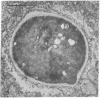
Abstract
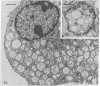
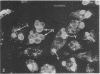
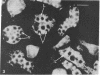
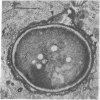
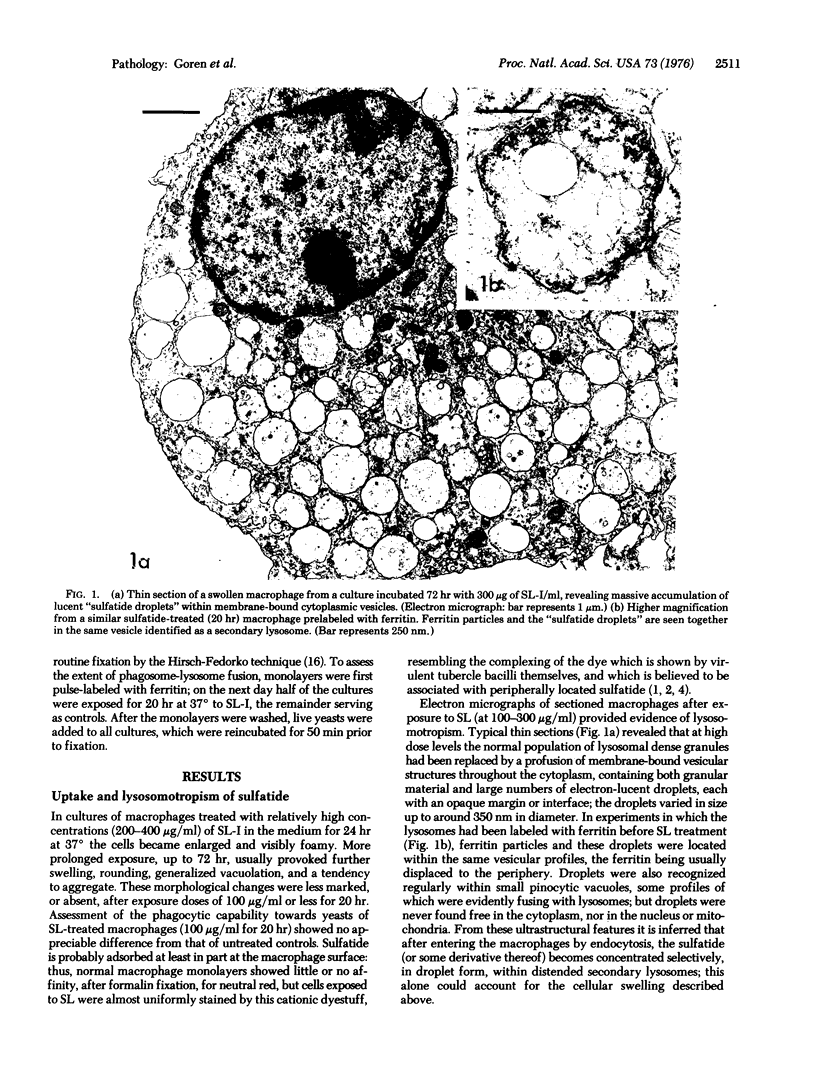
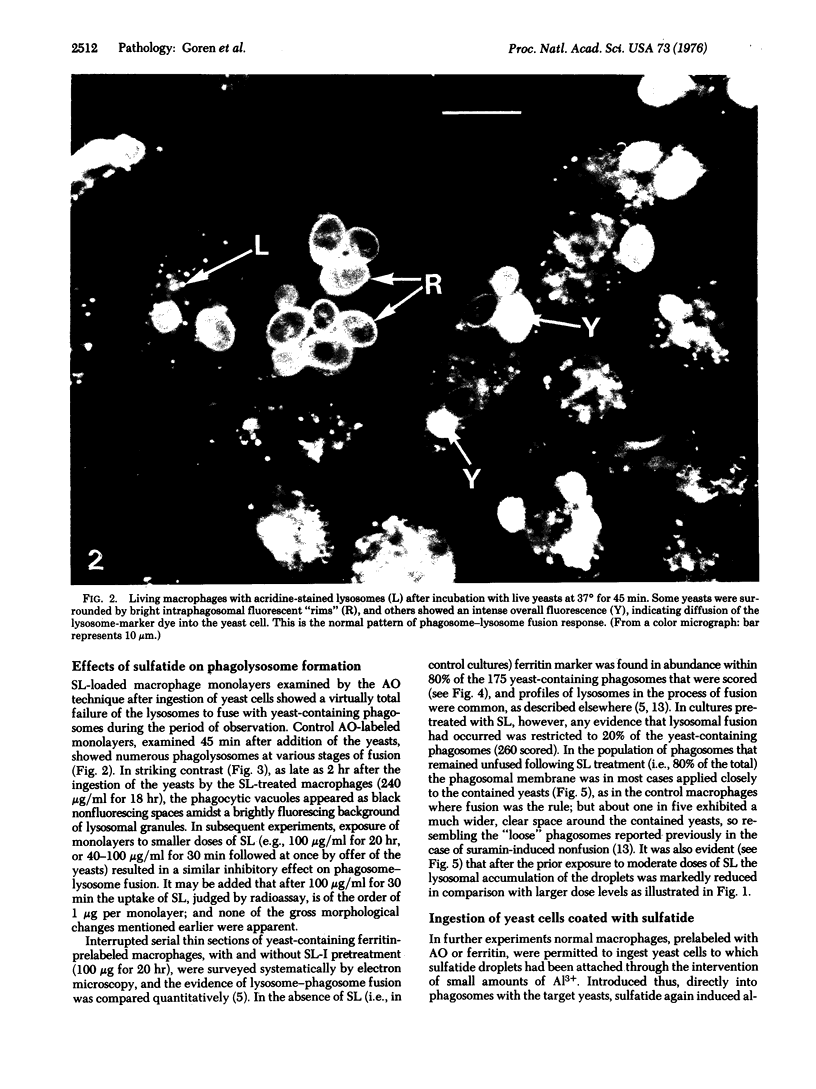
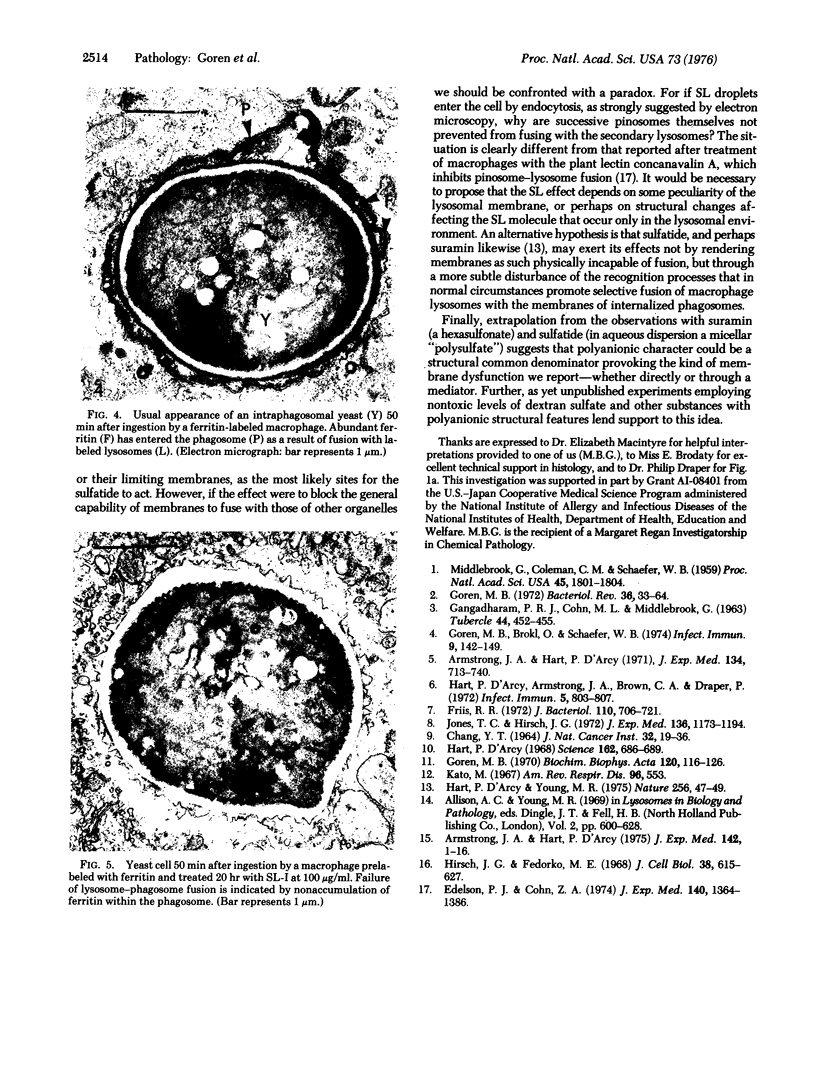
Intracellular parasites (e.g., Mycobacterium tuberculosis, Toxoplasma gondii, and some Chlamydiae) may promote their survival within the host by acting from within phagosomes to prevent phagolysosome formation, thus avoiding exposure to the lysosomal hydrolases. The present studies demonstrate that when sulfatides of M. tuberculosis (anionic trehalose glycolipids largely responsible for the neutral red reactivity of virulent strains) are administered to cultured mouse peritoneal macrophages, they accumulate in the secondary lysosomes, which are rendered incompetent for fusion with phagosomes containing suitable target particles such as viable yeasts. This antifusion effect is also exhibited when small amounts of sulfatide are introduced directly into phagosomes by attachment to the target yeasts prior to their ingestion. The sulfatides evidently exert a selective inhibitory influence on membrane fusion, analogous to what occurs typically when macrophage cultures are infected with tubercle bacilli. This effect may be due to ionic interaction between the polyanionic micelles of bacterial sulfatide and organelle membranes, modifying the latter and inducing dysfunction.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Phagosome-lysosome interactions in cultured macrophages infected with virulent tubercle bacilli. Reversal of the usual nonfusion pattern and observations on bacterial survival. J Exp Med. 1975 Jul 1;142(1):1–16. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong J. A., Hart P. D. Response of cultured macrophages to Mycobacterium tuberculosis, with observations on fusion of lysosomes with phagosomes. J Exp Med. 1971 Sep 1;134(3 Pt 1):713–740. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.3.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANG Y. T. LONG-TERM CULTIVATION OF MOUSE PERITONEAL MACROPHAGES. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1964 Jan;32:19–35. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelson P. J., Cohn Z. A. Effects of concanavalin A on mouse peritoneal macrophages. I. Stimulation of endocytic activity and inhibition of phago-lysosome formation. J Exp Med. 1974 Nov 1;140(5):1364–1386. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.5.1364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friis R. R. Interaction of L cells and Chlamydia psittaci: entry of the parasite and host responses to its development. J Bacteriol. 1972 May;110(2):706–721. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.2.706-721.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GANGADHARAM P. R., COHN M. L., MIDDLEBROOK G. INFECTIVITY, PATHOGENICITY AND SULPHOLIPID FRACTION OF SOME INDIAN AND BRITISH STRAINS OF TUBERCLE BACILLI. Tubercle. 1963 Dec;44:452–455. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(63)80087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B., Brokl O., Schaefer W. B. Lipids of putative relevance to virulence in Mycobacterium tuberculosis: correlation of virulence with elaboration of sulfatides and strongly acidic lipids. Infect Immun. 1974 Jan;9(1):142–149. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.1.142-149.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goren M. B. Mycobacterial lipids: selected topics. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Mar;36(1):33–64. doi: 10.1128/br.36.1.33-64.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Armstrong J. A., Brown C. A., Draper P. Ultrastructural study of the behavior of macrophages toward parasitic mycobacteria. Infect Immun. 1972 May;5(5):803–807. doi: 10.1128/iai.5.5.803-807.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D. Mycobacterium tuberculosis in macrophages: effect of certain surfactants and other membrane-active compounds. Science. 1968 Nov 8;162(3854):686–689. doi: 10.1126/science.162.3854.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hart P. D., Young M. R. Interference with normal phagosome-lysosome fusion in macrophages, using ingested yeast cells and suramin. Nature. 1975 Jul 3;256(5512):47–49. doi: 10.1038/256047a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch J. G., Fedorko M. E. Ultrastructure of human leukocytes after simultaneous fixation with glutaraldehyde and osmium tetroxide and "postfixation" in uranyl acetate. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):615–627. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. C., Hirsch J. G. The interaction between Toxoplasma gondii and mammalian cells. II. The absence of lysosomal fusion with phagocytic vacuoles containing living parasites. J Exp Med. 1972 Nov 1;136(5):1173–1194. doi: 10.1084/jem.136.5.1173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook G., Coleman C. M., Schaefer W. B. SULFOLIPID FROM VIRULENT TUBERCLE BACILLI. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1959 Dec;45(12):1801–1804. doi: 10.1073/pnas.45.12.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]