Abstract
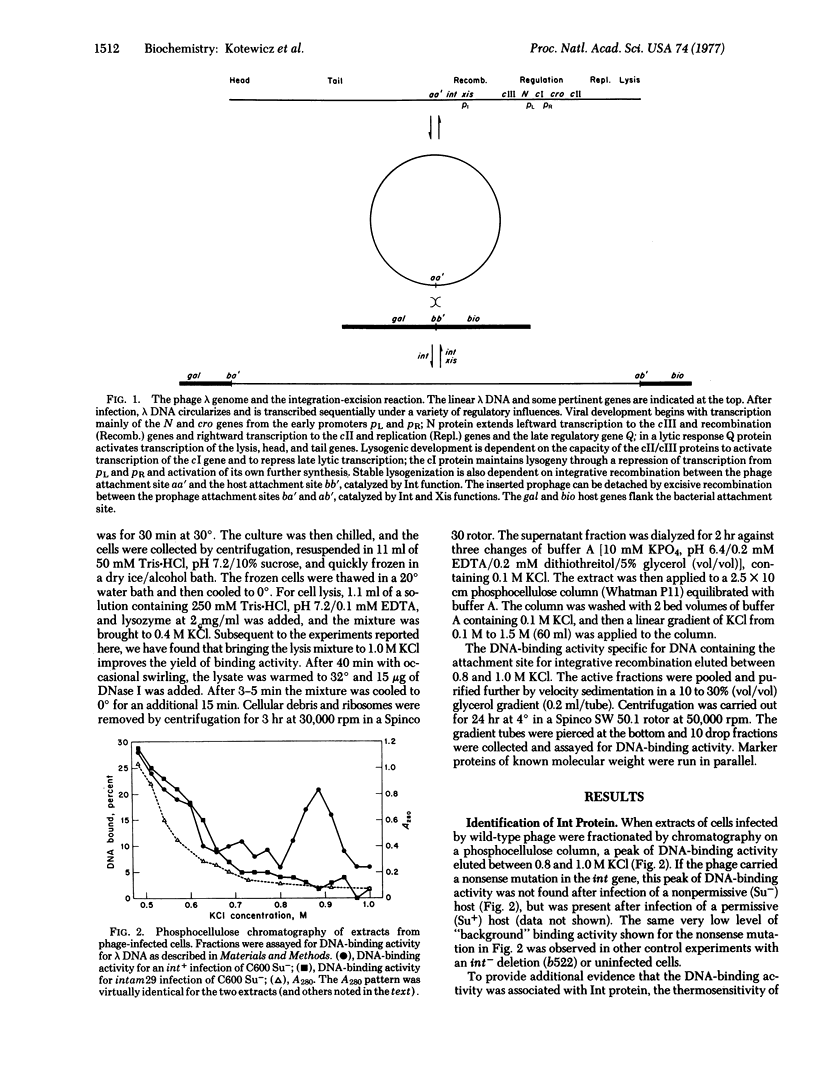
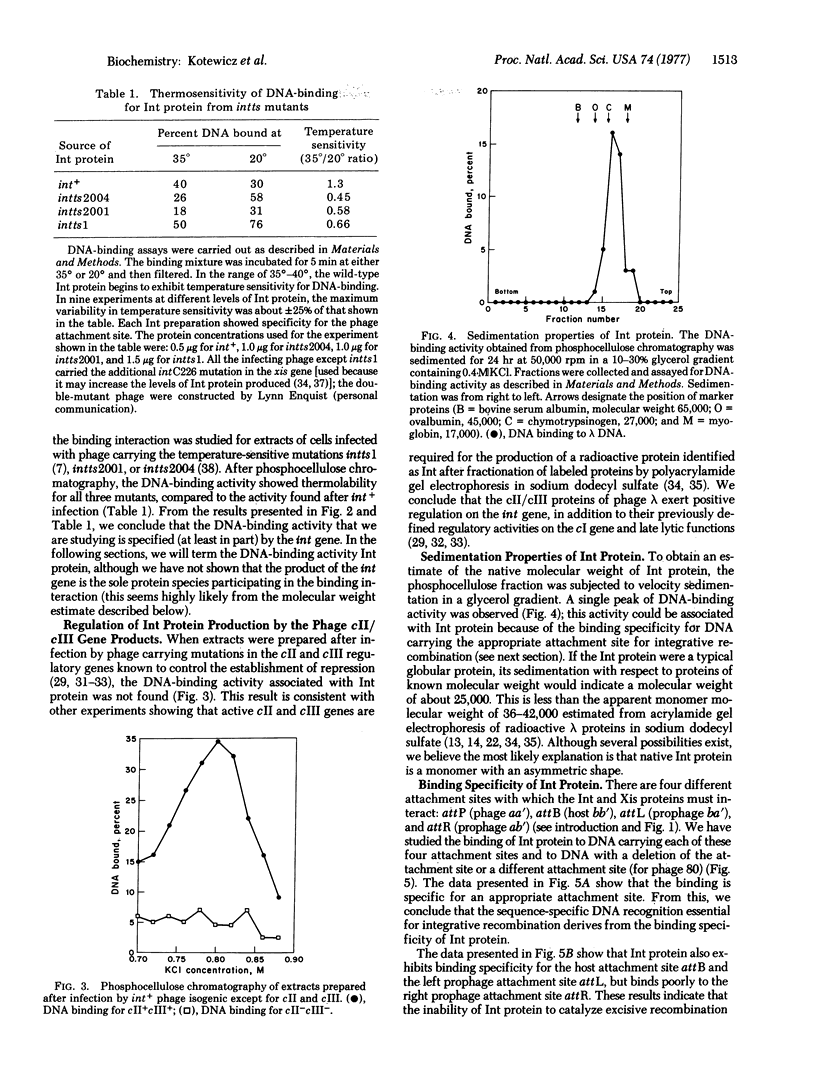
The Int protein specified by bacteriophage lambda is required for the recombination event that integrates the viral DNA into the host genome at its specific attachment site. Using a DNA-binding assay, we have partially purified the Int protein and studied some of the features of its binding specificity and regulation. The DNA-binding activity is attributed to Int protein because the activity is eliminated by a nonsense mutation or a deletion in the int gene, and is rendered thermolabile by temperature-sensitive mutations in the int gene. The DNA-binding activity is specific for DNA carrying an appropriate attachment site, suggesting that Int protein directs the sequence-specific recognition essential for integrative recombination. The specific DNA-binding activity is also missing after infection by phage carrying mutations in the cII and cIII regulatory genes of lambda. This finding corroborates the conclusion from other types of experiments that regulation of the int and cI genes by cII/cIII provides for coordinate regulation of both major events of the lysogenic response, establishment of repression and insertion of viral DNA.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ausubel F. M. Radiochemical purification of bacteriophage lambda integrase. Nature. 1974 Jan 18;247(5437):152–154. doi: 10.1038/247152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAMPBELL A. Sensitive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1961 May;14:22–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(61)90128-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Court D., Green L., Echols H. Positive and negative regulation by the cII and cIII gene products of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1975 Feb;63(2):484–491. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90321-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Gingery R., Moore L. Integrative recombination function of bacteriophage lambda: evidence for a site-specific recombination enzyme. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90250-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H., Green L. Establishment and maintenance of repression by bacteriophage lambda: the role of the cI, cII, and c3 proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2190–2194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echols H. Lysogeny: viral repression and site-specific recombination. Annu Rev Biochem. 1971;40:827–854. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.40.070171.004143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feiss M., Adyha S., Court D. L. Isolation of plaque-forming, galactose-transducing strains of phage lambda. Genetics. 1972 Jun;71(2):189–206. doi: 10.1093/genetics/71.2.189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkmanis A., Takeda Y., Simuth J., Gussin G., Echols H. Purification and properties of a DNA-binding protein with characteristics expected for the Cro protein of bacteriophage lambda, a repressor essential for lytic growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2249–2253. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingery R., Echols H. Mutants of bacteriophage lambda unable to integrate into the host chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Oct;58(4):1507–1514. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.4.1507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg A. R., Howe M. New mutations in the S cistron of bacteriophage lambda affecting host cell lysis. Virology. 1969 May;38(1):200–202. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90148-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. E., Yarmolinsky M. B. Integration-negative mutants of bacteriophage lambda. J Mol Biol. 1968 Feb 14;31(3):487–505. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90423-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman S., Gottesman M. Excision of prophage lambda in a cell-free system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2188–2192. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarneros G., Echols H. Thermal asymmetry of site-specific recombination by bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1973 Mar;52(1):30–38. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAISER A. D. Mutations in a temperate bacteriophage affecting its ability to lysogenize Escherichia coli. Virology. 1957 Feb;3(1):42–61. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(57)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser A. D., Masuda T. Evidence for a prophage excision gene in lambda. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):557–564. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90322-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzir N., Oppenheim A., Belfort M., Oppenheim A. B. Activation of the lambda int gene by the cii and ciii gene products. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):324–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90339-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieb M. Mapping missense and nonsense mutation in gene cI of bacteriophage lambda: marker effects. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Aug 2;146(3):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00701252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manly K. F., Signer E. R., Radding C. M. Nonessential functions of bacteriophage lambda. Virology. 1969 Feb;37(2):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90197-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Integrative recombination of bacteriophage lambda DNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Mar;72(3):1072–1076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nash H. A. Purification of bacteriophage lambda Int protein. Nature. 1974 Feb 22;247(5442):543–545. doi: 10.1038/247543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Huskey R. J. Deletion mutants of bacteriophage lambda. I. Isolation and initial characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):369–384. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90471-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reichardt L., Kaiser A. D. Control of lambda repressor synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Sep;68(9):2185–2189. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.9.2185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SUSSMAN R., JACOB F. [On a thermosensitive repression system in the Escherichia coli lambda bacteriophage]. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1962 Feb 19;254:1517–1519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Int-constitutive mutants of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):237–241. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada K., Campbell A. Lysogenization and curing by int-constitutive mutants of phage lambda. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):157–165. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90373-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Syvanen M. In vitro genetic recombination of bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2496–2499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil J., Signer E. R. Recombination in bacteriophage lambda. II. Site-specific recombination promoted by the integration system. J Mol Biol. 1968 Jul 14;34(2):273–279. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90252-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu A. M., Ghosh S., Echols H., Spiegelman W. G. Repression by the cI protein of phage lambda: in vitro inhibition of RNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):407–421. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90459-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



