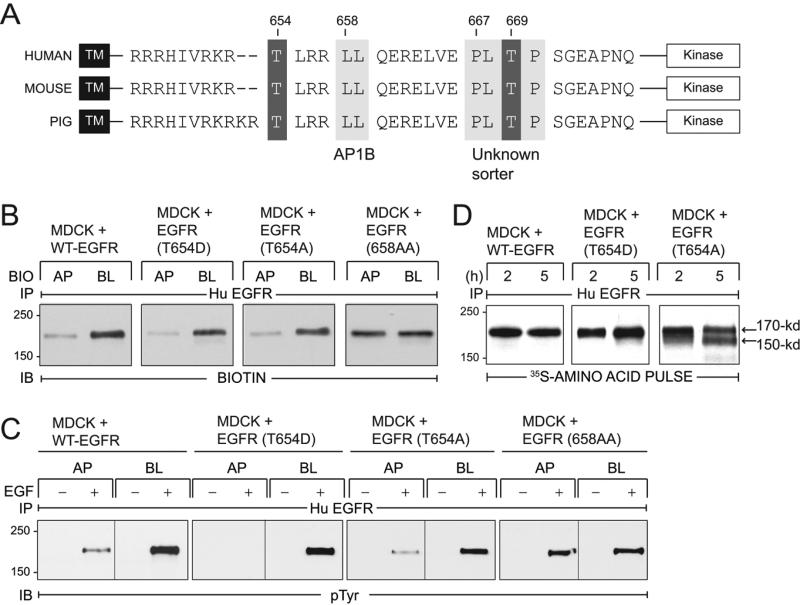
Figure 1. EGFRs with T654A and T654D substitutions localize to BL membranes in established MDCK cell monolayers.
(A) EGFR schematic showing transmembrane (TM) and kinase domains with intervening juxtamembrane (JM) amino acid sequence containing known BL sorting signals (light grey boxes): 658-LL that interacts with AP1B (31), and 667-PLTP whose interaction partner is unknown (27). Two known PKC substrates Thr654 and Thr669 are also denoted (dark grey boxes). EGFR JM sequences are highly conserved in human (76), mouse (77), and pig (NCBI Reference Sequence NM_214007.1). (B) Established MDCK cell monolayers with stable expression of human EGFRs listed in the figure were subjected to domain-specific biotinylation. Human EGFR immune complexes were immunoblotted with a biotin-specific antibody. (C) Established MDCK cell monolayers expressing EGFRs were harvested under basal conditions (−) or following a 15-min stimulation with domain-specific EGF (100 ng/ml) (+). Human EGFR immune complexes were immunoblotted with a phosphotyrosine antibody. (D) MDCK cells with human EGFRs were pulse-labeled with 35S-labeled amino acids and harvested after a 2 or 5 h incubation in non-radioactive amino acid chase medium. EGFR immune complexes detected by fluorography.