Abstract
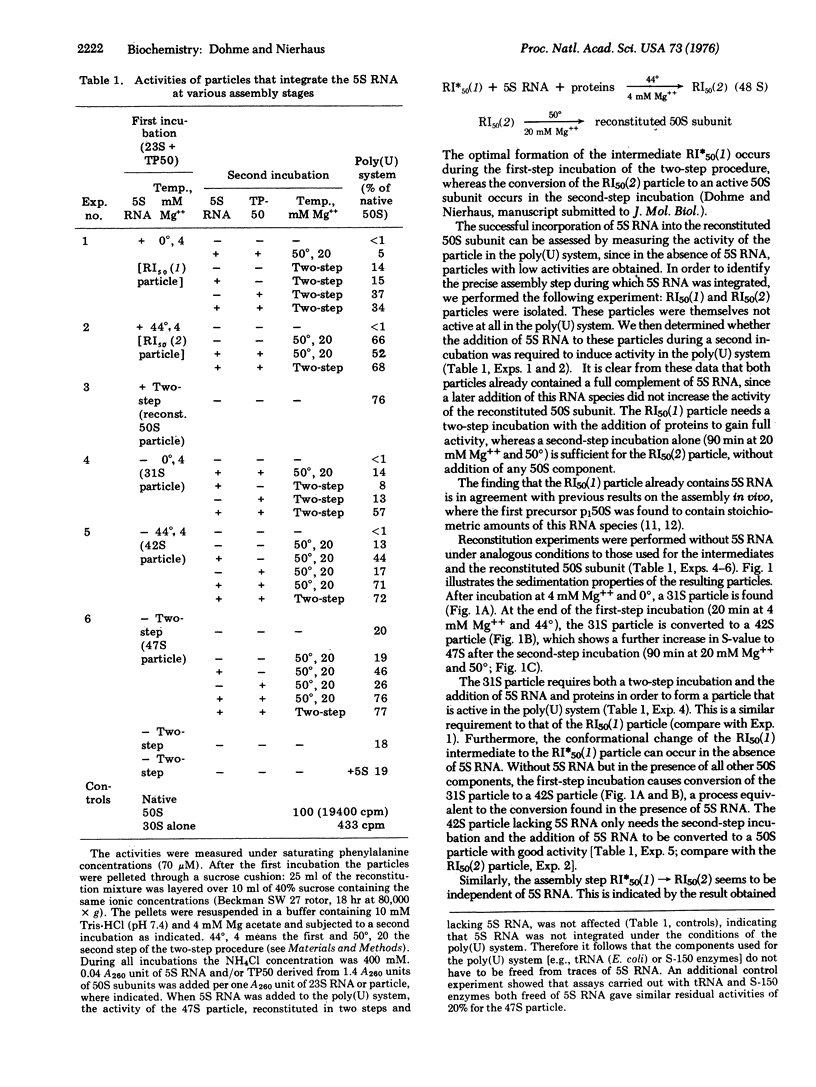
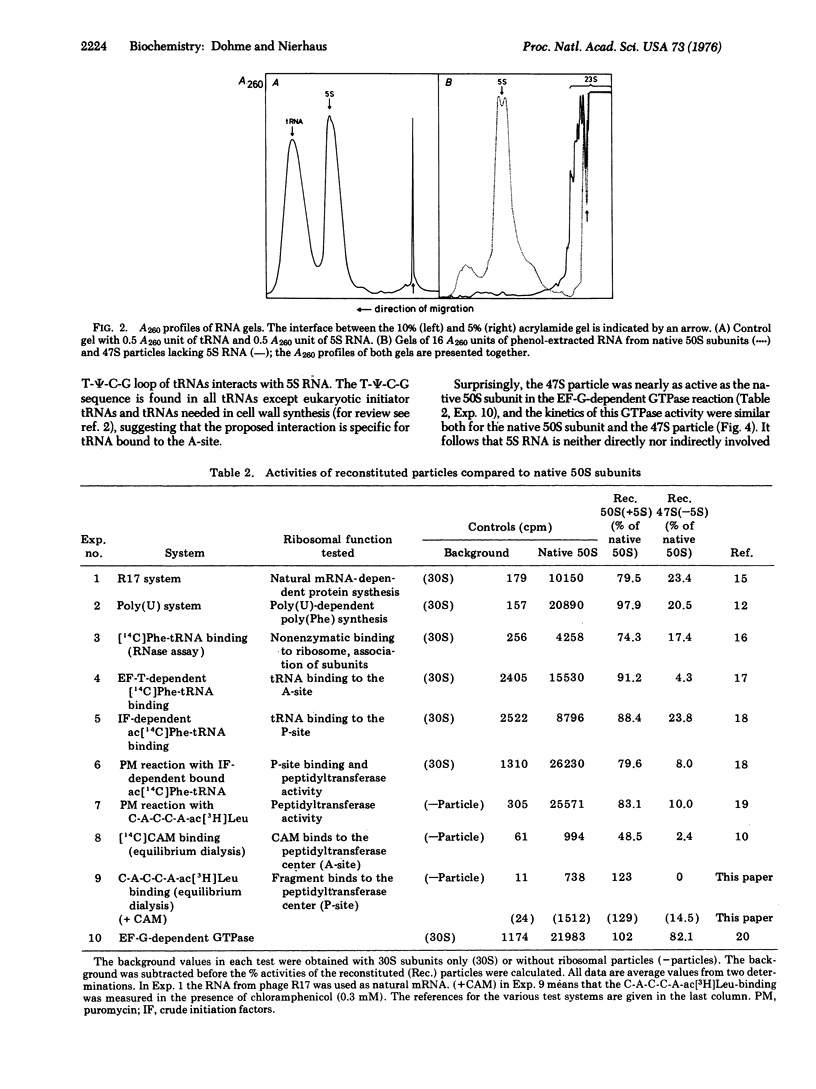
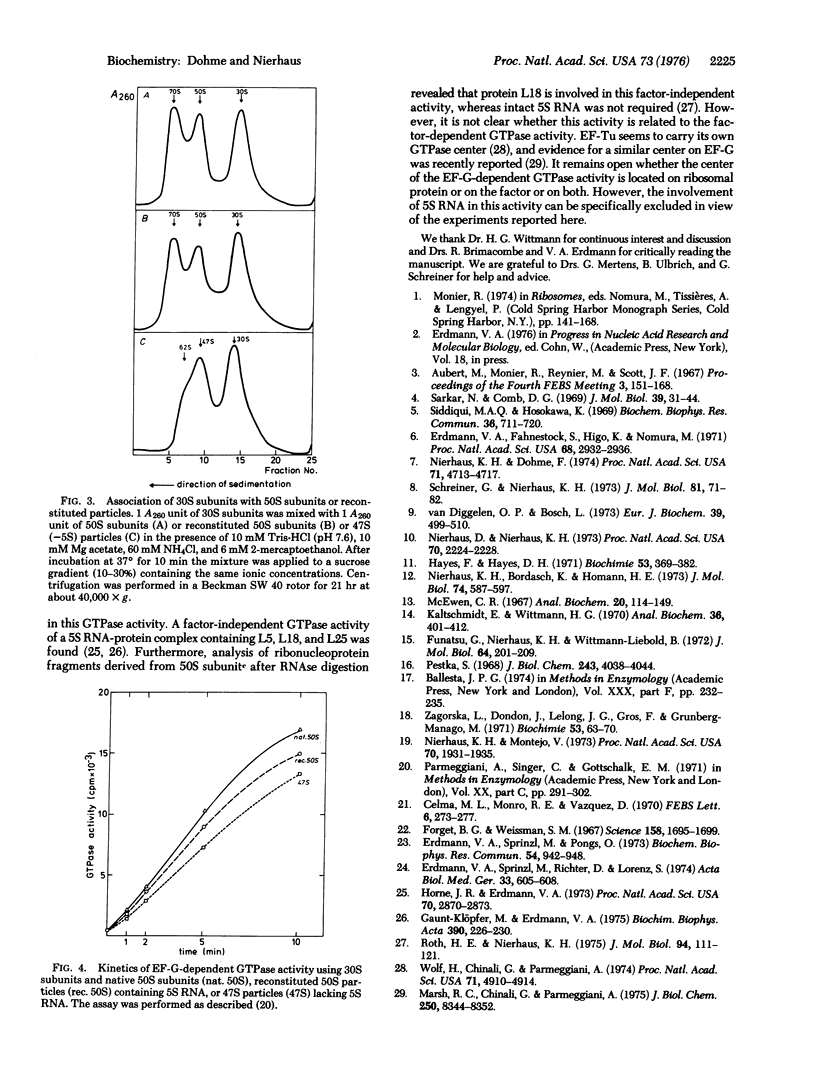
Total reconstitution experiments performed under various conditions revealed that 5S RNA plays an important role during the last assembly step in vitro leading to an active 50S particle. For the preceding steps this RNA species is dispensable. However, 50S RNA can be integrated efficiently during any of the assembly steps in vitro. The 47S particle, reconstituted in two steps and lacking 5S RNA, shows low but significant activity in many functional tests. High activity could be obtained by incubating this particle with 5S RNA alone, demonstrating the importance of the 5S RNA in generating an active ribosomal conformation. In particular, the activity of the peptidyltransferase (peptidyl-tRNA:aminoacyl-tRNA N-peptidyltransferase; EC 2.3.2.12) center is drastically influenced by 5S RNA. No significant factor-dependent tRNA binding to the A-site was observed with the 47S particle, in contrast to the corresponding P-site binding. The elongation factor G dependent GTPase activity was not affected by the lack of 5S RNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Celma M. L., Monro R. E., Vazquez D. Substrate and antibiotic binding sites at the peptidyl transferase centre of E. coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1970 Feb 16;6(3):273–277. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80076-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Fahnestock S., Higo K., Nomura M. Role of 5S RNA in the functions of 50S ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M., Pongs O. The involvement of 5S RNA in the binding of tRNA to ribosomes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Oct 1;54(3):942–948. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(73)90785-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Sprinzl M., Richter D., Lorenz S. Binding of aminoacyl tRNA to ribosomes: a function of 5S-RNA. Acta Biol Med Ger. 1974;33(5-6):605–608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forget B. G., Weissman S. M. Nucleotide sequence of KB cell 5S RNA. Science. 1967 Dec 29;158(3809):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3809.1695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Nierhaus K., Wittmann-Liebold B. Ribosomal proteins. XXII. Studies on the altered protein S5 from a spectinomycin-resistant mutant of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Feb 28;64(1):201–209. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90329-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaunt-Klöpfer M., Erdmann V. A. ATPase and GTPase activities associated with the 5-S RNA-protein complex of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 1;390(2):226–230. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90343-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes F., Hayes D. H. Biosynthesis of ribosomes in E. coli. I. Properties of ribosomal precursor particles and their RNA components. Biochimie. 1971;53(3):369–382. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80104-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horne J. R., Erdmann V. A. ATPase and GTPase activities associated with a specific 5S RNA-protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Oct;70(10):2870–2873. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.10.2870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. VII. Two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for fingerprinting of ribosomal proteins. Anal Biochem. 1970 Aug;36(2):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(70)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh R. C., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Function of sulfhydryl groups in ribosome-elongation factor G reactions. Assignment of guanine nucleotide binding site to elongation factor G. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 10;250(21):8344–8352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McEwen C. R. Tables for estimating sedimentation through linear concentration gradients of sucrose solution. Anal Biochem. 1967 Jul;20(1):114–149. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(67)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus D., Nierhaus K. H. Identification of the chloramphenicol-binding protein in Escherichia coli ribosomes by partial reconstitution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2224–2228. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Bordasch K., Homann H. E. Ribosomal proteins. 43. In vivo assembly of Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):587–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Dohme F. Total reconstitution of functionally active 50S ribosomal subunits from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4713–4717. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H., Montejo V. A protein involved in the peptidyltransferase activity of Escherichia coli ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):1931–1935. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.1931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Studies on the formation of transfer ribonucleic acid-ribosome complexes. IV. A new assay for codon recognition and interaction of transfer ribonucleic acid with 50 S subunits. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 10;243(15):4038–4044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth H. E., Nierhaus K. H. Structural and functional studies of ribonucleoprotein fragments isolated from Escherichia coli 50 S ribosomal subunits. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 5;94(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N., Comb D. G. Studies on the attachment and release of 5 s ribosomal RNA from the large ribosomal subunit. J Mol Biol. 1969 Jan 14;39(1):31–44. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90331-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiner G., Nierhaus K. H. Protein involved in the binding of dihydrostreptomycin to ribosomes of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1973 Nov 25;81(1):71–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90248-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddiqui M. A., Hosokawa K. Role of 5S ribosomal RNA in polypeptide synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1969 Aug 22;36(5):711–720. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(69)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin, an inhibitor of protein biosynthesis that acts on elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4910–4914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Diggelen O. P., Bosch L. The association of ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. 1. Two types of association products differing in their apparent sedimentation coefficient. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Nov 15;39(2):499–510. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb03149.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



