Abstract
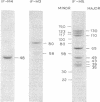
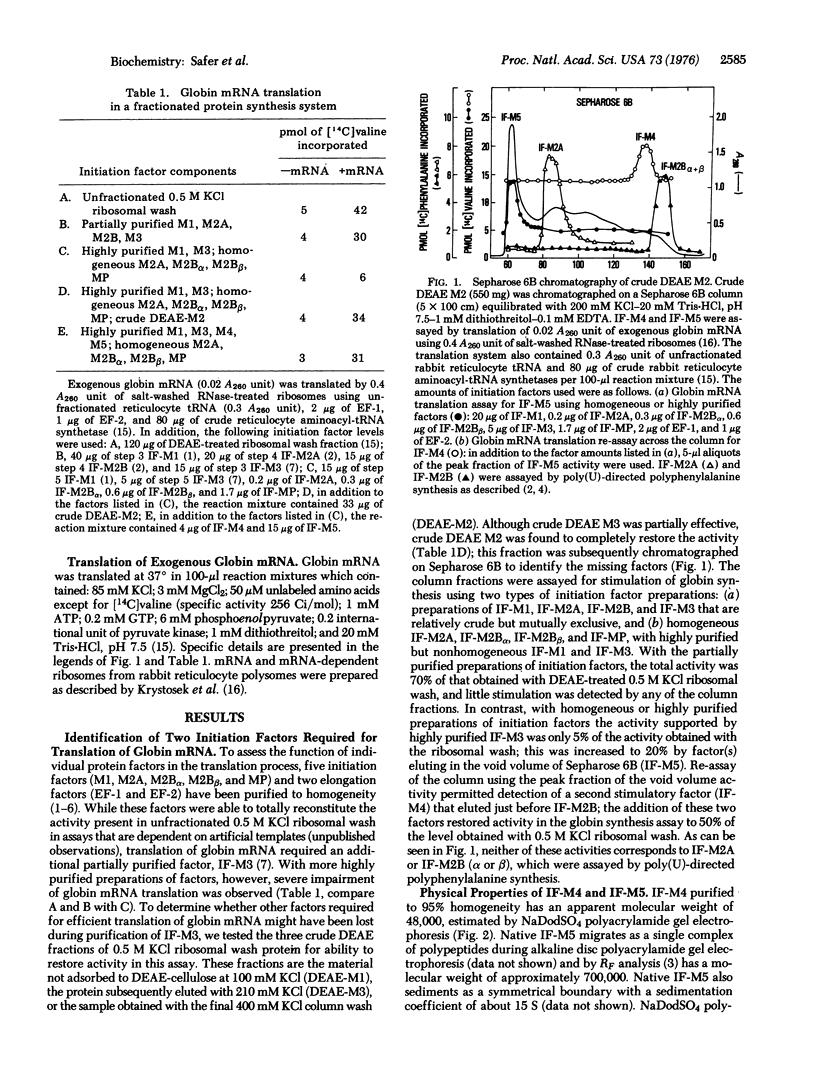
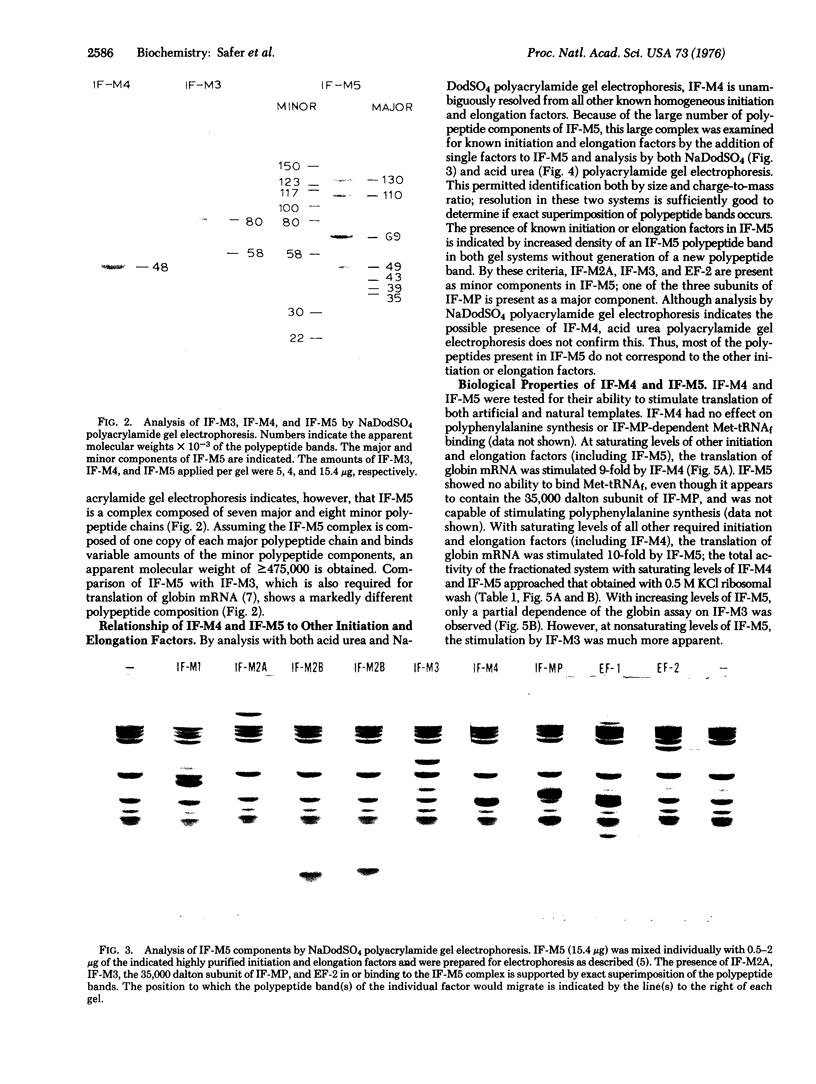
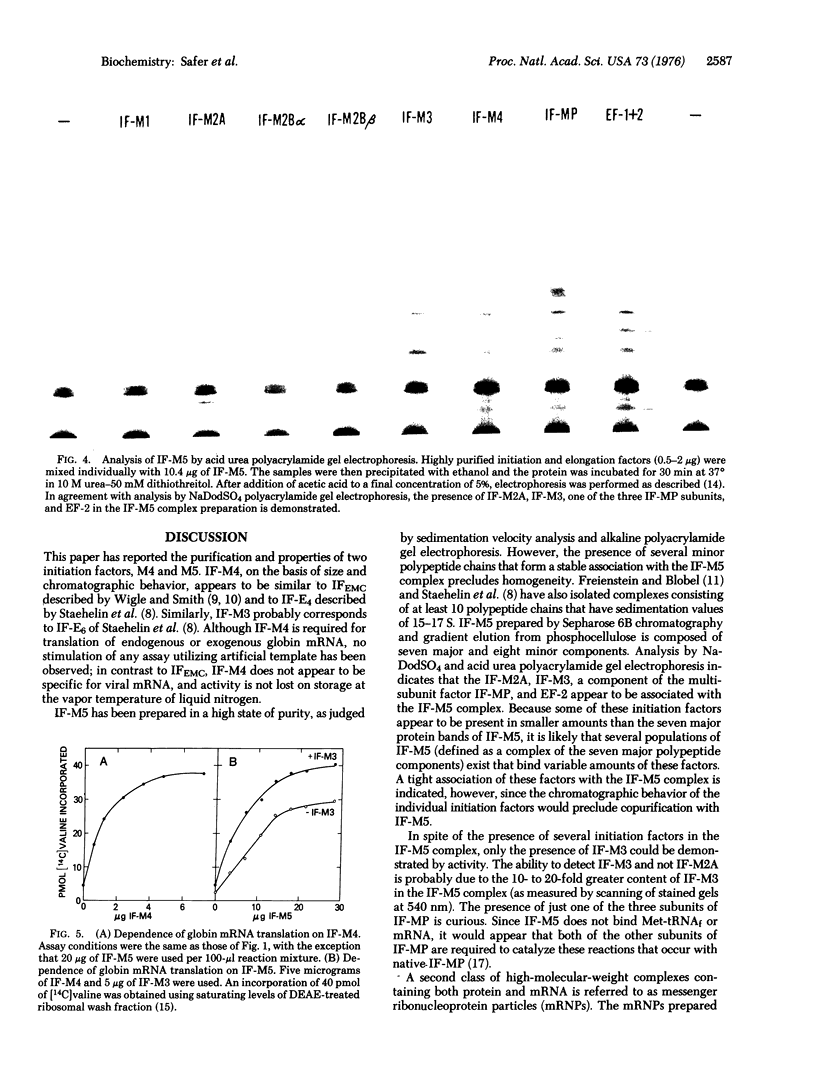
Two additional initiation factors (IF-M4 and IF-M5) have been purified and characterized both physically and biologically. IF-M4 is active as a single polypeptide chain with a molecular weight of 48,000. In contrast, IF-M5 is active as a complex with a molecular weight of about 500,000 and consists of seven major and several minor polypeptide components. Analysis of IF-M5 in two polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis systems indicated that one of the major polypeptide chains of IF-M5 was the 35,000 dalton subunit of IF-MP. This analysis also revealed that IF-M2A, IF-M3, and elongation factor 2 were present as minor components. Both IF-M4 and IF-M5 are required to achieve maximal activity in an assay system dependent on exogenous globin mRNA, but neither factor has been observed to stimulate model reactions that utilize artificial templates [poly(U) or AUG].
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blobel G. A protein of molecular weight 78,000 bound to the polyadenylate region of eukaryotic messenger RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):924–928. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freienstein C., Blobel G. Nonribosomal proteins associated with eukaryotic native small ribosomal subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3392–3396. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grummt F. Studies on two initiation factors of protein synthesis from rat-liver cytoplasm. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Apr 1;43(2):337–342. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03417.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellerman J. G., Shafritz D. A. Interaction of poly(A) and mRNA with eukaryotic initiator met-tRNA-f binding factor: identification of this activity on reticulocyte ribonucleic acid protein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1021–1025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper W. M., Merrick W. C., Redfield B., Liu C. K., Weissbach H. Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte elongation factor 1. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1976 Jun;174(2):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(76)90389-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystosek A., Cawthon M. L., Kabat D. Improved methods for purification and assay of eukaryotic messenger ribonucleic acids and ribosomes. Quantitative analysis of their interaction in a fractionated reticulocyte cell-free system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6077–6084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leader D. P., Klein-Bremhaar H., Wool I. G. Distribution of initiation factors in cell fractions from mammalian tissues. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 14;46(1):215–224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90652-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Marbaix G., Huez G., Temmerman J., Burny A., Chantrenne H. Characterization of the messenger ribonucleoprotein released from reticulocyte polyribosomes by EDTA treatment. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Mar 11;19(2):264–269. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01313.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Anderson W. F. Purification and characterization of homogeneous protein synthesis initiation factor M1 from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Feb 25;250(4):1197–1206. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Kemper W. M., Anderson W. F. Purification and characterization of homogeneous initiation factor M2A from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jul 25;250(14):5556–5562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrick W. C., Kemper W. M., Kantor J. A., Anderson W. F. Purification and properties of rabbit reticulocyte protein synthesis elongation factor 2. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 10;250(7):2620–2625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Anderson W. F., Merrick W. C. Purification and physical properties of homogeneous initiation factor MP from rabbit reticulocytes. J Biol Chem. 1975 Dec 10;250(23):9067–9075. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strycharz W. A., Ranki M., Dahl H. H. A high-molecular-weight protein component required for natural messenger translation in ascites tumor cells. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Oct 1;48(1):303–310. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T. Purification of a messenger-specific initiation factor from ascites-cell supernatant. Eur J Biochem. 1973 May;35(1):11–17. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigle D. T., Smith A. E. Specificity in initiation of protein synthesis in a fractionated mammalian cell-free system. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):136–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio242136a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]