Abstract
Recently, a novel and distinct pancreatic cystic tumor termed “mucinous nonneoplastic” cyst was described in the literature. We report our experience with a 71-year-old female with a cystic tumor in the body of the pancreas demonstrating features suggestive of this diagnosis. We also review the literature regarding this “novel” pathological entity and discuss critically its existence and its differential diagnoses.
Keywords: Pancreatic cyst, Mucinous nonneoplastic cyst, Mucinous cysts, Pancreatic cystic tumors, Pancreas, Cyst
INTRODUCTION
Cystic tumors of the pancreas consist of a diverse spectrum of pathological entities and they may be broadly classified into neoplastic and nonneoplastic cysts[1]. The predominant cystic neoplasms are intraductal papillary mucinous tumors (IPMTs), mucinous cystic tumors (MCTs) and solid pseudopapillary neoplasms (SPPNs) which are either premalignant or malignant[2]. Serous cystic lesions form the other major group of cystic neoplasms and these are almost always benign[3]. On the other hand, the nonneoplastic cystic tumors consist of congenital cysts, lymphoepithelial cysts, retention cysts and endometrial cysts[3].
Recently a novel nonneoplastic cystic change of the pancreas was described which was termed mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC)[1]. We describe below a case of a pancreatic cystic tumor, which demonstrated features that raised the possibility of this diagnosis.
CASE REPORT
A 71-year-old Chinese female on follow-up for low-grade small lymphocytic lymphoma was found incidentally on computed tomography (CT) to have a cystic lesion in the body of the pancreas measuring 1.0 cm×0.5 cm. The pancreatic ducts were not dilated. An interval CT performed 6 mo later demonstrated an increase in the size of the cyst to 1.7 cm×1.4 cm (Figure 1). Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) was performed to further characterize the lesion and it demonstrated a 1.8-cm cystic lesion in the body of the pancreas seemingly communicating with the main pancreatic duct (Figure 2). The main pancreatic duct and its branches were not dilated and there were no mural nodules. Laboratory investigations including the liver function test, serum carcinoembryonic antigen and carbohydrate antigen 19-9 were within normal limits. The patient underwent distal pancreatectomy and splenectomy for an indeterminate cystic neoplasm of the pancreas and final histology demonstrated a simple cyst lined by mucinous epithelium (Figure 3). There was no underlying stromal condensation or epithelial dysplasia and communication with the native pancreatic ducts could not be demonstrated pathologically. The rest of the pancreatic tissue was histologically unremarkable with no evidence of established chronic pancreatitis. At a follow-up of 1 year, there was no evidence of tumor recurrence.
Figure 1.
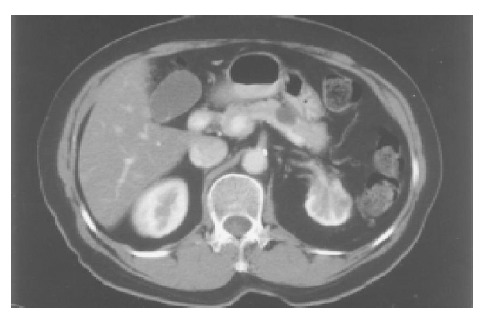
CT scan demonstrating a 1.7-cm cyst in the body of the pancreas.
Figure 2.
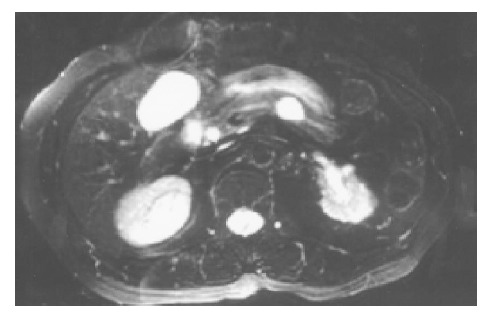
MRI demonstrating the 1.8-cm cystic lesion in the body of the pancreas seemingly communicating with the pancreatic duct.
Figure 3.
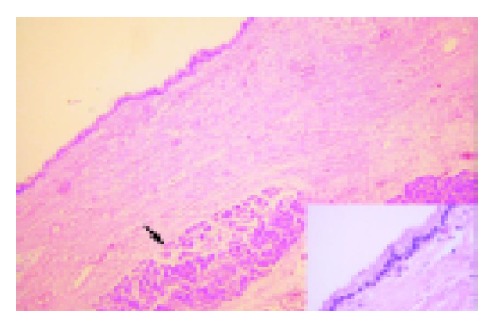
Cyst wall lined by single layered cuboidal to columnar epithelium, rimmed by fibrocollagenous stroma. Pancreatic acini are seen (arrow). Inset shows high magnification of the cyst epithelium, with no evidence of dysplasia (hematoxylin and eosin).
DISCUSSION
In 2002, Kosmahl et al[1], described a novel nonneoplastic cystic change of the pancreas in five patients for which they coined the term mucinous nonneoplastic cyst (MNC). The same group subsequently reported four cases (total of nine cases) demonstrating this novel cystic change in the pancreas in a recent review of 418 cases of cystic tumors of the pancreas[3]. MNCs occurred in five men and four women with a mean age of 58 years (range, 20-88 years). The cysts ranged in size from 3 to 12 cm and were localized to the head (five), head/tail (one) and head/body (two) regions. Three patients presented with obstructive jaundice secondary to external compression of the common bile duct by the cysts. MNCs are characterized pathologically by mucinous differentiation of the lining epithelium, lack of cellular atypia or increased proliferation, a thin rim of almost acellular supporting stroma and the absence of communication with the pancreatic ducts[1]. These cysts by definition do not demonstrate any neoplastic features such as dysplasia, proliferative activity, invasive growth pattern or metastatic spread. The origin and development of this entity are not known and can only be speculated. Pathologically, MNCs must be differentiated from other cystic tumors of the pancreas which are lined by mucinous epithelium such as MCTs, intraductal papillary mucinous tumors (IPMTs) and retention cysts.
Retention cysts may occur secondary to intraluminal obstruction of the pancreatic ducts from calculi or viscous mucin. It may also be caused by narrowing of its lumen from fibrosis due to chronic pancreatitis or neoplastic infiltration of the periductal tissue[1,4]. Thus, although retention cysts may share the similar mucinous lining epithelium as MNCs, this diagnosis may be excluded by the absence of potential causes or evidence of ductal obstruction and the lack of communication between the cyst and the pancreatic duct[1].
MCT of the pancreas is a large well-circumscribed tumor, which usually presents as a unilocular or multilocular cyst in the body and tail of the pancreas of middle-aged females[5,6]. These tumors like MNCs have a mucinous epithelial lining, which demonstrate periodic acid-Schiff and Alcian blue cytoplasmic positivity, expressing cytokeratins 7, 8, 18, 19 and 20, which decorate pancreatic ductal cells[7,8]. Further similarities between the two include expression of the mucin marker MUC5AC, which is seen in nearly all MNCs and MCTs[1]. Despite numerous similarities, histologically MCTs can be distinguished from MNCs by the presence of dysplasia of the columnar lining cells and more importantly the presence of a supporting ovarian-like stroma in the former[1,5,9]. Thus, the principal differences between these two entities lie within the stroma and epithelium which has the potential for malignant transformation[1].
IPMT is a novel and distinct clinicopathological entity described and distinguished from MCT by the World Health Organization in 1996 and the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology (AFIP) in 1997[4,9]. Like MCT and retention cysts, it presents as a cystic tumor of the pancreas lined with mucinous epithelium. This tumor is characterized by cystic dilatation of the main pancreatic duct or its branches due to large amount of mucin production and excretion through the patulous orifice of the ampulla of Vater affecting mainly elderly males[10]. IPMT is frequently associated with chronic pancreatitis, communication between cyst and pancreatic ducts and dilatation of the pancreatic ducts[11]. These tumors have tall, columnar, mucin-containing epithelium often with papillary proliferations and extensively involve the pancreatic ducts[12]. The epithelial cells of IPMT like that of MCT and unlike MNC usually demonstrate various grades of atypia and dysplasia and thus have malignant potential. According to Kosmahl et al[1] these tumors may be easily distinguished from MNCs and MCTs by their communication with the native pancreatic duct.
The pancreatic cyst in this report demonstrated histological features suggestive of MNC including a unilocular cyst lined by columnar cells with cytoplasmic mucin, absence of cellular proliferation or atypia, no pathologically demonstrable communication with the pancreatic duct and a thin rim of paucicellular supporting stroma. Arguing against this diagnosis, however, is the preoperative MRI that demonstrated cyst communication with the main pancreatic duct, making the alternate diagnosis of IPMT or retention cyst difficult to rule out equivocally.
This case raises many questions about the existence of MNC as a truly distinct entity. Kosmahl et al[1], emphasized the difficulty in distinguishing MNCs from retention cysts or MCTs. Apart from the lack of pathologic confirmation of communication with the main pancreatic duct after careful gross and microscopic examination, the absence of evidence of ductal obstruction such as calculi, chronic pancreatitis or neoplasm also supported the consideration of MNC. A factor against the diagnosis of MCT in this patient was that the supporting stroma was relatively acellular and it did not have a demonstrable ovarian-like stroma.
According to Kosmahl et al[1], MNCs can be easily differentiated from IPMT by the absence of communication with the pancreatic duct, which was not seen pathologically in all five cases of MNCs in their initial report. However, this criterion for the diagnosis of IPMT is potentially contentious as demonstration of ductal communication depends on several factors including the choice of preoperative imaging and the thoroughness of pathological evaluation. Occasionally, ductal communication not seen on CT or endoscopic retrogade cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) may be observed on MRI or pathological examination or vice versa[13]. Of the five patients reported, none of them underwent MRI and only one patient was subjected to an ERCP which did not reveal ductal communication[1]. The other four patients only underwent CT imaging, which is notoriously unreliable in demonstrating ductal communication. Thus, it is possible that ductal communication could have been demonstrated in some of the reported cases if the patients had undergone MRCP or ERCP. In our case, despite the demonstration of communication with the main pancreatic duct on MRCP, the diagnosis of IPMT was made less likely by the absence of characteristic pathological features such as tall columnar cells with papillary projections extensively involving the pancreatic ducts, some degree of cellular atypia, dilated pancreatic ducts, abundant mucin production and associated chronic pancreatitis.
In conclusion, it can be seen that the diagnosis of MNC may be extremely difficult as this tumor together with pancreatic retention cysts, MCTs and IPMTs share many overlapping clinicopathological features. The diagnosis of each of these entities does not depend on any one clinicopathological characteristic but a constellation of features (Table 1). We recommend that patients with the diagnosis of ‘benign’ MNC be followed up closely as in view of its recent description, its natural history cannot be assured to be benign. Furthermore, the existence of MNC as a truly unique cystic lesion remains contentious as reported cases of this entity may just represent variants of existing pancreatic pathology, which share the common pathological finding of a pancreatic cystic tumor lined with mucinous epithelium. All surgeons and pathologists areencouraged to report their experience with this entity to broaden our collective experience of this novel entity.
Table 1.
Comparison between pancreatic retention cysts, IPMT, MCT and MNC.
| Retention cyst | IPMT | MCT | MNC | |
| Mucinous epithelium | Present | Present | Present | Present |
| Cellular dysplasia | Absent | Usually present | Usually present | Absent |
| Communication between cyst and duct | Present | Present | Usually absent | Absent |
| Ductal obstruction with dilated duct | Present | Usually present | Usually absent | Absent |
| Secondary pancreatitis | May be present | Usually present | Usually absent | Absent |
| Ovarian-like stroma | Absent | Absent | Usually present | Absent |
| Gender | No predilection | Mostly male | Almost invariably female | No predilection |
Footnotes
Supported by Singapore Cancer Syndicate, MS0004
Science Editor Li WZ Language Editor Elsevier HK
References
- 1.Kosmahl M, Egawa N, Schröder S, Carneiro F, Lüttges J, Klöppel G. Mucinous nonneoplastic cyst of the pancreas: a novel nonneoplastic cystic change? Mod Pathol. 2002;15:154–158. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.3880507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Klöppel G, Kosmahl M. Cystic lesions and neoplasms of the pancreas. The features are becoming clearer. Pancreatology. 2001;1:648–655. doi: 10.1159/000055876. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Kosmahl M, Pauser U, Peters K, Sipos B, Lüttges J, Kremer B, Klöppel G. Cystic neoplasms of the pancreas and tumor-like lesions with cystic features: a review of 418 cases and a classification proposal. Virchows Arch. 2004;445:168–178. doi: 10.1007/s00428-004-1043-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Solcia E, Capella C, Kloppel G. Tumors of the pancreas. In: AFIP atlas of tumor pathology, 3rd series, Fascicle 20., editors. Washington, DC: Armed Forces Institute of Pathology;; 1997. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Wilentz RE, Albores-Saavedra J, Hruban RH. Mucinous cystic neoplasms of the pancreas. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000;17:31–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zamboni G, Scarpa A, Bogina G, Iacono C, Bassi C, Talamini G, Sessa F, Capella C, Solcia E, Rickaert F, et al. Mucinous cystic tumors of the pancreas: clinicopathological features, prognosis, and relationship to other mucinous cystic tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23:410–422. doi: 10.1097/00000478-199904000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Osborn M, van Lessen G, Weber K, Klöppel G, Altmannsberger M. Differential diagnosis of gastrointestinal carcinomas by using monoclonal antibodies specific for individual keratin polypeptides. Lab Invest. 1986;55:497–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Moll R, Löwe A, Laufer J, Franke WW. Cytokeratin 20 in human carcinomas. A new histodiagnostic marker detected by monoclonal antibodies. Am J Pathol. 1992;140:427–447. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kloppel G, Solcia E, Longnecker DS, Capella C, Sobin LH. Histological typing of tumours of the exocrine pancreas. 2nd ed. WHO international histological classification of tumours. Berlin: Springer;; 1996. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Shyr YM, Su CH, Tsay SH, Lui WY. Mucin-producing neoplasms of the pancreas. Intraductal papillary and mucinous cystic neoplasms. Ann Surg. 1996;223:141–146. doi: 10.1097/00000658-199602000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Suzuki Y, Atomi Y, Sugiyama M, Isaji S, Inui K, Kimura W, Sunamura M, Furukawa T, Yanagisawa A, Ariyama J, et al. Cystic neoplasm of the pancreas: a Japanese multiinstitutional study of intraductal papillary mucinous tumor and mucinous cystic tumor. Pancreas. 2004;28:241–246. doi: 10.1097/00006676-200404000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sohn TA, Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Iacobuzio-Donahue CA, Hruban RH, Lillemoe KD. Intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasms of the pancreas: an increasingly recognized clinicopathologic entity. Ann Surg. 2001;234:313–321; discussion 321-322. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200109000-00005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sugiyama M, Atomi Y. Recent topics in mucinous cystic tumor and intraductal papillary mucinous tumor of the pancreas. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2003;10:123–124. doi: 10.1007/s00534-002-0815-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


