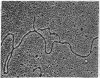
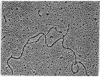
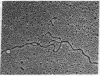
Abstract
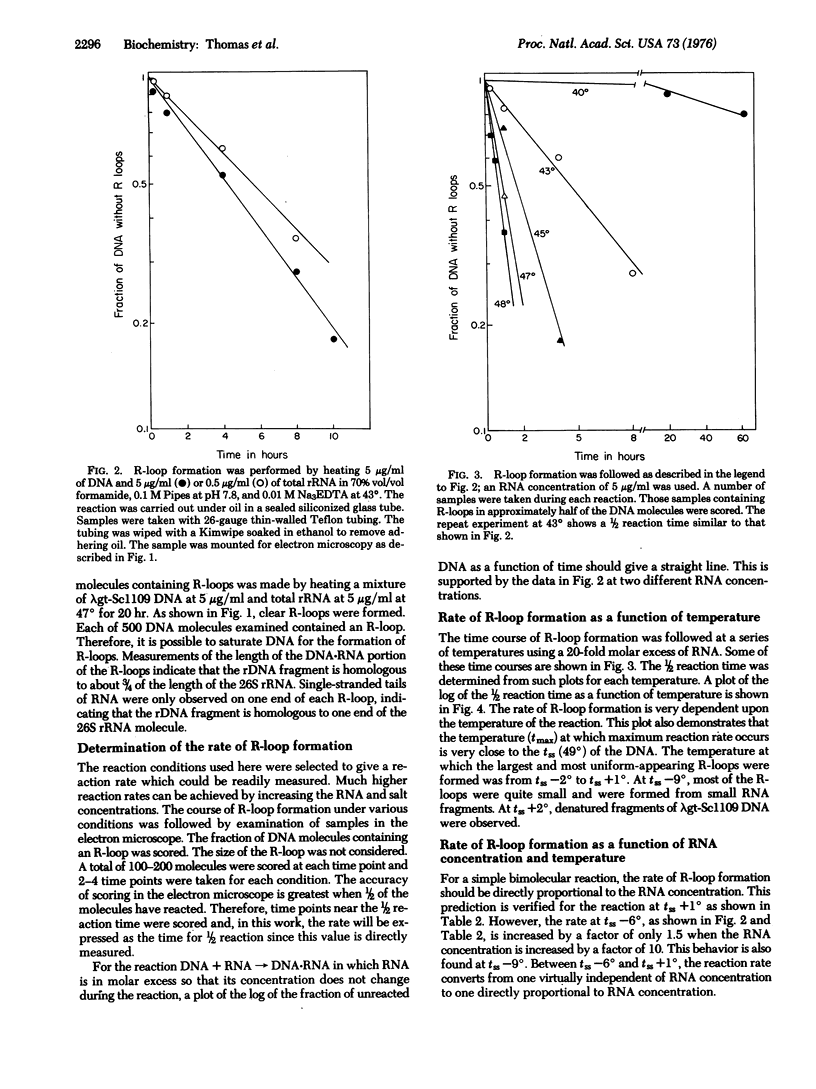
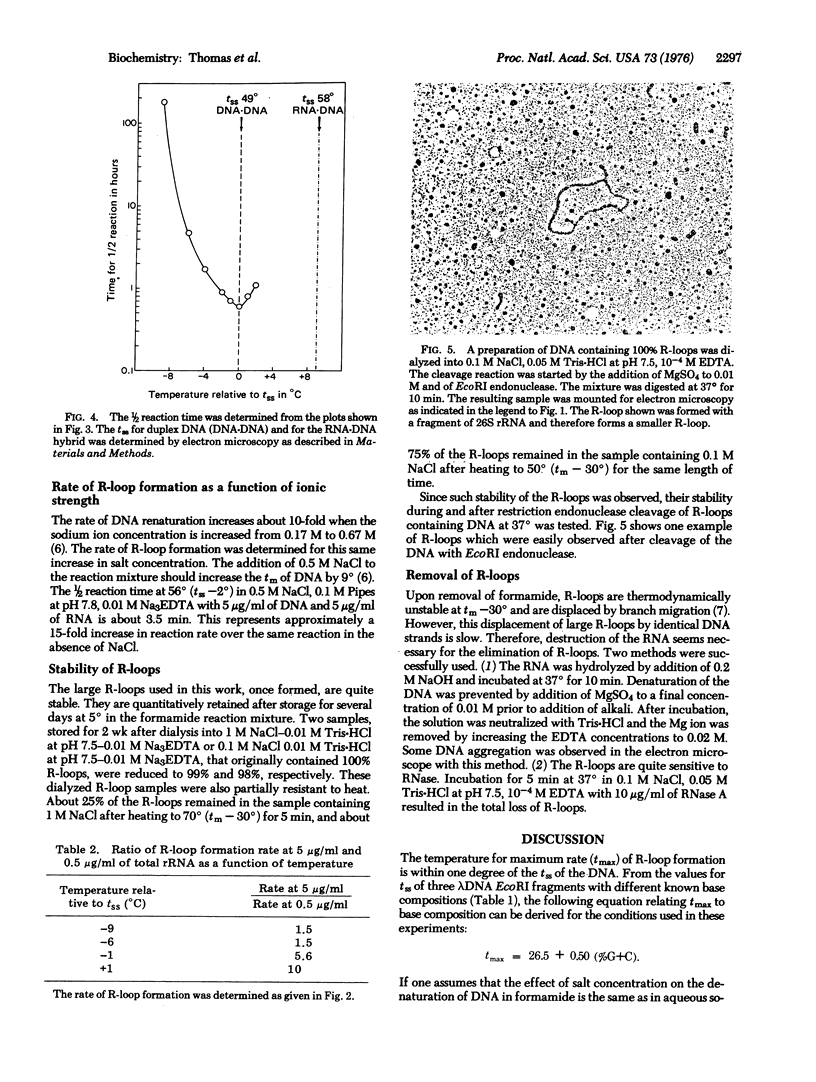
RNA can hybridize to double-stranded DNA in the presence of 70% formamide by displacing the identical DNA strand. The resulting structure, called an R-loop, is formed in formamide probably because of the greater thermodynamic stability of the RNA-DNA hybrid when it is near the denaturation temperature of duplex DNA. The rate of R-loop formation is maximal at the temperature at which half of the duplex DNA is irreversibly converted to single-stranded DNA (the strand separation temperature of tss) of the duplex DNA and falls precipitously a few degrees above or below that temperature. This maximal rate is similar to the rate of hybridization of RNA to single-stranded DNA under the same conditions. At temperatures above the tss the rate is proportional to the RNA concentration. However, at temperatures below tss the rate of R-loop formation is less dependent upon the RNA concentration. Once formed, the R-loops display considerable stability; the formamide can be removed and the DNA can be cleaved with restriction endonucleases without loss of R-loop structures.
Full text
PDF
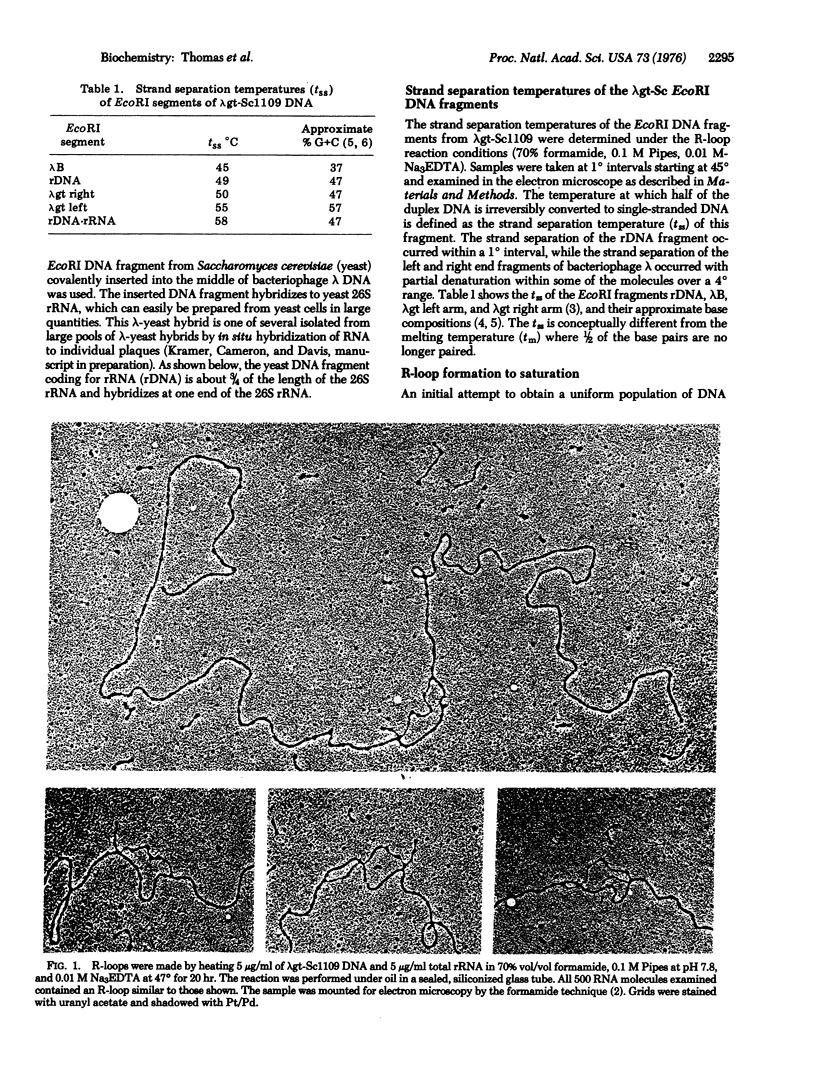

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Lee C. S., Davis R. W., Davidson N. A physical study by electron microscopy of the terminally reptitious, circularly permuted DNA from the coliphage particles of Escherichia coli 15. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):1–22. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90215-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Retèl J., Van Keulen H. Characterization of yeast ribosomal DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Oct 1;58(1):51–57. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robberson D. L., Kasamatsu H., Vinograd J. Replication of mitochondrial DNA. Circular replicative intermediates in mouse L cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):737–741. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schildkraut C. Dependence of the melting temperature of DNA on salt concentration. Biopolymers. 1965;3(2):195–208. doi: 10.1002/bip.360030207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas M., Cameron J. R., Davis R. W. Viable molecular hybrids of bacteriophage lambda and eukaryotic DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4579–4583. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wetmur J. G., Davidson N. Kinetics of renaturation of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):349–370. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90414-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]