Abstract
Partial amino-acid sequence analyses of the amino terminus of rabbit C-reactive protein and of a peptide isolated from human C-reactive protein after cyanogen bromide cleavage show an extensive sequence homology between these proteins. Computer analysis detected a distant but significant homology between rabbit C-reactive protein and the CH3 domain of human IgG, In addition, an examination of the limited data available for the amino-acid sequences of human and mouse histocompatibility antigens revealed a similarity between these proteins and C-reactive protein and, therefore, immunoglobulins; These relationships are presented as evidence in support of the hypothesis that C-reactive protein and immunoglobulins share, in addition to functional similarities, a common evolutionary origin with the major histocompatibility antigens.
Full text
PDF


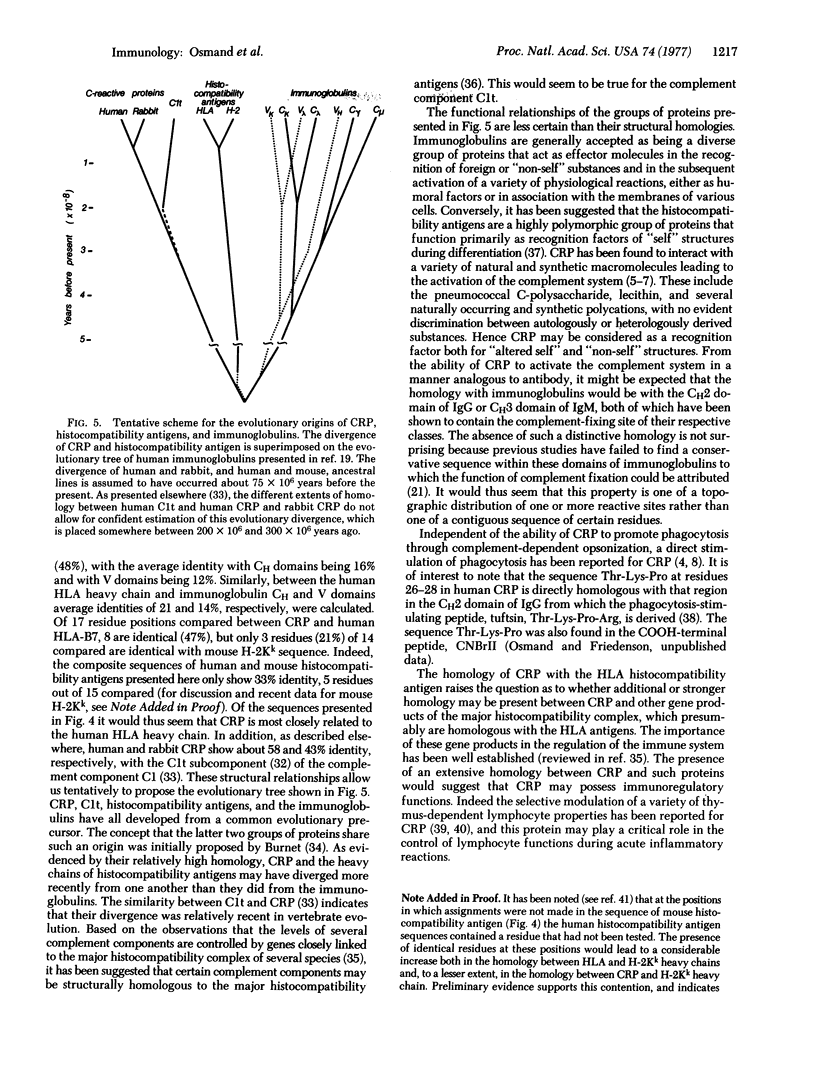

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Assimeh S. N., Painter R. H. The macromolecular structure of the first component of complement. J Immunol. 1975 Aug;115(2):488–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodmer W. F. Evolutionary significance of the HL-A system. Nature. 1972 May 19;237(5351):139–passim. doi: 10.1038/237139a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bridgen J., Snary D., Crumpton M. J. Isolation and N-terminal amino acid sequence of membrane-bound human HLA-A and HLA-B antigens. Nature. 1976 May 20;261(5557):200–205. doi: 10.1038/261200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnet F. M. A certain symmetry: histocompatibility antigens compared with immunocyte receptors. Nature. 1970 Apr 11;226(5241):123–126. doi: 10.1038/226123a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capra J. D., Vitetta E. S., Klapper D. G., Uhr J. W., Klein J. Structural studies on protein products of murine chromosome 17: partial amino acid sequence of an H-2Kb molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Oct;73(10):3661–3665. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.10.3661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. Surface modulation in cell recognition and cell growth. Science. 1976 Apr 16;192(4236):218–226. doi: 10.1126/science.769162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ewenstein B. M., Freed J. H., Mole L. E., Nathenson S. G. Localization of the papain cleavage site of H-2 glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):915–918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. An improved method of testing for evolutionary homology. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):9–16. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80258-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch W. M. Further improvements in the method of testing for evolutionary homology among proteins. J Mol Biol. 1970 Apr 14;49(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90372-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenson B., Appella E., Takeda Y., Roholt O. A., Pressman D. Immunoglobulin G antibodies from an individual rabbit in which several heavy chain variants are paired with one light chain sequence. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 25;248(20):7073–7079. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenson B., Hora J., Wang L. S. Partial sequence of the variable region of an anti-p-azobenzoate antibody light chain: a one solvent sequenator program. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 2;15(22):4876–4880. doi: 10.1021/bi00667a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedenson B., Takeda Y., Roholt O. A., Pressman D. The amino-acid compositions of CNBr fragment C1 from antihapten antibodies. Use of guanidine for reproducible isolation of the C1 fragment. Eur J Biochem. 1972 May;27(1):31–37. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1972.tb01806.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GAL K., MILTENYI M. Haemagglutination test for the demonstration of C-reactive protein. Acta Microbiol Acad Sci Hung. 1955;3(1-2):41–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs A. J., McIntyre G. A. The diagram, a method for comparing sequences. Its use with amino acid and nucleotide sequences. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Sep;16(1):1–11. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Edelman G. M. C-reactive protein: a molecule composed of subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Aug;54(2):558–566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.2.558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning R., Milner R. J., Reske K., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Subunit structure, cell surface orientation, and partial amino-acid sequences of murine histocompatibility antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):118–122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. III. Complement-dependent passive hemolysis initiated by CRP. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1065–1077. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan M. H., Volanakis J. E. Interaction of C-reactive protein complexes with the complement system. I. Consumption of human complement associated with the reaction of C-reactive protein with pneumococcal C-polysaccharide and with the choline phosphatides, lecithin and sphingomyelin. J Immunol. 1974 Jun;112(6):2135–2147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindmark C. O. Stimulating effect of C-reactive protein on phagocytosis of various species of pathogenic bacteria. Clin Exp Immunol. 1971 Jun;8(6):941–948. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low T. L., Liu Y. S., Putnam F. W. Structure, function, and evolutionary relationships of Fc domains of human immunoglobulins A, G, M, and E. Science. 1976 Jan 30;191(4225):390–392. doi: 10.1126/science.1246619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDevitt H. O. The evolution of genes in the major histocompatibility complex. Fed Proc. 1976 Aug;35(10):2168–2173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Gewurz H. Effects of C-reactive protein on the lymphoid system. II. Inhibition of mixed lymphocyte reactivity and generation of cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1976 May;116(5):1244–1250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Gewurz H. Effects on C-reactive protein on the lymphoid system. I. Binding to thymus-dependent lymphocytes and alteration of their functions. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):821–839. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortensen R. F., Osmand A. P., Lint T. F., Gewurz H. Interaction of C-reactive protein with lymphocytes and monocytes: complement-dependent adherence and phagocytosis. J Immunol. 1976 Sep;117(3):774–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishioka K., Constantopoulos A., Satoh P. S., Najjar V. A. The characteristics, isolation and synthesis of the phagocytosis stimulating peptide tuftsin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Apr 14;47(1):172–179. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80025-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osmand A. P., Friedenson B., Gewurz H., Painter R. H., Hofmann T., Shelton E. Characterization of C-reactive protein and the complement subcomponent C1t as homologous proteins displaying cyclic pentameric symmetry (pentraxins). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):739–743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson P. A., Cunningham B. A., Berggård I., Edelman G. M. 2 -Microglobulin--a free immunoglobulin domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1697–1701. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Osmand A. P., Wilson M. F., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. II. C-reactive protein-mediated consumption of complement by poly-L-lysine polymers and other polycations. J Exp Med. 1975 Sep 1;142(3):709–721. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.3.709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegel J., Rent R., Gewurz H. Interactions of C-reactive protein with the complement system. I. Protamine-induced consumption of complement in acute phase sera. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):631–647. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Hood L. Structure and evolution of transplantation antigens: partial amino-acid sequences of H-2K and H-2D alloantigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):599–603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Poulik M. D. Initiation of protein synthesis at an unusual position in an immunoglobulin gene? Science. 1972 Jan 14;175(4018):187–189. doi: 10.1126/science.175.4018.187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terhorst C., Parham P., Mann D. L., Strominger J. L. Structure of HLA antigens: amino-acid and carbohydrate compositions and NH2-terminal sequences of four antigen preparations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):910–914. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.910. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Capra J. D., Klapper D. G., Klein J., Uhr J. W. The partial amino-acid sequence of an H-2K molecule. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Mar;73(3):905–909. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.3.905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




