Abstract
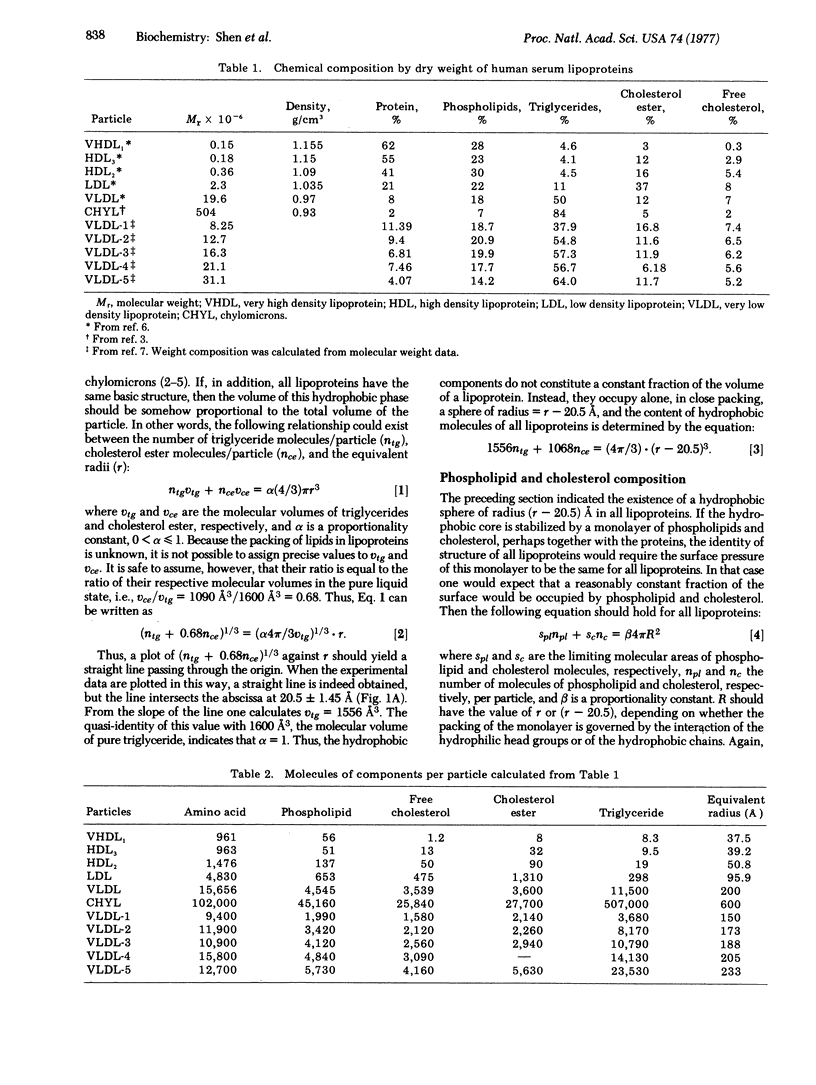
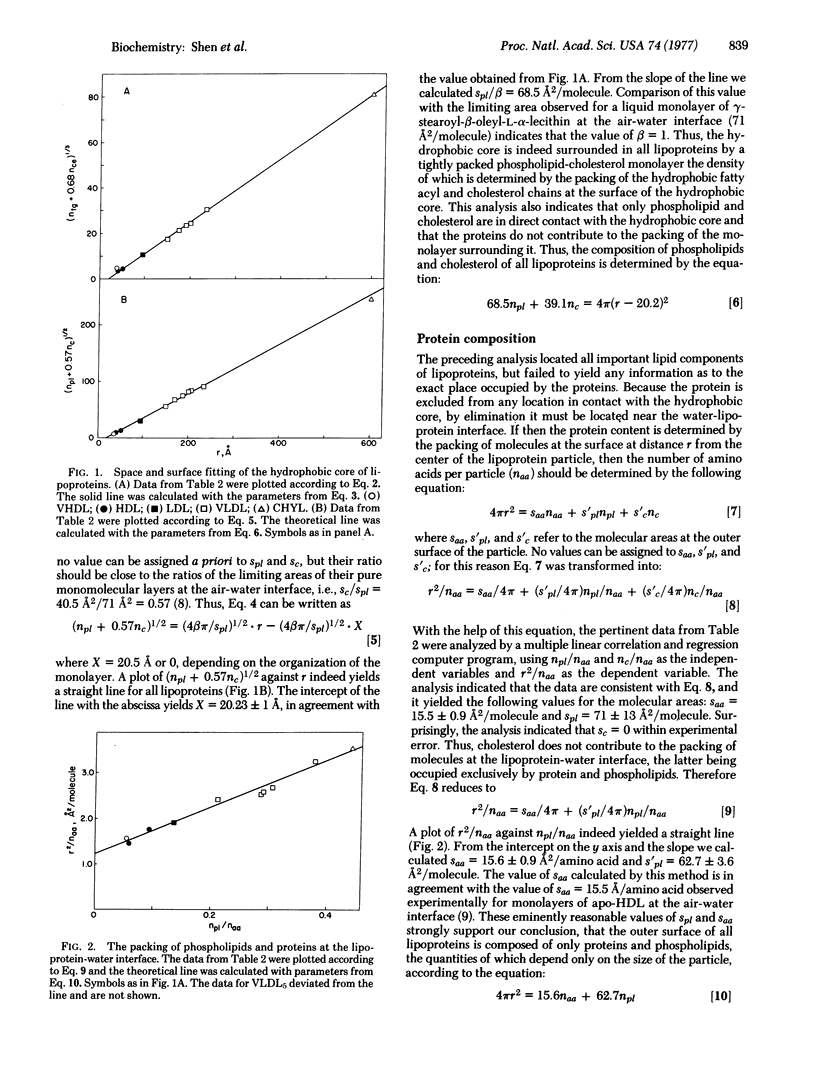
Analysis of the correlations between size and chemical composition of lipoproteins of normolipidemic human plasma shows that the structure of all circulating lipoproteins is consistent with a spherical model of radius r in which a spherical liquid core of cholesterol esters and triglycerides of radius = r --20.2 A is surrounded by a monolayer of cholesterol and phospholipids with closely hydrophobic ends on the surface of the core. The average molecular areas at this inner surface are Spl = 68.5 A2/molecule for phospholipids and Sc= 39.1 A2/molecule for cholesterol. The proteins are closely packed with the hydrophilic head groups of phospholipids at the outer surface of the particle, with S' pl = 62.7 A2/molecule for phospholipids and Saa = 15.6 A2/amino acid for proteins. The polar head group of free cholesterol does not participate in the packing of the outer layer and thus must be masked by proteins. Free cholesterol is distributed among the circulating lipoproteins--with the exception of very high density lipoprotein and perhaps chylomicrons--according to a thermodynamic equilibrium governed by the curvature of the surface of the particle.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Camejo G., Colacicco G., Rapport M. M. Lipid monolayers: interactions with the apoprotein of high density plasma lipoprotein. J Lipid Res. 1968 Sep;9(5):562–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S., Levy R. I. Lipoprotein metabolism. Adv Lipid Res. 1975;13:1–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Havel R. J. Lipoproteins and lipid transport. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1975;63:37–59. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-3258-9_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrisett J. D., Jackson R. L., Gotto A. M., Jr Lipoproteins: structure and function. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:183–207. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sata T., Havel R. J., Jones A. L. Characterization of subfractions of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins separated by gel chromatography from blood plasma of normolipemic and hyperlipemic humans. J Lipid Res. 1972 Nov;13(6):757–768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider H., Morrod R. S., Colvin J. R., Tattrie N. H. The lipid core model of lipoproteins. Chem Phys Lipids. 1973 May;10(4):328–353. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(73)90058-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verdery R. B., Nichols A. V. Arrangement of lipid and protein in human serum high density lipoproteins: a proposed model. Chem Phys Lipids. 1975 Apr;14(2):123–134. doi: 10.1016/0009-3084(75)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilversmit D. B. The composition and structure of lymph chylomicrons in dog, rat, and man. J Clin Invest. 1965 Oct;44(10):1610–1622. doi: 10.1172/JCI105267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



