLICK L. THE LIMITED IN VITRO LIFETIME OF HUMAN DIPLOID CELL STRAINS. Exp Cell Res. 1965 Mar;37:614–636. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(65)90211-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higuchi K. Cultivation of animal cells in chemically defined media, a review. Adv Appl Microbiol. 1973;16:111–136. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2164(08)70025-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuta H., Takaoka T. Cultivation of cells in protein- and lipid-free synthetic media. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;6:1–42. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60046-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levander O. A. Selenium and chromium in human nutrition. J Am Diet Assoc. 1975 Apr;66(4):338–344. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUTH O. H., OLDFIELD J. E., REMMERT L. F., SCHUBERT J. R. Effects of selenium and vitamin E on white muscle disease. Science. 1958 Oct 31;128(3331):1090–1090. doi: 10.1126/science.128.3331.1090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUTH O. H., SCHUBERT J. R., OLDFIELD J. E. White muscle disease (myopathy) in lambs and calves. VII. Etiology and prophylaxis. Am J Vet Res. 1961 May;22:466–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson F. C., Hidiroglou M., Hamilton H. A. The Effect of Prophylactic Treatment of Pregnant Beef Cows on the Incidence of Nutritional Muscular Dystrophy. A Field Trial. Can Vet J. 1964 Oct;5(10):268–273. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oh S. H., Ganther H. E., Hoekstra W. G. Selenium as a component of glutathione periodase isolated from ovine erythrocytes. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1825–1829. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PUCK T. T., MARCUS P. I., CIECIURA S. J. Clonal growth of mammalian cells in vitro; growth characteristics of colonies from single HeLa cells with and without a feeder layer. J Exp Med. 1956 Feb 1;103(2):273–283. doi: 10.1084/jem.103.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott M. L., Noguchi T., Combs G. F., Jr New evidence concerning mechanisms of action of vitamin E and selenium. Vitam Horm. 1974;32:429–444. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)60021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadtman T. C. Selenium biochemistry. Science. 1974 Mar 8;183(4128):915–922. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4128.915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor W. G., Richter A., Evans V. J., Sanford K. K. Influence of oxygen and pH on plating efficiency and colony development of WI-38 and Vero cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 May;86(1):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90660-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whanger P. D., Pedersen N. D., Weswig P. H. Selenium proteins in ovine tissues. II. Spectral properties of a 10,000 molecular weight selenium protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Aug 6;53(3):1031–1035. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





