Abstract
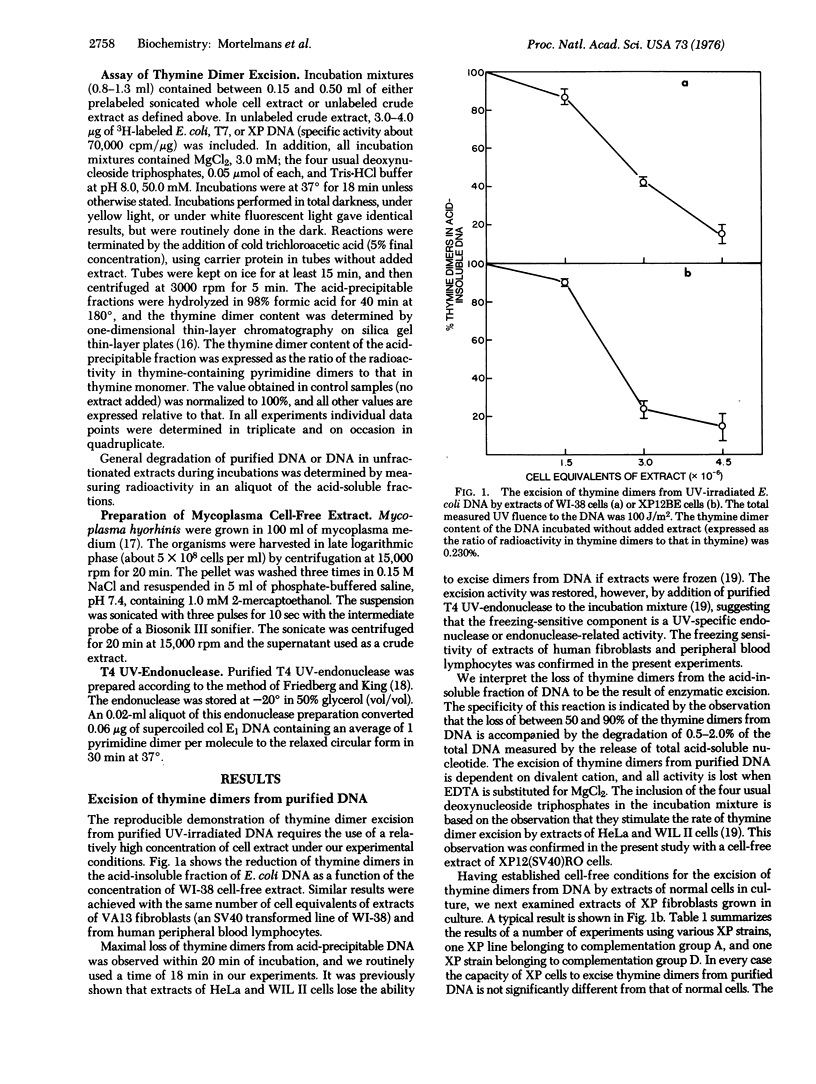
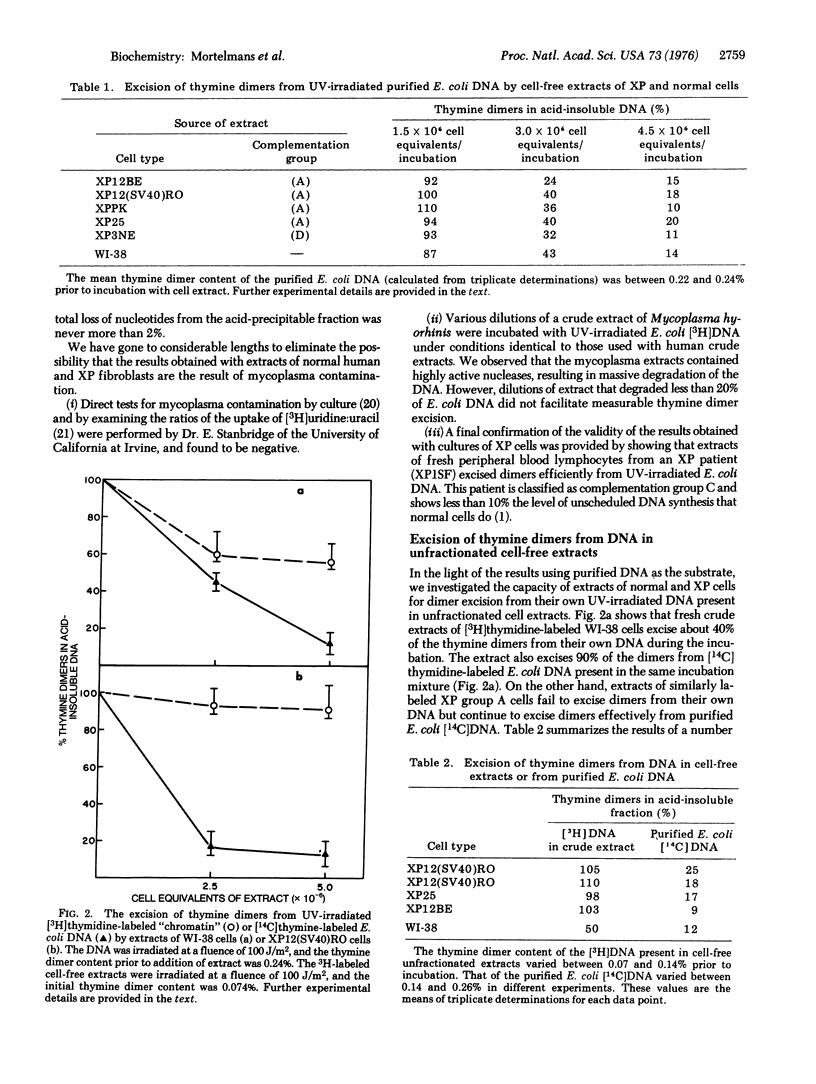
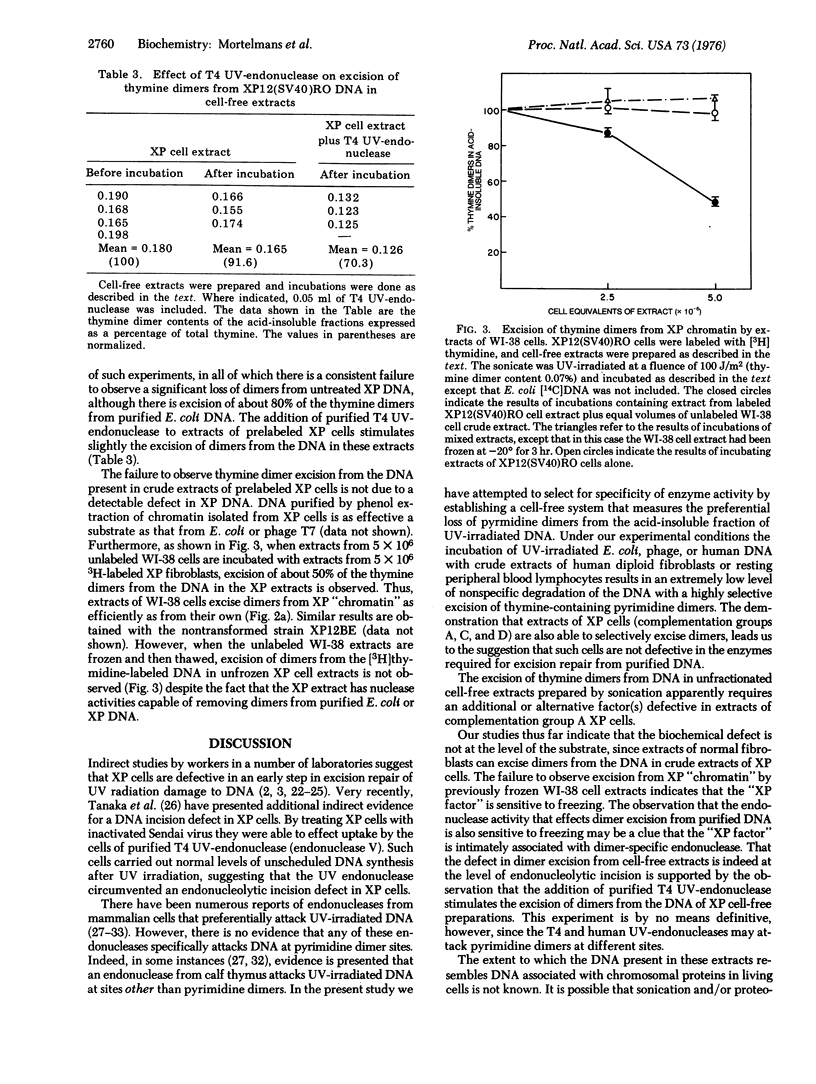
Crude extracts of normal human diploid fibroblasts and of human peripheral blood lymphocytes excise thymine dimers from purified ultraviolet-irradiated DNA, or from the DNA presumably present as chromatin in unfractionated cell-free preparations of cells that had been labeled with [3H]thymidine. Extracts of xeroderma pigmentosum cells from complementation groups A, C, and D also excise thymine dimers from purified DNA, but extracts of group A cells do not excise dimers from the DNA of radioactively labeled unfractionated cell-free preparations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bacchetti S., Benne R. Purification and characterization of an endonuclease from calf thymus acting on irradiated DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 May 16;390(3):285–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90349-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., van der Plas A., Veldhuisen G. A UV-specific endonucleolytic activity present in human cell extracts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Aug 7;48(3):662–669. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent T. P. A human endonuclease activity for gamma-irradiated DNA. Biophys J. 1973 Apr;13(4):399–401. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(73)85993-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent T. P. Partial purification of endonuclease activity from human lymphoblasts. Separation of activities for depurinated DNA and DNA irradiated with ultraviolet light. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Oct 1;407(2):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90284-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Bootsma D. Xeroderma pigmentosum: biochemical and genetic characteristics. Annu Rev Genet. 1975;9:19–38. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.09.120175.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Defective repair replication of DNA in xeroderma pigmentosum. Nature. 1968 May 18;218(5142):652–656. doi: 10.1038/218652a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Sedimentation of DNA from human fibroblasts irradiated with ultraviolet light: possible detection of excision breaks in normal and repair-deficient xeroderma pigmentosum cells. Radiat Res. 1974 Feb;57(2):207–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E., Trosko J. E. Absence of excision of ultraviolet-induced cyclobutane dimers in xeroderma pigmentosum. Photochem Photobiol. 1970 Jun;11(6):547–550. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1970.tb06025.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleaver J. E. Xeroderma pigmentosum: a human disease in which an initial stage of DNA repair is defective. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):428–435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weerd-Kastelein E. A., Keijzer W., Bootsma D. Genetic heterogeneity of xeroderma pigmentosum demonstrated by somatic cell hybridization. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):80–83. doi: 10.1038/newbio238080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duker N. J., Teebor G. W. Different ultraviolet DNA endonuclease activity in human cells. Nature. 1975 May 1;255(5503):82–84. doi: 10.1038/255082a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forger J. M., 3rd, Choie D. D., Friedberg E. C. Non-histone chromosomal proteins of chemically transformed neoplastic cells in tissue culture. Cancer Res. 1976 Jan;36(1):258–262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Kohn K. W., Kann H. E., Jr DNA single-strand breaks during repair of UV damage in human fibroblasts and abnormalities of repair in xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):39–43. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C., King J. J. Dark repair of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid by bacteriophage T4: purification and characterization of a dimer-specific phage-induced endonuclease. J Bacteriol. 1971 May;106(2):500–507. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.2.500-507.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayflick L. Tissue cultures and mycoplasmas. Tex Rep Biol Med. 1965 Jun;23(Suppl):285+–285+. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Coon H. G., Petinga R. A., Barrett S. F., Rahe A. E., Robbins J. H. National Cancer Institute, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, Maryland 20014, USA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., De Weerd-Kastelein E. A., Robbins J. H., Keijzer W., Barrett S. F., Petinga R. A., Bootsma D. Five complementation groups in xeroderma pigmentosum. Mutat Res. 1975 Dec;33(2-3):327–340. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(75)90208-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson M. C., Lohman P. H., Sluyter M. L. Use of UV endonuclease from Micrococcus luteus to monitor the progress of DNA repair in UV-irradiated human cells. Mutat Res. 1973 Aug;19(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90083-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J. H., Kraemer K. H., Lutzner M. A., Festoff B. W., Coon H. G. Xeroderma pigmentosum. An inherited diseases with sun sensitivity, multiple cutaneous neoplasms, and abnormal DNA repair. Ann Intern Med. 1974 Feb;80(2):221–248. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-80-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J. Comparison of methods for the detection of Mycoplasmal contamination of cell cultures: a review. In Vitro. 1975 Jan-Feb;11(1):20–34. doi: 10.1007/BF02615318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider E. L., Stanbridge E. J., Epstein C. J. Incorporation of 3H-uridine and 3H-uracil into RNA: a simple technique for the detection of mycoplasma contamination of cultured cells. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):311–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90411-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setlow R. B., Regan J. D., German J., Carrier W. L. Evidence that xeroderma pigmentosum cells do not perform the first step in the repair of ultraviolet damage to their DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Nov;64(3):1035–1041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Sekiguchi M., Okada Y. Restoration of ultraviolet-induced unscheduled DNA synthesis of xeroderma pigmentosum cells by the concomitant treatment with bacteriophage T4 endonuclease V and HVJ (Sendai virus). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):4071–4075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.4071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomura T., van Lancker J. L. The effect of a mammalian repair endonuclease on x-irradiated DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Sep 1;402(3):343–350. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(75)90270-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Weerd-Kastelein E. A., Kleijer W. J., Sluyter M. L., Keijzer W. Repair replication in heterokaryons deprived from different repair-deficient xeroderma pigmentosum strains. Mutat Res. 1973 Aug;19(2):237–243. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(73)90082-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Lancker J. L., Tomura T. Purification and some properties of a mammalian repair endonuclease. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Jun 14;353(1):99–114. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(74)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



