Abstract
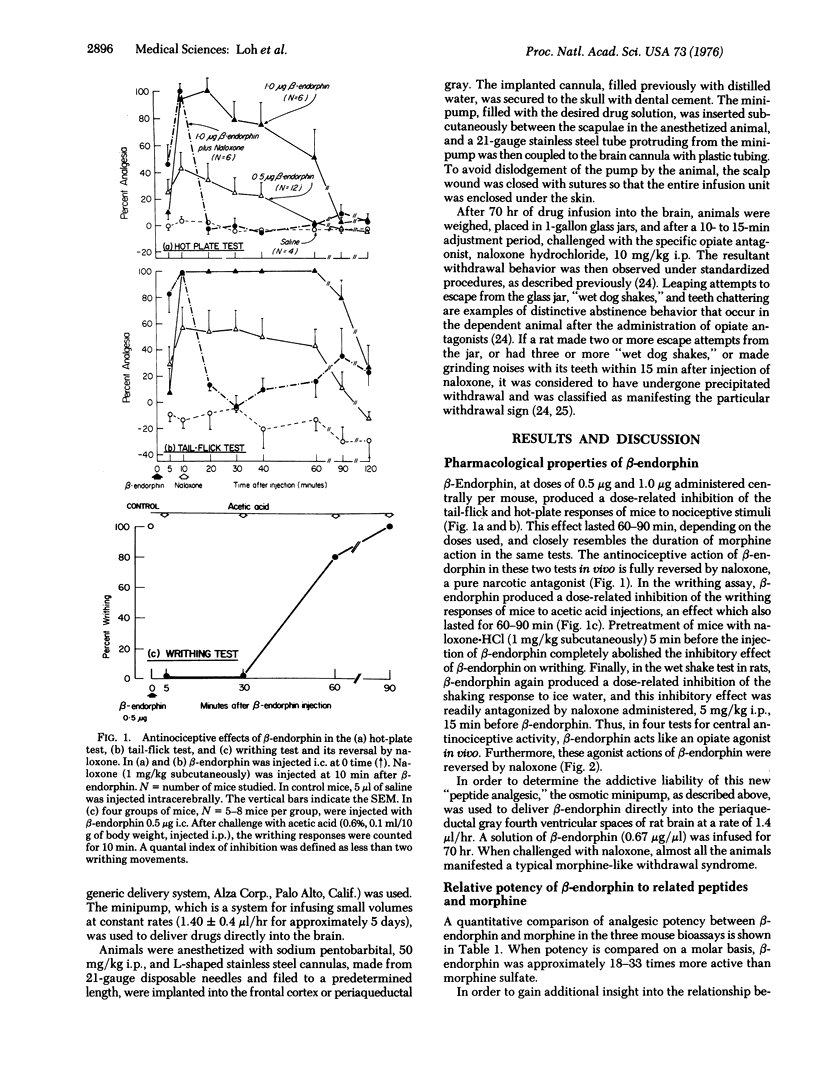
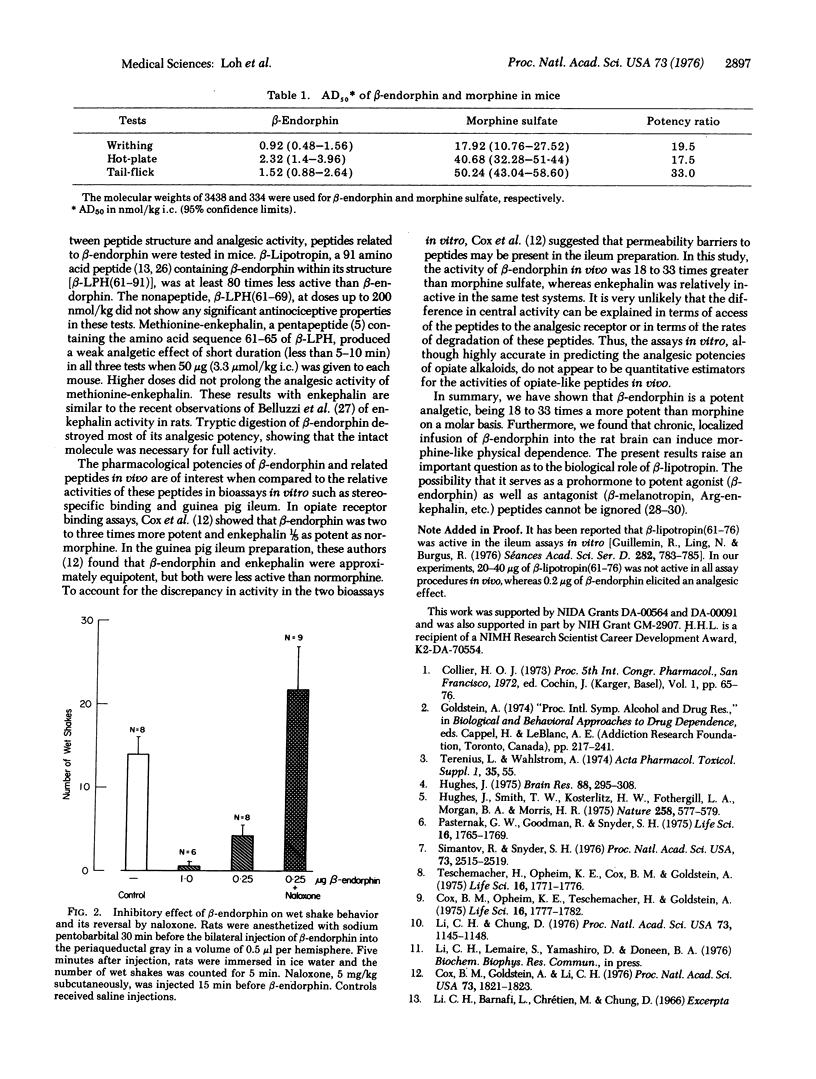
beta-Endorphin, an opiate-like peptide, has potent antinociceptive properties when it is administered directly into the brain and assayed in the the tail-flick, hot-plate, and writhing tests in mice and in the wet shake test in rats. On a molar basis, beta-endorphin is 18 to 33 times more potent than morphine and its actions are blocked by the specific opiate antagonist, naloxone hydrochloride. The activity of beta-endorphin in vivo is also compared to other peptides that show opiate-like activity in assays in vitro.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ankier S. I. New hot plate tests to quantify antinociceptive and narcotic antagonist activities. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Jun;27(1):1–4. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belluzzi J. D., Grant N., Garsky V., Sarantakis D., Wise C. D., Stein L. Analgesia induced in vivo by central administration of enkephalin in rat. Nature. 1976 Apr 15;260(5552):625–626. doi: 10.1038/260625a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Goldstein A., Hi C. H. Opioid activity of a peptide, beta-lipotropin-(61-91), derived from beta-lipotropin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jun;73(6):1821–1823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.6.1821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cox B. M., Opheim K. E., Teschemacher H., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. 2. Purification and properties. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1777–1782. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90272-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R. D., Tingstad J. E. Formulation of a morphine implantation pellet suitable for tolerance-physical dependence studies in mice. J Pharm Sci. 1970 Mar;59(3):426–427. doi: 10.1002/jps.2600590338. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guillemin R., Ling N., Burgus R. Endorphines, peptides, d'origine hypothalamique et neurohypophysaire à activité morphinomimétique. Isolement et structure moléculaire de l'alpha-endorphine. C R Acad Sci Hebd Seances Acad Sci D. 1976 Feb 23;282(8):783–785. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HALEY T. J., MCCORMICK W. G. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mouse. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957 Mar;12(1):12–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1957.tb01354.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herz A., Albus K., Metys J., Schubert P., Teschemacher H. On the central sites for the antinociceptive action of morphine and fentanyl. Neuropharmacology. 1970 Nov;9(6):539–551. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(70)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J. Isolation of an endogenous compound from the brain with pharmacological properties similar to morphine. Brain Res. 1975 May 2;88(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90391-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes J., Smith T. W., Kosterlitz H. W., Fothergill L. A., Morgan B. A., Morris H. R. Identification of two related pentapeptides from the brain with potent opiate agonist activity. Nature. 1975 Dec 18;258(5536):577–580. doi: 10.1038/258577a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacquet Y. F., Lajtha A. Paradoxical effects after microinjection of morphine in the periaqueductal gray matter in the rat. Science. 1974 Sep 20;185(4156):1055–1057. doi: 10.1126/science.185.4156.1055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krivoy W., Kroeger D., Taylor A. N., Zimmermann E. Antagonism of morphine by beta-melanocyte-stimulating hormone and by tetracosactin. Eur J Pharmacol. 1974 Aug;27(3):339–345. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(74)90009-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Chung D. Isolation and structure of an untriakontapeptide with opiate activity from camel pituitary glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1145–1148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pasternak G. W., Goodman R., Snyder S. H. An endogenous morphine-like factor in mammalian brain. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1765–1769. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharpe L. G., Garnett J. E., Cicero T. J. Analgesia and hyperreactivity produced by intracranial microinjections of morphine into the periaqueductal gray matter of the rat. Behav Biol. 1974 Jul;11(3):303–313. doi: 10.1016/s0091-6773(74)90548-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simantov R., Snyder S. H. Morphine-like peptides in mammalian brain: isolation, structure elucidation, and interactions with the opiate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teschemacher H., Opheim K. E., Cox B. M., Goldstein A. A peptide-like substance from pituitary that acts like morphine. I. Isolation. Life Sci. 1975 Jun 15;16(12):1771–1775. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(75)90271-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Brain sites of precipitated abstinence in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Apr;185(1):108–115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Loh H. H., Way E. L. Quantitative aspects of precipitated abstinence in morphine-dependent rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1973 Feb;184(2):398–403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei E., Sigel S., Way E. L. Regional sensitivity of the rat brain to the inhibitory effects of morphine on wet shake behavior. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1975 Apr;193(1):56–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann E., Krivoy W. Antagonism between morphine and the polypeptides ACTH, ACTH1-24 and beta-MSH in the nervous system. Prog Brain Res. 1973;39:383–394. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


