Abstract
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is a known pathogen implicated in genesis of gastritis, peptic ulcer disease, gastric carcinoma and gastric lymphoma. Beyond the stomach, the organism has also been implicated in the causation of immune thrombocytopenia and iron deficiency anemia. Although an area of active clinical research, the role of this gram negative organism in causation of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease (CAD) remains enigmatic. CAD is a multifactorial disease which results from the atherosclerosis involving coronary arteries. The major risk factors include age, diabetes mellitus, smoking, hypertension and dyslipidemia. The risk of CAD is believed to increase with chronic inflammation. Various organisms like Chlamydia and Helicobacter have been suspected to have a role in genesis of atherosclerosis via causation of chronic inflammation. This paper focuses on available evidence to ascertain if the role of H. pylori in CAD causation has been proven beyond doubt and if eradication may reduce the risk of CAD or improve outcomes in these patients.
Keywords: Extra gastric, Coronary artery disease, Helicobacter pylori, Atherosclerosis, Inflammation
Core tip: Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a multifactorial disease and inflammation plays an important role in Atherogenesis. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) is speculated to be one organism which may incite the inflammatory response thereby predisposing infected individuals to CAD. This paper looks at clinical evidence in relation to H. pylori infection and CAD and also examines the evidence of effects of eradication of H. pylori on CAD and its risk factors.
INTRODUCTION
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori), first identified by Marshall and Warren in 1982, is a ubiquitous gram negative bacterium. A mixture of serendipity and diligent research lifted the veil off this enigmatic organism which was first thought to be Campylobacter like. The Easter holidays of 1982 had ensured that the culture plates were not destroyed after 48 h of absence of growth and led on to the discovery of H. pylori[1]. However, it was after much perusal that the scientific community accepted the bacterium-ulcer-cancer dogma eventually culminating in the 2005 Nobel Prize[2]. Over years it has become clear that this bacterium is responsible for many disease other than the gastric diseases. In the stomach H. pylori is implicated in the causation of chronic gastritis, peptic ulcer (gastro-duodenal), gastric MALTOMA (mucosa associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma) and gastric adenocarcinoma. It is also associated with certain extra-gastric disorders like immune thrombocytopenia and iron deficiency anaemia[3,4]. Although the role of these in causation of gastric injury has emerged in recent times, the role of H. pylori and its virulence factors in causation of atherosclerosis and coronary artery disease is not entirely clear as yet. The present review will focus on the relationship between this bacterium and the coronary artery disease
THE BACTERIUM
H. pylori have an inherent ability to survive in the gastric epithelium where they reside in the mucous layer and remain protected from the gastric acid. Urease, an enzyme abundantly present in this flagellate organism, helps create an alkaline environment to help in survival in the otherwise acidic environment. While most infected individuals remain unaffected, others develop a myriad of clinical manifestations ranging from gastritis to gastric cancer. What fuels and drives the pathogenesis of these varied clinical spectrums is not completely understood. While it is estimated that around half the world’s population harbours infection with H. pylori, only a fraction of the infected manifest with the implicated diseases. The various factors implicated in disease causation following infection by H. pylori include both the bacterial virulence factors and the host response to the infection. The bacterial virulence factors include BabA (bacterial binding and inflammation), lipopolysaccharide (interaction with toll-like receptors and mediation of inflammation), Cag pathogenicity island (heightened inflammatory response to infection) and vacA toxin (impaired host responses). The host responses which affect the outcome of infection include interleukin (IL)-1β (certain polymorphisms associated with carcin-ogenesis), activation of nuclear factor (NF)-κB, IL-8 levels, recruitment of neutrophils, macrophages and oxidative injury and TH1 cell response may all mediate tissue injury and reaction to H. pylori infection.
CORONARY ARTERY DISEASE: A MULTIFACTORIAL DISEASE
Coronary artery disease (CAD) is a multifactorial disease manifesting in a number of clinical presentations including angina, myocardial infarction and heart failure. The CAD is primarily a result of coronary atherosclerosis for which a multitude of risk factors are implicated including hyperlipidemia, smoking, diabetes mellitus, lack of physical activity, male gender, increasing age, obesity amongst others[5]. There is a growing acknowledgement of inflammatory factors including C-reactive protein in prediction of increased risk of CAD[6]. H. pylori has also been implicated by some to have a role in predisposition to cardiac risk and causation of CAD. Indeed, in a polymerase chain reaction (PCR) based study for detection of H. pylori in the coronary plaques of patients who underwent coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), 29.5% patients had a detectable H. pylori on PCR. Also there was serological evidence of infection in 53.3% of these 105 patients[7]. Therefore the infection by H. pylori may play a role in plaque rupture and causation of ischemic heart disease. Interestingly, cytotoxin asso-ciated gene A (Cag-A) may also play a role in the path-ogenesis of CAD as results of one study suggest that anti-Cag-A antibody titres were higher in patients with CAD vis-à-vis normal subjects. Also patients with anti-Cag-A positivity had more severe lesions of CAD[8]. It is believed that the chronic inflammation associated with chronic infections may result in progressive atherosclerotic disease eventually manifesting as CAD[9].
CAD AND H. PYLORI
Epidemiological evidence
A number of reports have evaluated the role of H. pylori in causation of CAD. In a report on 120 patients who underwent coronary angiography, the prevalence of serologically detectable evidence of H. pylori infection was more in patients with angiographically documented CAD (> 50% stenosis in at least one coronary artery). The evidence of infection was found in 70% patients with single vessel disease, 76.3% patients with double vessel disease but only in 50% individuals with no CAD[10]. Coronary artery calcium is believed to be a marker of atherosclerosis and its progression a predictor of CAD events. The correlation of coronary artery calcium (CAC) with various pathogens is conflicting. In a report on 201 asymptomatic subjects, the antibodies to heat shock protein 65 correlated with CAC score as also with evidence of H. pylori infection[11]. Another large study from South Korea which evaluated 2029 individuals for H. pylori antibody and coronary artery calcification score found that H. pylori seropositivity was different amongst those with and those without CAC[12]. This association was more evident in patients with early coronary atherosclerosis[12]. However another report about presence of H. pylori infection in a large cohort of individuals who underwent repeat CAC assessment, the presence of H. pylori infection (IgG to H. pylori) did not correlate with development or progression of CAC[13]. In a report comparing patients with CAD and healthy controls, sero-positivity for H. pylori infection was significantly higher in patients of CAD (59%) vis-à-vis the healthy controls (39%)[14]. Similar reports from India also corroborate that H. pylori sero-positivity was much higher in patients with CAD when compared with asymptomatic controls[15-17]. Few reports have indicated, to the contrary, that there is no significant association between H. pylori infection and CAD. In a report from Asian Indian families which evaluated role of multiple pathogens in causation of CAD, while CMV infection appeared to elevate the risk of CAD infection with H. pylori did not increase the risk[18]. In a large Japanese study to assess seroprevalence of H. pylori in CAD and asymptomatic controls no significant differences were detected between the two groups[19]. However when a subgroup of patients younger than 55 years was analysed the seroprevalence of H. pylori antibody was higher in cases than controls (58.7% and 43.3%, respectively)[19]. Another report about incidence of CAD in elderly individuals who were assessed for H. pylori infection at baseline and followed up for 10 years indicated that H. pylori positivity was not associated with increased incidence of CAD[20]. As described previously, PCR based studies of the coronary plaque have been done and have detected H. pylori DNA in them. In a controlled study of atheromatous plaques of 46 patients who underwent CABG, 22 (47.8%) showed H. pylori DNA while none of the controls who underwent coronary artery biopsy had PCR detectable H. pylori[21]. Aortic biopsies from areas free of atheromatous plaque have also been reported to be positive in a significant number of patients with CAD but none of the controls[22]. Table 1 summarises the recent studies reporting about association of H. pylori with CAD.
Table 1.
Recent reports on association of Helicobacter pylori infection with coronary artery disease
| Ref. | Population (number of subjects) | Diagnosis of CAD | Association between H. pylori infection and CAD |
| Shmuely et al[23] | CAD (173) vs Controls (123) | Myocardial Perfusion imaging | Yes No association with Cag-A |
| Vafaeimanesh et al[10] | CAD (62) vs Controls (58) | Angiographic | Yes |
| Laek et al[13] | 5744 individuals, Age 45-84 yr, average follow-up of 2.4 yr | Newly detectable coronary artery calcium (CAC) | No correlation with CAC development |
| Mundkur et al[18] | CAD and controls (433 each) from South Asians | Angiography | None |
| Padmavati et al[24] | Acute myocardial infarction vs Controls | ECG, enzymes | None |
| Tewari et al[15] | 200 CAD cases and controls | ECG, treatment records | Yes |
| Grdanoska et al[25] | Acute coronary syndrome (64), CAD (53), controls (35) | ECG, enzymes | Yes |
| Grub et al[26] | Controls (30), CAD (52) and CAD with rheumatic diseases (67) | Patients referred for CABG | None |
| Park et al[12] | 2029 subjects | CAC | Yes |
| Al-Ghamdi et al[27] | CAD (50) and controls (15) | ECG, angiography | Yes |
| Azarkar et al[28] | Controls (78) and myocardial infarction (73) | ECG, enzymes | Yes |
| Khodaii et al[29] | Myocardial infarction (500) and controls (500) | ECG, enzymes | Yes Cag-A positivity also correlates with CAD |
CAD: Coronary artery disease; Cag-A: Cytotoxin associated gene A; ECG: Electrocardiography; CAC: Coronary artery calcium; CABG: Coronary artery bypass grafting; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
CAG-A AND CAD
As previously mentioned, role of Cag-A has also been evaluated as a predisposing factor for occurrence of coronary artery disease[8]. In a study of cardiac peptides including Brain Natriuretic Peptide in 103 patients with non-ST elevation myocardial infarction and their relation with H. pylori infection, it was found that individuals infected with Cag-A positive strains of H. pylori had higher levels of BNP in the serum[30]. BNP is a marker of heart failure and may predict a more serious course of the disease thereby suggesting that H. pylori infection with Cag-A positive strains may lead to an adverse outcome. Interestingly, IL-6 levels were also found to correlate with the Cag-A status. This suggests that the inflammatory response to Cag-A positive H. pylori may mediate athe-rogeneis in a subgroup of patients with CAD[30]. However other reports indicate that Cag-A positivity does not vary significantly between angiographically positive and negative group of individuals. In a report of 112 consecutive individuals who underwent coronary angiography, the Cag-A positivity did not affect the severity of CAD[31]. In a large study including 505 patients with CAD and 1025 matched controls, neither the prevalence of H. pylori infection was increased in the diseased subjects nor did the presence of Cag-A positive strains predict higher likelihood of CAD[32]. In a large population based report on 685 individuals, merely the presence of infection by H. pylori did not correlate with serum markers of inflammation. However those seropositive for Cag-A positive strains had increased values of common carotid artery intima-media thickness and the risk of atherosclerosis was enhanced by CRP positivity[33]. Another report also indicated that Cag-A positive strains appeared to raise the risk of CAD while merely the presence of H. pylori infection was not significantly different between cases and controls[34]. An interesting study reported about sero-prevalence of anti-Cag-A antibodies across a spectrum of presentations which included controls, stable and unstable angina and found that anti-Cag A titres were significantly higher in patients with unstable angina[35].
MECHANISMS BEHIND ATHEROGENESIS
One report has studied the association of atrophic gastritis with CAD. Atrophic gastritis is believed to be the end result of chronic gastric inflammation including that related to H. pylori infection. Decrease in serum pepsinogen I and a low Pepsinogen I/II ratio points to the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis. In this intriguing report based on a population based study, Senmaru et al[36] reported that prevalence of CAD was higher in the patients having atrophic gastritis (5.8%) when compared with individuals not having atrophic gastritis (2.8%). Atrophic gastritis may result in malabsorption of Vitamin B12 and Folate and result in increased homocysteine levels. Hyper-homocysteinemia is a recognised risk factor for CAD[37]. One report has also suggested structural homology between bacterial proteins and human tropo-myosin and cardiac ATPases thereby providing insight into molecular mechanism involved in the cardiac injury due to anti-H. pylori inflammatory response[30]. H. pylori has also been associated with dyslipidemia. In a Japanese study on 6289 subjects, infection with H. pylori was associated with low HDL and elevated LDL levels[38]. Other reports have also provided similar evidence[39]. Cag-A positive strains also exhibit elevated levels of highly sensitive CRP, oxidized LDL and apolipoprotein B all of which may participate in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis[40]. There is also a suggestion that H. pylori may have a prothrombotic role which may also increase the associated risk of atherosclerotic diseases. The bacterium may promote aggregation of platelets by binding to the von-Willibrand factor[41]. Infection with H. pylori may stimulate an inflammatory response against heat shock protein (hsp60) which may drive a helper T cell (TH1) response and increase the risk of atherosclerosis[42]. The high degree of homology between bacterial and eukaryotic HSP may result in molecular mimicry and collateral immune damage from immune response primarily directed against infectious agents[43]. The host reaction to the H. pylori lipopolysaccharide (LPS) may also be a risk factor for atherosclerosis[44]. Figure 1 depicts the predominant mechanisms purported to play a role in genesis of H. pylori-related CAD.
Figure 1.
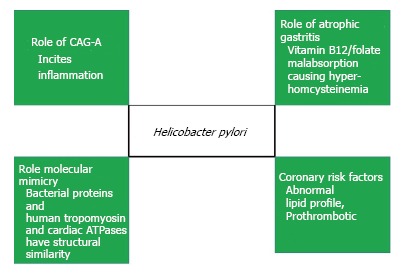
Postulated mechanisms of Atherogenesis in Helicobacter pylori infection.
EFFECT OF ERADICATION
The prognostic role of H. pylori infection has also been assessed in acute CAD. In 433 patients of acute coronary syndrome (ACS) the seroprevalence of H. pylori infection was determined using IgG and IgA serology. Those infected with H. pylori had an increased risk of short term adverse outcomes during the first month of follow-up[45]. Another report which evaluated role of eight pathogens on occurrence future events in patients diagnosed to have angiographic evidence of CAD. Serological evidence of H. pylori infection predicted an increased risk of future events and mortality in these 1018 patients and increase in pathogen burden also affected long term outcome[46]. An interesting study evaluated the role of H. pylori eradication on coronary artery lumen reduction in patients who underwent percutaneous intervention for CAD. A higher loss of coronary lumen was noted in those patients who had serological evidence of H. pylori infection. Also, eradication of H. pylori attenuated this reduction in lumen of the coronary artery vis-à-vis the placebo group[47]. Another report by the same group provides similar findings but it is not clear if the report was based on different patients[48]. This small but elegant study opens debate about possible benefit of H. pylori eradication in attenuating further atherosclerotic process which is driven primarily by inflammatory mediators. In a study assessing the effect of H. pylori eradication on coronary risk factors in 48 patients, no differences were observed in pre and post-treatment fasting sugars, lipid profile and levels of tissue-plasminogen activator, fibrinogen, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and D-dimer levels[49]. However a larger study of 496 patients and reporting about pre and post- H. pylori eradication profile, the eradication of H. pylori seemed to increase HDL levels and reduce the levels of C reactive protein and those of fibrinogen. This suggests that attenuation of inflammatory response is likely to occur after H. pylori eradication[50]. In a report documenting the effects of H. pylori eradication on insulin resistance in 159 patients using homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistance, the insulin resistance measured six weeks post-eradication was lower than the baseline. The study also reported changes in lipid profile including an increase in HDL levels and a fall in LDL levels with H. pylori eradication[51]. Another report also indicates that the H. pylori eradication may increase HDL levels and lead to reduction of CRP levels[52]. Table 2 depicts various studies reporting about the effects of H. pylori eradication on CAD and its risk factors.
Table 2.
Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on coronary artery disease
| Ref. | Population | Intervention | Results |
| Kowalski et al[47,48] | 40 patient with single vessel CAD and H. pylori infection | All underwent PTCA and 20 each received eradication or placebo | Attenuated reduction mean coronary artery lumen at 6 mo in those undergoing eradication |
| Lu et al[49] | H. pylori positive individuals | Testing of coronary risk factors before and after H. pylori eradication | No change in sugar, lipid and fibrinolytic parameters with eradication |
| Pellicano et al[50] | H. pylori positive individuals | Testing of coronary risk factors before and after H. pylori eradication | Improvement in HDL-C, reduction in CRP and fibrinogen levels. Elevation in BMI and diastolic blood pressure |
| Gen et al[51] | H. pylori positive individuals | Testing for insulin resistance, lipid profile and CRP before and after eradication | Improvement in insulin resistance, lipid abnormalities and CRP levels |
| Kanbay et al[52] | H. pylori positive individuals | Testing for lipid profile and CRP before and after eradication | Increase in HDL and reduction in CRP with successful eradication |
CAD: Coronary artery disease; CRP: C-reactive protein; HDL: High density lipoprotein; PTCA: Percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty; H. pylori: Helicobacter pylori.
ATHEROGENESIS BEYOND CORONARY ARTERIES
In contrast to CAD, data is scarce on the relation bet-ween H. pylori infection and stroke. A meta-analysis found that Cag-A-positive H. pylori increases the risk of both ischemic stroke and coronary heart disease[53].
A case-control study of 150 patients by Yang et al[54] in 2011 does not reveal any strong association between chronic H. pylori infection and ischemic stroke. However, another study by Pan[55] suggested lowering of inflammatory markers and decrease in cerebral infarction readmission rates in patients of stroke with positive urease test treated with (conventional therapy + anti- H. pylori therapy. Wu et al[56] suggested role of increased expression of CD62p on platelets and increase in clotting indexes in pathogenesis of stroke in H. pylori positive patients.
A meta-analysis of 13 studies including 4041 parti-cipants indicated that positive anti-H. pylori IgG, anti-Cag-A IgG and (13)C-urea breath test were significantly associated with increased risk of IS, respectively, and positive anti-Cag-A IgG was more effective for predication of IS risk[57].
But a formal meta-analysis of ten prospective observ-ational studies indicated no strong association between H. pylori infection and stroke, neither in those with cytotoxin-associated gene-A-positive infection[58].
All in all, the evidence supporting the role of H. pylori in causation of CAD is equivocal and interventions aimed at H. pylori eradication have not shown conclusive evidence of benefit in eradicating the organism vis-à-vis cardiovascular outcomes. Perhaps multicentre randomised trials comparing eradication of H. pylori in large populations at risk of CAD and then follow-up to deterimine risk of CAD may answer this question.
Footnotes
P- Reviewer: Peteiro J, Schoenhagen P S- Editor: Ji FF L- Editor: A E- Editor: Lu YJ
Conflict-of-interest: No conflicts.
Open-Access: This article is an open-access article which was selected by an in-house editor and fully peer-reviewed by external reviewers. It is distributed in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution Non Commercial (CC BY-NC 4.0) license, which permits others to distribute, remix, adapt, build upon this work non-commercially, and license their derivative works on different terms, provided the original work is properly cited and the use is non-commercial. See: http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/
Peer-review started: October 20, 2014
First decision: November 27, 2014
Article in press: January 4, 2015
References
- 1.Unidentified curved bacilli on gastric epithelium in active chronic gastritis. Lancet. 1983;1:1273–1275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Van Der Weyden MB, Armstrong RM, Gregory AT. The 2005 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Med J Aust. 2005;183:612–614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Tan HJ, Goh KL. Extragastrointestinal manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection: facts or myth? A critical review. J Dig Dis. 2012;13:342–349. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-2980.2012.00599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Franceschi F, Roccarina D, Gasbarrini A. Extragastric manifestations of Helicobacter pylori infection. Minerva Med. 2006;97:39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Fruchart JC, Nierman MC, Stroes ES, Kastelein JJ, Duriez P. New risk factors for atherosclerosis and patient risk assessment. Circulation. 2004;109:III15–III19. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000131513.33892.5b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Arroyo-Espliguero R, Avanzas P, Cosín-Sales J, Aldama G, Pizzi C, Kaski JC. C-reactive protein elevation and disease activity in patients with coronary artery disease. Eur Heart J. 2004;25:401–408. doi: 10.1016/j.ehj.2003.12.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Izadi M, Fazel M, Sharubandi SH, Saadat SH, Farahani MM, Nasseri MH, Dabiri H, SafiAryan R, Esfahani AA, Ahmadi A, et al. Helicobacter species in the atherosclerotic plaques of patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2012;21:307–311. doi: 10.1016/j.carpath.2011.09.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Niccoli G, Franceschi F, Cosentino N, Giupponi B, De Marco G, Merra G, Conte M, Montone RA, Ferrante G, Bacà M, et al. Coronary atherosclerotic burden in patients with infection by CagA-positive strains of Helicobacter pylori. Coron Artery Dis. 2010;21:217–221. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e3283399f36. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Kowalski M, Pawlik M, Konturek JW, Konturek SJ. Helicobacter pylori infection in coronary artery disease. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2006;57 Suppl 3:101–111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Vafaeimanesh J, Hejazi SF, Damanpak V, Vahedian M, Sattari M, Seyyedmajidi M. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with coronary artery disease: is Helicobacter pylori a risk factor? ScientificWorldJournal. 2014;2014:516354. doi: 10.1155/2014/516354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zhu J, Katz RJ, Quyyumi AA, Canos DA, Rott D, Csako G, Zalles-Ganley A, Ogunmakinwa J, Wasserman AG, Epstein SE. Association of serum antibodies to heat-shock protein 65 with coronary calcification levels: suggestion of pathogen-triggered autoimmunity in early atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2004;109:36–41. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000105513.37677.B3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Park MJ, Choi SH, Kim D, Kang SJ, Chung SJ, Choi SY, Yoon DH, Lim SH, Kim YS, Yim JY, et al. Association between Helicobacter pylori Seropositivity and the Coronary Artery Calcium Score in a Screening Population. Gut Liver. 2011;5:321–327. doi: 10.5009/gnl.2011.5.3.321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Laek B, Szklo M, McClelland RL, Ding J, Tsai MY, Bluemke DA, Tracy R, Matsushita K. The prospective association of Chlamydia pneumoniae and four other pathogens with development of coronary artery calcium: the multi-ethnic study of atherosclerosis (MESA) Atherosclerosis. 2013;230:268–274. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2013.07.053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Mendall MA, Goggin PM, Molineaux N, Levy J, Toosy T, Strachan D, Camm AJ, Northfield TC. Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection and coronary heart disease. Br Heart J. 1994;71:437–439. doi: 10.1136/hrt.71.5.437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tewari R, Nijhawan V, Mishra M, Dudeja P, Salopal T. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori, cytomegalovirus, and Chlamydia pneumoniae immunoglobulin seropositivity in coronary artery disease patients and normal individuals in North Indian population. Med J Armed Forces India. 2012;68:53–57. doi: 10.1016/S0377-1237(11)60121-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jha HC, Prasad J, Mittal A. High immunoglobulin A seropositivity for combined Chlamydia pneumoniae, Helicobacter pylori infection, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein in coronary artery disease patients in India can serve as atherosclerotic marker. Heart Vessels. 2008;23:390–396. doi: 10.1007/s00380-008-1062-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tamer GS, Tengiz I, Ercan E, Duman C, Alioglu E, Turk UO. Helicobacter pylori seropositivity in patients with acute coronary syndromes. Dig Dis Sci. 2009;54:1253–1256. doi: 10.1007/s10620-008-0482-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Mundkur LA, Rao VS, Hebbagudi S, Shanker J, Shivanandan H, Nagaraj RK, Kakkar VV. Pathogen burden, cytomegalovirus infection and inflammatory markers in the risk of premature coronary artery disease in individuals of Indian origin. Exp Clin Cardiol. 2012;17:63–68. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kinjo K, Sato H, Sato H, Shiotani I, Kurotobi T, Ohnishi Y, Hishida E, Nakatani D, Mizuno H, Sasaki T, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection and its link to coronary risk factors in Japanese patients with acute myocardial infarction. Circ J. 2002;66:805–810. doi: 10.1253/circj.66.805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Haider AW, Wilson PW, Larson MG, Evans JC, Michelson EL, Wolf PA, O’Donnell CJ, Levy D. The association of seropositivity to Helicobacter pylori, Chlamydia pneumoniae, and cytomegalovirus with risk of cardiovascular disease: a prospective study. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2002;40:1408–1413. doi: 10.1016/s0735-1097(02)02272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kowalski M, Rees W, Konturek PC, Grove R, Scheffold T, Meixner H, Brunec M, Franz N, Konturek JW, Pieniazek P, et al. Detection of Helicobacter pylori specific DNA in human atheromatous coronary arteries and its association to prior myocardial infarction and unstable angina. Dig Liver Dis. 2002;34:398–402. doi: 10.1016/s1590-8658(02)80036-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Iriz E, Cirak MY, Engin ED, Zor MH, Erer D, Ozdogan ME, Turet S, Yener A. Detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA in aortic and left internal mammary artery biopsies. Tex Heart Inst J. 2008;35:130–135. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Shmuely H, Wattad M, Solodky A, Yahav J, Samra Z, Zafrir N. Association of Helicobacter pylori with coronary artery disease and myocardial infarction assessed by myocardial perfusion imaging. Isr Med Assoc J. 2014;16:341–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Padmavati S, Gupta U, Agarwal HK. Chronic infections & amp; coronary artery disease with special reference to Chalmydia pneumoniae. Indian J Med Res. 2012;135:228–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Grdanoska T, Zafirovska P, Jaglikovski B, Pavlovska I, Zafirova B, Tosheska-Trajkovska K, Trajkovska-Dokic E, Petrovska M, Cekovska Z, Kondova-Topuzovska I, et al. Chlamydia pneumoniae and helicobacter pylori serology - importance in patients with coronary heart disease. Mater Sociomed. 2012;24:151–156. doi: 10.5455/msm.2012.24.151-156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Grub C, Brunborg C, Hasseltvedt V, Aukrust P, Førre O, Almdahl SM, Hollan I. Antibodies to common infectious agents in coronary artery disease patients with and without rheumatic conditions. Rheumatology (Oxford) 2012;51:679–685. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/ker251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Al-Ghamdi A, Jiman-Fatani AA, El-Banna H. Role of Chlamydia pneumoniae, helicobacter pylori and cytomegalovirus in coronary artery disease. Pak J Pharm Sci. 2011;24:95–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Azarkar Z, Jafarnejad M, Sharifzadeh G. The relationship between helicobacter pylori infection and myocardial infarction. Caspian J Intern Med. 2011;2:222–225. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Khodaii Z, Vakili H, Ghaderian SM, Najar RA, Panah AS. Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with acute myocardial infarction. Coron Artery Dis. 2011;22:6–11. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0b013e3283402360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Figura N, Palazzuoli A, Vaira D, Campagna M, Moretti E, Iacoponi F, Giordano N, Clemente S, Nuti R, Ponzetto A. Cross-sectional study: CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori infection, acute coronary artery disease and systemic levels of B-type natriuretic peptide. J Clin Pathol. 2014;67:251–257. doi: 10.1136/jclinpath-2013-201743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rogha M, Dadkhah D, Pourmoghaddas Z, Shirneshan K, Nikvarz M, Pourmoghaddas M. Association of helicobacter pylori infection with severity of coronary heart disease. ARYA Atheroscler. 2012;7:138–141. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Whincup P, Danesh J, Walker M, Lennon L, Thomson A, Appleby P, Hawkey C, Atherton J. Prospective study of potentially virulent strains of Helicobacter pylori and coronary heart disease in middle-aged men. Circulation. 2000;101:1647–1652. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.101.14.1647. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Mayr M, Kiechl S, Mendall MA, Willeit J, Wick G, Xu Q. Increased risk of atherosclerosis is confined to CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains: prospective results from the Bruneck study. Stroke. 2003;34:610–615. doi: 10.1161/01.STR.0000058481.82639.EF. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Gunn M, Stephens JC, Thompson JR, Rathbone BJ, Samani NJ. Significant association of cagA positive Helicobacter pylori strains with risk of premature myocardial infarction. Heart. 2000;84:267–271. doi: 10.1136/heart.84.3.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Franceschi F, Niccoli G, Ferrante G, Gasbarrini A, Baldi A, Candelli M, Feroce F, Saulnier N, Conte M, Roccarina D, et al. CagA antigen of Helicobacter pylori and coronary instability: insight from a clinico-pathological study and a meta-analysis of 4241 cases. Atherosclerosis. 2009;202:535–542. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2008.04.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Senmaru T, Fukui M, Tanaka M, Kuroda M, Yamazaki M, Oda Y, Naito Y, Hasegawa G, Toda H, Yoshikawa T, et al. Atrophic gastritis is associated with coronary artery disease. J Clin Biochem Nutr. 2012;51:39–41. doi: 10.3164/jcbn.11-106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Tamura A, Fujioka T, Nasu M. Relation of Helicobacter pylori infection to plasma vitamin B12, folic acid, and homocysteine levels in patients who underwent diagnostic coronary arteriography. Am J Gastroenterol. 2002;97:861–866. doi: 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2002.05601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Satoh H, Saijo Y, Yoshioka E, Tsutsui H. Helicobacter Pylori infection is a significant risk for modified lipid profile in Japanese male subjects. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2010;17:1041–1048. doi: 10.5551/jat.5157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jia EZ, Zhao FJ, Hao B, Zhu TB, Wang LS, Chen B, Cao KJ, Huang J, Ma WZ, Yang ZJ, et al. Helicobacter pylori infection is associated with decreased serum levels of high density lipoprotein, but not with the severity of coronary atherosclerosis. Lipids Health Dis. 2009;8:59. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-8-59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Huang B, Chen Y, Xie Q, Lin G, Wu Y, Feng Y, Li J, Zhuo Y, Zhang P. CagA-positive Helicobacter pylori strains enhanced coronary atherosclerosis by increasing serum OxLDL and HsCRP in patients with coronary heart disease. Dig Dis Sci. 2011;56:109–114. doi: 10.1007/s10620-010-1274-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Fagoonee S, De Angelis C, Elia C, Silvano S, Oliaro E, Rizzetto M, Pellicano R. Potential link between Helicobacter pylori and ischemic heart disease: does the bacterium elicit thrombosis? Minerva Med. 2010;101:121–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Ayada K, Yokota K, Kobayashi K, Shoenfeld Y, Matsuura E, Oguma K. Chronic infections and atherosclerosis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2009;37:44–48. doi: 10.1007/s12016-008-8097-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ayada K, Yokota K, Kobayashi K, Shoenfeld Y, Matsuura E, Oguma K. Chronic infections and atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2007;1108:594–602. doi: 10.1196/annals.1422.062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Grebowska A, Rechciński T, Bak-Romaniszyn L, Czkw-ianianc E, Moran A, Druszczyńska M, Kowalewicz-Kulbat M, Owczarek A, Dziuba M, Krzemińska-Pakuła M, et al. Potential role of LPS in the outcome of Helicobacter pylori related diseases. Pol J Microbiol. 2006;55:25–30. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Eskandarian R, Ghorbani R, Shiyasi M, Momeni B, Hajifathalian K, Madani M. Prognostic role of Helicobacter pylori infection in acute coronary syndrome: a prospective cohort study. Cardiovasc J Afr. 2012;23:131–135. doi: 10.5830/CVJA-2011-016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rupprecht HJ, Blankenberg S, Bickel C, Rippin G, Hafner G, Prellwitz W, Schlumberger W, Meyer J. Impact of viral and bacterial infectious burden on long-term prognosis in patients with coronary artery disease. Circulation. 2001;104:25–31. doi: 10.1161/hc2601.091703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Kowalski M. Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in coronary artery disease: influence of H. pylori eradication on coronary artery lumen after percutaneous transluminal coronary angioplasty. The detection of H. pylori specific DNA in human coronary atherosclerotic plaque. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001;52:3–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Kowalski M, Konturek PC, Pieniazek P, Karczewska E, Kluczka A, Grove R, Kranig W, Nasseri R, Thale J, Hahn EG, et al. Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori infection in coronary artery disease and effect of its eradication on coronary lumen reduction after percutaneous coronary angioplasty. Dig Liver Dis. 2001;33:222–229. doi: 10.1016/s1590-8658(01)80711-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Lu YH, Yen HW, Lin TH, Huang CH, Lee KT, Wang WM, Wu DC, Voon WC, Lai WT, Sheu SH. Changes of coronary risk factors after eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2002;18:266–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Pellicano R, Oliaro E, Fagoonee S, Astegiano M, Berrutti M, Saracco G, Smedile A, Repici A, Leone N, Castelli A, et al. Clinical and biochemical parameters related to cardiovascular disease after Helicobacter pylori eradication. Int Angiol. 2009;28:469–473. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Gen R, Demir M, Ataseven H. Effect of Helicobacter pylori eradication on insulin resistance, serum lipids and low-grade inflammation. South Med J. 2010;103:190–196. doi: 10.1097/SMJ.0b013e3181cf373f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Kanbay M, Gür G, Yücel M, Yilmaz U, Boyacioğlu S. Does eradication of Helicobacter pylori infection help normalize serum lipid and CRP levels? Dig Dis Sci. 2005;50:1228–1231. doi: 10.1007/s10620-005-2764-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Zhang S, Guo Y, Ma Y, Teng Y. Cytotoxin-associated gene-A-seropositive virulent strains of Helicobacter pylori and atherosclerotic diseases: a systematic review. Chin Med J (Engl) 2008;121:946–951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Yang X, Gao Y, Zhao X, Tang Y, Su Y. Chronic Helicobacter pylori infection and ischemic stroke subtypes. Neurol Res. 2011;33:467–472. doi: 10.1179/016164111X13007856083963. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Pan G. [Effect of anti-Helicobacter pylori on the prognosis in patients with acute cerebral infarction] Zhongnandaxue Xuebao Yixueban. 2011;36:872–875. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2011.09.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Wu HQ, Tang Y, Zhang X, Wei XH, Wang HQ, Zhang WT, Zhang GL. [Effect of Helicobacter pylori infection on platelet activation and coagulation function in patients with acute cerebral infarction] Zhejiangdaxue Xuebao Yixueban. 2012;41:547–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wang ZW, Li Y, Huang LY, Guan QK, Xu da W, Zhou WK, Zhang XZ. Helicobacter pylori infection contributes to high risk of ischemic stroke: evidence from a meta-analysis. J Neurol. 2012;259:2527–2537. doi: 10.1007/s00415-012-6558-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Yu M, Zhang Y, Yang Z, Ding J, Xie C, Lu N. Association between Helicobacter pylori infection and stroke: a meta-analysis of prospective observational studies. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2014;23:2233–2239. doi: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.04.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


