Abstract
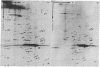
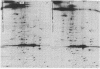
Flagellar polypeptides of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii were analyzed in two-dimensions by isoelectric focusing and electrophoresis in the presence of sodium dodecyl sulfate. In addition to flagellar tubulin, over 130 polypeptides were resolved and 100 of these were identified as axonemal components in wild-type organisms. Flagella of two nonconditional paralyzed mutants, pf 14 and pf 1, were also analyzed and, at the same time, electron microscopic studies were carried out. pf 14 flagella, which completely lack radial spokes and associated spokeheads, are missing 12 polypeptides. Six of these polypeptides are also missing from pf 1 flagella in which spokes are clearly present but spoke heads appear to be absent.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasey D. The three-dimensional arrangement of radial spokes in the flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Mar 15;84(1):374–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90418-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forest C. L., Togasaki R. K. Selection for conditional gametogenesis in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3652–3655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough U. W., Hwang C., Martin H. Isolation and genetic analysis of mutant strains of Chlamydomonas reinhardi defective in gametic differentiation. Genetics. 1976 Feb;82(2):169–186. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.2.169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins J. M. Subsidiary components of the flagella of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. J Cell Sci. 1970 Nov;7(3):823–839. doi: 10.1242/jcs.7.3.823. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang B., Rifkin M. R., Luck D. J. Temperature-sensitive mutations affecting flagellar assembly and function in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):67–85. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEWIN R. A. Mutants of Chlamydomonas moewusii with impaired motility. J Gen Microbiol. 1954 Dec;11(3):358–363. doi: 10.1099/00221287-11-3-358. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine R. P., Goodenough U. W. The genetics of photosynthesis and of the chloroplast in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Annu Rev Genet. 1970;4:397–408. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.04.120170.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linck R. W. Flagellar doublet microtubules: fractionation of minor components and alpha-tubulin from specific regions of the A-tubule. J Cell Sci. 1976 Mar;20(2):405–439. doi: 10.1242/jcs.20.2.405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchalonis J. J., Cone R. E., Santer V. Enzymic iodination. A probe for accessible surface proteins of normal and neoplastic lymphocytes. Biochem J. 1971 Oct;124(5):921–927. doi: 10.1042/bj1240921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neville D. M., Jr Molecular weight determination of protein-dodecyl sulfate complexes by gel electrophoresis in a discontinuous buffer system. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6328–6334. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Luck D. J. Microtubular proteins of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. An immunochemical study based on the use of an antibody specific for the beta-tubulin subunit. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringo D. L. Flagellar motion and fine structure of the flagellar apparatus in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jun;33(3):543–571. doi: 10.1083/jcb.33.3.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilney L. G., Bryan J., Bush D. J., Fujiwara K., Mooseker M. S., Murphy D. B., Snyder D. H. Microtubules: evidence for 13 protofilaments. J Cell Biol. 1973 Nov;59(2 Pt 1):267–275. doi: 10.1083/jcb.59.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner F. D., Satir P. The structural basis of ciliary bend formation. Radial spoke positional changes accompanying microtubule sliding. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):35–63. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witman G. B., Carlson K., Berliner J., Rosenbaum J. L. Chlamydomonas flagella. I. Isolation and electrophoretic analysis of microtubules, matrix, membranes, and mastigonemes. J Cell Biol. 1972 Sep;54(3):507–539. doi: 10.1083/jcb.54.3.507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]