Abstract
The axon initial segment (AIS) is a specialized structure near the start of the axon that is a site of neuronal plasticity. Changes in activity levels in vitro and in vivo can produce structural AIS changes in excitatory cells that have been linked to alterations in excitability, but these effects have never been described in inhibitory interneurons. In the mammalian olfactory bulb (OB), dopaminergic interneurons are particularly plastic, undergoing constitutive turnover throughout life and regulating tyrosine hydroxylase expression in an activity-dependent manner. Here we used dissociated cultures of rat and mouse OB to show that a subset of bulbar dopaminergic neurons possess an AIS and that these AIS-positive cells are morphologically and functionally distinct from their AIS-negative counterparts. Under baseline conditions, OB dopaminergic AISs were short and located distally along the axon but, in response to chronic 24 h depolarization, lengthened and relocated proximally toward the soma. These activity-dependent changes were in the opposite direction to both those we saw in non-GABAergic OB neurons and those reported previously for excitatory cell types. Inverted AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic cells was bidirectional, involved all major components of the structure, was dependent on the activity of L-type CaV1 calcium channels but not on the activity of the calcium-activated phosphatase calcineurin, and was opposed by the actions of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Such distinct forms of AIS plasticity in inhibitory interneurons and excitatory projection neurons may allow considerable flexibility when neuronal networks must adapt to perturbations in their ongoing activity.
Keywords: axon initial segment, dopamine, interneuron, olfactory bulb, plasticity
Introduction
The axon initial segment (AIS) is a structurally, molecularly, and functionally specialized subcompartment found close to the soma of axon-bearing neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010a; Rasband, 2010). Its location, morphology, and high densities of voltage-gated ion channels combine to make it the initiation site for action potential generation and therefore a key determinant of electrical activity in neuronal networks (Clark et al., 2009; Bender and Trussell, 2012; Kole and Stuart, 2012). It was found recently that this large macromolecular complex can undergo significant structural change not only in response to perturbations imposed by neuronal injury or disease (Buffington and Rasband, 2011) but also under conditions of altered neuronal activity (Grubb et al., 2011). These changes were associated with altered excitability (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Kaphzan et al., 2011, 2013), suggesting that AIS plasticity may contribute to compensatory neuronal responses to perturbations in electrical activity (Gründemann and Häusser, 2010; Grubb et al., 2011). However, although a range of pathological and plastic structural changes have been observed at the AIS in a variety of cell types, they have never been described in inhibitory interneurons.
In the mammalian olfactory bulb (OB), inhibitory interneurons play vital roles in shaping sensory processing (Shepherd, 2004). A distinct subset of GABAergic cells in the glomerular layer (GL) and external plexiform layer is dopaminergic (Halász et al., 1981), coreleasing dopamine and GABA from distinct vesicle pools (Maher and Westbrook, 2008; Borisovska et al., 2013). These dopaminergic cells operate local gain control of transmitter release from olfactory sensory neuron terminals (Hsia et al., 1999; Ennis et al., 2001; but see McGann, 2013) and more distant lateral inhibition of glomerular output (Liu et al., 2013) and can therefore influence fundamental features of olfactory sensory behavior (Wei et al., 2006; Serguera et al., 2008). They are also responsible for considerable activity-dependent plasticity, regulating expression of the dopamine-synthesizing enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) and the GABA-synthesizing enzyme GAD67 in an activity-dependent manner (Baker et al., 1983; Cave et al., 2010; Parrish-Aungst et al., 2011; Banerjee et al., 2013). In addition, bulbar dopaminergic cells are plastic to the point of whole-neuron replacement, forming part of the limited population of neurons that is constitutively generated throughout life (Lledo et al., 2006). Continual turnover with net addition of dopaminergic neurons occurs in the adult OB (Adam and Mizrahi, 2011), and survival of this interneuron subtype is dependent on sensory activity (Bastien-Dionne et al., 2010; Sawada et al., 2011).
Given this plasticity, alongside observations of dopaminergic AISs in the OB (Kosaka et al., 2008), we asked whether these AISs could undergo activity-dependent change. Using dissociated cultures of embryonic OB, we show here that a distinct subpopulation of dopaminergic neurons possesses a molecularly and functionally defined AIS and that structural AIS plasticity in these cells occurs in the opposite, inverted direction to activity-dependent AIS alterations in excitatory neurons.
Materials and Methods
Dissociated culture.
For rat cultures, we dissected the rostral half of the OB from E18 Wistar embryos of either sex (Charles River) into HBSS. Bulb tissue was then digested with trypsin (0.5 mg/ml; 15 min at 37°C; Worthington) and DNase (0.2 mg/ml; Sigma) before trituration and subsequent plating at 60,000 cells per well on 13 mm glass coverslips precoated with poly-l-lysine at 50 μg/ml (Sigma) and laminin at 40 μg/ml. Neurons were cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2 in Neurobasal medium supplemented with 1% B27, 1% fetal calf serum, and 500 μm Glutamax. At 4, 7, and 10 d in vitro (DIV), half of the media was changed with media supplemented with 2% B27 and 500 μm Glutamax.
Mouse cultures were prepared from litters of wild-type (C57BL/6; Charles River) or TH–Cre [B6.Cg–Tg(Th–cre)1Tmd/J (The Jackson Laboratory stock number 008601)] × Rosa–tdT [(B6.Cg–Gt(ROSA)26Sortm9(CAG-tdTomato)Hze/J (The Jackson Laboratory stock number 007909)] transgenic animals of either sex at P3. OBs were dissected in HBSS and then dissociated and triturated using a Papain Dissociation System (Worthington) before plating at 120–150,000 cells per well on 13 mm glass coverslips precoated with poly-l-lysine at 50 μg/ml (Sigma) and laminin at 40 μg/ml. Neurons were cultured at 37°C with 5% CO2 in Neurobasal medium supplemented with 1% B27, 1% fetal calf serum, and 500 μm Glutamax. At 7 DIV, half of the culture media was removed and filtered and then supplemented to 1 ml/well with Neurobasal medium supplemented with 2% B27 and 500 μm Glutamax. Unless otherwise stated, all cell-culture materials were obtained from Invitrogen.
Treatments.
For chronic depolarization, we treated rat OB cultures at 11 DIV and mouse OB cultures at 13 DIV for 24 h with 10 mm KCl or 10 mm NaCl as an osmolarity control. The efficacy of our high-potassium stimulus was verified for each experiment by briefly checking for an activity-dependent increase in TH expression, as described previously (Cigola et al., 1998); this was reflected in at least a 50% increase of detectable TH-positive (TH+) cells under low-resolution confocal microscopy with constant imaging settings. For recovery experiments, cultures that had been depolarized for 24 h were placed back into conditioned media containing 10 mm NaCl for the remainder of the experiment. All pharmacological agents were made up as per the instructions of the manufacturers and added to our neurons at previously described effective working concentrations [1 μm tetrodotoxin (TTX; Alomone Labs), 1 μm nifedipine (Sigma), 1 μm FK-506 [(3S,4R,5S,8R,9E,12S,14S,15R,16S,18R,19R,26aS)-5,6,8,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19,24,25,26,26a-hexadecahydro-5,19-dihydroxy-3-[(1E)-2-[(1R,3R,4R)-4-hydroxy-3-methoxycyclohexyl]-1-methylethenyl]-14,16-dimethoxy-4,10,12,18-tetramethyl-8-(2-propen-1-yl)-15,19-epoxy-3H-pyrido[2,1-c][1,4]oxaazacyclotricosine-1,7,20,21(4H,23H)tetrone] (Abcam), 1 μm tatCN21 (University of Colorado, Boulder, CO; Vest et al., 2007), 10 μm Rp-cAMPs (Biolog), and 20 μm roscovitine (Merck)] at least 30 min before control or depolarizing treatment.
Immunocytochemistry.
Our standard immunolabeling protocol was to first fix cultures in 4% paraformaldehyde (in 3% sucrose, 60 mm PIPES, 25 mm HEPES, 5 mm EGTA, and 1 mm MgCl2; TAAB Laboratories) for 30 min at room temperature. Cells were permeabilized for 5 min with 0.25% Triton X-100 (Sigma) before blocking for 1 h in 10% goat serum (GS; Sigma). Coverslips were then placed in primary antibody, made in 2% GS, to relevant concentrations: mouse monoclonal anti-ankyrin-G (clone N106/36, 1:500; catalog #75-146; NeuroMab); rabbit polyclonal anti-TH (1:500; catalog #AB152; Millipore); mouse monoclonal anti-sodium channel (PanNaV; clone K85/35, 1:100; catalog #S8809; Sigma); rabbit polyclonal anti-GABA (1:500; catalog #A2052; Sigma); and mouse monoclonal anti-TH (1:500; catalog # MAB318; Millipore). After subsequent washing steps, coverslips were placed in relevant secondary antibody solution (Invitrogen Alexa Fluor-conjugated antibodies in 2% GS, all at 1:1000) for an additional hour, before additional washing and mounting in MOWIOL-488 (Calbiochem).
For extracellular pan-neurofascin label, we used a live incubation of primary antibody (clone A12/18, 1:500; catalog #75-172; NeuroMab) in Neurobasal media at 37°C for 30 min before the fixation step. For PanNaV label, we digested cultures in 0.2 mg/ml pepsin (in 0.2 m HCl; Dako; Lorincz and Nusser, 2008) for 2 min at 37°C between the fixation and permeabilization steps. All other steps were identical to those described above.
Imaging and analysis.
All imaging and subsequent analysis steps were performed blind to experimental group. Neurons were imaged using a laser scanning confocal microscope (Zeiss LSM 710) with appropriate excitation and emission filters, a pinhole of 1 AU, and a 40× oil-immersion objective (Zeiss). Laser power and gain settings were adjusted to prevent signal saturation in AIS label; TH signal was usually saturated to enable clear delineation of the axon. Images were taken with 3× zoom, 512 × 512 pixels (0.138 μm/pixel) and in z-stacks with 0.45 μm steps. For AIS quantification, we exclusively imaged neurons with a single axon emanating from the soma. z-stack images were flattened into single maximum intensity projections and imported into MATLAB (MathWorks) for analysis using custom-written functions (Matthew Grubb and Thomas Watkins, King's College London, London, UK; Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013; freely available at www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/28181-ais-quantification). We drew a line profile along each maximum intensity projection starting at the soma that extended down the axon, through and past the AIS. At each pixel along this profile, fluorescence intensity values were averaged over a 3 × 3 pixel square centered on the pixel of interest. Averaged profiles were then smoothed using a 40-point (∼5 μm) sliding mean and normalized between 1 (maximum smoothed fluorescence, location of the AIS maximum position) and 0 (minimum smoothed fluorescence). AIS start and end positions were obtained at the proximal and distal axonal positions, respectively, where the normalized and smoothed profile declined to 0.33. Using NIH Image J, soma area was measured from maximum intensity projections of TH immunofluorescence or TH–tdT fluorescence. In a smaller sample of cells for which somatic TH signal was imaged under nonsaturating conditions, with identical processing and imaging settings across coverslips, mean gray value across the whole soma was used to calculate TH immunofluorescence intensity.
Electrophysiology.
With experimenters blind to treatment group, we made visually targeted (Zeiss LSM 710) whole-cell somatic patch-clamp recordings from 13–15 DIV cultures. Pipettes were pulled from borosilicate glass (1.5 mm outer diameter, 1.17 mm inner diameter; Harvard Apparatus), with a resistance of 3–7 MΩ, and were filled with an internal solution containing the following (in mm): 130 K-gluconate, 10 NaCl, 1 EGTA, 0.133 CaCl2, 2 MgCl2, 10 HEPES, 3.5 MgATP, and 1 NaGTP, pH 7.4 (290 mOsm). Recordings were obtained at room temperature with a Heka EPC10/2 amplifier coupled to Patchmaster acquisition software. Signals were Bessel filtered at 10 kHz (filter 1) and 2.9 kHz (filter 2; active filters used in voltage-clamp only), digitized, and sampled at 20–200 kHz (5–50 μs sample interval). Fast capacitance was compensated in the on-cell configuration. After membrane rupture, in voltage clamp at a holding voltage of −60 mV and with slow capacitance compensation inactive, we used responses to a 10 mV hyperpolarization step to estimate the series resistance of the recording (<30 MΩ for all cells; from the current peak) and both the membrane resistance (from the steady holding current at the new voltage) and membrane capacitance (from the area under the exponentially decaying current from peak to holding) of the neuron. Recordings in which the series resistance changed by >20% from its starting value or when a current of >100 pA was required to hold the membrane potential at −60 mV were discarded from our analyses.
For assessment of high potassium-induced depolarization, coverslips were treated with either 10 mm NaCl or 10 mm KCl for at least 30 min before both neurons and culture media were transferred to the recording chamber. Immediately on membrane rupture, resting potential was assessed and recorded at I = 0 in current clamp. Voltages were uncorrected for an estimated liquid junction potential of ∼14 mV.
For recordings of action potential properties, coverslips were treated with either 10 mm NaCl or 10 mm KCl for 24 h, before being placed in an identical HEPES-buffered saline extracellular solution, pH 7.4 (∼290 mOsm) containing the following (in mm): 136 NaCl, 2.5 KCl, 10 HEPES, 10 d-glucose, 2 CaCl2, 1.3 MgCl2, 0.01 SR-95531 (gabazine [2-(3-carboxypropyl)-3-amino-6-(4-methoxyphenyl)pyridazinium bromide]; Sigma), 0.02 NBQX (Sigma), and 0.025 dl-2-amino-5-phosphonovaleric acid (Sigma). Voltages were uncorrected for an estimated liquid junction potential of ∼15 mV. In current-clamp mode, evoked spikes were measured with Vhold set to −60 ± 3 mV. For action potential waveform measures, we injected 10-ms-duration current steps of increasing amplitude under full bridge balance until we reached the current threshold at which the neuron reliably fired an action potential (Vm > 0 mV). For multiple spiking measures, we injected 500-ms-duration current steps of increasing amplitude until the neuron passed its maximum firing frequency.
Exported traces were analyzed using custom-written routines in MATLAB (MathWorks). Before differentiation for dV/dt and associated phase plane plot analyses, recordings at high temporal resolution (5 μs sample interval) were smoothed using a 20 point (100 μs) sliding filter. Average phase plane plots were generated from mean ± SEM voltage and dV/dt values, taken from threshold spikes aligned in time to the point of peak rate-of-rise. Voltage threshold was taken as the potential at which dV/dt first passed 10 V/s. Onset rapidness was taken from the slope of a linear fit to the phase plane plot at voltage threshold. Monophasic versus biphasic phase plane plots and the peak amplitude of the first phase in biphasic responses were visually determined. Spike width was measured at the midpoint between voltage threshold and maximum voltage. Rheobase and the afterhyperpolarization were both measured from responses to 500 ms current injection, the latter from the local voltage minimum after the first spike fired at rheobase. Maximum firing frequency was determined from the sweep containing the maximum number of spikes and was calculated across the full 500 ms stimulus. The coefficient of variation (CV) for interspike intervals was calculated for every sweep with more than two action potentials, and then a mean of these values was taken across all such sweeps for each cell.
For recordings of spontaneous firing, coverslips were treated with either 10 mm NaCl or 10 mm KCl before both neurons and culture media were transferred to a heated chamber (TC-344B; Harvard Apparatus) and maintained at 37°C. Cell-attached recordings were obtained in voltage-clamp mode using fresh Neurobasal medium as “internal” solution. Spikes were subsequently identified offline (MATLAB) by their characteristic biphasic waveform.
Statistics.
Sample distributions were assessed for normality using the D'Agostino and Pearson's omnibus test and compared using parametric or nonparametric tests accordingly using Prism (GraphPad Software) or SPSS (IBM) software. All tests were two-tailed with the level of significance (α) set to 0.05, except Mann–Whitney post hoc comparisons following two-way ANOVAs on ranks (Akritas, 1990), in which six possible pairwise comparisons in a 2 × 2 experimental design necessitated a Bonferroni's-corrected α of 0.05/6 = 0.0083. Power calculations were performed using GPower (Franz Faul, Kiel University, Kiel, Germany).
Results
The AIS defines a subset of OB dopaminergic neurons
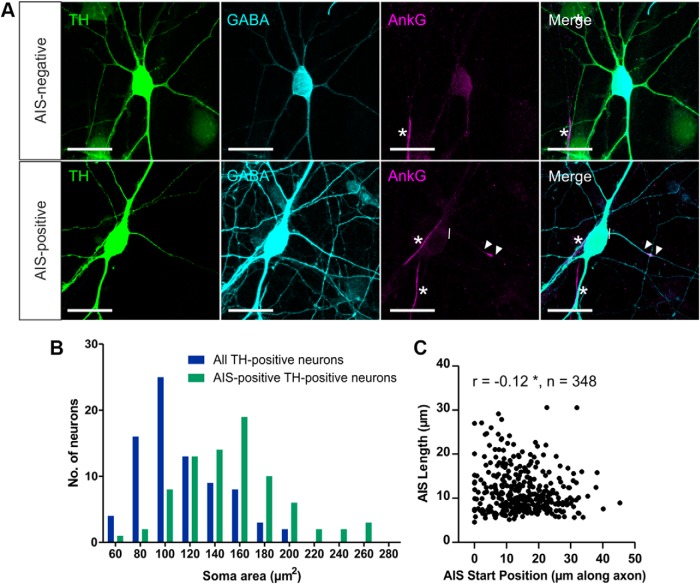
In dissociated cultures of rat OB at 12–14 DIV, ∼3% of all neurons under control conditions were dopaminergic as defined by the presence of the dopamine-synthesizing enzyme TH (Fig. 1A; 161 of 5203 MAP-2+ cells, three coverslips). These dopaminergic OB neurons all coexpressed GABA (Fig 1A; 147 of 147 TH+ cells, three coverslips; Panzanelli et al., 2007) but could be divided into two distinct subpopulations based on the presence or absence of an AIS. A distinct, coherent band of the scaffolding protein and master AIS organizing molecule ankyrin-G (Zhou et al., 1998; Hedstrom et al., 2008) was observed in the proximal processes of 19.5% of OB dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 1A; 138 of 709 TH+ neurons, five coverslips). These AIS+ dopaminergic cells had significantly larger cell bodies compared with the wider OB dopaminergic population (Fig. 1B; all TH+ neurons, mean ± SEM, soma area, 112 ± 4 μm2; AIS+ TH-expressing neurons, 153 ± 5 μm2; Mann–Whitney U = 1360, p < 0.0001).
Figure 1.
Subtypes of dopaminergic cells in dissociated rat OB culture can be defined based on the presence or absence of an AIS. A, Example images of dopaminergic neurons in OB cultures stained for TH, GABA, and ankyrin-G (AnkG). AIS− cells (top) lack AnkG staining; AIS+ cells (bottom) have a clear AnkG-defined axonal region. Lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions; asterisks show AISs of non-dopaminergic neighboring neurons. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, Histogram of soma area. C, Scatter plot of AIS start position and length for OB dopaminergic neurons in control conditions. Each dot represents one cell; Spearman's correlation, *p < 0.05.
AISs in these large OB dopaminergic cells were very short (mean length, 11.7 μm) and were located rather distally along the axon (mean start position, 15.2 μm from the soma). They were also extremely variable from cell to cell (length, SD = 4.9 μm, CV = 0.42; start position, SD = 8.5 μm, CV = 0.56). Across this variable population, we observed a weak but significant negative relationship between size and position: more distal AISs tended to be shorter (Fig. 1C; Spearman's r = −0.12, p = 0.03, n = 348 cells, 37 coverslips; Kuba et al., 2006).
Functional subdivision of OB dopaminergic neurons
To investigate functional differences between subtypes of OB dopaminergic neuron required a means of identifying and targeting these cells in a live preparation, and, to this end, we turned to dissociated cultures from transgenic mice. We first confirmed that dissociated cultures of wild-type mouse OB at 14 DIV also contained two distinct subtypes of TH+ dopaminergic neuron—AIS+ and AIS-negative (AIS−)—distinguished by the absence or presence, respectively, of a distinct axonal band of ankyrin-G immunofluorescence (Fig. 2A). As in rat neurons, the ankyrin-G-defined initial segments of mouse OB dopaminergic cells under control conditions were short (mean length, 14.32 μm), located distally from the soma (mean start position, 16.96 μm), and highly variable from cell to cell (length, SD = 7.46, CV = 0.52; start position, SD = 11.42, CV = 0.67).
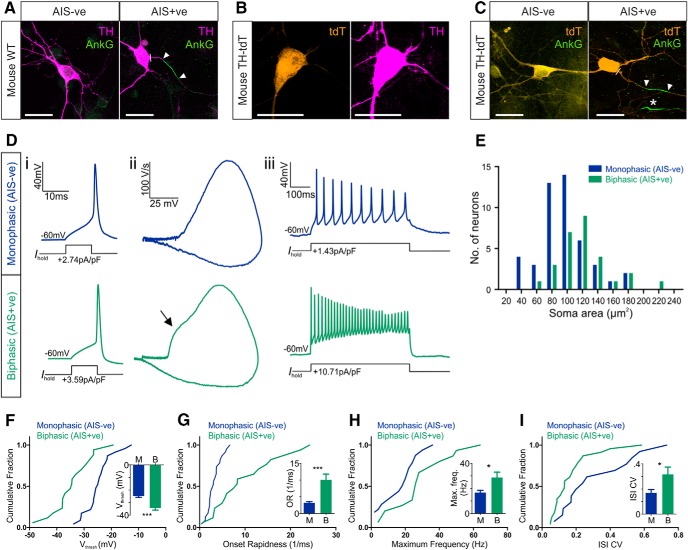
Figure 2.
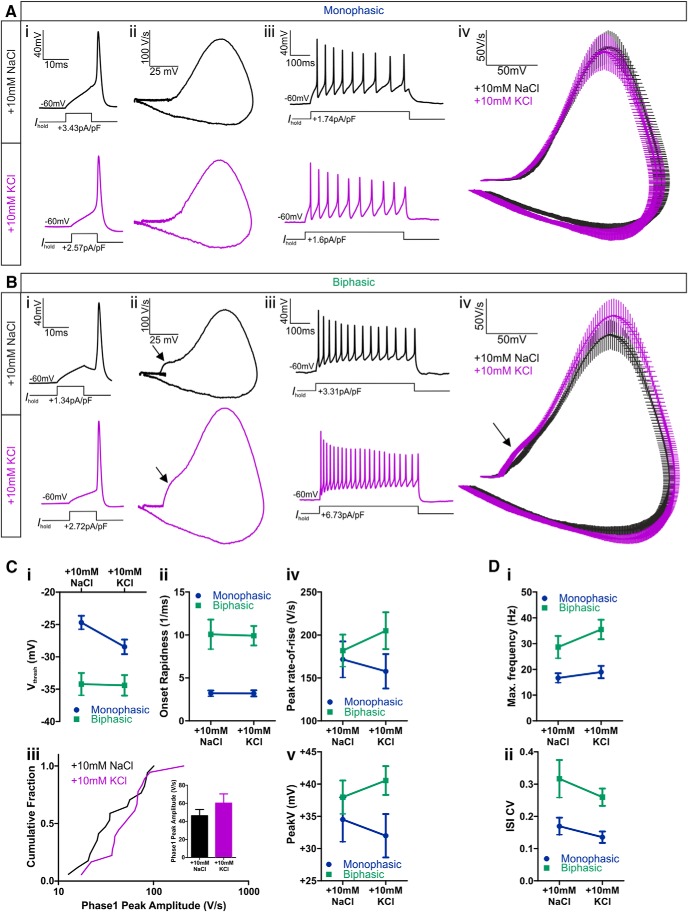
Functional differences between AIS− and AIS+ OB dopaminergic neurons. A, Example maximum intensity projection images of wild-type (WT) mouse OB dopaminergic neurons costained for TH and ankyrin-G (AnkG). AIS− cells (left) lack AnkG staining; AIS+ cells (right) have a clear AnkG-defined axonal region. In these and all subsequent images, lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, Example maximum intensity projection image of a tdT-expressing neuron from a TH–Cre × Rosa–Tdt mouse OB culture, colabeled for TH. C, Example maximum intensity projection images of TH–tdT neurons costained for AnkG. AIS− cells (left) lack AnkG staining; AIS+ cells (right) have a clear AnkG-defined axonal region. Asterisk shows the AIS of a tdT− neighboring cell. D, Example current-clamp traces from monophasic (AIS−; top) or biphasic (AIS+; bottom) TH–tdT neurons. i, Action potentials fired to threshold 10 ms somatic current injection. ii, Phase plane plots of the spikes shown in i. Arrow points to the AIS-dependent first action potential phase. iii, Action potentials fired at maximum frequency to 500 ms somatic current injection. E, Histogram of soma area. F–I, Cumulative distributions and mean ± SEM plots (insets) for voltage threshold (Vthresh; F), onset rapidness (OR; G), maximum frequency (Max. freq.; H), and interstimulus interval CV (ISI CV; I) in monophasic (M) and biphasic (B) TH–tdT neurons. t test (F, H) or Mann–Whitney test (G, I), *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.
We then prepared OB cultures from the litters of crosses between TH–Cre and Rosa–tdT conditional transgenic mice, in which a proportion of dopaminergic neurons express a red fluorescent marker that enables them to be targeted for electrophysiological recordings. Most of these tdT+ neurons were positive for TH in fixed, immunostained control tissue [Fig. 2B; 37 of 43 neurons, five coverslips; a similar proportion of Cre–Lox combined yet TH− neurons (14% here) has been reported previously for fluorescent label driven by TH–Cre expression in the OB and is thought to reflect developmental variability in TH expression in bulbar neurons; Lindeberg et al., 2004; Adam and Mizrahi, 2011; Sawada et al., 2011]. Like their wild-type counterparts, dopaminergic neurons in these transgenic cultures at 14 DIV (referred to as TH–tdT cells from here on) could also be divided into AIS− and AIS+ structural subgroups based on immunofluorescence for ankyrin-G (Fig. 2C). Initial segments in AIS+ TH–tdT neurons under control conditions were again short (mean length, 12.32 μm), distally localized (mean start position, 21.22 μm from the soma), and variable (length, SD = 5.62 μm, CV = 0.46; start position, SD = 12.74 μm, CV = 0.6).
We could now assess the functional properties of OB dopaminergic cells by targeting TH–tdT neurons in our cultures for patch-clamp electrophysiology. We started by using cell-attached recordings to confirm previous reports (Pignatelli et al., 2005; Puopolo et al., 2005) that many of these neurons display high levels of spontaneous firing. Spontaneous spikes were observed in 11 of 16 (69%) of TH–tdT cells in control conditions, with considerable variability in firing rates (mean ± SEM frequency, 8.43 ± 1.25 Hz; CV = 0.49, n = 11). To detect the presence or absence of an AIS in live dopaminergic neurons, we then used whole-cell current-clamp recordings of action potentials induced by threshold levels of somatic current injection and assessed classic spike waveform features that reflect non-somatic action potential initiation (Coombs et al., 1957; Jenerick, 1963; Khaliq and Raman, 2006; Bean, 2007; Shu et al., 2007). TH–tdT neurons were classified as “biphasic” and therefore AIS+ if a phase plane plot of spike voltage versus rate-of-rise displayed a clear double-peaked waveform (Fig. 2Di,Dii). As reported previously for midbrain dopaminergic neurons in which spike initiation often occurs rather distal to the soma (Grace and Bunney, 1983; Häusser et al., 1995; Tucker et al., 2012), the two peaks in the phase plane plot of biphasic OB TH–tdT cells were usually very clearly segregated. Conversely, TH–tdT neurons with smooth, single-peaked phase plane plots were classified as “monophasic” and therefore AIS− (Fig. 2Di,Dii). Soma area measurements confirmed that TH–tdT neurons with biphasic phase plane plots were significantly larger than monophasic TH–tdT cells (Fig. 2E; mean ± SEM, monophasic, 96.62 ± 4.80 μm2, n = 46; biphasic, 120.50 ± 6.74 μm2, n = 28; Mann–Whitney U = 373, p = 0.0026).
Our recordings revealed a number of clear functional differences between TH–tdT cells with monophasic (AIS−) and biphasic (AIS+) phase plane plots under control culture conditions. Biphasic neurons had significantly lower membrane resistance (mean ± SEM, monophasic, 928 ± 92 MΩ, n = 32; biphasic, 578 ± 106 MΩ, n = 19; Mann–Whitney U = 123, p = 0.0004) and in response to 10 ms somatic current injections (Fig. 2Di) fired spikes at more hyperpolarized voltage thresholds (Fig. 2F; mean ± SEM, monophasic, −24.7 ± 1.04 mV, n = 23; biphasic, −34.21 ± 1.73 mV, n = 17; t test, t(38) = 4.98, p < 0.0001) with faster onset rapidness (Fig. 2G; mean ± SEM, monophasic, 3.20 ± 0.33 ms−1, n = 23; biphasic, 10.07 ± 1.72 ms−1, n = 17; Mann–Whitney U = 63, p = 0.0003). Multiple spiking in response to 500 ms somatic current injections (Fig. 2Diii) also revealed important functional distinctions between dopaminergic subtypes: the lower membrane resistance of biphasic neurons led to higher rheobase values (mean ± SEM, monophasic, 2.05 ± 0.97 pA/pF, median of 0.63 pA/pF, n = 24; biphasic, 1.40 ± 0.19 pA/pF, median of 1.40 pA/pF, n = 15; Mann–Whitney U = 93, p = 0.013), but these cells then fired at higher maximum frequencies (Fig. 2H; mean ± SEM, monophasic, 16.69 ± 1.83 Hz, n = 32; biphasic, 28.67 ± 4.33 Hz, n = 15; Welch's corrected t test, t(19) = 2.55, p = 0.020) with higher CVs in interspike intervals (Fig. 2I; mean ± SEM, monophasic, 0.17 ± 0.03, n = 23; biphasic, 0.32 ± 0.06, n = 13; Mann–Whitney U = 80, p = 0.023). These differences in excitability may stem directly from the presence or absence of an AIS (Zhou et al., 1998; Zonta et al., 2011) but could equally be produced by cell type-dependent differences in non-axonal morphology (Eyal et al., 2014), biophysical properties (Baranauskas et al., 2013), and/or active conductances (Pignatelli et al., 2009).
Inverted structural plasticity at the AIS of OB dopaminergic neurons
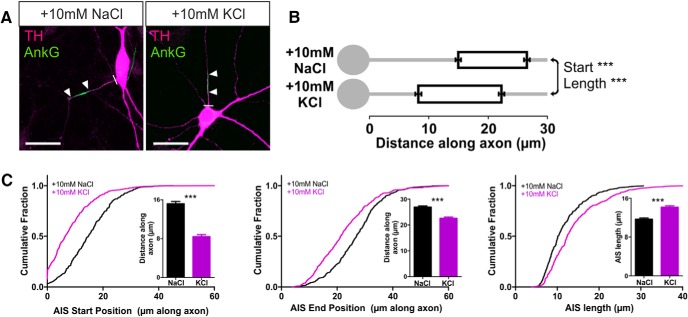
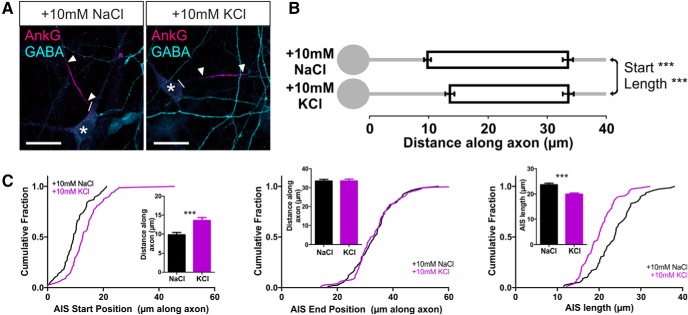
The presence of an AIS in a distinct structural and functional subset of OB dopaminergic neurons opens the possibility of a particular form of plasticity in these cells: activity-dependent structural change at the AIS itself (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Evans et al., 2013; Muir and Kittler, 2014). To study activity-dependent AIS plasticity in rat OB dopaminergic neurons, we used elevated extracellular potassium to chronically depolarize our cultures for 24 h. Increasing [K+]o by 10 mm from 11–12 DIV produced two distinct effects on the distribution of ankyrin-G in these neurons. First, the position of the AIS shifted significantly, moving toward the soma (Fig. 3; mean ± SEM AIS start position, 10 mm NaCl, 15.20 ± 0.46 μm, n = 348 cells, 37 coverslips, 8 experiments; 10 mm KCl, 8.42 ± 0.39 μm, n = 455 cells, 42 coverslips, 8 experiments; Mann–Whitney U = 41,580, p < 0.0001). Second, because this shift was more marked for the start compared with the end position of the AIS, we also observed an increase in AIS length (Fig. 3; AIS end position, 10 mm NaCl, 26.88 ± 0.49 μm; 10 mm KCl, 22.57 ± 0.48 μm, U = 56,580, p < 0.0001; AIS length, 10 mm NaCl, 11.68 ± 0.27 μm; 10 mm KCl, 14.15 ± 0.31 μm, U = 60220, p < 0.0001). These effects are in the opposite direction to those reported previously in excitatory projection neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Evans et al., 2013) but were highly reproducible when large sample sizes counteracted the considerable variability in the OB dopaminergic population and remained significant when analyses were performed at the coverslip or experiment level (by coverslip: start, Mann–Whitney U = 184, p < 0.0001; end, Mann–Whitney U = 284, p < 0.0001; length, U = 372, p < 0.0001; by experiment: start, Wilcoxon's paired test W = 36, p = 0.0078; end, W = 36, p = 0.0078; length, W = −36, p = 0.0078).
Figure 3.
Inverted structural AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons. A, Example maximum intensity projection images of rat TH+ neurons costained for ankyrin-G (AnkG) after 24 h treatment in control (10 mm NaCl) or depolarizing (10 mm KCl) conditions. Lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, AIS plot shows the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001. C, Cumulative distributions and mean ± SEM plots (insets) for AIS start position, end position, and length for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001.
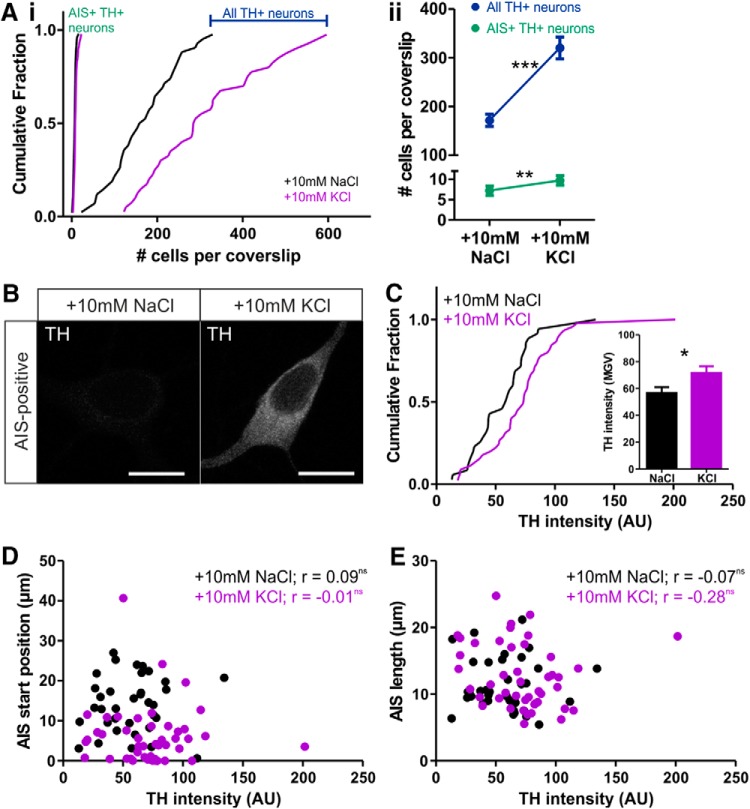
Depolarization over 24 h also reproduced another previously reported form of plasticity in these cells. Activity-dependent TH expression (Baker et al., 1983; Cave et al., 2010; Banerjee et al., 2013) resulted in a large increase in the total number of TH+ neurons detectable in our cultures (Cigola et al., 1998; Fig. 4A; mean ± SEM, 10 mm NaCl, 172 ± 13 cells per coverslip, n = 42; 10 mm KCl, 320 ± 23, n = 40; Welch's corrected t test, t(61) = 5.74, p < 0.0001). This raises the possibility that 24 h depolarization reveals a large, entirely new population of OB dopaminergic neurons with dramatically different AIS properties and that this is the cause of structural AIS differences between treatment groups. However, multiple lines of evidence show that AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons cannot be explained in this manner. Although the total number of detectable TH+ neurons per coverslip increased dramatically after 24 h of 10 mm KCl treatment, the total number of AIS+ TH-expressing neurons meeting our analysis criteria (see Materials and Methods) increased far less, leading to a decrease in the proportion of analyzable AIS+ cells among the total OB dopaminergic population (Fig. 4A; total number: mean ± SEM, 10 mm NaCl, 7.25 ± 0.53 cells per coverslip, median of 7, n = 48; 10 mm KCl, 9.68 ± 0.71, median of 8, n = 47; Mann–Whitney U = 769, p = 0.007; proportion of all TH+ neurons: mean ± SEM, 10 mm NaCl, 5.62 ± 0.63%, n = 42; 10 mm KCl, 3.70 ± 0.37%, n = 40; Mann–Whitney U = 584.5, p = 0.018). Simple calculations show that this median increase of a single AIS+ TH-expressing cell per coverslip cannot possibly account for the depolarization-induced change in, for example, AIS start position; for this to happen, each additional cell would need to possess an AIS that begins >10 μm before the start of the axon. In addition, although we found a significant increase in TH immunofluorescence intensity in AIS+ OB dopaminergic neurons after 24 h treatment with 10 mm KCl (Fig. 4B,C; mean ± SEM, 10 mm NaCl, 56.6 ± 4.4 AU, n = 35; 10 mm KCl, 71.7 ± 4.9, n = 45; Mann–Whitney U = 537, p = 0.015), TH label intensity did not correlate significantly with any structural AIS parameter in either control or depolarized treatment groups (Fig. 4D,E; 10 mm NaCl: AIS start, Spearman's r = 0.09, p = 0.61, n = 35; AIS end, Spearman's r = 0.05, p = 0.77, n = 35; AIS length, Spearman's r = −0.07, p = 0.69, n = 35; 10 mm KCl: AIS start, Spearman's r = −0.01, p = 0.93, n = 45; AIS end, Spearman's r = −0.13, p = 0.39, n = 45; AIS length, Spearman's r = −0.28, p = 0.06, n = 45). Together, these data clearly show that depolarization-induced differences in AIS structure are not a byproduct of activity-dependent TH expression in OB dopaminergic neurons.
Figure 4.
Activity-dependent TH expression does not account for AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons. A, Cumulative distributions (i) and mean ± SEM plots (ii) of TH+ cell number. Mann–Whitney test, **p < 0.01; Welch's corrected t test, ***p < 0.0001. B, Example maximum intensity projection images of AIS+ TH-expressing neurons in control (10 mm NaCl) and depolarizing (10 mm KCl) conditions. Scale bars, 10 μm. C, Cumulative distributions and mean ± SEM plot (inset) for TH intensity in each group. Mann–Whitney test, *p < 0.05. D, E, Scatter plots of TH intensity versus AIS start position (D) or length (E). Each dot represents one cell. Spearman's correlation; ns, nonsignificant.
AIS plasticity is cell-type specific in the OB
The inverted nature of activity-dependent AIS structural change in our dopaminergic neurons led us to ask whether such plasticity was a wider feature of cultured OB cells. However, studying projection neurons in dissociated rat OB culture showed that inverted AIS plasticity is a distinct feature of dopaminergic neurons in this preparation. Measuring ankyrin-G distributions in large, GABA−, presumptive mitral/tufted cells (Trombley and Westbrook, 1990) revealed a combination of “standard” activity-dependent AIS changes (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Evans et al., 2013; Muir and Kittler, 2014) that were in the opposite direction to those in their dopaminergic interneuron neighbors: a distal shift in start position was coupled with no change in end position, leading to a decrease in length after 24 h depolarization (Fig. 5A–C; mean ± SEM, start: 10 mm NaCl, 9.83 ± 0.59 μm, n = 76 cells, 8 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 13.60 ± 0.77 μm, n = 77 cells, 6 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 1852, p < 0.0001; end: 10 mm NaCl, 33.47 ± 0.87 μm, n = 76 cells, 8 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 33.53 ± 0.92 μm, n = 77 cells, 6 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 2904, p = 0.94; length: 10 mm NaCl, 22.63 ± 0.62 μm; 10 mm KCl, 19.93 ± 0.47 μm; U = 1671, p < 0.0001).
Figure 5.
Standard AIS plasticity in non-GABAergic OB neurons. A, Example maximum intensity projection images show ankyrin-G (AnkG)-positive AISs in rat GABA− OB neurons in 24 h control and depolarized conditions. Asterisks highlight non-GABAergic cell bodies. Lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. B, AIS plots show the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001. C, Cumulative distributions and mean ± SEM plots (insets) for AIS start position, end position, and length for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001.
These differences in the direction of activity-dependent AIS plasticity in two OB cell types were not attributable to differences in their immediate response to elevated extracellular potassium. Whole-cell recordings in transgenic mouse OB cultures at 14 DIV showed that our 10 mm KCl stimulus elevated the resting membrane potential by ∼12 mV in both dopaminergic tdT+ cells and neighboring large, tdT−, presumptive mitral/tufted neurons (TH–tdT: mean ± SEM, 10 mm NaCl, −37.2 ± 2.1 mV; 10 mm KCl, −26.7 ± 1.3 mV; tdT−: 10 mm NaCl, −38.3 ± 1.4 mV; 10 mm KCl, −24.9 ± 1.5 mV; two-way ANOVA, effect of treatment, F(1,35) = 55.89, p < 0.0001; effect of cell type, F(1,35) = 0.04, p = 0.84).
Inverted plasticity of sodium channel and neurofascin distributions
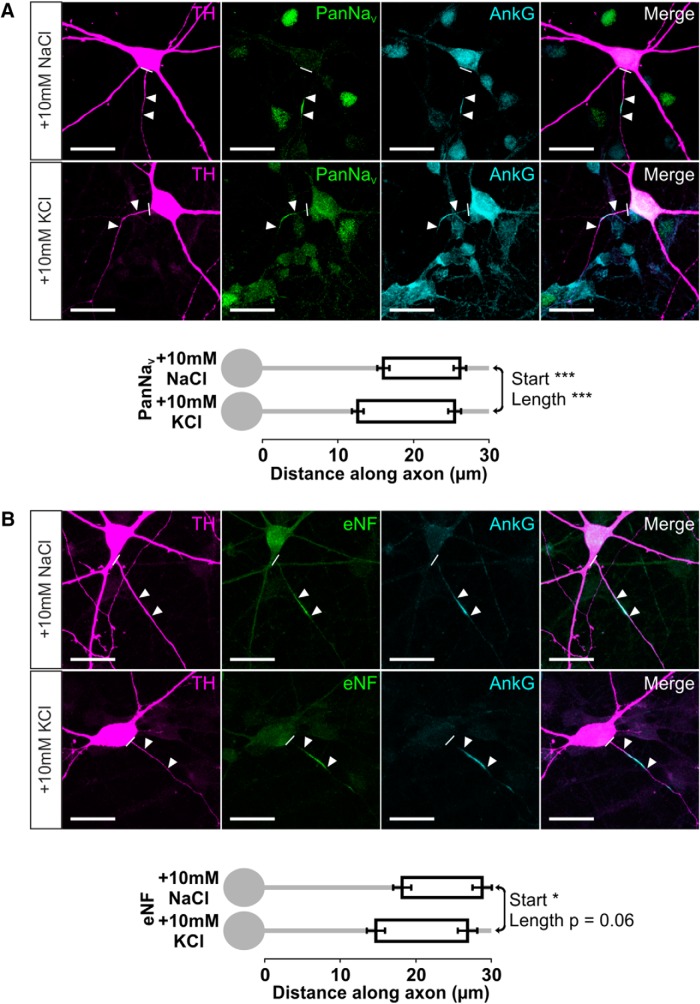
We also observed significant inverted plasticity when we examined different molecular components of the AIS in rat OB dopaminergic neurons. The distribution of all voltage-gated sodium channels (PanNaV) followed that of their binding partner ankyrin-G (Garrido et al., 2003; Lemaillet et al., 2003), moving proximally and lengthening after 24 h high potassium treatment (Fig. 6A; mean ± SEM, start: 10 mm NaCl, 16.02 ± 0.79 μm, n = 140 cells, 15 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 12.63 ± 0.77 μm, n = 155 cells, 16 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 7934, p < 0.0001; length: 10 mm NaCl, 10.07 ± 0.30 μm; 10 mm KCl, 12.76 ± 0.39 μm; U = 6772, p < 0.0001). We saw similar effects for the cell adhesion molecule neurofascin, with proximal movement and a strong trend toward lengthening after 24 h depolarization (Fig. 6B; mean ± SEM, start: 10 mm NaCl, 18.27 ± 1.20 μm, n = 66 cells, 8 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 14.79 ± 1.20 μm, n = 84 cells, 11 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 2111, p = 0.012; length: 10 mm NaCl, 10.59 ± 0.41 μm; 10 mm KCl, 12.12 ± 0.54 μm; U = 2267, p = 0.056). These experiments displayed notably variable effects of depolarization on AIS end position, but this was not attributable to protein-specific structural AIS changes. In individual neurons in both control and depolarized conditions, start position, end position, and length measures for both PanNaV and neurofascin correlated strongly and positively with values for colabeled ankyrin-G (Fig. 6; PanNaV vs ankyrin-G, 10 mm NaCl: start, r = 0.91; end, r = 0.98; length, r = 0.67, n = 47; 10 mm KCl: start, r = 0.68; end, r = 0.89; length, r = 0.74, n = 46; neurofascin vs ankyrin-G, 10 mm NaCl: start, r = 0.98; end, r = 0.99; length, r = 0.89, n = 28; 10 mm KCl: start, r = 0.79; end, r = 0.95; length, r = 0.82, n = 44; all Spearman's nonparametric correlations, p < 0.0001). Instead, although the proximal shift in AIS end position after 24 h depolarization was significant when analyzed on an experiment-by-experiment level (see above), there was considerable experiment-by-experiment variability in AIS end position effects (five of eight experiments with significant change). This could not be accounted for by the efficacy of the depolarizing stimulus, as approximated by the fold change in total detectable TH+ neurons (AIS end position change vs fold change in TH+ cell count, Pearson's r = 0.38, p = 0.36, n = 8) nor by differences in control group AIS end position (AIS end position change vs control AIS end position, Pearson's r = 0.11, p = 0.79, n = 8) but was fully predicted by power calculations based solely on the large variability of end position across individual OB dopaminergic neurons (57% power calculated post hoc from overall mean and SD values, with n = 50 in each group). Put simply, the high cell-to-cell variability in AIS end position (CV = 0.71) made it most difficult to observe depolarization-induced changes in this parameter. Nevertheless, as in other neuron types (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010), it is clear that AIS plasticity in dopaminergic neurons of the OB involves coherent changes in the distributions of all major components of the structure.
Figure 6.
Inverted AIS plasticity also occurs in the sodium channel and neurofascin distributions of OB dopaminergic neurons. A, Example maximum intensity projection images (top) of TH+ rat OB neurons costained for all NaV1 subunits (PanNaV) and ankyrin-G (AnkG) in 24 h control and depolarized conditions. Note the high background in AnkG staining attributable to pepsin treatment for PanNaV antigen retrieval (see Materials and Methods). In these and all subsequent images, lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. AIS plots (bottom) show the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001. B, Example maximum intensity projection images (top) of TH+ rat OB neurons costained for an extracellular epitope of neurofascin (eNF) and AnkG in 24 h control and depolarized conditions. AIS plots (bottom) show the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group. Mann–Whitney test, *p < 0.05.
AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic cells is bidirectional
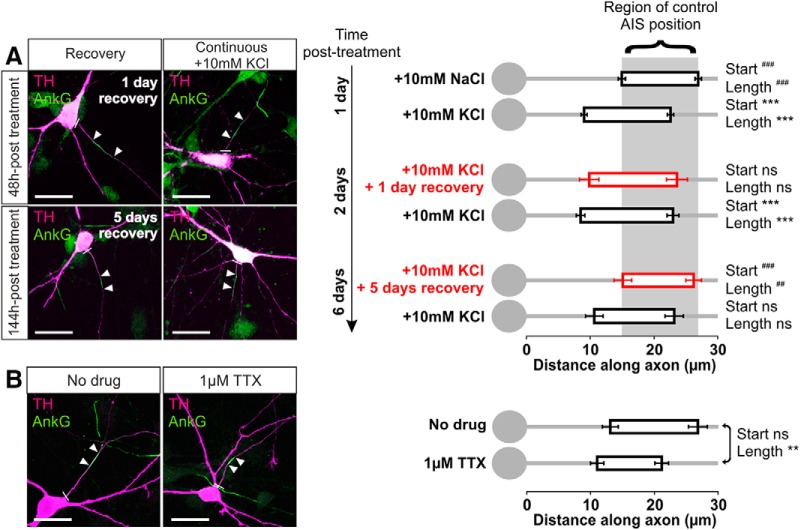
Structural AIS changes in rat OB cells were bidirectional, also occurring in response to decreases in neuronal activity induced by two separate manipulations. First, dopaminergic neurons were able to fully recover from the effects of a 24 h high potassium stimulus. When rat OB cells were treated with 10 mm KCl for 24 h and then placed back into 10 mm NaCl media, the AIS moved distally along the axon and shortened to completely recover its original position and length after 5 d (Fig. 7A; mean ± SEM, ankyrin-G start: for 24 h KCl and then 5 d NaCl, 15.11 ± 1.38 μm, n = 34 cells, 6 coverslips; Dunn's post hoc test following Kruskal–Wallis one-way ANOVA vs 24 h NaCl, p > 0.05; vs 24 h KCl, p < 0.001; length: 11.07 ± 0.87 μm vs 24 h NaCl, p > 0.05; vs 24 h KCl, p < 0.01; all effects were identical in terms of significance for concurrent PanNaV label).
Figure 7.
Bidirectional AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons. A, Example maximum intensity projection images (left) and AIS plots (right) of rat OB neurons depolarized for 1 d and then either returned to control conditions (recovery) or subjected to continued high potassium treatment for an additional 1 or 5 d. Note the high background in AnkG staining attributable to pepsin treatment for concurrent PanNaV label (see Materials and Methods, Results). In these and subsequent images, lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. Dunn's post hoc test following Kruskal-Wallis one-way ANOVA, ***p < 0.001 versus 10 mm NaCl 24 h; ##p < 0.01 and ###p < 0.001 versus 10 mm KCl 24 h; ns, nonsignificant versus both 10 mm NaCl 24 h and 10 mm KCl 24 h. B, Example maximum intensity projection images (left) and AIS plots (right) of control (no drug) or 24 h TTX-treated rat OB neurons. Mann–Whitney test, **p < 0.01; ns, nonsignificant.
We also observed structural AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons when spontaneous activity (Pignatelli et al., 2005; Puopolo et al., 2005; see above) was reduced below baseline by 24 h application of the specific voltage-gated sodium channel blocker TTX (1 μm). Interestingly, this 24 h TTX treatment did not alter AIS start position but did significantly decrease AIS length via a proximal shift in end position (Fig. 7B; mean ± SEM, ankyrin-G, start: control, 13.12 ± 1.24 μm, n = 51 cells, 4 coverslips; TTX, 11.06 ± 1.04 μm, n = 29 cells, 4 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 682, p = 0.56; end: control, 26.79 ± 1.47 μm; TTX, 21.15 ± 1.07 μm; U = 501, p = 0.017; length: control, 13.68 ± 0.86 μm; TTX, 10.09 ± 0.76 μm; U = 452, p = 0.0041). Differing effects of chronic depolarization and spike blockade on AIS start position and length suggest that these two AIS structural parameters can be regulated independently by activity (Kuba et al., 2014). However, the similar effects of both activity manipulations on AIS end position—shifted proximally in both cases—raise the possibility that they could also share some common mechanisms of action. Indeed, as reported previously for hippocampal neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b), we found that the chronic depolarization produced by 10 mm KCl was sufficient to entirely block spontaneous spike activity in OB dopaminergic cells (0 total spikes in >30 min total of cell-attached recording from 12 TH–tdT neurons), presumably by inducing chronic NaV inactivation. Formally, this spike blockade might at least partially account for the effect of 24 h depolarization on AIS end position; however, we note here that there may be crucial differences between an AIS end position shift that occurs in isolation (TTX; Fig. 7B) and one that occurs in the context of a larger start position movement (10 mm KCl; Fig. 3), and we return to this question with more pertinent data below.
Inverted AIS plasticity in dopaminergic neurons of the mouse OB
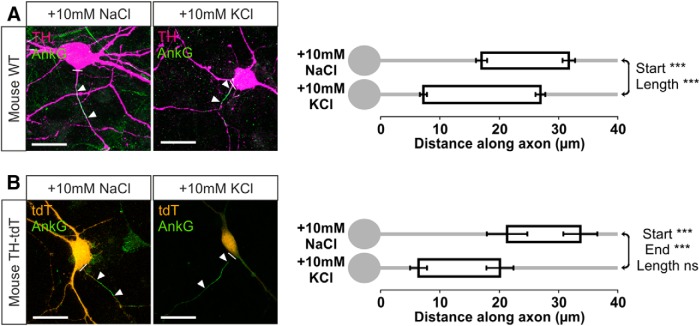
Having characterized the inverted AIS plasticity of dopaminergic neurons in rat OB cultures, we next confirmed that depolarization-induced AIS changes took the same form in dopaminergic cells from the mouse OB. In cultures of wild-type mouse OB, 24 h treatment with 10 mm KCl from 13–14 DIV induced strikingly similar effects on distributions of ankyrin-G in TH+ neurons. A proximal shift in AIS start position was accompanied by a lesser but significant proximal shift in AIS end position, leading to a concomitant increase in AIS length (Fig. 8A; mean ± SEM, start: 10 mm NaCl, 16.96 ± 0.93 μm, n = 152 cells, 12 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 7.20 ± 0.59 μm, n = 150 cells, 10 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 5165, p < 0.0001; end: 10 mm NaCl, 31.61 ± 1.06 μm; 10 mm KCl, 26.84 ± 0.83 μm; U = 9060, p = 0.002; length: 10 mm NaCl, 14.65 ± 0.60 μm; 10 mm KCl, 19.65 ± 0.65 μm; U = 6909, p < 0.0001).
Figure 8.
Inverted AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons from wild-type and TH–tdT mice. A, Example maximum intensity projection images (left) of wild-type (WT) mouse OB neurons colabeled for TH and ankyrin-G (AnkG) after 24 h control or depolarizing treatment. In this and all subsequent images, lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. AIS plots (right) show the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001. B, Example maximum intensity projection images (left) and AIS plots (right) of TH–Tdt+ neurons after 24 h control or depolarization treatment. Mann–Whitney test, ***p < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant.
We found similar effects in a smaller sample of TH–tdT neurons from transgenic cultures. Here, 24 h depolarization with 10 mm KCl produced a large and significant inward shift of both AIS start and end positions, resulting in a nonsignificant trend toward increased AIS length (Fig. 8B; mean ± SEM, start: 10 mm NaCl, 21.22 ± 3.41 μm, n = 14 cells, 12 coverslips; 10 mm KCl, 6.35 ± 1.42 μm, n = 28 cells, 14 coverslips; Mann–Whitney U = 54, p = 0.0002; end: 10 mm NaCl, 33.54 ± 2.86 μm; 10 mm KCl, 20.03 ± 2.29 μm; U = 61, p = 0.0003; length: 10 mm NaCl, 12.32 ± 1.50 μm; 10 mm KCl, 13.68 ± 1.20 μm; U = 173, p = 0.55). These AIS changes occurred on a background of stable TH–tdT cell numbers in both treatment groups (mean ± SEM, total tdT+ cells per coverslip: 10 mm NaCl, 7.05 ± 0.73, n = 22; 10 mm KCl, 8.79 ± 1.04, n = 19; t test, t(39) = 1.40, p = 0.17), demonstrating again (see above; Fig. 4) that structural AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons cannot be explained by the activity-dependent emergence of a new population of detectable TH+ cells.
Functional correlates of structural AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons
Structural changes in the presumed zone of action potential initiation in rat (Fig. 3) and mouse (Fig. 8) OB dopaminergic neurons, especially the activity-dependent alterations of sodium channel distributions in these cells (Fig. 6), would be predicted to have functional effects on neuronal excitability (Kuba et al., 2006, 2010, 2014; Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kaphzan et al., 2011, 2013). Indeed, in current-clamp recordings from TH–tdT neurons in transgenic mouse culture, we observed trends toward increased excitability in biphasic (AIS+) dopaminergic cells that had undergone 24 h depolarization. Under identical recording conditions, mean action potential phase plane plots for biphasic neurons revealed a stronger voltage rate-of-rise in 10 mm KCl-treated cells. This was most pronounced in the initial portion of the waveform (Fig. 9Biv) but continued throughout the entire rising phase of the spike. No such differences were observed between the mean action potential phase plane plots of monophasic (AIS−) TH–tdT cells (Fig. 9Aiv).
Figure 9.
Action potential properties of AIS+ and AIS− OB dopaminergic cells after 24 h control or depolarization treatment. A, B, Example current-clamp traces from monophasic (A) or biphasic (B) TH–tdT neurons after 24 h 10 mm NaCl or KCl treatment. i, Action potentials fired to threshold 10 ms somatic current injection. ii, Phase plane plots of the spikes shown in i. iii, Action potentials fired at maximum frequency to 500 ms somatic current injection. iv, Overlaid mean ± SEM phase plane plots from each treatment group. Arrows point to the AIS-dependent first action potential phase in biphasic neurons. C, Comparisons of single spike properties. i–v, Plots of the mean ± SEM for all groups. i, Voltage threshold (Vthresh); ii, onset rapidness; iv, peak rate-of-rise; v, peak voltage (V). iii, Cumulative fraction plot and mean ± SEM plot (inset) for first phase peak amplitude in biphasic neurons. D, Comparisons of multiple spiking properties. Plots of mean ± SEM for all groups. i, Maximum firing frequency; ii, CV in interspike interval (ISI).
Individual measures of spike waveform parameters also revealed trends toward faster and larger action potentials in 10 mm KCl-treated biphasic cells. The amplitude of the first, AIS-dependent phase of the biphasic spike waveform was larger on average in high potassium-treated neurons (Fig. 9Ciii; Table 1), as were the maximum voltage rate-of-rise (Fig. 9Civ; Table 1) and the peak spike voltage (Fig. 9Cv; Table 1). However, there was marked variability within both treatment groups—mirroring the variability in AIS structural measures described above—and these differences did not reach statistical significance (Table 1; phase 1 peak amplitude, CV = 0.62, Mann–Whitney U = 119, p = 0.27; maximum rate-of-rise, CV = 0.42, two-way ANOVA effect of treatment, F(1,75) = 0.05, p = 0.82; effect of treatment × cell-type interaction, F(1,75) = 0.80, p = 0.37; peak spike voltage, CV = 0.28, two-way ANOVA on ranks effect of treatment, F(1,75) = 0.09, p = 0.77; effect of treatment × cell-type interaction, F(1,75) = 0.99, p = 0.32). We found a similar effect for maximum spike number: there was a trend toward higher frequencies in potassium-treated biphasic neurons (Fig. 9Di; Table 1), but this was accompanied by large inter-neuron variability and a lack of statistical significance (Table 1; CV = 0.59, two-way ANOVA effect of treatment, F(1,90) = 2.42, p = 0.12; effect of treatment × cell-type interaction, F(1,90) = 0.60, p = 0.44). Additionally, we observed no effect of depolarization in biphasic neurons on any of the other measures—voltage threshold, onset rapidness, rheobase, or interspike interval CV—that differed significantly between monophasic and biphasic OB dopaminergic cells (Fig. 9C,D; Table 1), nor did we find significant effects of depolarization treatment on any spike parameter in monophasic neurons (Fig. 9C,D; Table 1). Finally, although membrane resistance is regulated by activity in excitatory hippocampal neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; O'Leary et al., 2010; Evans et al., 2013), it was not affected by 24 h depolarization in either subtype of OB dopaminergic interneuron (mean ± SEM, monophasic: 10 mm NaCl, 928 ± 92 MΩ, n = 32; 10 mm KCl, 1160 ± 114 MΩ, n = 40; biphasic: 10 mm NaCl, 578 ± 106 MΩ, n = 19; 10 mm KCl, 582 ± 67 MΩ n = 20; two-way ANOVA on ranks effect of treatment, F(1,107) = 1.53, p = 0.22; effect of treatment × cell-type interaction, F(1,107) = 0.11, p = 0.74). Together, these data suggest that high variability in AIS structural parameters is accompanied by similar variability in functional spike parameters in OB dopaminergic neurons and that inverted AIS plasticity in these cells is therefore associated only with suggestive trends toward altered excitability (see Discussion).
Table 1.
Action potential parameters of OB dopaminergic neurons
| Parameter | Monophasic mean ± SEM (n) |
Biphasic mean ± SEM (n) |
Effect p value |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 mm NaCl | 10 mm KCl | 10 mm NaCl | 10 mm KCl | Cell type | Treatment | Interaction | |
| Vthresh (mV) | −24.7 ± 1.0 (23) | −27.7 ± 1.1 (21) | −34.2 ± 1.7 (17) | −34.6 ± 1.5 (18) | <0.0001*** | 0.15 | 0.19 |
| Onset rapidness (ms−1) | 3.2 ± 0.3 (23) | 3.2 ± 0.4 (19) | 10.7 ± 1.7 (17) | 9.9 ± 1.1 (18) | <0.0001*** | 0.52 | 0.55 |
| Phase 1 peak amplitude (V/s) | n/a | n/a | 46.1 ± 7.0 (17) | 60.1 ± 10.1 (18) | n/a | 0.27 | n/a |
| Peak rate-of-rise (V/s) | 172 ± 21 (23) | 158 ± 20 (21) | 182 ± 19 (17) | 205 ± 21 (18) | 0.17 | 0.82 | 0.37 |
| Peak voltage (mV) | 34.5 ± 3.4 (23) | 32.0 ± 3.4 (21) | 38.0 ± 2.6 (17) | 40.5 ± 2.2 (18) | 0.14 | 0.77 | 0.32 |
| Action potential width (ms) | 1.06 ± 0.06 (23) | 1.02 ± 0.06 (21) | 1.09 ± 0.07 (17) | 1.00 ± 0.06 (18) | 0.81 | 0.24 | 0.87 |
| Rheobase (pA/pF) | 2.05 ± 0.97 (24) | 1.37 ± 0.56 (26) | 1.40 ± 0.19 (15) | 1.52 ± 0.27 (15) | 0.001*** | 0.84 | 0.66 |
| Afterhyperpolarization (mV) | −53.4 ± 1.5 (24) | −55.5 ± 1.2 (26) | −54.1 ± 1.3 (15) | −57.0 ± 1.4 (15) | 0.63 | 0.12 | 0.53 |
| Maximum frequency (Hz) | 16.7 ± 1.8 (32) | 19.0 ± 2.4 (31) | 28.7 ± 4.3 (15) | 35.5 ± 3.8 (16) | <0.0001*** | 0.12 | 0.43 |
| Interstimulus interval CV | 0.17 ± 0.03 (23) | 0.14 ± 0.02 (26) | 0.32 ± 0.06 (13) | 0.26 ± 0.03 (15) | <0.0001*** | 0.60 | 0.40 |
Voltage threshold (Vthresh), peak rate-of-rise, peak voltage, and maximum frequency variables were normally distributed and analyzed with a standard two-way ANOVA. All other variables were non-normally distributed and analyzed with a two-way ANOVA on ranks, except phase 1 peak amplitude—measurable only in biphasic neurons—for which the result of a Mann–Whitney two-sample test is reported.
***p ≤ 0.0001.
Signaling pathways for inverted AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons
Given the inverted nature of activity-dependent AIS changes in OB dopaminergic neurons, it was important to finally address the signaling pathways responsible for this form of plasticity—might they be entirely different to those used by excitatory neurons?
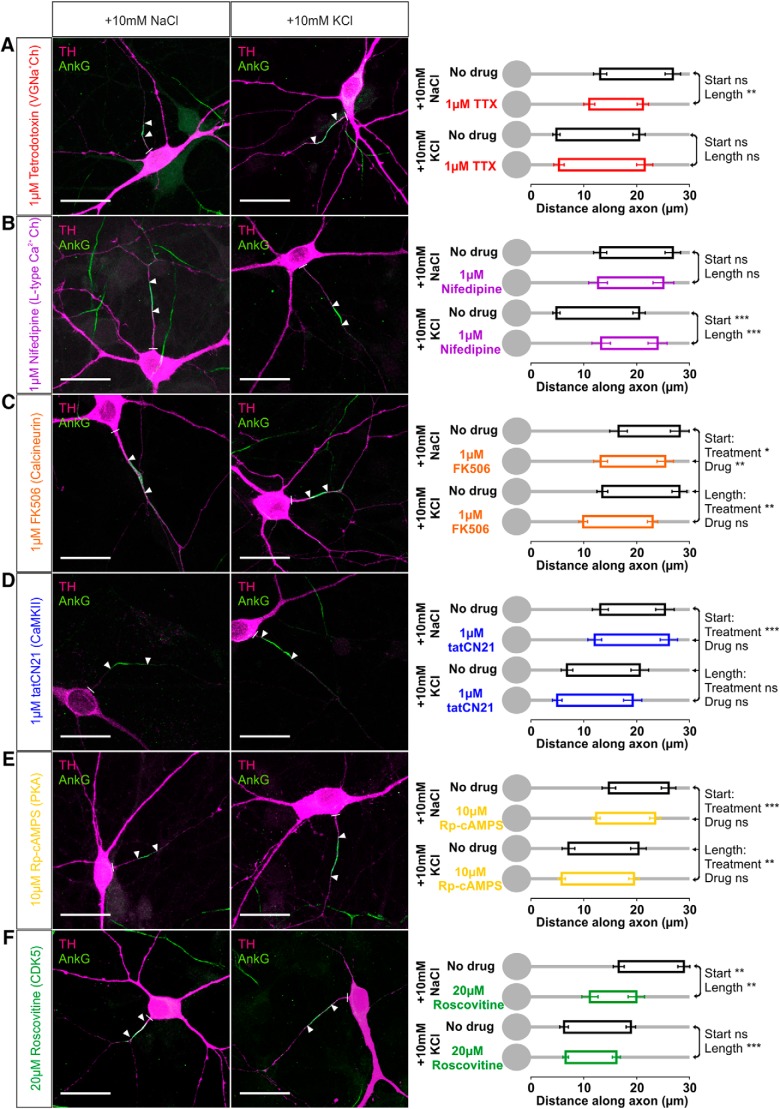
In fact, using 24 h depolarization in rat cultures in the presence of specific pharmacological agents showed that the trigger for AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic cells is the same as in glutamatergic hippocampal neurons: activation of L-type CaV1 calcium channels (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013). We first found that, although blocking spontaneous firing could induce a limited form of structural AIS change in OB dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 7B), action potentials per se were not required for depolarization-induced plasticity in these cells (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013). In the presence of 1 μm TTX, a 10 mm KCl stimulus still resulted in AISs at the same position and with the same length as the 10 mm KCl stimulus alone (Fig. 10A; start: two-way ANOVA on ranks, effect of treatment, F(1,193) = 52.08, p < 0.0001; drug, F(1,193) = 0.16, p = 0.69; treatment × drug interaction, F(3,193) = 0.66, p = 0.42; Mann–Whitney post hoc test for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 1124, p = 0.19; length: effect of treatment × drug interaction, F(1,193) = 7.06, p = 0.009; post hoc test for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 1233, p = 0.54). In contrast, selectively blocking L-type voltage-gated calcium channels with 1 μm nifedipine (Lee et al., 2006) produced no effect on its own but completely prevented depolarization-induced changes in AIS start position and length (Fig. 10B; start: effect of treatment × drug interaction, F(1,196) = 11.88, p = 0.001; post hoc test for control vs control with drug, U = 524, p = 0.89; for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 813, p < 0.0001; length: effect of treatment × drug interaction, F(1,196) = 3.14, p = 0.078; post hoc test for control vs control with drug, U = 476, p = 0.46; for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 1076, p = 0.0002). Importantly, AIS end position under 10 mm KCl plus nifedipine conditions was not significantly different from control (post hoc test for control vs depolarization with drug, U = 875, p = 0.13), showing that all of the AIS structural changes induced by 24 h depolarization are dependent on L-type channel activation. Although we cannot rule it out as a formal possibility, this suggests that chronic depolarization and TTX treatments do not in fact share common mechanisms in determining AIS end position in OB dopaminergic neurons (see above), because if they did, spike blockade with TTX would need to act by the improbable mechanism of increasing L-type signaling.
Figure 10.
Signaling pathways for AIS plasticity in rat OB dopaminergic neurons. Example maximum intensity projection images (left) show colabel for TH and ankyrin-G (AnkG) in 24 h control and depolarized conditions in the presence of various pharmacological agents: A, TTX for voltage-gated sodium channels; B, nifedipine for L-type CaV1 calcium channels; C, FK-506 for calcineurin; D, tatCN21 for CaMKII; E, Rp-cAMPs for PKA; F, roscovitine for cdk5. Lines show axon start; arrowheads show AIS start and end positions. Scale bars, 20 μm. AIS plots (right) show the mean ± SEM AIS start and end positions for each group in a 2 × 2 treatment × drug design. Post hoc pairwise comparisons between control and drug conditions in both treatment groups are reported when there was a significant treatment × drug interaction in a two-way ANOVA on ranks (A, B, F); Mann–Whitney test with Bonferroni's correction, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant. Otherwise, two-way ANOVA effects of treatment and drug across all groups are reported (C, D, E); *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ns, nonsignificant.
However, although the activity-dependent trigger for AIS plasticity remains the same, the signaling pathways downstream of L-type calcium channels are different in OB dopaminergic cells. Whereas AIS relocation in excitatory hippocampal neurons depends on the calcium-dependent phosphatase calcineurin (Evans et al., 2013), blocking this pathway with 1 μm FK-506 produced an independent inward shift of AIS position in dopaminergic OB cells but did not prevent an additional proximal shift and length increase after high potassium stimulation (Fig. 10C; two-way ANOVA on ranks, start: effect of treatment, F(1,190) = 5.42, p = 0.021; effect of drug, F(1,190) = 9.31, p = 0.003; effect of treatment × drug interaction, F(1,190) = 0.03, p = 0.86; length: treatment, F(1,190) = 8.33, p = 0.004; drug, F(1,190) = 0.15, p = 0.70; treatment × drug, F(1,190) = 0.91, p = 0.34). Therefore, calcineurin plays a role in determining AIS position but does not mediate depolarization-induced AIS plasticity in bulbar dopaminergic neurons. Neither is there a role in these cells for the second pathway contributing to AIS plasticity in hippocampal neurons (Evans et al., 2013): blocking CaMKII with 1 μm tatCN21 had no effect on either baseline or depolarization-induced AIS position or length in OB dopaminergic cells (Fig. 10D; start: treatment, F(1,154) = 28.08, p < 0.0001; drug, F(1,154) = 0.71, p = 0.40; treatment × drug, F(1,154) = 0.36, p = 0.55; length: treatment, F(1,154) = 0.05, p = 0.83; drug, F(1,154) = 1.70, p = 0.20; treatment × drug, F(1,154) = 0.86, p = 0.36). Protein kinase A (PKA), known to play a role in depolarization-induced plasticity in dopaminergic cells in culture (Cigola et al., 1998), does not mediate activity-dependent AIS plasticity in these neurons either, because blocking its activity with 10 μm Rp-cAMPs also had no effect on AIS position or length in either baseline or depolarized conditions (Fig. 10E; start: treatment, F(1,212) = 77.58, p < 0.0001; drug, F(1,212) = 0.77, p = 0.38; treatment × drug, F(1,212) = 0.08, p = 0.78; length: treatment, F(1,212) = 9.60, p = 0.002; drug, F(1,212) = 0.33, p = 0.57; treatment × drug, F(1,212) = 0.36, p = 0.55).
Although our data show that none of the pathways that promote AIS plasticity in excitatory hippocampal neurons (Evans et al., 2013) are responsible for inverted plasticity in OB dopaminergic cells, we did identify a pathway that opposes activity-dependent AIS position changes in these neurons. In Drosophila mushroom body gamma neurons, reductions in cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (cdk5) activity led to proximal relocation and decreased length of an AIS-like structure (Trunova et al., 2011), and we saw strikingly similar effects in OB dopaminergic neurons. Blocking cdk5 with 20 μm roscovitine over 24 h produced an inward movement of AIS position in our OB dopaminergic cells in baseline conditions (Fig. 10F; two-way ANOVA on ranks, start: effect of treatment, F(1,212) = 58.61, p < 0.0001; effect of drug, F(1,212) = 4.5, p = 0.035; effect of treatment × drug interaction, F(1,212) = 11.97, p = 0.001; Mann–Whitney post hoc test for control vs control with drug, U = 488, p = 0.002). Importantly, unlike the activity-independent effects of calcineurin described above, this effect was not additive with high potassium-induced inward movement (Fig. 10F; post hoc test for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 1785, p = 0.12), suggesting that depolarization and cdk5 act in opposite directions in a common pathway to control this structural feature. However, as well as inducing an inward shift of AIS position, roscovitine treatment also produced a decrease in AIS length that was independent of depolarization treatment (Fig. 10F; length: treatment, F(1,212) = 0.76, p = 0.39; drug, F(1,212) = 28.48, p < 0.0001; treatment × drug, F(1,212) = 0.17, p = 0.68; Mann–Whitney post hoc test for control vs control with drug, U = 510, p = 0.0038; for depolarization vs depolarization with drug, U = 1145, p < 0.0001).
Together, these data show that multiple cellular pathways control activity-dependent and activity-independent changes in the AIS of OB dopaminergic neurons, a complex arrangement that may give these cells control over all elements of AIS structure.
Discussion
Our results reveal structural and functional subdivision within the dopaminergic population of the OB: a minority of large, AIS-possessing OB dopaminergic neurons are more excitable than their more numerous, smaller, AIS− neighbors. Initial segments in this subpopulation of inhibitory interneurons relocated proximally and lengthened in response to elevated neuronal activity. These changes were in the opposite direction to those in non-GABAergic OB cells and to those reported previously for excitatory neurons elsewhere in the brain.
Heterogeneity in dopaminergic cells of the OB
The classification of distinct cellular subtypes can be crucial for understanding their functional roles, not least for dopaminergic neurons (Henny et al., 2012; Roeper, 2013; Lammel et al., 2014). In the OB, dopaminergic cells have long been known to be heterogeneous, with at least two TH+ subtypes identified on histological criteria in multiple species, including humans (Halász et al., 1981; Baker, 1986; Smith et al., 1991; Hoogland and Huisman, 1999; Kosaka and Kosaka, 2009, 2011). Morphological analysis recently divided OB dopaminergic neurons into “oligoglomerular” cells that contact a few local glomeruli and “polyglomerular” cells that ramify across large stretches of the GL, identifying both types as “short-axon” cells (Kiyokage et al., 2010). Although the nomenclature differs, this scheme may fit with an alternative framework based on cell size, developmental origin, and the presence of an AIS (Kosaka and Kosaka, 2009, 2011). Here, large, AIS+ OB dopaminergic neurons—possibly equivalent to polyglomerular cells—are generated exclusively in early embryonic development, whereas smaller AIS− cells—possibly equivalent to oligoglomerular neurons—are continually produced throughout adult life (Kosaka and Kosaka, 2009, 2011). Our data further support this classification, showing that the presence of an AIS in OB dopaminergic cells is associated with significantly larger soma size (Figs. 1, 2). That this subdivision is maintained in dissociated culture shows that OB dopaminergic cell types can be intrinsically determined in the absence of both bulbar architecture and external input.
We also found the first evidence, to our knowledge, of functional differences between subclasses of OB dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 2). Although physiological distinctions have been identified between OB dopaminergic neurons at different stages of maturity (Pignatelli et al., 2009), segregating GL dopaminergic cells on the basis of their membrane capacitance revealed no obvious differences between groups (Pignatelli et al., 2005). Given the overlap in soma size distributions between different subclasses of OB dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 1; Kosaka and Kosaka, 2009), segregating these cells on the basis of their AIS signatures (Fig. 2; Bean, 2007) may allow cleaner functional separation of individual subtypes.
Inverted AIS plasticity in inhibitory interneurons
The AISs of inhibitory interneurons can differ markedly from those of excitatory projection neurons in baseline position and length (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013) and/or the expression and spatial distribution of voltage-gated ion channels (Lorincz and Nusser, 2008). However, previous studies have not reported activity-dependent plasticity at the AIS of inhibitory cells (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013), perhaps because of significant heterogeneity within hippocampal GABAergic neurons (Klausberger and Somogyi, 2008). Therefore, our data provide the first description of structural AIS plasticity in an interneuron population. We find that elevated activity produces a proximal relocation coupled with a lengthening of the AIS in OB dopaminergic neurons (Fig. 3), changes that are in the opposite direction to those in non-GABAergic OB cells (Fig. 5) and also in the opposite direction to all previously reported activity-dependent alterations of AIS structure in excitatory neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Kaphzan et al., 2011, 2013; Evans et al., 2013; Muir and Kittler, 2014). Interestingly, although the voltage-dependent trigger for AIS plasticity—L-type CaV1 calcium channels—is the same in OB dopaminergic cells (Fig. 10) and hippocampal excitatory neurons (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Evans et al., 2013), different pathways operate downstream of these channels to produce opposing changes in AIS structure (Fig. 10; Evans et al., 2013).
These results fit a wider general pattern in which long-term plasticity assumes the opposite form in inhibitory versus excitatory neurons. Homeostatic synaptic plasticity, for example, generally results in opposing alterations in glutamatergic and GABAergic transmission (Turrigiano et al., 1998; Kilman et al., 2002; Hartman et al., 2006; Frias and Wierenga, 2013). Sensory deprivation leads to decreases in the density of dendritic spines (Keck et al., 2011) and branch tips (Chen et al., 2011) along with reductions in axonal bouton density (Marik et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2011; Keck et al., 2011) in inhibitory cortical neurons, which contrasts with concomitant elevations in spine turnover (Keck et al., 2008) or axonal growth (Yamahachi et al., 2009; Marik et al., 2010) in neighboring pyramidal cells. In the OB, activity-dependent alterations in the structure of postnatally generated interneurons (Saghatelyan et al., 2005; Mizrahi, 2007; Livneh et al., 2009) contrast not only with the lack of such changes in the resident developmentally generated GABAergic population (Saghatelyan et al., 2005) but also with the striking structural stability of mitral/tufted cell dendrites (Mizrahi and Katz, 2003). Therefore, our data reveal a novel form of plasticity in OB dopaminergic cells, which, like many other forms of structural plasticity in inhibitory interneurons, takes the opposite form to changes observed in excitatory cells.
Functional consequences of inverted AIS plasticity
Why might inverted activity-dependent changes to dopaminergic neuron AISs occur in the OB? If these changes are, like other forms of AIS plasticity, associated with alterations in intrinsic excitability (Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Kaphzan et al., 2011, 2013), they should result in coordinated effects on the spike-dependent release of both GABA and dopamine from these neurons (Maher and Westbrook, 2008; Borisovska et al., 2013). At the local level, this could alter chronic and phasic inhibitory feedback of release probability at olfactory sensory neuron terminals (Hsia et al., 1999; Ennis et al., 2001; McGann et al., 2005; McGann, 2013), fine-tuning levels of gain control at this first synapse in the olfactory system. However, it is unclear whether AIS-containing OB dopaminergic cells contribute to this local feedback inhibition. If they indeed represent the population of large polyglomerular cells that ramify across large areas of the GL (see above), their primary functional role may instead be to provide lateral inhibition of spatially segregated bulbar inputs (Liu et al., 2013; Whitesell et al., 2013). Here the dual effect of excitability changes on both GABA and dopamine release would be extremely interesting, given that release of these dual transmitters follows distinct time courses (Borisovska et al., 2013) and has opposing inhibitory and rebound-excitation effects on postsynaptic external tufted cells (Liu et al., 2013).
However, predicting any functional consequences of inverted AIS plasticity in OB dopaminergic neurons on information processing in glomerular circuits is made difficult by the lack of significant functional change we observe in these neurons (Fig. 9). This could be attributable to a number of factors. First, the highly significant structural effects we observed (Fig. 3) are nevertheless subtle and occur on a background of high baseline variability. Observing any associated functional changes may therefore require a prohibitive number of electrophysiological recordings. Indeed, a priori analyses based on our current data predict that sample sizes upward of 80 cells per group would be needed for 80% power in detecting group differences. Previous studies finding small changes in AIS structure have relied on computational models rather than experimental data to predict associated changes in excitability (Baalman et al., 2013; Harty et al., 2013). Second, structural changes at OB dopaminergic AISs may be compensatory at the single-cell level or at the level of the AIS itself. The predicted effects of AIS relocation within the proximal axon are complex and depend on a number of factors, including axon morphology, axoplasmic resistivity, and baseline AIS structure (Kuba et al., 2006, 2010, 2014; Grubb and Burrone, 2010b; Wang et al., 2011; Baranauskas et al., 2013). In certain models, a proximal shift in AIS location, as observed here, is predicted to decrease neuronal excitability by moving the site of action potential initiation closer to the substantial current sink formed by the somatodendritic compartment (Kuba et al., 2006; Baranauskas et al., 2013). If this is the case in OB dopaminergic neurons, any associated decrease in excitability might offset the increased excitability expected to arise from AIS lengthening (Kuba et al., 2010, 2014; Kaphzan et al., 2011, 2013). Alternatively, functional changes produced by activity-dependent AIS structural plasticity might be offset by activity-dependent alterations of intrinsic or voltage-dependent currents either at the AIS or elsewhere in the neuron. Finally, given the crucial role of the AIS in controlling transport into the axon (Song et al., 2009; Rasband, 2010), perhaps activity-dependent changes at the structure are necessary not to alter excitability but to allow altered axonal transport (MacAskill and Kittler, 2010) and/or axonal growth dynamics (Marik et al., 2010; Chen et al., 2011; Keck et al., 2011; Frias and Wierenga, 2013) in the face of perturbed network input.
Footnotes
This work was supported by a Wellcome Trust Career Development Fellowship (M.S.G.) and a Wellcome Trust Sir Henry Wellcome Fellowship (E.G.). We thank Robert Hindges for Rosa-tdT mice, Miles Houslay for Rp-cAMPs, Mark Evans and Adna Dumitrescu for assistance with cell culture and discussions throughout the project, and Laura Andreae for comments on this manuscript.
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0), which permits unrestricted use, distribution and reproduction in any medium provided that the original work is properly attributed.
References
- Adam Y, Mizrahi A. Long-term imaging reveals dynamic changes in the neuronal composition of the glomerular layer. J Neurosci. 2011;31:7967–7973. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0782-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akritas MG. The rank transform method in some two-factor designs. J Am Stat Assoc. 1990;85:73–78. doi: 10.1080/01621459.1990.10475308. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Baalman KL, Cotton RJ, Rasband SN, Rasband MN. Blast wave exposure impairs memory and decreases axon initial segment length. J Neurotrauma. 2013;30:741–751. doi: 10.1089/neu.2012.2478. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H. Species differences in the distribution of substance P and tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactivity in the olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 1986;252:206–226. doi: 10.1002/cne.902520206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker H, Kawano T, Margolis FL, Joh TH. Transneuronal regulation of tyrosine hydroxylase expression in olfactory bulb of mouse and rat. J Neurosci. 1983;3:69–78. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.03-01-00069.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerjee K, Akiba Y, Baker H, Cave JW. Epigenetic control of neurotransmitter expression in olfactory bulb interneurons. Int J Dev Neurosci. 2013;31:415–423. doi: 10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2012.11.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baranauskas G, David Y, Fleidervish IA. Spatial mismatch between the Na+ flux and spike initiation in axon initial segment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:4051–4056. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1215125110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bastien-Dionne PO, David LS, Parent A, Saghatelyan A. Role of sensory activity on chemospecific populations of interneurons in the adult olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 2010;518:1847–1861. doi: 10.1002/cne.22307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean BP. The action potential in mammalian central neurons. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2007;8:451–465. doi: 10.1038/nrn2148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender KJ, Trussell LO. The physiology of the axon initial segment. Annu Rev Neurosci. 2012;35:249–265. doi: 10.1146/annurev-neuro-062111-150339. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borisovska M, Bensen AL, Chong G, Westbrook GL. Distinct modes of dopamine and GABA release in a dual transmitter neuron. J Neurosci. 2013;33:1790–1796. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4342-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buffington SA, Rasband MN. The axon initial segment in nervous system disease and injury. Eur J Neurosci. 2011;34:1609–1619. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2011.07875.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cave JW, Akiba Y, Banerjee K, Bhosle S, Berlin R, Baker H. Differential regulation of dopaminergic gene expression by Er81. J Neurosci. 2010;30:4717–4724. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0419-10.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen JL, Lin WC, Cha JW, So PT, Kubota Y, Nedivi E. Structural basis for the role of inhibition in facilitating adult brain plasticity. Nat Neurosci. 2011;14:587–594. doi: 10.1038/nn.2799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cigola E, Volpe BT, Lee JW, Franzen L, Baker H. Tyrosine hydroxylase expression in primary cultures of olfactory bulb: role of L-type calcium channels. J Neurosci. 1998;18:7638–7649. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.18-19-07638.1998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark BD, Goldberg EM, Rudy B. Electrogenic tuning of the axon initial segment. Neuroscientist. 2009;15:651–668. doi: 10.1177/1073858409341973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coombs JS, Curtis DR, Eccles JC. The generation of impulses in motoneurones. J Physiol. 1957;139:232–249. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ennis M, Zhou FM, Ciombor KJ, Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Hayar A, Borrelli E, Zimmer LA, Margolis F, Shipley MT. Dopamine D2 receptor-mediated presynaptic inhibition of olfactory nerve terminals. J Neurophysiol. 2001;86:2986–2997. doi: 10.1152/jn.2001.86.6.2986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans MD, Sammons RP, Lebron S, Dumitrescu AS, Watkins TBK, Uebele VN, Renger JJ, Grubb MS. Calcineurin signaling mediates activity-dependent relocation of the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2013;33:6950–6963. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0277-13.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eyal G, Mansvelder HD, de Kock CPJ, Segev I. Dendrites impact the encoding capabilities of the axon. J Neurosci. 2014;34:8063–8071. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5431-13.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frias CP, Wierenga CJ. Activity-dependent adaptations in inhibitory axons. Front Cell Neurosci. 2013;7:219. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2013.00219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrido JJ, Giraud P, Carlier E, Fernandes F, Moussif A, Fache MP, Debanne D, Dargent B. A targeting motif involved in sodium channel clustering at the axonal initial segment. Science. 2003;300:2091–2094. doi: 10.1126/science.1085167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grace AA, Bunney BS. Intracellular and extracellular electrophysiology of nigral dopaminergic neurons–2. Action potential generating mechanisms and morphological correlates. Neuroscience. 1983;10:317–331. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(83)90136-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb MS, Burrone J. Building and maintaining the axon initial segment. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2010a;20:481–488. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2010.04.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb MS, Burrone J. Activity-dependent relocation of the axon initial segment fine-tunes neuronal excitability. Nature. 2010b;465:1070–1074. doi: 10.1038/nature09160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grubb MS, Shu Y, Kuba H, Rasband MN, Wimmer VC, Bender KJ. Short- and long-term plasticity at the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2011;31:16049–16055. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4064-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gründemann J, Häusser M. Neuroscience: A plastic axonal hotspot. Nature. 2010;465:1022–1023. doi: 10.1038/4651022a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halász N, Johansson O, Hökfelt T, Ljungdahl A, Goldstein M. Immunohistochemical identification of two types of dopamine neuron in the rat olfactory bulb as seen by serial sectioning. J Neurocytol. 1981;10:251–259. doi: 10.1007/BF01257970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman KN, Pal SK, Burrone J, Murthy VN. Activity-dependent regulation of inhibitory synaptic transmission in hippocampal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2006;9:642–649. doi: 10.1038/nn1677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harty RC, Kim TH, Thomas EA, Cardamone L, Jones NC, Petrou S, Wimmer VC. Axon initial segment structural plasticity in animal models of genetic and acquired epilepsy. Epilepsy Res. 2013;105:272–279. doi: 10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.03.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Häusser M, Stuart G, Racca C, Sakmann B. Axonal initiation and active dendritic propagation of action potentials in substantia nigra neurons. Neuron. 1995;15:637–647. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90152-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedstrom KL, Ogawa Y, Rasband MN. AnkyrinG is required for maintenance of the axon initial segment and neuronal polarity. J Cell Biol. 2008;183:635–640. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200806112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henny P, Brown MTC, Northrop A, Faunes M, Ungless MA, Magill PJ, Bolam JP. Structural correlates of heterogeneous in vivo activity of midbrain dopaminergic neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2012;15:613–619. doi: 10.1038/nn.3048. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoogland PV, Huisman E. Tyrosine hydroxylase immunoreactive structures in the aged human olfactory bulb and olfactory peduncle. J Chem Neuroanat. 1999;17:153–161. doi: 10.1016/S0891-0618(99)00035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsia AY, Vincent JD, Lledo PM. Dopamine depresses synaptic inputs into the olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol. 1999;82:1082–1085. doi: 10.1152/jn.1999.82.2.1082. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenerick H. Phase plane trajectories of the muscle spike potential. Biophys J. 1963;3:363–377. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(63)86827-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaphzan H, Buffington SA, Jung JI, Rasband MN, Klann E. Alterations in intrinsic membrane properties and the axon initial segment in a mouse model of Angelman syndrome. J Neurosci. 2011;31:17637–17648. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4162-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaphzan H, Buffington SA, Ramaraj AB, Lingrel JB, Rasband MN, Santini E, Klann E. Genetic reduction of the α1 subunit of Na/K-ATPase corrects multiple hippocampal phenotypes in Angelman syndrome. Cell Rep. 2013;4:405–412. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2013.07.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck T, Mrsic-Flogel TD, Vaz Afonso M, Eysel UT, Bonhoeffer T, Hübener M. Massive restructuring of neuronal circuits during functional reorganization of adult visual cortex. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:1162–1167. doi: 10.1038/nn.2181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck T, Scheuss V, Jacobsen RI, Wierenga CJ, Eysel UT, Bonhoeffer T, Hübener M. Loss of sensory input causes rapid structural changes of inhibitory neurons in adult mouse visual cortex. Neuron. 2011;71:869–882. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.06.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khaliq ZM, Raman IM. Relative contributions of axonal and somatic Na channels to action potential initiation in cerebellar Purkinje neurons. J Neurosci. 2006;26:1935–1944. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4664-05.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kilman V, van Rossum MCW, Turrigiano GG. Activity deprivation reduces miniature IPSC amplitude by decreasing the number of postsynaptic GABAA receptors clustered at neocortical synapses. J Neurosci. 2002;22:1328–1337. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.22-04-01328.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiyokage E, Pan YZ, Shao Z, Kobayashi K, Szabo G, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Okano H, Toida K, Puche AC, Shipley MT. Molecular identity of periglomerular and short axon cells. J Neurosci. 2010;30:1185–1196. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3497-09.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausberger T, Somogyi P. Neuronal diversity and temporal dynamics: the unity of hippocampal circuit operations. Science. 2008;321:53–57. doi: 10.1126/science.1149381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kole MHP, Stuart GJ. Signal processing in the axon initial segment. Neuron. 2012;73:235–247. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T, Kosaka K. Two types of tyrosine hydroxylase positive GABAergic juxtaglomerular neurons in the mouse main olfactory bulb are different in their time of origin. Neurosci Res. 2009;64:436–441. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2009.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T, Kosaka K. “Interneurons” in the olfactory bulb revisited. Neurosci Res. 2011;69:93–99. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2010.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka T, Komada M, Kosaka K. Sodium channel cluster, betaIV-spectrin and ankyrinG positive “hot spots” on dendritic segments of parvalbumin-containing neurons and some other neurons in the mouse and rat main olfactory bulbs. Neurosci Res. 2008;62:176–186. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2008.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba H, Ishii TM, Ohmori H. Axonal site of spike initiation enhances auditory coincidence detection. Nature. 2006;444:1069–1072. doi: 10.1038/nature05347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba H, Oichi Y, Ohmori H. Presynaptic activity regulates Na(+) channel distribution at the axon initial segment. Nature. 2010;465:1075–1078. doi: 10.1038/nature09087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba H, Adachi R, Ohmori H. Activity-dependent and activity-independent development of the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2014;34:3443–3453. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4357-13.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammel S, Lim BK, Malenka RC. Reward and aversion in a heterogeneous midbrain dopamine system. Neuropharmacology. 2014;76:351–359. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.03.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee TS, Kaku T, Takebayashi S, Uchino T, Miyamoto S, Hadama T, Perez-Reyes E, Ono K. Actions of mibefradil, efonidipine and nifedipine block of recombinant T- and L-type Ca channels with distinct inhibitory mechanisms. Pharmacology. 2006;78:11–20. doi: 10.1159/000094900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaillet G, Walker B, Lambert S. Identification of a conserved ankyrin-binding motif in the family of sodium channel alpha subunits. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:27333–27339. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M303327200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindeberg J, Usoskin D, Bengtsson H, Gustafsson A, Kylberg A, Söderström S, Ebendal T. Transgenic expression of Cre recombinase from the tyrosine hydroxylase locus. Genesis. 2004;40:67–73. doi: 10.1002/gene.20065. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S, Plachez C, Shao Z, Puche A, Shipley MT. Olfactory bulb short axon cell release of GABA and dopamine produces a temporally biphasic inhibition-excitation response in external tufted cells. J Neurosci. 2013;33:2916–2926. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3607-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livneh Y, Feinstein N, Klein M, Mizrahi A. Sensory input enhances synaptogenesis of adult-born neurons. J Neurosci. 2009;29:86–97. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4105-08.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lledo PM, Alonso M, Grubb MS. Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2006;7:179–193. doi: 10.1038/nrn1867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorincz A, Nusser Z. Cell-type-dependent molecular composition of the axon initial segment. J Neurosci. 2008;28:14329–14340. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4833-08.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAskill AF, Kittler JT. Control of mitochondrial transport and localization in neurons. Trends Cell Biol. 2010;20:102–112. doi: 10.1016/j.tcb.2009.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maher BJ, Westbrook GL. Co-transmission of dopamine and GABA in periglomerular cells. J Neurophysiol. 2008;99:1559–1564. doi: 10.1152/jn.00636.2007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marik SA, Yamahachi H, McManus JNJ, Szabo G, Gilbert CD. Axonal dynamics of excitatory and inhibitory neurons in somatosensory cortex. PLoS Biol. 2010;8:e1000395. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGann JP. Presynaptic inhibition of olfactory sensory neurons: new mechanisms and potential functions. Chem Senses. 2013;38:459–474. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjt018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGann JP, Pírez N, Gainey MA, Muratore C, Elias AS, Wachowiak M. Odorant representations are modulated by intra- but not interglomerular presynaptic inhibition of olfactory sensory neurons. Neuron. 2005;48:1039–1053. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.10.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi A. Dendritic development and plasticity of adult-born neurons in the mouse olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci. 2007;10:444–452. doi: 10.1038/nn1875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizrahi A, Katz LC. Dendritic stability in the adult olfactory bulb. Nat Neurosci. 2003;6:1201–1207. doi: 10.1038/nn1133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muir J, Kittler JT. Plasticity of GABAA receptor diffusion dynamics at the axon initial segment. Front Cell Neurosci. 2014;8:151. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2014.00151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Leary T, van Rossum MCW, Wyllie DJA. Homeostasis of intrinsic excitability in hippocampal neurones: dynamics and mechanism of the response to chronic depolarization. J Physiol. 2010;588:157–170. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panzanelli P, Fritschy JM, Yanagawa Y, Obata K, Sassoè-Pognetto M. GABAergic phenotype of periglomerular cells in the rodent olfactory bulb. J Comp Neurol. 2007;502:990–1002. doi: 10.1002/cne.21356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parrish-Aungst S, Kiyokage E, Szabo G, Yanagawa Y, Shipley MT, Puche AC. Sensory experience selectively regulates transmitter synthesis enzymes in interglomerular circuits. Brain Res. 2011;1382:70–76. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2011.01.068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli A, Kobayashi K, Okano H, Belluzzi O. Functional properties of dopaminergic neurones in the mouse olfactory bulb. J Physiol. 2005;564:501–514. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2005.084632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pignatelli A, Ackman JB, Vigetti D, Beltrami AP, Zucchini S, Belluzzi O. A potential reservoir of immature dopaminergic replacement neurons in the adult mammalian olfactory bulb. Pflugers Arch. 2009;457:899–915. doi: 10.1007/s00424-008-0535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puopolo M, Bean BP, Raviola E. Spontaneous activity of isolated dopaminergic periglomerular cells of the main olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol. 2005;94:3618–3627. doi: 10.1152/jn.00225.2005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasband MN. The axon initial segment and the maintenance of neuronal polarity. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2010;11:552–562. doi: 10.1038/nrn2852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roeper J. Dissecting the diversity of midbrain dopamine neurons. Trends Neurosci. 2013;36:336–342. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saghatelyan A, Roux P, Migliore M, Rochefort C, Desmaisons D, Charneau P, Shepherd GM, Lledo PM. Activity-dependent adjustments of the inhibitory network in the olfactory bulb following early postnatal deprivation. Neuron. 2005;46:103–116. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.02.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada M, Kaneko N, Inada H, Wake H, Kato Y, Yanagawa Y, Kobayashi K, Nemoto T, Nabekura J, Sawamoto K. Sensory input regulates spatial and subtype-specific patterns of neuronal turnover in the adult olfactory bulb. J Neurosci. 2011;31:11587–11596. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0614-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serguera C, Triaca V, Kelly-Barrett J, Banchaabouchi MA, Minichiello L. Increased dopamine after mating impairs olfaction and prevents odor interference with pregnancy. Nat Neurosci. 2008;11:949–956. doi: 10.1038/nn.2154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd GM. The synaptic organization of the brain. Oxfordm UK: Oxford UP; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Shu Y, Duque A, Yu Y, Haider B, McCormick DA. Properties of action-potential initiation in neocortical pyramidal cells: evidence from whole cell axon recordings. J Neurophysiol. 2007;97:746–760. doi: 10.1152/jn.00922.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith RL, Baker H, Kolstad K, Spencer DD, Greer CA. Localization of tyrosine hydroxylase and olfactory marker protein immunoreactivities in the human and macaque olfactory bulb. Brain Res. 1991;548:140–148. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(91)91115-H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song AH, Wang D, Chen G, Li Y, Luo J, Duan S, Poo MM. A selective filter for cytoplasmic transport at the axon initial segment. Cell. 2009;136:1148–1160. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2009.01.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trombley PQ, Westbrook GL. Excitatory synaptic transmission in cultures of rat olfactory bulb. J Neurophysiol. 1990;64:598–606. doi: 10.1152/jn.1990.64.2.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trunova S, Baek B, Giniger E. Cdk5 regulates the size of an axon initial segment-like compartment in mushroom body neurons of the Drosophila central brain. J Neurosci. 2011;31:10451–10462. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0117-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tucker KR, Huertas MA, Horn JP, Canavier CC, Levitan ES. Pacemaker rate and depolarization block in nigral dopamine neurons: a somatic sodium channel balancing act. J Neurosci. 2012;32:14519–14531. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1251-12.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turrigiano GG, Leslie KR, Desai NS, Rutherford LC, Nelson SB. Activity-dependent scaling of quantal amplitude in neocortical neurons. Nature. 1998;391:892–896. doi: 10.1038/36103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vest RS, Davies KD, O'Leary H, Port JD, Bayer KU. Dual mechanism of a natural CaMKII inhibitor. Mol Biol Cell. 2007;18:5024–5033. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E07-02-0185. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Wang H, Yu L, Chen Y. Role of axonal sodium-channel band in neuronal excitability. Phys Rev E Stat Nonlin Soft Matter Phys. 2011;84 doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.84.052901. 052901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei CJ, Linster C, Cleland TA. Dopamine D(2) receptor activation modulates perceived odor intensity. Behav Neurosci. 2006;120:393–400. doi: 10.1037/0735-7044.120.2.393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitesell JD, Sorensen KA, Jarvie BC, Hentges ST, Schoppa NE. Interglomerular lateral inhibition targeted on external tufted cells in the olfactory bulb. J Neurosci. 2013;33:1552–1563. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3410-12.2013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamahachi H, Marik SA, McManus JNJ, Denk W, Gilbert CD. Rapid axonal sprouting and pruning accompany functional reorganization in primary visual cortex. Neuron. 2009;64:719–729. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2009.11.026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D, Lambert S, Malen PL, Carpenter S, Boland LM, Bennett V. AnkyrinG is required for clustering of voltage-gated Na channels at axon initial segments and for normal action potential firing. J Cell Biol. 1998;143:1295–1304. doi: 10.1083/jcb.143.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonta B, Desmazieres A, Rinaldi A, Tait S, Sherman DL, Nolan MF, Brophy PJ. A critical role for Neurofascin in regulating action potential initiation through maintenance of the axon initial segment. Neuron. 2011;69:945–956. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2011.02.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]