Abstract
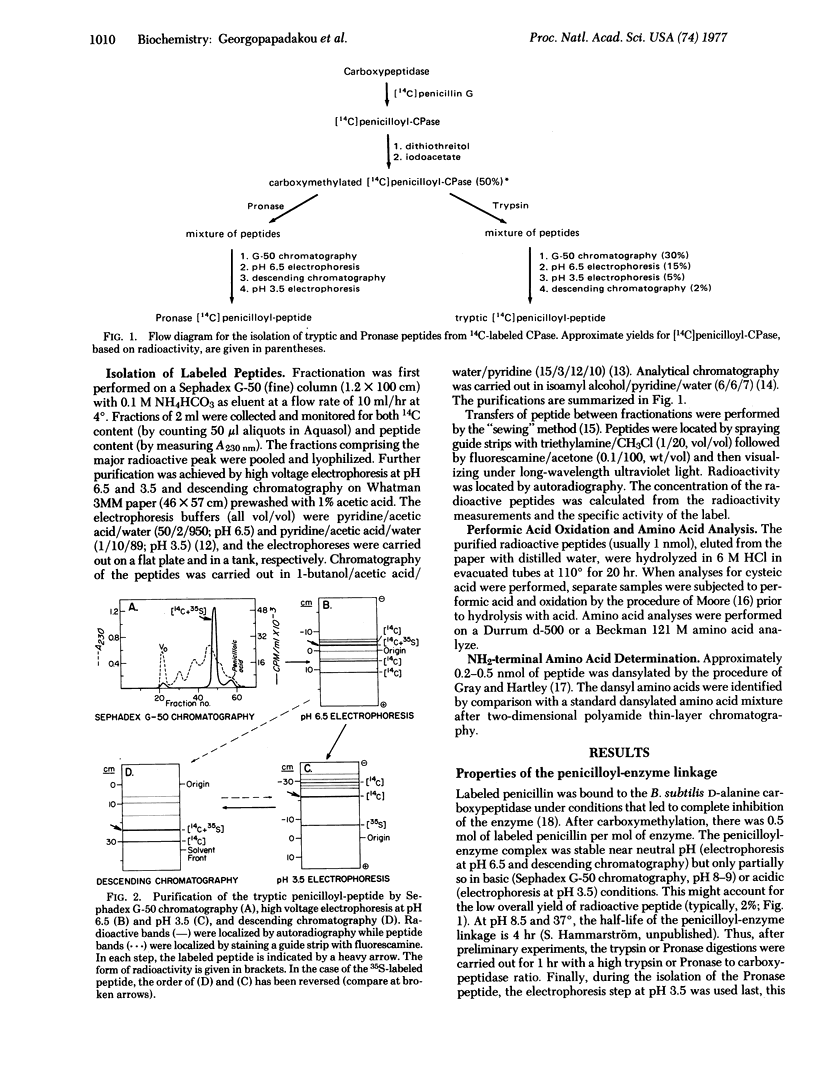
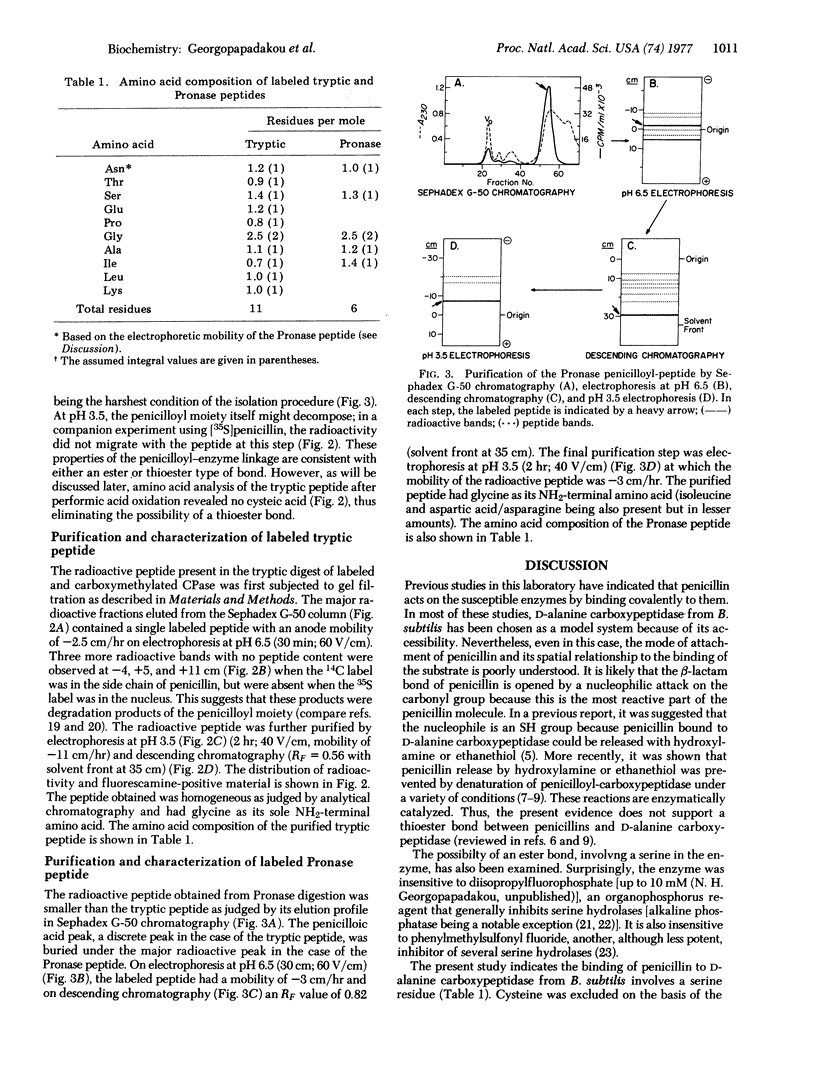
The D-alanine carboxypeptidase of B. subtilis is a membrane-bound enzyme which is inhibited by penicillins and binds them covalently. The enzyme has been labeled with [14C]- or [35S]penicillin. After tryptic or Pronase digestion of the labeled, denatured, reduced, and carboxymethylated enzyme, a radioactive peptide was isolated in each case. The amino acid compositions of these two peptides are reported. The Pronase peptide was a subset of the tryptic peptide. Neither contained a cysteine residue and the only amino acid in the Pronase peptide to which the penicillin could be bound was a serine residue.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BAGLIONI C. An improved method for the fingerprinting of human hemoglobin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Apr 1;48:392–396. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90490-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop D. G., Rutberg L., Samuelsson B. The chemical composition of the cytoplasmic membrane of Bacillus subtilis. Eur J Biochem. 1967 Nov;2(4):448–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1967.tb00158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Five penicillin-binding components occur in Bacillus subtilis membranes. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):8107–8113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Inactivation of D-alanine carboxypeptidase by penicillins and cephalosporins is not lethal in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Nov;68(11):2814–2817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.11.2814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Interaction of penicillin with the bacterial cell: penicillin-binding proteins and penicillin-sensitive enzymes. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Sep;38(3):291–335. doi: 10.1128/br.38.3.291-335.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Strominger J. L. Isolation by covalent affinity chromatography of the penicillin-binding components from membranes of Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3751–3755. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3751. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Yocum R. R., Willoughby E., Strominger J. L. Binding of (14C)penicillin G to the membrane-bound and the purified D-alanine carboxypeptidases from Bacillus stearothermophilus and Bacillus subtilis and its release. J Biol Chem. 1974 Nov 10;249(21):6828–6835. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. R., Hartley B. S. Location of disulphide bridges by diagonal paper electrophoresis. The disulphide bridges of bovine chymotrypsinogen A. Biochem J. 1966 Oct;101(1):214–228. doi: 10.1042/bj1010214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabich D., Neuhaus O. W. Purification and properties of bovine synovial fluid alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jan 25;241(2):415–420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frère J. M., Duez C., Ghuysen J. M., Vandekerkhove J. Occurrence of a serine residue in the penicillin-binding site of the exocellular DD-carboxy-peptidase-transpeptidase from Streptomyces R61. FEBS Lett. 1976 Nov;70(1):257–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80770-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY W. R., HARTLEY B. S. THE STRUCTURE OF A CHYMOTRYPTIC PEPTIDE FROM PSEUDOMONAS CYTOCHROME C-551. Biochem J. 1963 Nov;89:379–380. doi: 10.1042/bj0890379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Strominger J. L. Degradation of penicillin G to phenylacetylglycine by D-alanine carboxypeptidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3463–3467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammarström S., Strominger J. L. Formation of 5,5-dimethyl-delta2-thiazoline-4-carboxylic acid during cleavage of penicillin G by D-alanine carboxypeptidase from Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Biol Chem. 1976 Dec 25;251(24):7947–7949. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHT A., SMITH E. L. Chymotryptic digest of papain. J Biol Chem. 1962 Aug;237:2537–2546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence P. J., Strominger J. L. Biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan of bacterial cell walls. XVI. The reversible fixation of radioactive penicillin G to the D-alanine carboxypeptidase of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3660–3666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. The substrate specificity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatases of cow's milk and calf intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1955 Oct;61(2):232–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0610232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYLE A. P., SANGER F., SMITH L. F., KITAI R. The disulphide bonds of insulin. Biochem J. 1955 Aug;60(4):541–556. doi: 10.1042/bj0600541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J., Strominger J. L. Mechanism of action of penicillins: a proposal based on their structural similarity to acyl-D-alanyl-D-alanine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Oct;54(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umbreit J. N., Strominger J. L. D-alanine carboxypeptidase from Bacillus subtilis membranes. I. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6759–6766. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



