Abstract
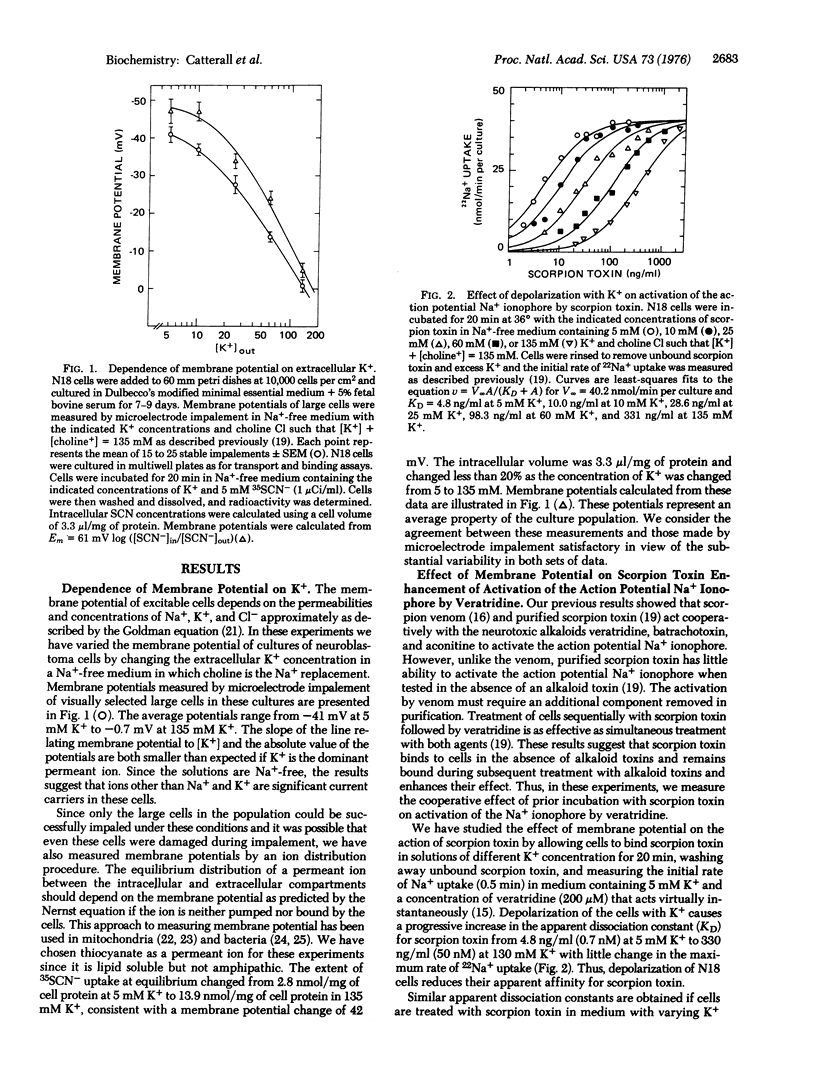
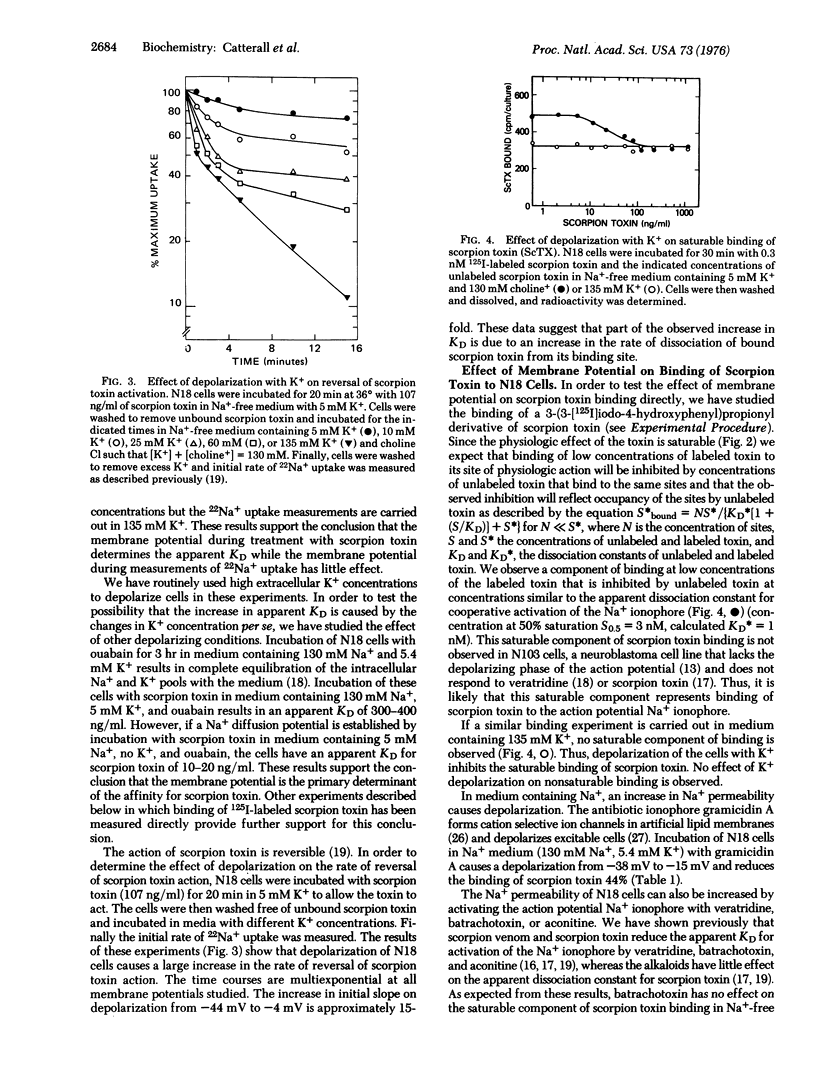
Depolarization of neuroblastoma cells causes a 70-fold increase in the apparent dissociation constant KD for scorpion toxin enhancement of activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore by veratridine and a large increase in the rate of reversal of scorpion toxin action. Depolarization also inhibits binding of 125I-labeled scorpion toxin to a small number of saturable binding sites on electrically excitable neuroblastoma cells and increases the rate of dissociation of scorpion toxin from these sites. The results suggest that scorpion toxin binds to a regulatory component of the action potential Na+ ionophore whose conformation changes on depolarization.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altendorf K., Harold F. M., Simoni R. D. Impairment and restoration of the energized state in membrane vesicles of a mutant of Escherichia coli lacking adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jul 25;249(14):4587–4593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balerna M., Fosset M., Chicheportiche R., Romey G., Lazdunski M. Constitution and properties of axonal membranes of crustacean nerves. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5500–5511. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnola F. V., Villegas R., Camejo G. Tetrodotoxin receptors in plasma membranes isolated from lobster nerve fibers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Feb 27;298(1):84–94. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90012-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzer T. I., Raftery M. A. Partial characterization of a tetrodotoxin-binding component from nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3634–3637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton A. E., Hunter W. M. The labelling of proteins to high specific radioactivities by conjugation to a 125I-containing acylating agent. Biochem J. 1973 Jul;133(3):529–539. doi: 10.1042/bj1330529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cahalan M. D. Modification of sodium channel gating in frog myelinated nerve fibres by Centruroides sculpturatus scorpion venom. J Physiol. 1975 Jan;244(2):511–534. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore of cultured neuroblastoma cells by veratridine and batrachotoxin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 10;250(11):4053–4059. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A. Cooperative activation of action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1782–1786. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catterall W. A., Nirenberg M. Sodium uptake associated with activation of action potential ionophores of cultured neuroblastoma and muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3759–3763. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colquhoun D., Henderson R., Ritchie J. M. The binding of labelled tetrodotoxin to non-myelinated nerve fibres. J Physiol. 1972 Dec;227(1):95–126. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp010022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conti F., De Felice L. J., Wanke E. Potassium and sodium ion current noise in the membrane of the squid giant axon. J Physiol. 1975 Jun;248(1):45–82. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp010962. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomez M. V., Diniz C. R. Separation of toxic components from the brazillian scorpion Tityus serrulatus venom. Mem Inst Butantan. 1966;33(3):899–902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L. L., Jasaitis A. A., Kadziauskas Y. P., Liberman E. A., Skulachev V. P., Topali V. P., Tsofina L. M., Vladimirova M. A. Conversion of biomembrane-produced energy into electric form. I. Submitochondrial particles. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 4;216(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(70)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HODGKIN A. L., HUXLEY A. F. A quantitative description of membrane current and its application to conduction and excitation in nerve. J Physiol. 1952 Aug;117(4):500–544. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1952.sp004764. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hafemann D. R. Binding of radioactive tetrodotoxin to nerve membrane preparations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 May 9;266(2):548–556. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90110-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. Evidence that tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin act at a metal cation binding site in the sodium channels of nerve membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):3936–3940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.3936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson R., Ritchie J. M., Strichartz G. R. The binding of labelled saxitoxin to the sodium channels in nerve membranes. J Physiol. 1973 Dec;235(3):783–804. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. The receptor for tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin. A structural hypothesis. Biophys J. 1975 Jun;15(6):615–619. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(75)85842-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hladky S. B., Haydon D. A. Ion transfer across lipid membranes in the presence of gramicidin A. I. Studies of the unit conductance channel. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Aug 9;274(2):294–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(72)90178-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keynes R. D., Bezanilla F., Taylor R. E., Rojas E. The rate of action of tetrodotoxin on sodium conductance in the squid giant axon. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):365–375. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhöfer E., Schmidt H. Die Wirkung von Skorpiongift auf die Ionenströme des Ranvierschen Schnürrings. II. Unvollständiage Natrium-Inaktivierung. Pflugers Arch. 1968;303(2):150–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00592632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koppenhöfer E., Schmidt H. Incomplete sodium inactivation in nodes of Ranvier treated with scorpion venom. Experientia. 1968 Jan 15;24(1):41–42. doi: 10.1007/BF02136780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leung J., Eisenberg R. S. The effects of the antibiotics gramicidin A, amphotericin B, and nystatin on the electrical properties of frog skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Mar 29;298(3):718–723. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson S. R., Meves H. The binding of tritiated tetrodotoxin to squid giant axons. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Jun 10;270(908):349–352. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minna J., Nelson P., Peacock J., Glazer D., Nirenberg M. Genes for neuronal properties expressed in neuroblastoma x L cell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jan;68(1):234–239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.1.234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miranda F., Kupeyan C., Rochat H., Rochat C., Lissitzky S. Purification of animal neurotoxins. Isolation and characterization of eleven neurotoxins from the venoms of the scorpions Androctonus australis hector, Buthus occitanus tunetanus and Leiurus quinquestriatus quinquestriatus. Eur J Biochem. 1970 Nov;16(3):514–523. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1970.tb01111.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narahashi T., Shapiro B. I., Deguchi T., Scuka M., Wang C. M. Effects of scorpion venom on squid axon membranes. Am J Physiol. 1972 Apr;222(4):850–857. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.222.4.850. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P. G., Peacock J. H., Amano T., Minna J. Electrogenesis in mouse neuroblastoma cells in vitro. J Cell Physiol. 1971 Jun;77(3):337–352. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040770308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson P., Ruffner W., Nirenberg M. Neuronal tumor cells with excitable membranes grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1004–1010. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholls D. G. Hamster brown-adipose-tissue mitochondria. The control of respiration and the proton electrochemical potential gradient by possible physiological effectors of the proton conductance of the inner membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Dec 2;49(3):573–583. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03861.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. K., Raftery M. A. Properties of the tetrodotoxin binding component in plasma membranes isolated from Electrophorus electricus. Biochemistry. 1976 Mar 9;15(5):944–953. doi: 10.1021/bi00650a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romey G., Chicheportiche R., Lazdunski M., Rochat H., Miranda F., Lissitzky S. Scorpion neurotoxin - a presynaptic toxin which affects both Na+ and K+ channels in axons. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 May 5;64(1):115–121. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90226-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuldiner S., Kaback H. R. Membrane potential and active transport in membrane vesicles from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Dec 16;14(25):5451–5461. doi: 10.1021/bi00696a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector I., Kimhi Y., Nelson P. G. Tetrodotoxin and cobalt blockade of neuroblastoma action potentials. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 28;246(152):124–126. doi: 10.1038/newbio246124a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



