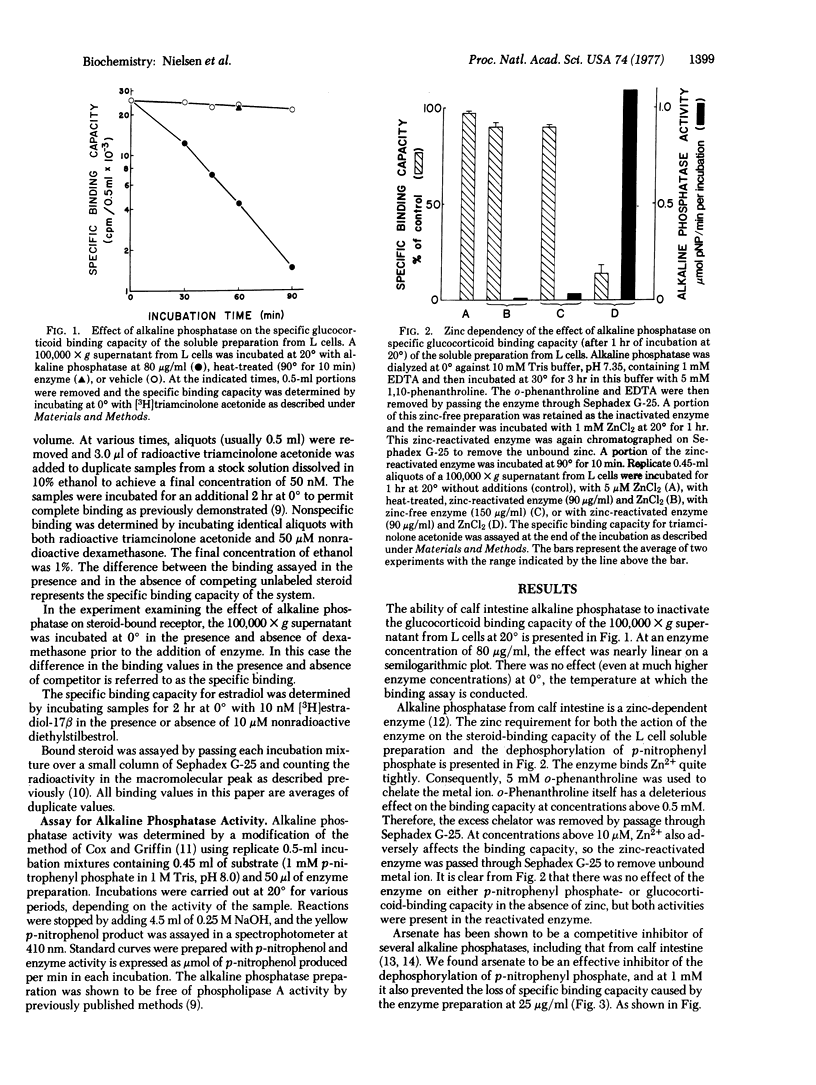
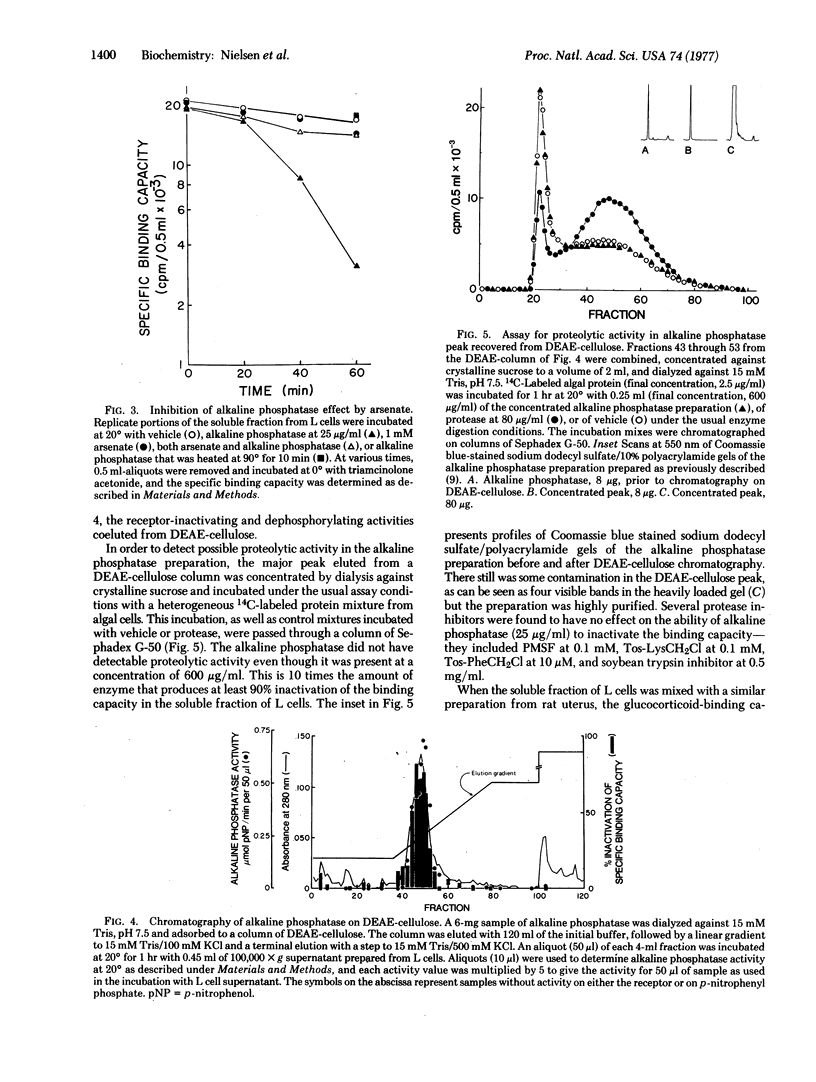
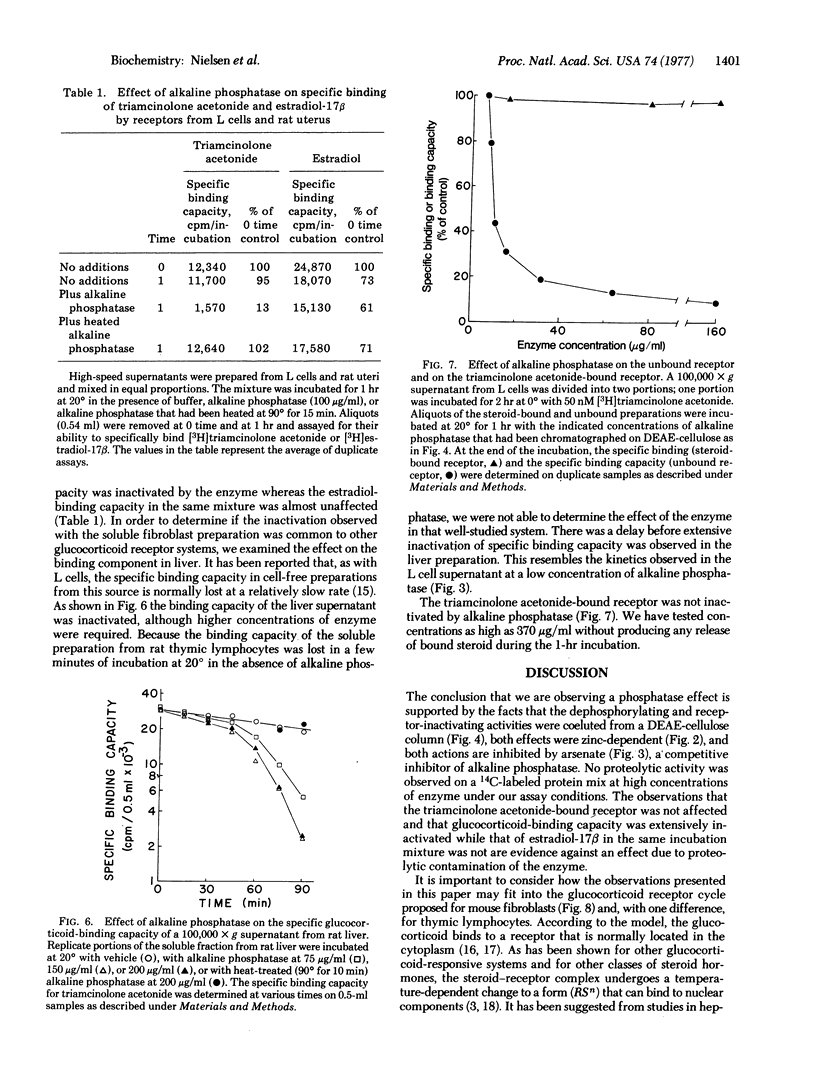
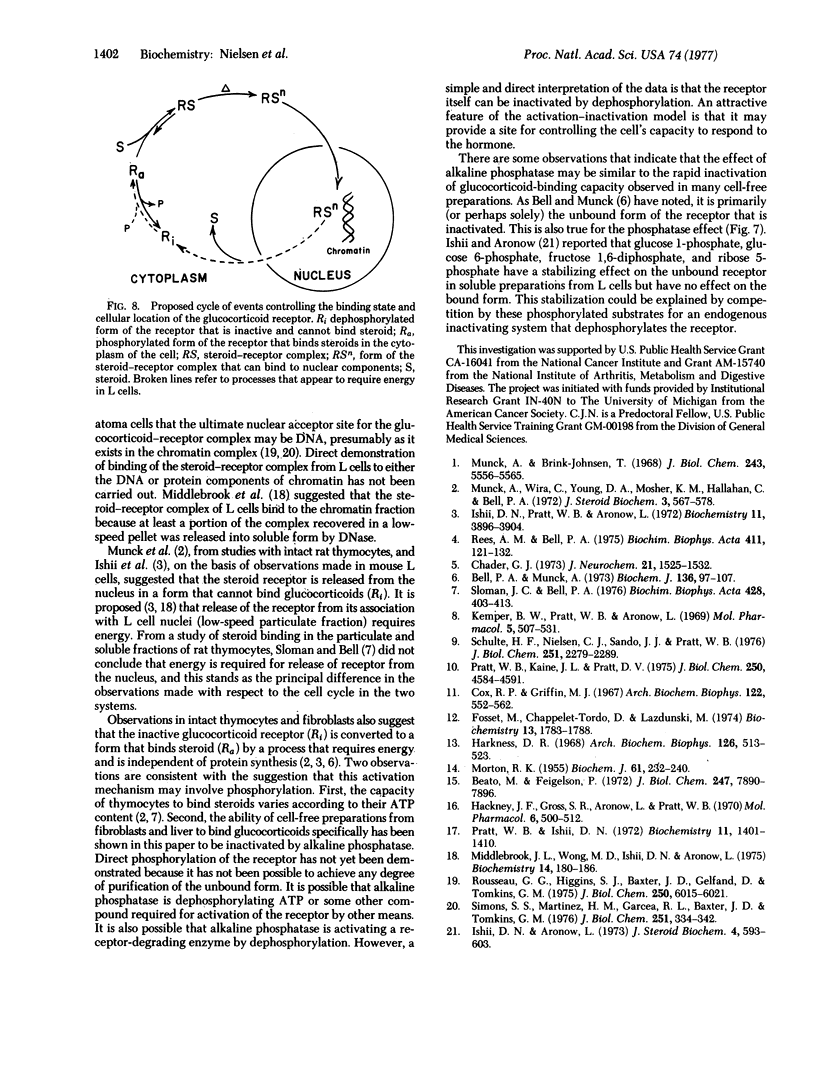
Abstract
Highly purified alkaline phosphatase [orthophosphoric-monoester phosphohydrolase (alkaline optimum), EC 3.1.3.1] from calf intestine inactivates the glucocorticoid-binding capacity of soluble preparations from mouse fibroblasts (L cells) and rat liver. The unbound receptor is sensitive to inactivation whereas the steroid-bound receptor is unaffected. The ability of the enzyme preparation to inactivate the receptor, like its ability to dephosphorylate p-nitrophenyl phosphate, is dependent on zinc and inhibited by arsenate. Both the dephosphorylating and receptor inactivating activities coelute during DEAE-cellulose purification of the enzyme. There is no detectable proteolytic activity in the purified alkaline phosphatase preparation. In a mixed system containing both glucocorticoid and estrogen receptors, the glucocorticoid receptor is selectively inactivated. Although these observations do not prove that the receptor molecule itself is the substrate, they are consistent with the proposal that the glucocorticoid receptor can be inactivated by dephosphorylation and that only the phosphorylated form of the molecule is capable of binding steroid. A phosphorylation-dephosphorylation mechanism may be responsible for determining the level of active receptor in the cell.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beato M., Feigelson P. Glucocorticoid-binding proteins of rat liver cytosol. I. Separation and identification of the binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1972 Dec 25;247(24):7890–7896. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell P. A., Munck A. Steroid-binding properties and stabilization of cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptors from rat thymus cells. Biochem J. 1973 Sep;136(1):97–107. doi: 10.1042/bj1360097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chader G. J. Some factors affecting the uptake, binding and retention of (3H)cortisol by the chick embryo retina as related to enzyme induction. J Neurochem. 1973 Dec;21(6):1525–1532. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1973.tb06036.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fosset M., Chappelet-Tordo D., Lazdunski M. Intestinal alkaline phosphatase. Physical properties and quaternary structure. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1783–1788. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackney J. F., Gross S. R., Aronow L., Pratt W. B. Specific glucocorticoid-binding macromolecules from mouse fibroblasts growing in vitro. A possible steroid receptor for growth inhibition. Mol Pharmacol. 1970 Sep;6(5):500–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harkness D. R. Studies on human placental alkaline phosphatase. II. Kinetic properties and studies on the apoenzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Aug;126(2):513–523. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90436-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Aronow L. In vitro degradation and stabilization of the glucocorticoid binding component from mouse fibroblasts. J Steroid Biochem. 1973 Nov;4(6):593–603. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(73)90034-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishii D. N., Pratt W. B., Aronow L. Steady-state level of the specific glucocorticoid binding component in mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1972 Oct 10;11(21):3896–3904. doi: 10.1021/bi00771a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemper B. W., Pratt W. B., Aronow L. Nucleic acid synthesis in intact nuclei isolated from mouse fibroblasts. Characterization of the system and effects of glucocorticoids. Mol Pharmacol. 1969 Sep;5(5):507–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MORTON R. K. The substrate specificity and inhibition of alkaline phosphatases of cow's milk and calf intestinal mucosa. Biochem J. 1955 Oct;61(2):232–240. doi: 10.1042/bj0610232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middlebrook J. L., Wong M. D., Ishii D. N., Aronow L. Subcellular distribution of glucocorticoid receptors in mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1975 Jan 14;14(1):180–186. doi: 10.1021/bi00672a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Brinck-Johnsen T. Specific and nonspecific physicochemical interactions of glucocorticoids and related steroids with rat thymus cells in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1968 Nov 10;243(21):5556–5565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munck A., Wira C., Young D. A., Mosher K. M., Hallahan C., Bell P. A. Glucocorticoid-receptor complexes and the earliest steps in the action of glucocorticoids on thymus cells. J Steroid Biochem. 1972 Apr;3(3):567–578. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(72)90103-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Ishii D. N. Specific binding of glucocorticoids in vitro in the soluble fraction of mouse fibroblasts. Biochemistry. 1972 Apr 11;11(8):1401–1410. doi: 10.1021/bi00758a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Kaine J. L., Pratt D. V. The kinetics of glucocorticoid binding to the soluble specific binding protein of mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4584–4591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees A. M., Bell P. A. The involvement of receptro sulphydryl groups in the binding of steroids to the cytoplasmic glucocorticoid receptor from rat thymus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Nov 10;411(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(75)90291-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousseau G. G., Higgins S. J., Baxter J. D., Gelfand D., Tomkins G. M. Binding of glucocorticoid receptors to DNA. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6015–6021. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte H. F., Nielsen C. J., Sando J. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence for a phospholipid requirement in the specific binding of glucocorticoids to receptors of fibroblasts and thymic lymphocytes. J Biol Chem. 1976 Apr 25;251(8):2279–2289. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons S. S., Jr, Martinez H. M., Garcea R. L., Baxter J. D., Tomkins G. M. Interaction of glucocorticoid receptor-steroid complexes with acceptor sites. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 25;251(2):334–343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sloman J. C., Bell P. A. The dependence of specific nuclear binding of glucocorticoids by rat thymus cells on cellular ATP levels. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Apr 23;428(2):403–413. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(76)90048-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



