Abstract
AIM: While colorectal cancer (CRC) is an ideal target for population screening, physician and patient attitudes contribute to low levels of screening uptake. This study was carried out to find feasible economic strategies to improve the CRC screening compliance in Korea.
METHODS: The natural history of a simulated cohort of 50-year-old Korean in the general population was modeled with CRC screening until the age of 80 years. Cases of positive results were worked up with colonoscopy. After polypectomy, colonoscopy was repeated every 3 years. Baseline screening compliance without insurance coverage by the national health insurance (NHI) was assumed to be 30%. If NHI covered the CRC screening or the reimbursement of screening to physicians increased, the compliance was assumed to increase. We evaluated 16 different CRC screening strategies based on Markov model.
RESULTS: When the NHI did not cover the screening and compliance was 30%, non-dominated strategies were colonoscopy every 5 years (COL5) and colonoscopy every 3 years (COL3). In all scenarios of various compliance rates with raised coverage of the NHI and increased reimbursement of colonoscopy, COL10, COL5 and COL3 were non-dominated strategies, and COL10 had lower or minimal incremental medical cost and financial burden on the NHI than the strategy of no screening. These results were stable with sensitivity analyses.
CONCLUSION: Economic strategies for promoting screening compliance can be accompanied by expanding insurance coverage by the NHI and by increasing reimbursement for CRC screening to providers. COL10 was a cost-effective and cost saving screening strategy for CRC in Korea.
Keywords: Cost-effectiveness analysis, Colorectal cancer, Screening, Compliance, National health insurance, Coverage, Reimbursement
INTRODUCTION
Korea is known to be a low-risk area for colorectal cancer (CRC), but the incidence has been rapidly increasing during the last decade. From 1987 to 1996, the age-standardized mortality rate for CRC has roughly doubled from 8.7 to 16.5 per 100000 for men and 6.3 to 14.3 per 100000 for women[1]. Screening for CRC reduces mortality through detection of malignancy at an earlier, more treatable stage as well as by identification and removal of precursor lesion, the adenomatous polyp[2]. Recent panel in Korea recommends that an average-risk individual should begin CRC screening at the age of 50 with one of the two following guidelines[3]: 1. Colonoscopy (COL) every 5-10 years. 2. Flexible sigmoidoscopy (SIG) and double-contrast barium enema (DCBE) every 5 years.
However, these recommendations condoned by expert panels, were not based on economic evaluation. CRC screening tests vary considerably in terms of their performance characteristics, complication rates, acceptability and cost. Especially the cost structure for reimbursement of CRC screening and treatment in Korea is different from that in other countries. Colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and DCBE for CRC screening are not covered by national health insurance (NHI) scheme in Korea. Previous studies have demonstrated that out-of-pocket payment was a barrier to cancer screening and health insurance was an important determinant of the utilization of cancer screening[4,5]. In addition, physician’s noncompliance with screening recommendation was known to be a major barrier to effective CRC control[6]. Perceived inadequacy of the reimbursement of colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy was one of the factors affecting physician’s compliance[7].
To improve the physician and patient compliance for CRC screening, some reports have demonstrated that the third-party payer should remove financial barriers by providing insurance coverage and raising reimbursement of CRC screening to physicians[8]. However, Korean NHI has experienced an annual deficit since 1997 and fiscal stability is a major concern[9]. At the current status, new national policy on screening should not put financial burden on the Korean NHI system and needs to take into account economic consequences.
To suggest a feasible economic model to improve the compliance by raising insurance coverage and reimbursement without increasing financial burden on the NHI, we constructed a decision-analytic model to evaluate the cost-effectiveness of CRC screening for average-risk Korean individuals.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Model
The natural history of a simulated cohort of 50-year-old Koreans in the general population was modeled with and without CRC screening until the age of 80 years (Figure 1). We evaluated 16 different screening strategies with Markov model. Persons representative of the 50-year-old Korean population were placed into health states defined by the presence or absence of a polyp or cancer (early or advanced). Cases of positive screening test results were worked up with a colonoscopy, and individuals diagnosed with polyp underwent polypectomy. Colonoscopy was repeated every 3 years for surveillance after polypectomy[10]. The probability of perforation was assigned to DCBE, SIG, COL and polypectomy[11-13]. Mortality caused by the risk of perforation was assumed to be 0.02%[13,14].
Figure 1.
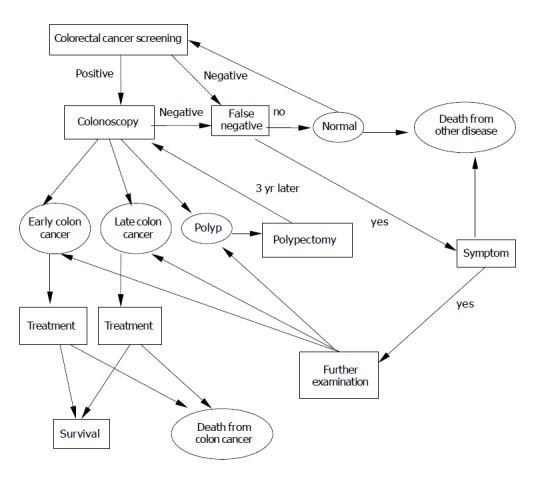
Markov model of colorectal cancer screening. The ovals represent Markov states in which patients remain for at least full 1-year cycle. The squares represent intermediate states of screening procedures, in which patients may enter and leave during one cycle. The arrows represent transitions between various states.
Our main outcome measures were discounted lifetime costs, life expectancy, lifetime NHI’s financial burden and incremental cost-effectiveness ratio (ICER), which were compared for 16 different CRC screening strategies. Incremental cost-effectiveness analysis was performed by ranking the 16 strategies in the order of increasing effectiveness. After eliminating strategies, that were more or equally costly and less effective than a competing strategy (i.e., ruled out by simple dominance), we calculated the ICER for each strategy (additional cost divided by additional benefit) compared with the next least expensive strategy. If a strategy was less effective and had a higher ICER than another strategy, it was ruled out by extended dominance[15]. Strategies exhibiting extended dominance were eliminated from the rank-ordered list, and ICERs of the remaining strategies were recalculated. Future costs and life-years were discounted at an annual rate of 3%. The model was programmed in DATA Pro 4.0 software (TreeAge Software Inc., Williamstown, MA).
Clinical data
Natural history of colorectal polyps and cancer Table 1 showed selected parameter estimates. We estimated the age-specific prevalence of adenomatous polyps from previous studies in Korea[3,16]. The incidence of polyp is assumed to be constant calibrated with the two prevalence rates between age 50 and 65. The probability of transformation from polyp to cancer was estimated from the study of patients who refused the resection of polyp[17]. We assumed that the longer the duration of polyp, the greater the probability of transformation from polyp to cancer.
Table 1.
Summary of assumption.
| Parameter | Base case value | Reference | |
| Sensitivity and specificity of screening and diagnosis | Sensitivity of FOBT for polyps/cancer | 0.1/0.5 | [15], [28], [29], [30] |
| Sensitivity of colonoscopy for polyps/cancer | 0.85/0.97 | [2], [31], [32] | |
| Sensitivity of colon study for polyps/cancer | 0.5/0.8 | [2], [33], [34] | |
| Sensitivity of sigmoidoscopy for polyps/cancer | 0.67 | [1], [2], [31], [32] | |
| Specificity of FOBT | 0.9 | [15], [28], [29], [30] | |
| Specificity of colonoscopy | 1 | [2], [31], [32] | |
| Specificity of colon study | 0.9 | [2], [33], [34] | |
| Specificity of sigmoidoscopy | 1 | [2], [31], [32] | |
| Natural history of polyp/cancer sequence | Prevalence of polyps at age 50 | 0.25 | [13], [36] |
| Annual polyp incidence rate | 0.005 | [13], [36] | |
| Percent of cancers originating as polyps | 100% | [37], [38] | |
| Annual cancer incidence of polyp whose duration is below 5 yr | 0.005 | [17], [39], [40], [41] | |
| Annual cancer incidence of polyp whose duration is from 5 to 10 yr | 0.01 | [17], [39], [40], [41] | |
| Annual cancer incidence of polyp whose duration is above 10 yr | 0.016 | [17], [39], [40], [41] | |
| Dwelling time of cancer in early stages | 2 yr | [29], [42] | |
| Percent of cancers detected in early stages with no screening | 5% | [21] | |
| Five-year all cause survival for early cancer | 90% | [21], [20] | |
| Five-year all cause survival for advanced cancer | 54% | [20], [21], [23] | |
| Polyp recurrence rate after polypectomy in the first year | 0.11 | [2], [3] | |
| Polyp recurrence rate after polypectomy thereafter | 0.03 | [2], [3] | |
| Complications and unintended consequences | Rate of perforation of colon in colonoscopy | 0.002 | [12], [13] |
| Rate of perforation of colon in polypectomy | 0.004 | [12], [13] | |
| Rate of perforation from sigmoidoscopy | 0.0001 | [12], [13] | |
| Rate of perforation from colon study | 0.00005 | [7] | |
| Death rate from perforated colon | 0.002 | [16], [17] | |
| Cost (won1) | Sigmoidoscopy | 26620 | [24] |
| Colonoscopy | 52560 | [24] | |
| Colon study | 58600 | [24] | |
| FOBT | 2290 | [24] | |
| Polypectomy | 134600 | [24] | |
| Biopsy | 24160 | [24] | |
| Treatment of early cancer for first year | 5150000 | [3], [17], [23] | |
| Treatment of advanced cancer for first year | 10300000 | [3], [17], [23] | |
| Treatment of cancer after first year | 2164000 | [3], [17], [23] | |
| Treatment of colonic perforation | 3000000 | [3] |
Exchange rate: 1200 Korean won for one US dollar.
We defined early stage cancer as modified Duke’s stage A and advanced stage as modified Duke’s stage B-D[18,19]. The latent period between early stage and advanced stage was assumed to be 2 years[14]. The stage-specific CRC mortality was applied uniformly to all malignancies, regardless of the means of detection (by symptoms or screen) or the state of detection (diagnose vs undiagnose cancer). Five-year survival rates from previous studies were used for the yearly probability of dying from CRC based on the stage and number of years with cancer[20,21]. Age-specific mortality from other causes was estimated, based on the above source combined with statistics published by the National Center for Health Statistics[22].
Cost
We obtained the data on the costs of CRC treatment by stage and time period from the National Health Insurance Corporation (social insurer of the NHI with a universal coverage of population)[23]. However, the co-payment that patients pay at the point of service amounts to about 50% of the total medical expenses of CRC treatment in Korea[3,9]. Therefore, the total medical cost of CRC treatment was assumed to be twice the expense that the NHI reimburses. Costs of screening test were obtained from the fee schedule of the National Health Insurance Corporation (the NHI of Korea has a fee schedule applied to all insured services)[24].
Compliance and screening cost
Compliance rates of 50-70% were obtained in the optimized setting of clinical trials of CRC screening[2]. However, colonoscopy, sigmoidoscopy and DCBE for CRC screening are not covered by the NHI in Korea. Therefore, the compliance is likely to be lower than that in other countries where CRC screening is covered by health insurance. At each particular screening event without NHI benefit coverage, we assumed that 30% of population underwent the initial screening test, independent of whether they were compliant with past tests. The compliance of follow-up or surveillance colonoscopy was assumed to be 20% higher than that of the initial screening.
If the NHI covered the CRC screening or the amount of reimbursement for screening to providers increased, the compliance was assumed to increase. If the NHI covered 50% and 100% of screening cost, the compliance was assumed to be 15% and 30% higher than that in case of non-coverage respectively, by reducing the financial barrier of patients. The Korean Medical Association had insisted that current reimbursement of colonoscopy to physicians was too low and the appropriate level should be 60% higher than the current level[25]. An increase in colonoscopy reimbursement, to 60% higher than the current level, was assumed to lead to 10% increase in the compliance due to financial incentives for physicians.
As there were no data available on the compliance changes resulting from the change in insurance coverage or reimbursement level, we performed sensitivity analysis to assess the stability of the results to plausible ranges of compliances. The compliance rate was set to vary from 10% lower to 10% higher than the baseline value.
RESULTS
In the base-case analysis at 30% screening compliance without NHI coverage, all screening strategies extended life expectancy. And the strategies which were not ruled out by simple dominance or extended dominance (non-dominated strategies) were colonoscopy every 5 years (COL5) and colonoscopy every 3 years (COL3). The screening strategies with colonoscopy or sigmoidoscopy showed lower total medical cost and lower financial burden on the NHI than the strategy of no screening (Table 2).
Table 2.
Cost-effectiveness of 16 strategies of colorectal screening among Korean adults without NHI coverage (NHIa coverage = 0%, screening compliance = 30%, follow-up compliance = 50%).
| Strategy (abbreviation) | Lifetime cost per person, won2 | Life expectancy, cost per day | Incremental person, won2 | Incremental days of life gained | Lifetime financial burden of NHI1, won2 | Incremental C/E3, won2 per life-year gained |
| COL5 | 311682 | 6176.1 | 139043 | |||
| COL3 | 313877 | 6181.1 | 2195 | 5 | 128757 | 160965 |
| COL10 | 321407 | 6171.7 | 7530 | 151394 | (Dominated)4 | |
| COL at 55 | 336367 | 6167.9 | 22490 | 164547 | (Dominated) | |
| SIG3 | 346903 | 6172.4 | 33026 | 155607 | (Dominated) | |
| SIG5 | 352290 | 6167.9 | 38413 | 164996 | (Dominated) | |
| SIG10 | 356222 | 6165.8 | 42345 | 171689 | (Dominated) | |
| SIG at 55 | 359939 | 6164.4 | 46062 | 177231 | (Dominated) | |
| SIG5+DCBE5 | 368560 | 6168.1 | 54683 | 165557 | (Dominated) | |
| No screening | 370726 | 6161.9 | 56849 | 185236 | (Dominated) | |
| FOBT2 | 375772 | 6165.5 | 61894 | 187015 | (Dominated) | |
| FOBT1+SIG5 | 384709 | 6169.7 | 70832 | 187443 | (Dominated) | |
| FOBT1 | 387912 | 6168.1 | 74035 | 192309 | (Dominated) | |
| DCBE10 | 390767 | 6164.1 | 76890 | 177826 | (Dominated) | |
| DCBE5 | 410554 | 6165.3 | 96677 | 174392 | (Dominated) | |
| DCBE3 | 435775 | 6169.3 | 121898 | 169661 | (Dominated) |
COL, colonoscopy; SIG, sigmoidoscopy; DCBE, double contrast barium enema; FOBT, fecal occult blood test. Ellipses indicate no data (incremental days or life gained and incremental CE ratio were not calculated for these strategies because they were dominated or extended dominated).
National Health Insurance of Korea.
Exchange rate: 1200 Korean won for one US dollar.
Incremental CE ratio (won/year) = Incremental cost per person/Incremental days of life gained×365 d.
Dominated strategy is a strategy that is more or equally costly and less effective than a competing strategy.
If the NHI covered 50% of the screening cost and the screening compliance was 45%, non-dominated strategies were colonoscopy every 10 years (COL10), COL5 and COL3. As the coverage of NHI increased, the financial burden on NHI increased. Nevertheless, the financial burden on the NHI associated with COL10 was smaller than that associated with no screening (Table 3). In the case that NHI covered 100% of screening cost, non-dominated strategies were COL10, COL5 and COL3, but theses strategies showed greater financial burden on the NHI than the strategy of no screening did (Table 3).
Table 3.
Cost-effectiveness of 16 strategies of colorectal screening among Korean adults with changing NHI1 coverage and compliance.
| Strategy (abbreviation) | Lifetime cost per person, won2 | Lifetime financial burden of NHI1, won2 | Incremental C/E3, won2 per life-year gained | Strategy (abbreviation) | Lifetime cost per person, won2 | Lifetime financial burden of NHI1, won2 | Incremental C/E3, won2 per life-year gained |
| NHI1 coverage = 50% | NHI1 coverage = 100% | ||||||
| Screening compliance = 45%, | Screening compliance = 60%, | ||||||
| Follow-up compliance = 65% | Follow-up compliance = 80% | ||||||
| COL10 | 310354 | 178233 | COL10 | 307395 | 226848 | ||
| COL5 | 311640 | 188051 | 93440 | COL at 55 | 308933 | 192405 | (Dominated) |
| COL at 55 | 321624 | 172824 | (Dominated)4 | SIG5 | 316541 | 235951 | (Dominated) |
| SIG3 | 328365 | 197511 | (Dominated) | SIG10 | 321728 | 214095 | (Dominated) |
| SIG5 | 332244 | 191881 | (Dominated) | SIG3 | 323691 | 261056 | (Extended Dominated)5 |
| COL3 | 336101 | 207072 | 2113350 | COL5 | 325435 | 267054 | 1371670 |
| SIG10 | 339760 | 186587 | (Dominated) | SIG at 55 | 330560 | 191573 | (Dominated) |
| SIG at 55 | 347179 | 181334 | (Dominated) | FOBT2 | 370827 | 216521 | (Dominated) |
| SIG5+DCBE5 | 369225 | 213205 | (Dominated) | No screening | 370968 | 185809 | (Dominated) |
| No screening | 370847 | 185499 | (Dominated) | COL3 | 374192 | 323357 | 5656770 |
| FOBT2 | 373988 | 208794 | (Dominated) | FOBT1+SIG5 | 382870 | 277687 | (Dominated) |
| FOBT1+SIG5 | 380512 | 238067 | (Dominated) | SIG5+DCBE5 | 383934 | 303581 | (Dominated) |
| FOBT1 | 388456 | 234316 | (Dominated) | FOBT1 | 389668 | 248595 | (Dominated) |
| DCBE10 | 394938 | 209420 | (Dominated) | DCBE10 | 397017 | 260523 | (Dominated) |
| DCBE5 | 420550 | 229974 | (Dominated) | DCBE5 | 429376 | 316022 | (Dominated) |
| DCBE3 | 455758 | 255914 | (Dominated) | DCBE3 | 478144 | 384805 | (Dominated) |
COL, colonoscopy; SIG, sigmoidoscopy; DCBE, double contrast barium enema; FOBT, fecal occult blood test.
National Health Insurance of Korea.
Exchange rate: 1 200 Korean won for one US dollar.
Incremental CE ratio (won/year) = Incremental cost per person/incremental days of life gained×365 d.
Dominated strategy is a strategy that is more or equally costly and less effective than a competing strategy.
Extended dominated: Extended dominated strategy is a strategy which is less effective and had a higher ICER than another strategy.
When the reimbursement of colonoscopy was 60% higher than the current level, along with 50% coverage of screening cost by the NHI and the compliance rate of 55%, non-dominated strategies were COL at age 55, COL10, COL5 and COL3. Total medical costs of COL at age 55 and COL10 were less than that associated with no screening. In addition, the NHI’s financial burden in case of COL at 55 was lower than that of no screening, and COL10 had relatively low incremental burden on the financial status of the NHI (Table 4).
Table 4.
Cost-effectiveness of 16 strategies of colorectal screening among Korean adults with raising reimbursement of colonoscopy to 60% higher than current level (Cost of colonoscopy = 85000 won1, NHI2 coverage = 50% screening compliance = 55%, follow-up compliance = 75%).
| Strategy (abbreviation) | Lifetime cost per person, won1 | Life expectancy, day | Lifetime financial burden of NHI2, won1 | Incremental C/E3, won1 per life-year gained |
| COL at 55 | 339486 | 6173.1 | 184815 | |
| SIG at 55 | 353851 | 6169.0 | 182912 | (Dominated)4 |
| COL10 | 362230 | 6179.1 | 208801 | 1401600 |
| SIG10 | 364257 | 6173.3 | 192838 | (Dominated) |
| No screening | 371238 | 6161.9 | 185704 | (Dominated) |
| SIG5 | 377039 | 6178.0 | 201390 | (Dominated) |
| FOBT2 | 384067 | 6170.8 | 219587 | (Dominated) |
| SIG3 | 399919 | 6183.0 | 210271 | (Extended dominated)5 |
| COL5 | 402824 | 6184.0 | 238433 | 2992270 |
| FOBT1 | 409771 | 6176.2 | 254521 | (Dominated) |
| DCBE10 | 410690 | 6169.1 | 221430 | (Dominated) |
| FOBT1+SIG5 | 426305 | 6180.8 | 262952 | (Dominated) |
| SIG5+DCBE5 | 435850 | 6178.8 | 235034 | (Dominated) |
| DCBE5 | 448356 | 6173.0 | 249784 | (Dominated) |
| COL3 | 474893 | 6187.5 | 281257 | 7487245 |
| DCBE3 | 499560 | 6178.5 | 284941 | (Dominated) |
COL, colonoscopy; SIG, sigmoidoscopy; DCBE, double contrast barium enema; FOBT, fecal occult blood test. Current level of colonoscopy cost in Korea is about 53000 won.
Exchange rate: 1200 Korean won for one US dollar.
National Health Insurance of Korea.
Incremental CE ratio (won/year) = incremental cost per person/incremental days of life gained×365 d.
Dominated strategy is a strategy that is more or equally costly and less effective than a competing strategy.
Extended dominated: Extended dominated strategy is a strategy which is less effective and had a higher ICER than another strategy.
Results of sensitivity analyses consistently showed the dominance of colonoscopy. In all cases, COL10, COL5 and COL3 were non-dominated strategies. When the reimbursement of colonoscopy was 60% higher than the current level, along with NHI’s 50% coverage of screening cost and the compliance rate of 65%, COL10 had slightly higher total medical cost than no screening. In other cases, total medical cost of COL10 was lower than that of no screening, and NHI’s financial burden associated with COL10 was lower or slightly higher than that of no screening. In all scenarios of various compliance rates, COL10, COL5 and COL3 were non-dominated strategies, and COL10 had lower or minimal incremental total medical cost and NHI’s financial burden than the strategy of no screening.
DISCUSSION
We compared 16 strategies for CRC screening, varying in the level of insurance coverage and reimbursement of colonoscopy by NHI to providers. In all scenarios, COL every 10 years, 5 years and 3 years were not ruled out by either simple or extended dominance, and COL every 10 years was associated with lower total medical cost than the strategy of no screening.
Public awareness of the importance of CRC screening is increasing although the rate of screening remains low[8]. Previous studies have shown that the cost was a barrier to cancer screening[4,26]. Removing the financial barrier by providing insurance coverage is one of the effective methods to raise the screening compliance, but the financial burden on the NHI can be increasing as well. In other countries, screening for CRC usually leads to greater life expectancy but is more costly than no screening. Interestingly, in our study of Korea, COL every 10 years has lower total medical cost than the case of no screening. This difference might be due to the difference in cost structure. In the US, published cost estimates for the medical care of patients with CRC range from $25000 to $45000 and the cost of COL is approximately $1000[14]. In Korea, the cost estimate of CRC treatment in the first year ranges from $5000 to $10000 and the cost of COL was approximately $50[23,24]. The ratio of treatment cost to COL cost ranges from 25:1 to 45:1 in the US and 100:1 to 200:1 in Korea. Since the cost of COL is relatively low in Korea, the screening is more cost-effective than in the US.
In Korea, the government started the national cancer-screening program (NCSP) in 1999, which included CRC screening in 2004. The government covers 50% of the screening cost for the insured and 100% for the low-income people. The primary method for CRC screening in NCSP is FOBT. Our study shows that the strategy of ‘FOBT annually’ costs more and carries heavier burden on NHI than the strategy of no screening, while COL every 10 years is less costly than no screening. These results suggest that COL every 10 years can be recommended as a primary screening strategy for CRC in NCSP. However, if COL is to be promoted as a screening tool, there must be sufficient manpower to deliver colonoscopy to the public. Unfortunately, there are only a few medical endoscopists available to undertake COL in Korea. Korean physicians insist that they are not willing to contribute to increase in CRC screening rate because of low reimbursement of COL[25]. Some surveys indicate that strong recommendation from the physician is highly correlated with patient participation in CRC screening[27]. Therefore, raising reimbursement rate for CRC screening to physicians can be effective in changing their behavior, which will eventually improve compliance rate. Our model shows that when the reimbursement for COL increases up to 85000 (Korean) won, which is 60% higher than the current level, along with NHI’s 50% coverage of screening cost, COL every 10 years or 5 years not only has lower total medical cost and lower financial burden on the NHI, but also improves lifetime expectancy than FOBT annually (Table 4). In addition, the total medical cost of COL every 10 years was lower than that of no screening in Korea. More investment in CRC screening is ideal because it reduces the cost of conventional treatment and extends life expectancy. Health policy makers should understand the need to train medical, and possibly even non-medical, personnel to perform endoscopy and to find an effective policy to lead physicians to perform colonoscopy[26].
Our analysis has several limitations. In the design of the model, we tried to reduce the complex natural history of CRC to a few essential states and to avoid assumptions on treatments for which little or no published data existed. For instance, we assumed that all cancers arose from polyps. And we used data from western countries if there were no published data available in Asia. There were possible differences between the races. Finally, we calculated only the direct costs and did not take into account the impact of CRC and screening on indirect costs.
In our conclusion, economic strategies for promoting screening compliance can be accompanied by expanding insurance coverage by the NHI and by increasing reimbursement for CRC screening to providers. And COL every 10 years is a cost-effective and cost saving screening strategy for CRC in Korea.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Bong Min Yang and Yoo Seon Hwang for their support and collaboration.
Footnotes
Science Editor Li WZ Language Editor Elsevier HK
References
- 1.Kim DH, Shin MH, Ahn YO. Incidence pattern of colorectal cancer in Korea by subsite of origin. J Korean Med Sci. 2000;15:675–681. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2000.15.6.675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Frazier AL, Colditz GA, Fuchs CS, Kuntz KM. Cost-effectiveness of screening for colorectal cancer in the general population. JAMA. 2000;284:1954–1961. doi: 10.1001/jama.284.15.1954. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Park SM, Chang YJ, Yun YH, Yoo TW, Huh BY, Kwon SM. Cost-effectiveness analysis of colorectal cancer screening in Korean General Population. J Korean Acad Fam Med. 2004;25:297–306. [Google Scholar]
- 4.Kiefe CI, McKay SV, Halevy A, Brody BA. Is cost a barrier to screening mammography for low-income women receiving Medicare benefits? A randomized trial. Arch Intern Med. 1994;154:1217–1224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Blustein J. Medicare coverage, supplemental insurance, and the use of mammography by older women. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1138–1143. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199504273321706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Schroy PC, Geller AC, Crosier Wood M, Page M, Sutherland L, Holm LJ, Heeren T. Utilization of colorectal cancer screening tests: a 1997 survey of Massachusetts internists. Prev Med. 2001;33:381–391. doi: 10.1006/pmed.2001.0903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Levin B, Smith RA, Feldman GE, Colditz GA, Fletcher RH, Nadel M, Rothenberger DA, Schroy PS, Vernon SW, Wender R. Promoting early detection tests for colorectal carcinoma and adenomatous polyps: a framework for action: the strategic plan of the National Colorectal Cancer Roundtable. Cancer. 2002;95:1618–1628. doi: 10.1002/cncr.10890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rex DK. Current colorectal cancer screening strategies: overview and obstacles to implementation. Rev Gastroenterol Disord. 2002;2 Suppl 1:S2–S11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kwon S. Payment system reform for health care providers in Korea. Health Policy Plan. 2003;18:84–92. doi: 10.1093/heapol/18.1.84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Winawer SJ. Appropriate intervals for surveillance. Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;49:S63–S66. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(99)70528-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Shimbo T, Glick HA, Eisenberg JM. Cost-effectiveness analysis of strategies for colorectal cancer screening in Japan. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 1994;10:359–375. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300006607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kavic SM, Basson MD. Complications of endoscopy. Am J Surg. 2001;181:319–332. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9610(01)00589-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Anderson ML, Pasha TM, Leighton JA. Endoscopic perforation of the colon: lessons from a 10-year study. Am J Gastroenterol. 2000;95:3418–3422. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2000.03356.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Wagner JL, Herdman RC, Wadhwa S. Cost effectiveness of colorectal cancer screening in the elderly. Ann Intern Med. 1991;115:807–817. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-115-10-807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Hunink M, Glasziou P, Siegel J, Weeks J, Pliskin J, Elstein A, Weinstein MC. Decision-Making in Health and Medicine: Integrating evidence and values. New York, NY, Cambridge University Press 2001 [Google Scholar]
- 16.Kim TS, Kang YS, Jung SY, Cho HJ, Kim DS, Lee DH. Prospective evaluation of colorectal polyps in 1 683 consecutive colonoscopies. Korean J Gastrointest Endosc. 1999;19:887–896. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Stryker SJ, Wolff BG, Culp CE, Libbe SD, Ilstrup DM, MacCarty RL. Natural history of untreated colonic polyps. Gastroenterology. 1987;93:1009–1013. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(87)90563-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Shimoda T, Ikegami M, Fujisaki J, Matsui T, Aizawa S, Ishikawa E. Early colorectal carcinoma with special reference to its development de novo. Cancer. 1989;64:1138–1146. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19890901)64:5<1138::aid-cncr2820640529>3.0.co;2-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Morson BC, Dawson IMP. 3rd ed. P604, Oxford, London, Blackwell Scientific 1990. Gastrointestinal pathology. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Bae JM, Won YJ, Jung KW, Shh KA, Yun YH, Shin MH, Ahn YO, Lee DH, Shin HR, Ahn DH, et al. Survival of korean cancer patients diagnosed in 1995. Cancer Res Treat. 2002;34:319–325. doi: 10.4143/crt.2002.34.5.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kim KH, Lee YS, Lee BC. A clinical study on the carcinoma of the colon and rectum. J Korean Surg Soc. 1991;41:215–222. [Google Scholar]
- 22.Annual report on the cause of death statistics (based on vital registration) National Statistical Office, Republic of Korea. Seoul 2001 [Google Scholar]
- 23.National health insurance corporation. 2002. 2001 Research on clinical practice pattern of cancer patient in national health insurance. Seoul: National health insurance corporation (in Korea) [Google Scholar]
- 24.National health insurance corporation. 2004. Contracting medical price in national health insurance corporation. Seoul: National health insurance corporation (in Korea) [Google Scholar]
- 25.Korean medical association. 2003. Research on the improvement of resource-based relative value. Seoul: Korean medical association (in Korea) [Google Scholar]
- 26.Keighley M, Arnold R. Is colonoscopic screening of a low-risk (normal) population ethically justifiable? Dig Dis. 2002;20:246–252. doi: 10.1159/000067683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Montaño DE, Phillips WR, Kasprzyk D. Explaining physician rates of providing flexible sigmoidoscopy. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2000;9:665–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Lieberman DA, Weiss DG. One-time screening for colorectal cancer with combined fecal occult-blood testing and examination of the distal colon. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:555–560. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa010328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khandker RK, Dulski JD, Kilpatrick JB, Ellis RP, Mitchell JB, Baine WB. A decision model and cost-effectiveness analysis of colorectal cancer screening and surveillance guidelines for average-risk adults. Int J Technol Assess Health Care. 2000;16:799–810. doi: 10.1017/s0266462300102077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ahlquist DA. Occult blood screening. Obstacles to effectiveness. Cancer. 1992;70:1259–1265. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920901)70:3+<1259::aid-cncr2820701511>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rex DK, Cutler CS, Lemmel GT, Rahmani EY, Clark DW, Helper DJ, Lehman GA, Mark DG. Colonoscopic miss rates of adenomas determined by back-to-back colonoscopies. Gastroenterology. 1997;112:24–28. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5085(97)70214-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Hixson LJ, Fennerty MB, Sampliner RE, Garewal HS. Prospective blinded trial of the colonoscopic miss-rate of large colorectal polyps. Gastrointest Endosc. 1991;37:125–127. doi: 10.1016/s0016-5107(91)70668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Winawer SJ, Stewart ET, Zauber AG, Bond JH, Ansel H, Waye JD, Hall D, Hamlin JA, Schapiro M, O'Brien MJ, et al. A comparison of colonoscopy and double-contrast barium enema for surveillance after polypectomy. National Polyp Study Work Group. N Engl J Med. 2000;342:1766–1772. doi: 10.1056/NEJM200006153422401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Glick S, Wagner JL, Johnson CD. Cost-effectiveness of double-contrast barium enema in screening for colorectal cancer. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1998;170:629–636. doi: 10.2214/ajr.170.3.9490943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Vatn MH, Stalsberg H. The prevalence of polyps of the large intestine in Oslo: an autopsy study. Cancer. 1982;49:819–825. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19820215)49:4<819::aid-cncr2820490435>3.0.co;2-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Eide TJ, Stalsberg H. Polyps of the large intestine in Northern Norway. Cancer. 1978;42:2839–2848. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197812)42:6<2839::aid-cncr2820420645>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Jackman RJ, Mayo CW. The adenoma-carcinoma sequence in cancer of the colon. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1951;93:327–330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Spratt JS, Ackerman LV. Small primary adenocarcinomas of the colon and rectum. JAMA. 1962;179:337–346. doi: 10.1001/jama.1962.03050050027005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Muto T, Bussey HJ, Morson BC. The evolution of cancer of the colon and rectum. Cancer. 1975;36:2251–2270. doi: 10.1002/cncr.2820360944. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Figiel LS, Figiel SJ, Wieterson FK. Roentgenologic observation of growth rates of colonic polyp and carcinoma. Acta Radiol Diagn. 1965;3:417. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Schulmann K, Reiser M, Schmiegel W. Colonic cancer and polyps. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2002;16:91–114. doi: 10.1053/bega.2002.0268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Eddy DM. Screening for colorectal cancer. Ann Intern Med. 1990;113:373–384. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-113-5-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


