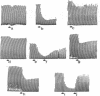
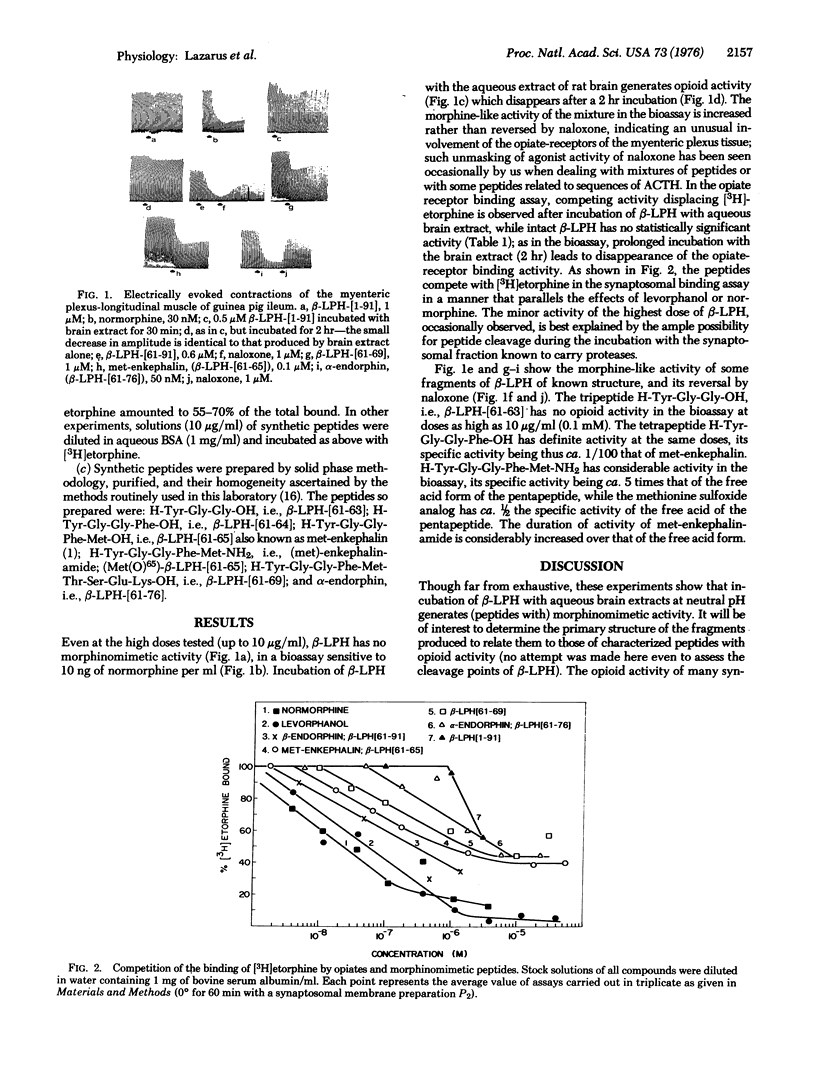
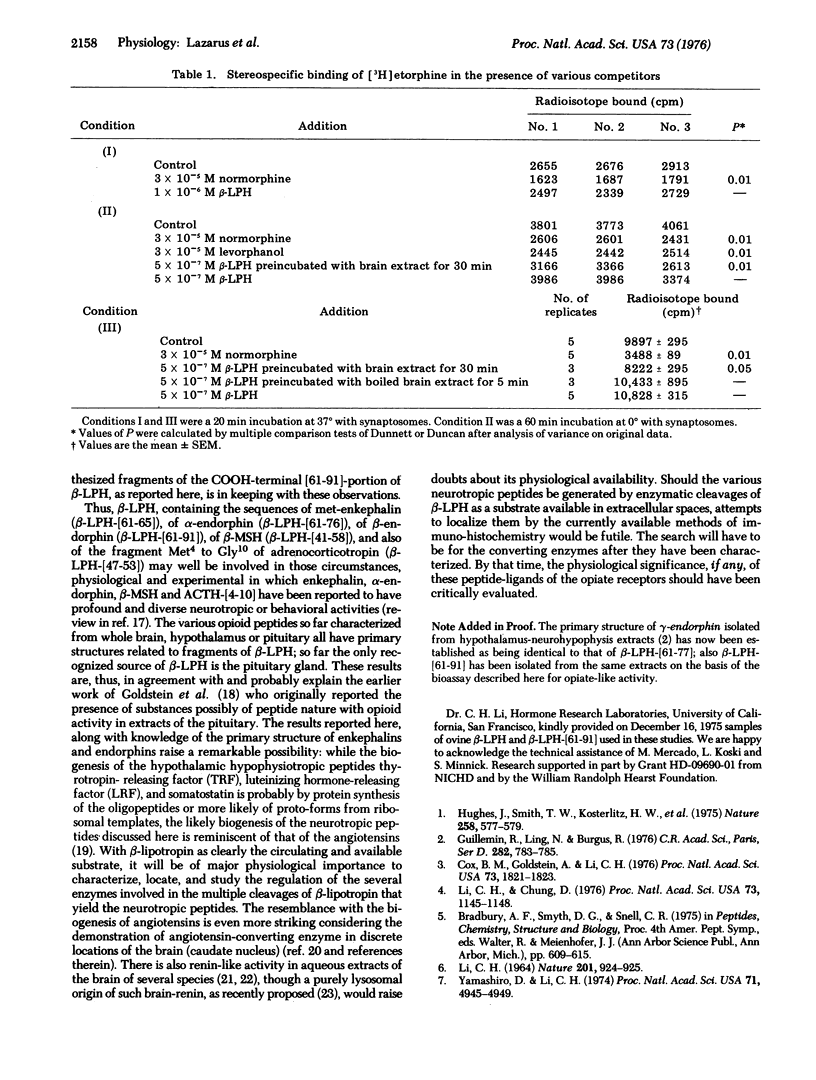
Abstract
The hypophysial homomeric peptide beta-lipotropin (beta-LPH-[1-91]) has no morphinomomimetic activity in a bioassay (myenteric plexus-longitudinal muscle of the guinea pig's ileum) or binding assays with stereospecific opiate-receptors of rat brain synaptosome preparations. Incubating beta-LPH-[1-91] at neutral pH with the supernatant aqueous extracts of rat brain generates (fragments of beta-LPH with) morphinomimetic activity in the same assay systems. These results are related to the recently recognized structural relationships between beta-LPH, the newly isolated peptides met-enkephalin (beta-LPH-[61-65]) and alpha-endorphin (beta-LPH-[61-76]) and also to the biologically active fragments of analogs: beta-LPH-[61-64], beta-LPH-[61-65[-NH2, (Met(O)65)-BETA-LPH-[61-65], beta-LPH-[61-69], and beta-LPH-[61-69]. Enzymatic biogenesis of these morphinomimetic peptides would preclude localizing them as such in cellular or subcellular elements with currently available methodology.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cox B. M., Goldstein A., Hi C. H. Opioid activity of a peptide, beta-lipotropin-(61-91), derived from beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1821–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Opheim K. E., Teschemacher H., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. 2. Purification and properties. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1777–1782. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daul C. B., Heath R. G., Garey R. E. Angiotensin-forming enzyme in human brain. Neuropharmacology. 1975 Jan;14(1):75–80. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(75)90068-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. P., Reid I. A. Renin activity in dog brain: enzymological similarity to cathepsin D. Endocrinology. 1976 Jul;99(1):93–100. doi: 10.1210/endo-99-1-93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganten D., Minnich J. L., Granger P., Hayduk K., Brecht H. M., Barbeau A., Boucher R., Genest J. Angiotensin-forming enzyme in brain tissue. Science. 1971 Jul 2;173(3991):64–65. doi: 10.1126/science.173.3991.64. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Burgus R. Endorphines, peptides, d'origine hypothalamique et neurohypophysaire à activité morphinomimétique. Isolement et structure moléculaire de l'alpha-endorphine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Feb 23;282(8):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee W. A., Streaty R. A. Narcotic receptor sites in morphine-dependent rats. Nature. 1974 Mar 1;248(5443):61–63. doi: 10.1038/248061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI C. H. LIPOTROPIN, A NEW ACTIVE PEPTIDE FROM PITUITARY GLANDS. Nature. 1964 Feb 29;201:924–924. doi: 10.1038/201924a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LONG J. M., KRIVOY W. A., GUILLEMIN R. On a possible role of beta-melanocyte stimulating hormone (beta-MSH) in the central nervous system of the Mammalia: enzymatic inactivation in vitro of beta-MSH by brain tissue. Endocrinology. 1961 Jul;69:176–181. doi: 10.1210/endo-69-1-176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Chung D. Isolation and structure of an untriakontapeptide with opiate activity from camel pituitary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1145–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohmar P., Li C. H. Biological proprtie of ovine beta-lipotropic hormone. Endocrinology. 1968 May;82(5):898–904. doi: 10.1210/endo-82-5-898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks N., Stern F. Inactivation of somatostatin (GH-RIH) and its an analogs by crude and partially purified rat brain extracts. FEBS Lett. 1975 Jul 15;55(1):220–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(75)80996-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon H. D., Li C. H., Jennings B. M. Immunohistochemical and histochemical studies of pituitary beta-lipotrophs. Anat Rec. 1973 Mar;175(3):529–537. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091750303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PEART W. S. THE RENIN-ANGIOTENSIN SYSTEM. Pharmacol Rev. 1965 Jun;17:143–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paton W. D., Zar M. A. The origin of acetylcholine released from guinea-pig intestine and longitudinal muscle strips. J Physiol. 1968 Jan;194(1):13–33. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1968.sp008392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poth M. M., Heath R. G., Ward M. Angiotensin-converting enzyme in human brain. J Neurochem. 1975 Jul;25(1):83–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1975.tb07698.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott A. P., Lowry P. J. Adrenocorticotrophic and melanocyte-stimulating peptides in the human pituitary. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):593–602. doi: 10.1042/bj1390593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whittaker V. P., Michaelson I. A., Kirkland R. J. The separation of synaptic vesicles from nerve-ending particles ('synaptosomes'). Biochem J. 1964 Feb;90(2):293–303. doi: 10.1042/bj0900293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashiro D., Li C. H. Synthesis of a pentekontapeptide with high lipolytic activity corresponding to the carboxyl-terminal fifty amino acids of ovine beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4945–4949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wied D., Witter A., Greven H. M. Commentary: behaviourally active ACTH analogues. Biochem Pharmacol. 1975 Aug 15;24(16):1463–1468. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(75)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]