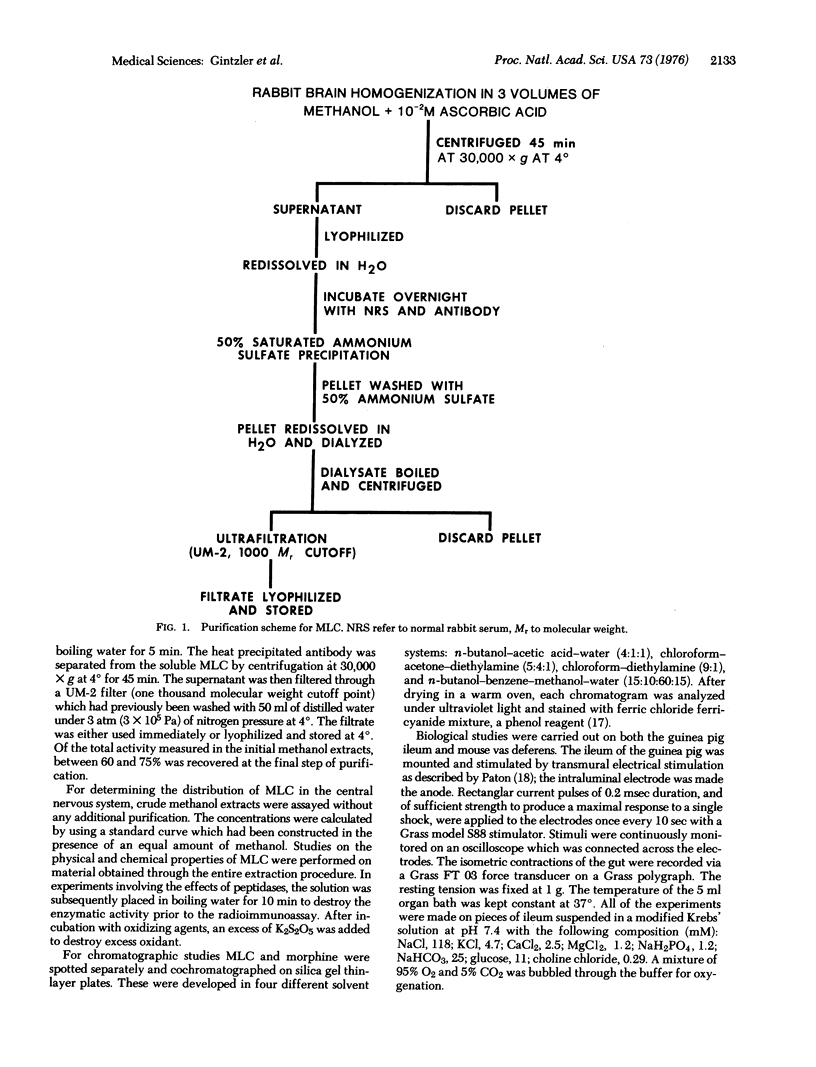
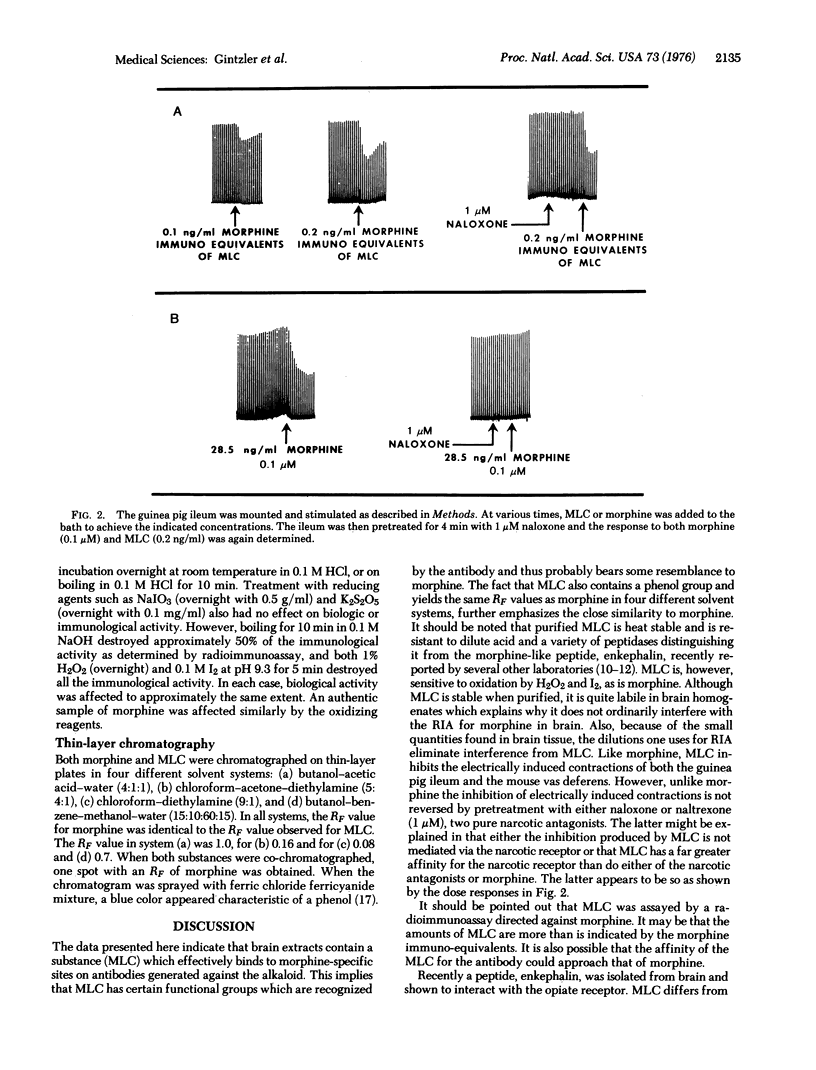
Abstract
Antibodies generated against small molecular weight substances such as drugs are being used to isolate and characterize biologically active agonists. A morphine-like compound can be extracted from brain of various species which has determinant groups that are recognized by specific morphine antibodies. It has a regional distribution which can be quantitated as immuno-equivalents. Immunological, chemical and chromatographic tests show great similatiries of the compound to morphine. This morphine-like compound has biological activity as it inhibits the electrically induced contractions both of the guinea pig ileum and mouse vas deferens but the inhibition is not reversed by naloxone or naltrexone.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BECKETT A. H., CASY A. F. Synthetic analgesics: stereochemical considerations. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1954 Dec;6(12):986–1001. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1954.tb11033.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg H., Dayton H. B., Wolf P. S. Counteraction of narcotic antagonist analgesics by the narcotic antagonist Naloxone. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1966 Dec;123(3):755–758. doi: 10.3181/00379727-123-31595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Opheim K. E., Teschemacher H., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. 2. Purification and properties. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1777–1782. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARR R. S. A quantitative immunochemical measure of the primary interaction between I BSA and antibody. J Infect Dis. 1958 Nov-Dec;103(3):239–262. doi: 10.1093/infdis/103.3.239. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FOLDES F. F., LUNN J. N., MOORE J., BROWN I. M. N-Allylnoroxy-morphone: a new potent narcotic antagonist. Am J Med Sci. 1963 Jan;245:23–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Kosterlitz H. W., Leslie F. M. Effect of morphine on adrenergic transmission in the mouse vas deferens. Assessment of agonist and antogonist potencies of narcotic analgesics. Br J Pharmacol. 1975 Mar;53(3):371–381. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1975.tb07373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jasinski D. R., Martin W. R., Haertzen C. A. The human pharmacology and abuse potential of N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1967 Aug;157(2):420–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosterlitz H. W., Watt A. J. Kinetic parameters of narcotic agonists and antagonists, with particular reference to N-allylnoroxymorphone (naloxone). Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1968 Jun;33(2):266–276. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1968.tb00988.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhar M. J., Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Regional distribution of opiate receptor binding in monkey and human brain. Nature. 1973 Oct 26;245(5426):447–450. doi: 10.1038/245447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasagna L. Drug interaction in the field of analgesic drugs. Proc R Soc Med. 1965 Nov;58(11 Pt 2):978–983. doi: 10.1177/003591576505811P207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClane T. K., Martin W. R. Effects of morphine, nalorphine, cyclazocine, and naloxone on the flexor reflex. Int J Neuropharmacol. 1967 Mar;6(2):89–98. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(67)90057-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PATON W. D. The action of morphine and related substances on contraction and on acetylcholine output of coaxially stimulated guinea-pig ileum. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):119–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01373.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pert C. B., Snyder S. H. Opiate receptor: demonstration in nervous tissue. Science. 1973 Mar 9;179(4077):1011–1014. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4077.1011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon E. J., Hiller J. M., Edelman I. Stereospecific binding of the potent narcotic analgesic (3H) Etorphine to rat-brain homogenate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1947–1949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S., Parker C. W. Morphine: radioimmunoassay. Science. 1970 Jun 12;168(3937):1347–1348. doi: 10.1126/science.168.3937.1347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector S. Quantitative determination of morphine in serum by radioimmunoassay. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1971 Aug;178(2):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TPERENIUS L., Wahlström A. Morphine-like ligand for opiate receptors in human CSF. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1759–1764. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90269-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenius L. Characteristics of the "receptor" for narcotic analgesics in synaptic plasma membrane fraction from rat brain. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1973;33(5):377–384. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1973.tb01539.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



