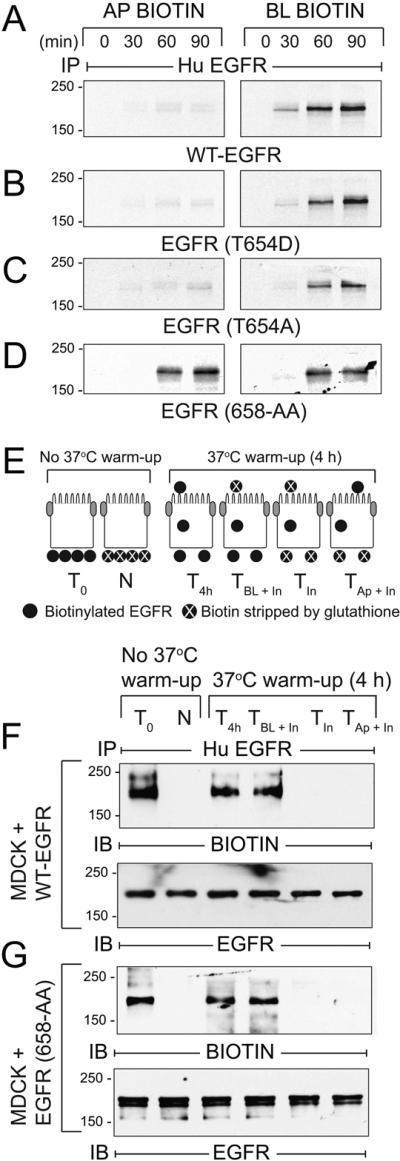
Figure 9. AP1B regulates BL EGFR membrane delivery in the biosynthetic route in established MDCK cell monolayers.
(A - D) AP1B-positive epithelial cells expressing human EGFRs listed in the figure were pulse-labeled with 35S-labeled amino acids and biotinylated at Ap or BL surface at times indicated during non-radioactive amino acid chase. EGFR immune complexes were purified using streptavidin beads for SDS-PAGE and fluorography. (E) Schematic showing experimental procedure for evaluating BL-to-Ap EGFR transcytosis [adapted from (78)]. Established MDCK cell monolayers were biotinylated from the BL side. T0, total biotinylated EGFR (positive control); N, biotin stripped immediately after biotinylation from BL side (negative control); T4h, total biotinylated EGFR from cells incubated at 37°C for 4 h (control for stability of biotinylated EGFR); TBL + In, biotin stripped from Ap surface after 4 h 37°C incubation (internalized biotinylated EGFR and biotinylated EGFR remaining on BL membrane); TIn, biotin stripped from both surfaces after 4 h 37°C incubation (internalized biotinylated EGFR); TAp + In, biotin stripped from BL surface after 4 h 37°C incubation (internalized biotinylated EGFR and biotinylated EGFR transcytosed to Ap membrane). (F - G) MDCK cells expressing WT-EGFR (F) or EGFR (658-AA) (G) treated according to the scheme in (E) were lysed and human EGFR immune complexes were resolved by non-reducing SDS-PAGE for immunoblotting with a biotin antibody (top panels), or an EGFR antibody to control for protein loading (bottom panels). Representative immunoblots from at least two independent experiments.