Abstract
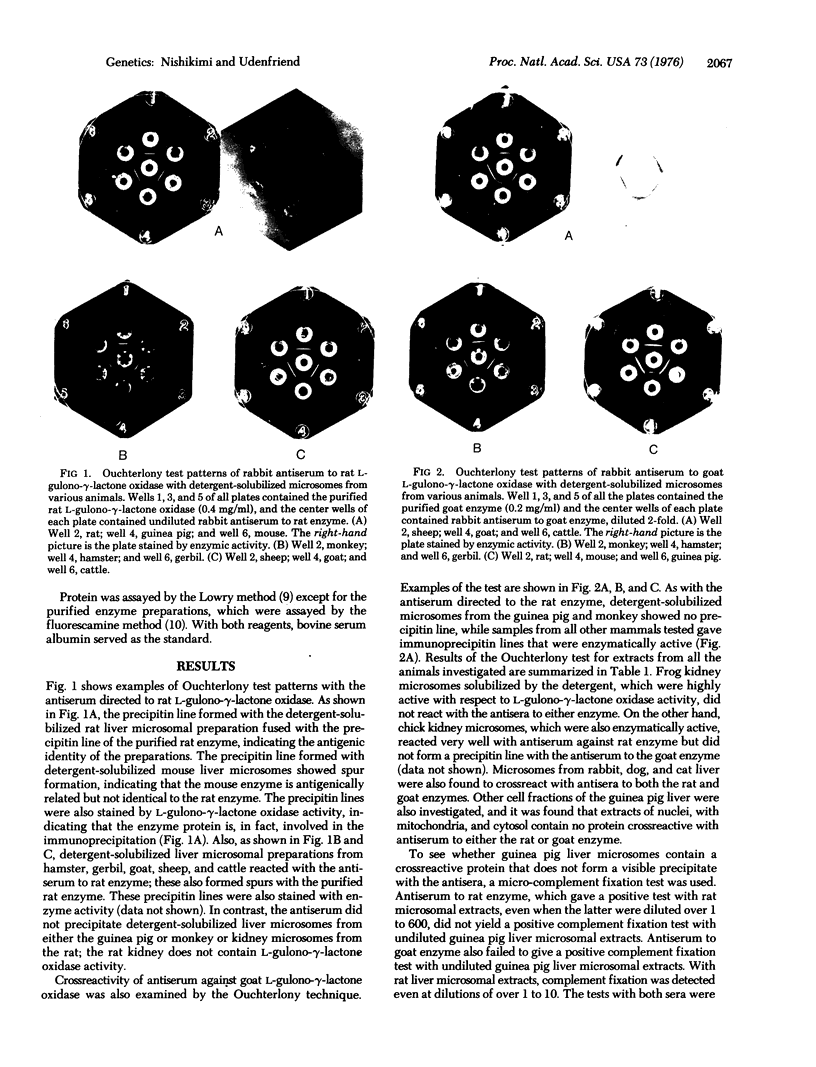
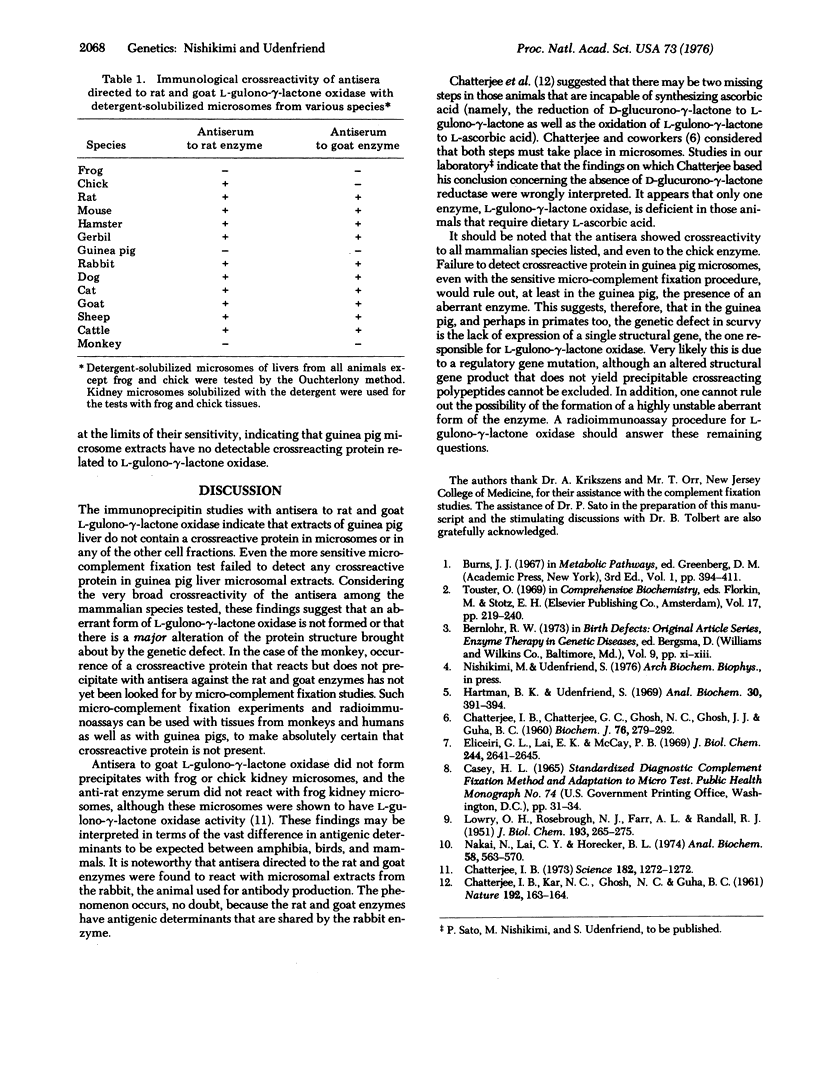
L-Gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase (L-gulono-gamma-lactone:oxygen 2-oxidoreductase, EC 1.1.3.8) is the enzyme that catalyzes the terminal step of L-ascorbic acid biosynthesis in mammalian liver. The absence of the oxidase activity in primates and guinea pigs is the reason why these animals are subject to scurvy, which must be considered an inborn error of metabolism. Attempts were made to determine if a protein immunologically crossreactive with L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase is present in these animals. Detergent-solubilized microsomal preparations from guinea pig and African green monkey liver did not precipitate the antisera directed to either rat or goat enzyme, nor did any of the other cell fractions obtained from guinea pig liver react with either antiserum. No crossreactive protein was detectable in guinea pig microsomes even with the sensitive procedure or micro-complement fixation. On the other hand, extracts of all 10 other mammalian (4 orders) liver microsomes tested were shown to contain L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase activity that did crossreact with antibodies to the rat and goat enzymes. One explanation of these findings is that, in the guinea pig, and perhaps in primates too, the structural gene for L-gulono-gamma-lactone oxidase is not expressed.
Full text
PDF
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CHATTERJEE I. B., CHATTERJEE G. C., GHOSH N. C., GHOSH J. J., GUHA B. C. Biological synthesis of L-ascorbic acid in animal tissues: conversion of D-glucuronolactone and L-gulonolactone into L-ascorbic acid. Biochem J. 1960 Aug;76:279–292. doi: 10.1042/bj0760279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHATTERJEE I. B., KAR N. C., GHOSH N. C., GUHA B. C. Biosynthesis of L-ascorbic acid: missing steps in animals incapable of synthesizing the vitamin. Nature. 1961 Oct 14;192:163–164. doi: 10.1038/192163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee I. B. Evolution and the biosynthesis of ascorbic acid. Science. 1973 Dec 21;182(4118):1271–1272. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4118.1271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliceiri G. L., Lai E. K., McCay P. B. Gulonolactone oxidase. Solubilization, properties, and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1969 May 25;244(10):2641–2645. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman B. K., Udenfriend S. A method for immediate visualization of proteins in acrylamide gels and its use for preparation of antibodies to enzymes. Anal Biochem. 1969 Sep;30(3):391–394. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90132-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai N., Lai C. Y., Horecker B. L. Use of fluorescamine in the chromatographic analysis of peptides from proteins. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):563–570. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]