Abstract
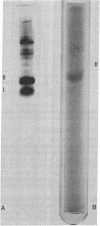
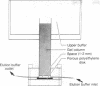
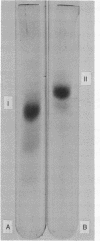
Determination of the amino acid sequence of the immunogenic polypeptides of hepatitis B surface antigen may not only permit molecular localization of the distinct determinants a, d, and y but may also lead to the synthesis of a hapten useful in prophylactic immunization against hepatitis B virus infection. For this purpose, purified monotypic hepatitis B surface antigen of adw subtype was resolved into equal amounts of two major polypeptides (22,000 and 28,000 daltons) and up to six other minor polypeptides by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. With the periodate staining reaction, only the 28,000-dalton polypeptide stained as a glycoprotein. Guinea pigs immunized with the 22,000-dalton polypeptide produced potent antisera against determinants a and d, but the 28,000-dalton glycoprotein did not induce a response. Both polypeptides isolated by preparative polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis showed amino acid composition identical with that of the intact antigen. For both polypeptides, hydrazinolysis gave Ile as the carboxyterminus, and carboxypeptidase A digestion gave the same terminal sequence, Val-Tyr-Ile. Both peptides also yielded an identical sequence of amino acids in nine steps of Edman degradation--Met-Glu-Asn-Ile-Thr-Ser(Cys)-Gly-Phe-Leu. Our data suggest that hepatitis B surface antigen contains a single major immunogenic 22,000-dalton polypeptide component, part of which is modified by the addition of carbohydrate to give rise to the glycopeptide of apparent molecular weight 28,000.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bayer M. E., Blumberg B. S., Werner B. Particles associated with Australia antigen in the sera of patients with leukaemia, Down's Syndrome and hepatitis. Nature. 1968 Jun 15;218(5146):1057–1059. doi: 10.1038/2181057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bensadoun A., Ehnholm C., Steinberg D., Brown W. V. Purification and characterization of lipoprotein lipase from pig adipose tissue. J Biol Chem. 1974 Apr 10;249(7):2220–2227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond H. E., Hall W. T. Separation and purification of hepatitis-associated antigen into morphologic types by zonal ultracentrifugation. J Infect Dis. 1972 Mar;125(3):263–268. doi: 10.1093/infdis/125.3.263. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dane D. S., Cameron C. H., Briggs M. Virus-like particles in serum of patients with Australia-antigen-associated hepatitis. Lancet. 1970 Apr 4;1(7649):695–698. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(70)90926-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Hollinger F. B., Melnick J. L. Biophysical and biochemical properties of purified preparations of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBs Ag). Am J Med Sci. 1975 Jul-Aug;270(1):123–129. doi: 10.1097/00000441-197507000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Hollinger F. B., Suriano J. R., Fujioka R. S., Brunschwig J. P., Melnick J. L. Biophysical and biochemical heterogeneity of purified hepatitis B antigen. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):469–476. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.469-476.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin J. L., Holland P. V., Purcell R. H. Australia antigen: large-scale purification from human serum and biochemical studies of its proteins. J Virol. 1971 May;7(5):569–576. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.5.569-576.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirschman R. J., Shulman N. R., Barker L. F., Smith K. O. Virus-like particles in sera of patients with infectious and serum hepatitis. JAMA. 1969 Jun 2;208(9):1667–1670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hugli T. E., Moore S. Determination of the tryptophan content of proteins by ion exchange chromatography of alkaline hydrolysates. J Biol Chem. 1972 May 10;247(9):2828–2834. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly P. J., Catley B. J. A purification of trehalase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:353–358. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90541-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. Y., Tilles J. G. Purification and biophysical characterization of hepatitis B antigen. J Clin Invest. 1973 May;52(5):1176–1186. doi: 10.1172/JCI107284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOCKER R. H. C-Terminal groups in myosin, tropomyosin and actin. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1954 Aug;14(4):533–542. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(54)90233-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bouvier G. L. Editorial: Subtypes of hepatitis B antigen: clinical relevance? Ann Intern Med. 1973 Dec;79(6):894–896. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-6-894. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marquardt G. M., DiStefano V. The hepatic microsomal metabolism of beta-3,4-methylenedioxyamphetamine (MDA). Life Sci. 1974 Nov 1;15(9):1603–1610. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(74)90326-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pataki G. Anwendung der Dünnschichtchromatographie zur Sequenzanalyse von Peptiden. 4. Untersuchungen über den Abbau von Peptiden mit Phenylisothiocyanat. J Chromatogr. 1966 Jan;21(1):133–135. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)91274-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisano J. J., Bronzert T. J. Analysis of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by gas chromatography. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 25;244(20):5597–5607. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao K. R., Vyas G. N. Biochemical characterization of hepatitis B surface antigen in relation to serologic activity. J Biol Stand. 1976;4(4):295–304. doi: 10.1016/s0092-1157(76)80014-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson W. S., Clayton D. A., Greenman R. L. DNA of a human hepatitis B virus candidate. J Virol. 1974 Aug;14(2):384–391. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.2.384-391.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih J. W., Gerin J. L. Immunochemistry of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg): preparation and characterization of antibodies to the constituent polypeptides. J Immunol. 1975 Sep;115(3):634–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slutzky G. M., Ji T. H. The dissimilar nature of two forms of the major human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Dec 24;373(3):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90013-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steiner S., Huebner M. T., Dreesman G. R. Major polar lipids of hepatitis B antigen preparations: evidence for the presence of a glycosphingolipid. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):572–577. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.572-577.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephens R. E. High-resolution preparative SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis: fluorescent visualization and electrophoretic elution-concentration of protein bands. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 12;65(1-2):369–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90521-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutnick A. I., London W. T., Blumberg B. S. Australia antigen and the quest for a hepatitis virus. Am J Dig Dis. 1969 Mar;14(3):189–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02235880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuszynski G. P., Warren L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins. Anal Biochem. 1975 Jul;67(1):55–65. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90271-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Adelberg S. G., Perkins H. A. Letter: Nonspecificity of hepatitis B antigen detected with iodine-125-labeled antibody. Science. 1973 Dec 28;182(4119):1368–1371. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4119.1368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Rao K. R., Ibrahim A. B. Australia antigen (hepatitis B antigen): a conformational antigen dependent on disulfide bonds. Science. 1972 Dec 22;178(4067):1300–1301. doi: 10.1126/science.178.4067.1300. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vyas G. N., Williams E. W., Klaus G. G., Bond H. E. Hepatitis-associated Australia antigen. Protein, peptides and amine acid composition of purified antigen with its use in determining sensitivity of the hemagglutination test. J Immunol. 1972 Apr;108(4):1114–1118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]