Abstract
Objectives
The primary goal of this study was to identify CpG sites in the human genome that are differentially methylated in DNA obtained from chorionic villus samples (CVS) and gestational age-matched maternal blood cell (MBC) samples.
Methods
We used the HumanMethylation27 DNA Analysis BeadChip to characterize DNA methylation in samples of CVS and MBC. We then selected a subset of differentially methylated CpG sites on chromsome 13 and subjected them to analysis by mass spectrometry using the Epityper platform.
Results
We identified 718 tissue-specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs) between MBC and CVS. 563 of these were hypermethylated in MBC and hypomethylated in CVS whereas 155 sites were hypomethylated in MBC and hypermethylated in CVS. Further analysis of 13 DMRs on chromosome 13 by Epityper confirmed the microarray data and provided us with additional data about the methylation patterns of surrounding CpG sites.
Conclusions
Analysis of the resulting data identified a large number of CpGs that are potential biomarkers for the selective amplification of fetal DNA from maternal plasma and the subsequent non-invasive detection of trisomy 13.
Keywords: Fetal, DNA, Plasma, DNA Methylation, Aneuploidy, NIPD
Introduction
Every year in the USA, thousands of procedures are carried out for the prenatal diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy. These conventional methods require the direct collection of fetal materials through invasive procedures such as amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling (CVS). Unfortunately these procedures are associated with a risk of miscarriage that has been reported to be somewhere between 0.1–1.0% (Mujezinovic and Alfirevic, 2007, Tabor and Alfirevic, Tabor et al., 1986, Odibo et al., 2008). Not surprisingly these methods are also a source of considerable parental stress and anxiety (Hewison et al., 2007, Hewison et al., 2006, Hertling-Schaal et al., 2001). Several screening methods have been developed to stratify pregnant women according to their risk of carrying a fetus affected by chromosomal aneuploidy. These include various combinations of ultrasonography and biochemical screening of maternal serum (Malone et al., 2005). However, these methods are targeted at epiphenomena associated with the chromosomal aneuploidy rather than the underlying core molecular abnormalities. Significantly they also have limited accuracy, with strictly defined gestational age windows that must be used for specific tests. For example the standard first trimester screen, involving measurement of pregnancy-associated plasma protein (PAPP-A) and free beta subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) combined with ultrasound measurement of nuchal translucency, has a detection rate for trisomy 21 of between 87–82% between 10–13 weeks gestation with a false positive rate of 5% (Malone et al., 2005).
Developments in the non-invasive analysis of fetal nucleic acids have begun to transform the clinical practice of prenatal care. For example, methods for the detection of paternally inherited fetal alleles in maternal plasma are so robust that they are now widely used for the prediction of fetal Rhesus D blood group status (Chiu et al., 2005, Lo, 2000, Lo, 1999) and have also been used for the diagnosis of paternally inherited thalassemia and achondroplasia (Li et al., 2006, Li et al., 2007, Li et al., 2005, Saito et al., 2000). Not surprisingly there is considerable interest in the development of similar methods for the non-invasive detection of fetal aneuploidy and recessive monogenic diseases. However, the most significant obstacle preventing progress towards this goal is the fact that maternally inherited fetal alleles are identical in primary sequence to their endogenous maternal counterparts. To overcome this, recent advances in the field involve the use of high throughput shotgun DNA sequencing for the non-invasive detection of aneuploidy (Fan et al., 2008, Chiu et al., 2008, Chu et al., 2009a). Although these methods show great promise, they require expensive and complex instrumentation and are relatively low in throughput (Tong et al., 2010). Therefore there is still considerable interest in the development of specific biomarkers for the non-invasive detection of aneuploidy that may interface effectively with established analytical platforms such as real time PCR or mass spectrometry for the non-invasive prenatal detection of aneuploidy.
One strategy to identify such biomarkers for non-invasive detection of aneuploidy relies upon the observation that maternally-derived nucleic acids that are present in plasma originate largely from maternal leukocytes whereas maternally circulating fetal DNA and RNA are derived from syncytiotrophoblastic microparticles or other trophoblast-derived apoptotic bodies (Hasselmann et al., 2001, Gupta et al., 2004). It has been shown that differences in DNA methylation patterns between samples of placental villus and paired maternal leukocytes can be used to identify uniquely placental methylation marks which, if subsequently identified in maternal plasma, can be assumed to be of placental origin (Chan et al., 2006, Tong et al., 2006, Lo et al., 2007, Papageorgiou et al., 2009, Chu et al., 2009b, Old et al., 2007). These unique features of placental nucleic acids can then be used for the selective recovery of trophoblast-derived nucleic acid and subsequent fetal genetic analysis. Selective recovery may be achieved, for example, via methylation specific PCR following bisulphate conversion (Tong et al., 2006, Della Ragione et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2009) or methylation sensitive restriction digestion (Brown et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2010, Della Ragione et al., 2010) or via immunoprecipitation of methylated fetal DNA (Papageorgiou et al., 2009, Papageorgiou et al., 2011). Aneuploidy can then be confirmed or excluded by quantifying levels of locus specific markers on chromosomes of interest, for example, via the analysis of allelic ratios at heterozygous fetal polymorphisms (Tong et al., 2006), locus specific quantitative PCR (Papageorgiou et al., 2011, Tong et al., 2009, Della Ragione et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2010) or via microarray based analysis (Brown et al., 2010).
In the current study we have utilized a commercially available microarray based platform to identify cytosine-guanine dinucleotides (CpGs) that are differentially methylated between maternal blood cells (MBCs) and chorionic villus tissue. These loci have potential as biomarkers for selective amplification of fetal DNA in maternal plasma and subsequent detection of aneuploidy (Tong et al., 2006, Tsui et al., 2011).
Materials and Methods
Tissue Handling and DNA Extraction
All samples used in this study were discarded de-identified tissues. CVS were obtained between gestational weeks 11 and 13 from the Magee Womens Hospital Cytogenetic Screening Laboratory. All samples were confirmed to have normal euploid karyotypes using standard cytogenetic techniques. Samples were dissected under a microscope and separated from any decidual tissue or flecks of blood. The culture media was removed and the tissue was stored in 1.5ml centrifuge tubes at −80°C until use. To extract DNA, one 5mm stainless steel bead and 180μL buffer ATL (from Qiagen’s DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit, Qiagen, Valencia, CA) were added to each CVS sample. The samples were placed in the TissueLyser (Qiagen) Adaptor set 2 × 24, and the TissueLyser was operated for 20 seconds at 30Hz. The DNA was then purified using the DNeasy Blood and Tissue kit as per the manufacturer’s protocol. MBCs were obtained between gestational weeks 11 and 13 from the Magee Womens Hospital Prenatal Screening lab. DNA was extracted from the MBC’s using a modified protocol previously described by Iovannisci, et al., 2006 (Iovannisci et al., 2006), using reagents from the MasturePure DNA Purification Kit (Epincentre Technologies, Madison, WI, Cat. No. MCD85201). Briefly, clotted blood (approximately 1mL) was mixed with an equal volume (1mL) of 2X Tissue and Cell Lysis Solution, vortexed for 10s and combined with 2mL Tissue and Cell Lysis Solution (MasturePure kit) containing 25ng/μL proteinase K. 2mL of MPC Protein Precipitation Reagent was added to the total volume (4mL) of the lysed sample and vortex vigorously for 10–15 sec, after which samples were cooled on ice for ≥ 1 hour. Cell debris were then pelleted by centrifugation (×2) for at least 30 min at ≥ 2000g and supernatants transferred to a new 50mL conical tube. DNA was precipitated in 2 volumes of isopropanol, purified by phenol/chloroform extraction and resuspended in 50μL DNAse/RNAse free water.
Infinium Microarray Analysis
The HumanMethylation27 DNA Analysis BeadChip (Illumina) allows interrogation of 27,578 CpG sites based on the NCBI CCDS database (Genome Build 36) and also targets the promoter regions of 110 miRNA genes. Bisulfite conversion of DNA was carried out using the EZ DNA Methylation™ Kit (Zymo Research Corp., Irvine, CA) to convert unmethylated cytosine nucleotides to uracil. Following denaturation with 0.1N NaOH, converted DNA samples were amplified by incubation at 37°C for 20 hours in a proprietary amplification reaction mix. Amplified DNA was fragmented using vendor-supplied reagents by incubation for 1 hour at 37°C. Fragmented DNA samples were precipitated and resuspended in hybridization buffer. Infinium BeadChips were cleaned and activated by washing with ethanol, formamide and vendor supplied pre-hybridization buffers. DNA samples were denatured, applied to the Infinium arrays and hybridized 16–24 hours with rocking at 48°C. The BeadChips were placed into a flow-through chamber, unhybridized and non-specifically hybridized DNA were washed away, and single base extension was performed on bound primers with labeled nucleotides. Hybridized DNA samples were removed by washing using proprietary buffers. Staining steps were performed to attach fluorescent dyes to the labeled nucleotides and the array surface was sealed to protect the dyes from atmospheric degradation. The final array was scanned using an Illumina BeadArray Reader and the data analyzed using Bead Studio 2.0.
Determination of the methylation status of CpG sites using Infinium Array Data
On an Infinium array, each targeted CpG site was interrogated by 2 probes: probe A to determine hypomethylation level and probe B to determine hypermethylation level. The A probe signals and B probe signals were normalized separately, using the cyclic loess algorithm (Wu). We then computed the log ratio of probe B to probe A, log(B/A), as well as the beta value, which was defined as approximately B/(A+B+100), assuming A, B≥0. Both beta and log(B/A) can be used as a measurement of the methylation level of a CpG site. In particular, a CpG site was hypomethylated if the log (B/A) value of that site was significantly lower than 0. It was hypermethylated if log(B/A) is significantly higher than 0. Student’s t tests were used to test if a CpG site was methylated in a group of samples, or if two groups of samples had identical methylation rates at a given CpG site. Empirical Bayesian method proposed in Smyth (2004) was used to estimate the within group variance. P values were adjusted using Benjamini and Hochberg’s method to control the false discovery rate (FDR) at 5%.
Sequenom Epityper/Quantitative Methylation Analysis
Quantitative Methylation Analysis was performed using the MassARRAY Compact system (Sequenom, San Diego, CA). 1ug genomic DNA was bisulfite converted using the EZ DNA Methylation (Zymo Research) as per manufacturer’s instructions. PCR primers were designed by MethPrimer (www.urogene.org/methprimer) to flank the CpG regions of interest and were purchased from Integrated DNA Technologies (Coralville, IA). Primer sequences are presented in Table 1. Amplicons for use with the MassARRAY system are typically 200–600 bp in length and are independent of the methylation state of the genomic DNA, meaning they bind to both methylated and non-methylated template (as opposed to methylation-specific primers). Amplification of 1 μL bisulfite treated DNA (20 ng/μL) was performed using HotStar Taq Polymerase (Qiagen) and primers at a final concentration of 200nM each in a 5 μL reaction volume using a 384 well plate. PCR amplification was performed in a PTC225 thermal cycler (MJ Research, Inc.) with the following parameters: 94°C for 15 min hot start, followed by denaturing at 94°C for 20 sec, annealing at 62°C for 30 sec, extension at 72°C for 1 min for 45 cycles, and final incubation at 72°C for 3 min. The PCR products were then treated with shrimp alkaline phosphatase (SAP), in vitro transcribed and analyzed according to the manufacturer’s instructions (Sequenom).
Table 1.
Primer Sequences for Epityper Analysis
| Primer Name | Primer Sequence |
|---|---|
| Pet_cg22131172_F | AGGAAGAGAGTTTGTTTTGGGTATGGAAAATGTT |
| Pet_cg22131172_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAAACCAAAATCATACCACTACACTCC |
| Pet_cg25734864_F | AGGAAGAGAGTTAGGGTTTATTTTATTTTTATTGATTA |
| Pet_cg25734864_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAATACCTACCTAAAAACTCCACAC |
| Pet_cg05823029_F | AGGAAGAGAGGAAGGATTTTAGGGAGAGGTTAGG |
| Pet_cg05823029_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTCCTACCAACCCAACTCCAACTAC |
| Pet_cg25829729_F | AGGAAGAGAGTGGTAGATAATTGAGGAAGTTATGGT |
| Pet_cg25829729_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTCCTAAAAACCCCCAAAACAACTTA |
| Pet_cg00448720_F | AGGAAGAGAGGGTTTTTGTTTTTGTTTTGTG |
| Pet_cg00448720_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAAATTCAATATCCATTCCCCTCTC |
| Pet_cg15726245_F | AGGAAGAGAGGTGGTTAGGAAGTGGTGTTGTAGG |
| Pet_cg15726245_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTTCAATCAAAAACCACCAAACTAATC |
| Pet_cg15901783_F | AGGAAGAGAGTTGGTTGTAGAGATAAAATGAGATGAAG |
| Pet_cg15901783_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTACCAAAAAAAACTTCCAAAAAAAA |
| Pet_cg22398616_F | AGGAAGAGAGTTTTTTGGGTATTTTGGGATTTGT |
| Pet_cg22398616_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAACCTCCAACCAATTATCACAACA |
| Pet_cg00094319_F | AGGAAGAGAGAGAGATTAAGGTTTTTTTGTTGTT |
| Pet_cg00094319_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTATTCATAATATCCAAAACATACTC |
| Pet_cg11679069_F | AGGAAGAGAGTTTTTTTTGTTAGTTGATTTTGTAAAGG |
| Pet_cg11679069_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAACTCACTACACCCTCTACCTCCC |
| Pet_cg12682367_F | AGGAAGAGAGGATTTTGTTTGGATGAGGGGTATT |
| Pet_cg12682367_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTACAAAAACAACTCCCCAACCTTAT |
| Pet_cg18735146_F | AGGAAGAGAGATGATTTAGGTTTTAGGTGGTTGG |
| Pet_cg18735146_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTAAATACCCAAAAAATAATAATAAACTTA |
| Pet_cg24821554_F | AGGAAGAGAGTGTGATTTGTAGTTGTGTAGTTTTGG |
| Pet_cg24821554_R | CAGTAATACGACTCACTATAGGGAGAAGGCTTCAACACCCTTAACCCTAACTTTC |
Each forward primer (F) is tagged with: aggaagagag
Each reverse primer (R) is tagged with: cagtaatacgactcactatagggagaaggct
Results
We performed a genome wide analysis of DNA methylation in first trimester CVS samples and gestational age matched MBCs using the Infinium “humanmethylation27” platform marketed by Illumina. This platform targets 27,578 CpGs mostly contained within CpG islands and well characterized promoter sequences that are spread throughout the genome. Using this method we analyzed DNA samples obtained from 12 CVS samples and 12 MBC samples.
Of the 27,578 CpG sites targeted by the Infinium array, we identified 563 that were hypermethylated in MBC and hypomethylated in CVS versus 155 sites that were hypomethylated in MBC and hypermethylated in CVS (Supplementary Tables 1A and 1B, respectively). These can be considered to be tissue-specific differentially methylated regions (DMRs).
Because the Infinium microarray contains probes for CpG loci on all human chromosomes, we filtered the data to identify DMRs that are located on chromosomes 13, 18, 21 and X. CpG sites on these chromsomes that were found to be hypermethylated in MBC and hypomethylated in CVS and visa versa are shown in Table 2A and 2B respectively.
Table 2A.
| SYMBOL | ACCESSION | CHROMOSOME | MAPINFO | cg# | PRODUCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| STS | NM_000351.3 | X | 7147332 | cg00596686 | steryl-sulfatase precursor |
| RAI2 | NM_021785.2 | X | 17731018 | cg20154346 | retinoic acid induced 2 |
| NLGN3 | NM_018977.2 | X | 70281268 | cg02345317 | neuroligin 3 |
| MAGEA9 | NM_005365.4 | X | 148670955 | cg09607232 | melanoma antigen family A; 9 |
| AR | NM_000044.2 | X | 66680170 | cg14807303 | androgen receptor isoform 1 |
| TMPRSS3 | NM_024022.1 | 21 | 42689424 | cg25608949 | transmembrane protease; serine 3 isoform 1 |
| TPTE | NM_013315.2 | 21 | 10013225 | cg02148834 | transmembrane phosphatase with tensin homology isoform alpha |
| KCNJ15 | NM_002243.3 | 21 | 38550993 | cg18248112 | potassium inwardly-rectifying channel J15 |
| KRTAP19-5 | NM_181611.1 | 21 | 30797319 | cg07374637 | keratin associated protein 19-5 |
| KRTAP15-1 | NM_181623.1 | 21 | 30734946 | cg16812893 | keratin associated protein 15-1 |
| KRTAP13-4 | NM_181600.1 | 21 | 30724700 | cg14062083 | keratin associated protein 13-4 |
| KRTAP11-1 | NM_175858.2 | 21 | 31175631 | cg07014174 | keratin associated protein 11-1 |
| C21orf70 | NM_058190.2 | 21 | 45183130 | cg20884362 | hypothetical protein LOC85395 |
| SETD4 | NM_017438.2 | 21 | 36373719 | cg08632701 | hypothetical protein LOC54093 isoform a |
| KIAA0179 | NM_015056.1 | 21 | 43902770 | cg05965188 | hypothetical protein LOC23076 |
| C21orf6 | NM_016940.1 | 21 | 29314090 | cg05406101 | hypothetical protein LOC10069 |
| DNMT3L | NM_013369.2 | 21 | 44507956 | cg27076046 | cytosine-5-methyltransferase 3-like protein isoform 1 |
| CXADR | NM_001338.3 | 21 | 17805938 | cg00744433 | coxsackie virus and adenovirus receptor precursor |
| BACH1 | NM_001186.2 | 21 | 29592287 | cg09143663 | BTB and CNC homology 1 isoform a |
| TCEB3C | NM_145653.2 | 18 | 42811633 | cg02432101 | transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 3C |
| TCEB3C | NM_145653.2 | 18 | 42811405 | cg16907024 | transcription elongation factor B polypeptide 3C |
| SERPINB5 | NT_025028.13 | 18 | 59308458 | cg07331725 | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor; clade B (ovalbumin); member 5 |
| SERPINB5 | NM_002639.2 | 18 | 59295157 | cg20837735 | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor; clade B (ovalbumin); member 5 |
| SERPINB5 | NM_002639.2 | 18 | 59295230 | cg08411049 | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor; clade B (ovalbumin); member 5 |
| SERPINB5 | NT_025028.13 | 18 | 59308595 | cg06682185 | serine (or cysteine) proteinase inhibitor; clade B (ovalbumin); member 5 |
| ENOSF1 | NM_017512.2 | 18 | 703200 | cg16112050 | rTS beta protein |
| KCTD1 | NM_198991.1 | 18 | 22474735 | cg10539808 | potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 1 |
| METTL4 | NM_022840.2 | 18 | 2562965 | cg06454226 | methyltransferase like 4 |
| C18orf16 | NM_153010.3 | 18 | 22699132 | cg00729275 | hypothetical protein LOC147429 |
| DSC1 | NM_024421.1 | 18 | 26996631 | cg18356799 | desmocollin 1 isoform Dsc1a preproprotein |
| CTAGE1 | NM_022663.1 | 18 | 18251801 | cg02847216 | cutaneous T-cell lymphoma-associated antigen 1 isoform 2 |
| APCDD1 | NM_153000.3 | 18 | 10444085 | cg19264571 | adenomatosis polyposis coli down-regulated 1 |
| TTC10 | NM_006531.2 | 13 | 20038606 | cg18735146 | Tg737 protein isoform 2 |
| PROZ | NM_003891.1 | 13 | 112860987 | cg25734864 | protein Z; vitamin K-dependent plasma glycoprotein |
| KCTD12 | NM_138444.2 | 13 | 76359427 | cg15901783 | potassium channel tetramerisation domain containing 12 |
| PABPC3 | NM_030979.2 | 13 | 24568530 | cg00094319 | poly(A) binding protein; cytoplasmic 3 |
| LECT1 | NM_007015.2 | 13 | 52212204 | cg22398616 | leukocyte cell derived chemotaxin 1 isoform 1 precursor |
| TEB1 | NM_017826.1 | 13 | 35686667 | cg25829729 | hypothetical protein LOC54937 |
| FLJ46358 | NM_207439.2 | 13 | 23421698 | cg12682367 | hypothetical protein LOC400110 |
| MGC48915 | NM_178540.3 | 13 | 23781014 | cg00448720 | hypothetical protein LOC338872 |
| LOC283487 | NM_178514.3 | 13 | 110320866 | cg22131172 | hypothetical protein LOC283487 |
| GPR12 | NM_005288.1 | 13 | 26231506 | cg15726245 | G protein-coupled receptor 12 |
| DNAJC15 | NM_013238.2 | 13 | 42494577 | cg11679069 | DNAJ domain-containing |
| ATP4B | NM_000705.2 | 13 | 113360759 | cg05823029 | ATPase; H+/K+ exchanging; beta polypeptide |
Table 2b.
| SYMBOL | ACCESSION | CHROMOSOME | MAPINFO | cg# | PRODUCT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KCNE1 | NM_000219.2 | 21 | 34806378 | cg03801286 | potassium voltage-gated channel; Isk-related family; member 1 |
| ONECUT2 | NM_004852.1 | 18 | 53254351 | cg02250594 | one cut domain; family member 2 |
| GUCY1B2 | NM_004129.2 | 13 | 50537954 | cg24821554 | guanylate cyclase 1; soluble; beta 2 |
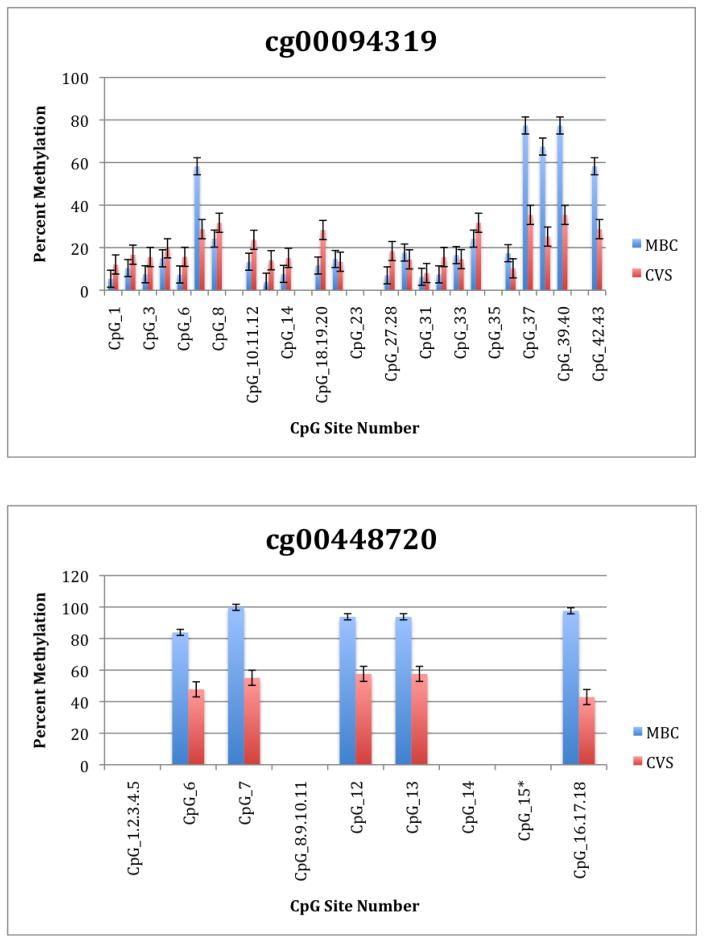
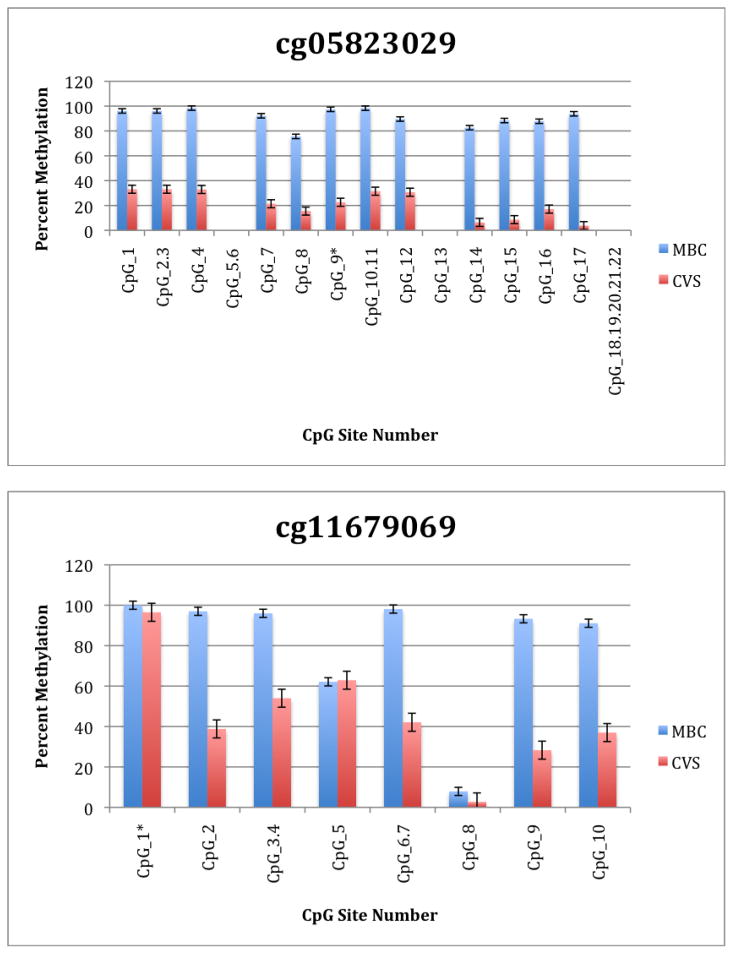
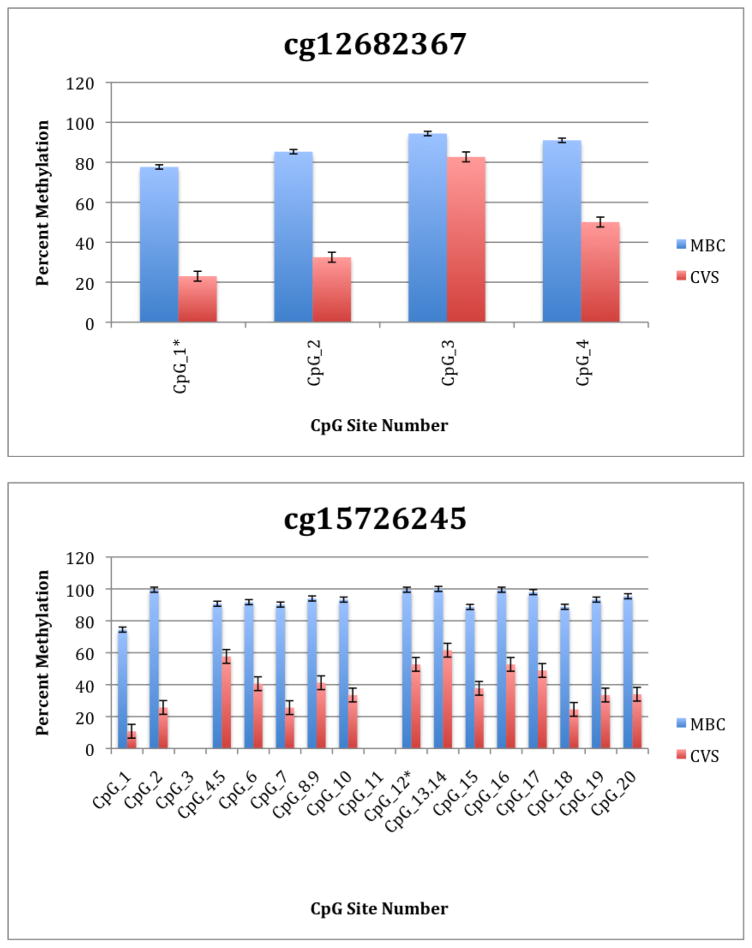
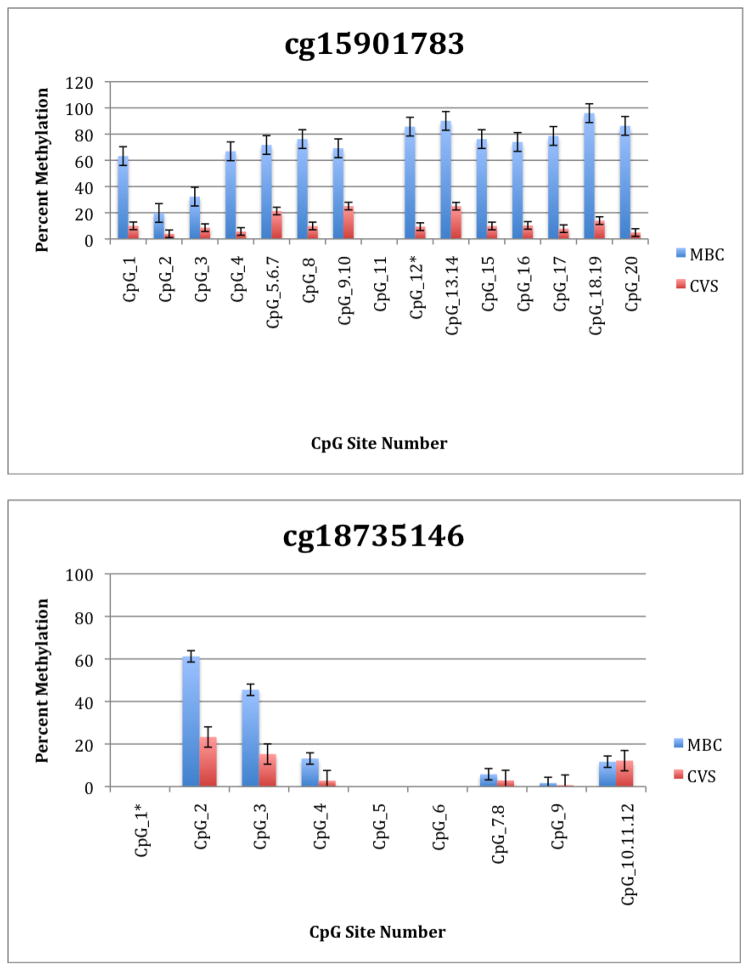
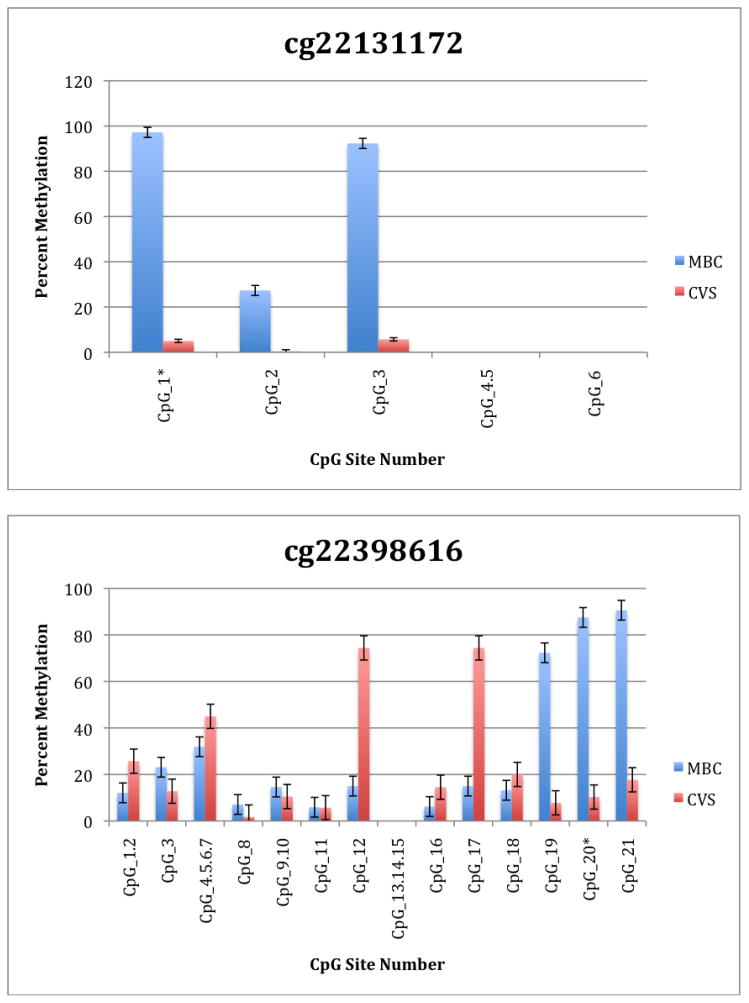
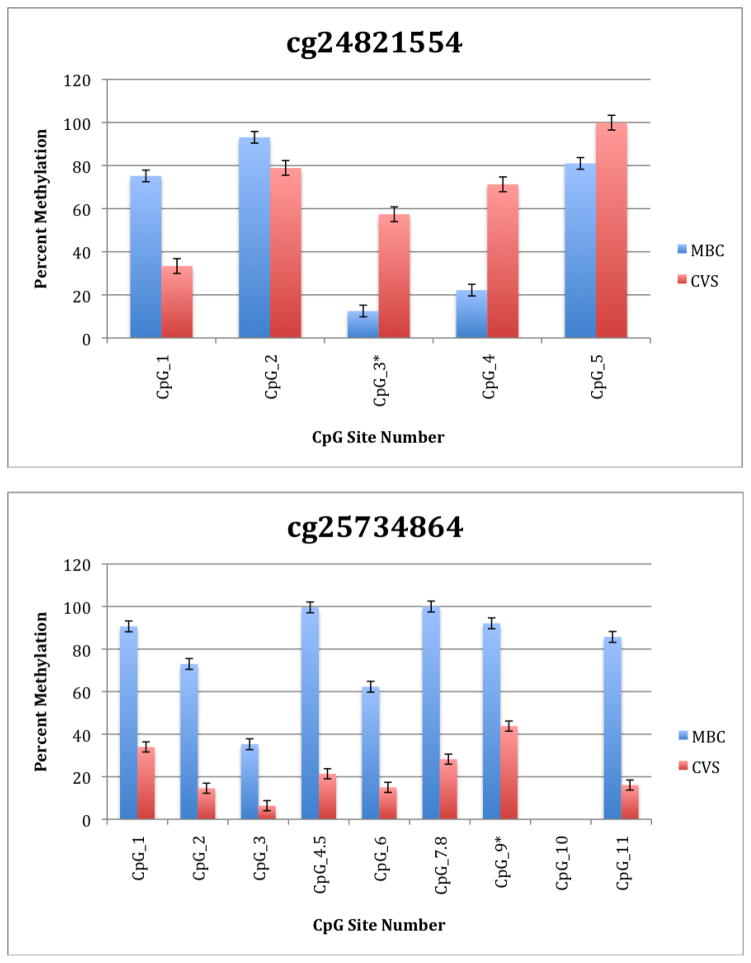
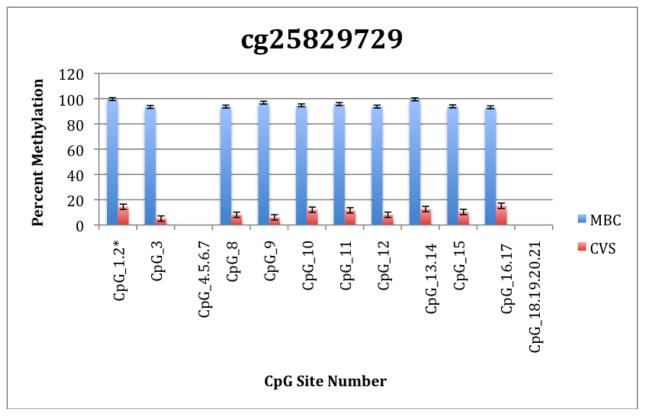
To further explore these DMRs we selected a subset of differentially methylated CpG sites on chromsome 13 and subjected them to analysis by mass spectrometry using the Epityper platform (Sequenom) (Supplementary Table 2). These loci were chosen for this analysis because of the relative lack of information in the literature relating to potential DMR biomarkers of aneuploidy on chromosome 13. As shown in Supplementary Table 3 and Figure 1, DMRs identified by Infinium analysis were confirmed by the Epityper approach in most cases. Furthermore, considerable information about the methylation state of flanking CpG sites was provided by the Epityper analysis (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Epityper Analysis of MBC and CVS.
DNA from 10 CVS samples and 10 MBC samples was isolated, bisulfite converted and assayed for methylation by Epityper at 13 different loci on chromosome 13. Each graph represents a different locus. For each locus, the number of CpG sites analyzed varies based on successful assay design. Multiple CpGs in a short span of the genome were read as one value. The sentinel CpG that was assayed by the microarray analysis is marked by an asterisk (*). CpG site numbers that have no data indicates that these sites were present but not assayed for by epityper. The percent methylation is the average for each of the 10 samples per sample group, and the error bars are the deviation between samples within the group. Chart names (eg “cg00094319”) correspond to CpG sites listed in Tables 2A and 2B.
Discussion
The primary goal of this study was to identify CpG sites in the human genome that are differentially methylated in DNA obtained from chorionic villus samples (CVS) and gestational age-matched maternal blood cell (MBC) samples. As demonstrated previously, CpG sites identified in this way are potential biomarkers for the selective amplification of fetal DNA from maternal plasma and subsequent detection of fetal trisomy (Tsui et al., 2009, Tong et al., 2009, Tong et al., 2006, Papageorgiou et al., 2011, Della Ragione et al., 2010). When analyzing our data we focused our efforts on identifying differentially methylated CpG sites located on chromsomes 13, 18, 21, X and Y because these are most commonly found aneuploidies in human populations. Therefore biomarkers on these chromosomes have the greatest potential clinical utility. The resulting data are provided for the research community as a resource with which to develop novel biomarkers for the future diagnosis of fetal genetic disease and complex placental dysfunction during early gestation. Such biomarkers could be potentially be assayed in a clinical context by a variety of previously demonstrated methods, which involve the selective recovery of fetal DNA either via methylation specific PCR after bisulphate treatment (Tong et al., 2006, Della Ragione et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2009) or methylation sensitive restriction digestion (Brown et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2010, Della Ragione et al., 2010) or via immunoprecipitation (Papageorgiou et al., 2009, Papageorgiou et al., 2011). These approaches could then be followed by one of a number of methods for the detection or exclusion of aneuploidy. Previously published examples include the detection of allelic ratio changes at heterozygous biallelic fetal loci (Tong et al., 2006), quantitative PCR in which a marker or multiple markers on chromosomes of interest are quantified relative to a control sequence(s) (Papageorgiou et al., 2011, Tong et al., 2009, Della Ragione et al., 2010, Tong et al., 2010) or microarray based analysis (Brown et al., 2010). Work is currently underway in our laboratory to explore some of these, and other, approaches.
One negative aspect of our study design is the relatively small number of loci (n = 27,578) interrogated by the Infinium microarray. Unlike a gene expression microarray, in which reasonably comprehensive genome wide data can be obtained with a small number of probes representing each gene, methylation analysis ideally requires much higher resolution so that methylation status of many individual CpGs per gene can be determined. Recent developments in high-throughput DNA sequencing of bisulfite converted genomic DNA promise significant developments in this area (Cokus et al., 2008). Unfortunately the Infinium platform contains very few (<4) CpG-targeted probes per target gene and these are located primarily in promoters and/or CpG islands. However, whereas this limitation might be problematic in the context of a functional genomics study, in which the goal is to investigate the relationship between DNA methylation and gene expression at high resolution, it is less of an issue in the context of biomarker discovery in which the goal is merely to identify DMRs.
A second negative aspect of our study is the fact that some of the “sentinal” CpGs (that is, those identified as being differentially methylated by the microarray) were not assayable by our Sequenom assay. We believe this to be a minor drawback, however, because in all these instances we identified flanking CpG sites that were differentially methylated. In only one instance we found that the sentinal CpG was not identified as differentially methylated by the Sequenom assay (cg11679069). In the case of most CpGs that were assayed we found that there is potential for their further development as biomarkers for fetal chromosome 13-specific enrichment. Such potential is based upon the fact that, with the exception of cg2584155, the tissue specific difference in methylation is large with, ideally, one or both tissues displaying a methylation rate of or approaching 100% or 0%. In one instance (cg22398616) we found hypermethylation in CVS versus hypomethylation in MBC and the exact opposite pattern (hypermethylation in MBC versus hypomethylation in CVS) at adjacent CpG sites. This locus may have potential for development of an internally controlled biomarker in which maternal and fetal alleles could be targeted in parallel.
Previous studies have identified a number of potentially significant DMRs in the context of non-invasive fetal diagnosis (Tsui et al., 2010, Della Ragione et al., 2010, Brown et al., 2010, Lo, 2009, Chim et al., 2008, Tong et al., 2006, Chu et al., 2009b, Papageorgiou et al., 2009). The study presented here is the first to describe the identification of DMRs between CVS and MBC in a genome wide fashion and, to our knowledge, is the first to confirm CpG-specific differential DNA methylation using targeted single locus assays directed towards chromosome 13 markers using samples from multiple pregnancies.
In summary, we have undertaken a genome wide analysis of DNA methylation in CVS and MBC samples obtained from pregnant women between gestational weeks 10 and 13. Analysis of the resulting data identifies a large number of CpGs that are potential biomarkers for the selective amplification of fetal DNA from maternal plasma and the subsequent non-invasive detection of trisomy 13.
Supplementary Material
What is already known/what does this study add?
Differential DNA methylation between placenta and maternal leukocytes has been exploited for the specific amplification of fetal DNA from maternal plasma.
Previous efforts to identify differentially methylated loci have largely focused on chromosomes 21, 18, 13 and X. In previous studies, follow up analysis using targeted approaches for single loci have generally not focused on chromosome 13 markers.
We present a systematic analysis of DNA methylation in a genome wide fashion, with follow up of specific markers on chromosome 13.
The currently described discovery platform has not previously been used in this context
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants (to DGP) from the Magee Womens Research Institute and Foundation and The NIH (1R01HD068578-01). The funders had no role or influence regarding study design, data collection, data analysis, manuscript preparation and/or publication decision.
References
- BROWN L, BROWN G, VACEK P, BROWN S. Aneuploidy detection in mixed DNA samples by methylation-sensitive amplification and microarray analysis. Clin Chem. 2010;56:805–13. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.137877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAN KC, DING C, GEROVASSILI A, YEUNG SW, CHIU RW, LEUNG TN, LAU TK, CHIM SS, CHUNG GT, NICOLAIDES KH, LO YM. Hypermethylated RASSF1A in maternal plasma: A universal fetal DNA marker that improves the reliability of noninvasive prenatal diagnosis. Clin Chem. 2006;52:2211–8. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.074997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIM SS, JIN S, LEE TY, LUN FM, LEE WS, CHAN LY, JIN Y, YANG N, TONG YK, LEUNG TY, LAU TK, DING C, CHIU RW, LO YM. Systematic search for placental DNA-methylation markers on chromosome 21: toward a maternal plasma-based epigenetic test for fetal trisomy 21. Clin Chem. 2008;54:500–11. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2007.098731. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIU RW, CHAN CW, ZHONG XY, LAPAIRE O, HOLZGREVE W, HAHN S, LO YM. Fetal rhesus D mRNA is not detectable in maternal plasma. Clin Chem. 2005;51:2210–1. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2005.056937. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHIU RW, CHAN KC, GAO Y, LAU VY, ZHENG W, LEUNG TY, FOO CH, XIE B, TSUI NB, LUN FM, ZEE BC, LAU TK, CANTOR CR, LO YM. Noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of fetal chromosomal aneuploidy by massively parallel genomic sequencing of DNA in maternal plasma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:20458–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0810641105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHU T, BUNCE K, HOGGE WA, PETERS DG. Statistical model for whole genome sequencing and its application to minimally invasive diagnosis of fetal genetic disease. Bioinformatics. 2009a;25:1244–50. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHU T, BURKE B, BUNCE K, SURTI U, ALLEN HOGGE W, PETERS DG. A microarray-based approach for the identification of epigenetic biomarkers for the noninvasive diagnosis of fetal disease. Prenat Diagn. 2009b;29:1020–30. doi: 10.1002/pd.2335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COKUS SJ, FENG S, ZHANG X, CHEN Z, MERRIMAN B, HAUDENSCHILD CD, PRADHAN S, NELSON SF, PELLEGRINI M, JACOBSEN SE. Shotgun bisulphite sequencing of the Arabidopsis genome reveals DNA methylation patterning. Nature. 2008;452:215–9. doi: 10.1038/nature06745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DELLA RAGIONE F, MASTROVITO P, CAMPANILE C, CONTI A, PAPAGEORGIOU EA, HULTEN MA, PATSALIS PC, CARTER NP, D’ESPOSITO M. Differential DNA methylation as a tool for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis (NIPD) of X chromosome aneuploidies. J Mol Diagn. 2010;12:797–807. doi: 10.2353/jmoldx.2010.090199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FAN HC, BLUMENFELD YJ, CHITKARA U, HUDGINS L, QUAKE SR. Noninvasive diagnosis of fetal aneuploidy by shotgun sequencing DNA from maternal blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008;105:16266–71. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0808319105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUPTA AK, HOLZGREVE W, HUPPERTZ B, MALEK A, SCHNEIDER H, HAHN S. Detection of fetal DNA and RNA in placenta-derived syncytiotrophoblast microparticles generated in vitro. Clin Chem. 2004;50:2187–90. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2004.040196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HASSELMANN DO, RAPPL G, TILGEN W, REINHOLD U. Extracellular tyrosinase mRNA within apoptotic bodies is protected from degradation in human serum. Clin Chem. 2001;47:1488–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERTLING-SCHAAL E, PERROTIN F, DE PONCHEVILLE L, LANSAC J, BODY G. Maternal anxiety induced by prenatal diagnostic techniques: detection and management. Gynecol Obstet Fertil. 2001;29:440–6. doi: 10.1016/s1297-9589(01)00158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEWISON J, NIXON J, FOUNTAIN J, COCKS K, JONES C, MASON G, MORLEY S, THORNTON J. Amniocentesis results: investigation of anxiety. The ARIA trial. Health Technol Assess. 2006;10:iii, ix–x, 1–78. doi: 10.3310/hta10500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEWISON J, NIXON J, FOUNTAIN J, HAWKINS K, JONES CR, MASON G, MORLEY S, THORNTON JG. A randomised trial of two methods of issuing prenatal test results: the ARIA (Amniocentesis Results: Investigation of Anxiety) trial. BJOG. 2007;114:462–8. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2007.01276.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IOVANNISCI DM, HA TT, SHAW GM. Recovery of genomic DNA from residual frozen archival blood clots suitable for amplification and use in genotyping assays. Genet Test. 2006;10:44–9. doi: 10.1089/gte.2006.10.44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI Y, DI NARO E, VITUCCI A, ZIMMERMANN B, HOLZGREVE W, HAHN S. Detection of paternally inherited fetal point mutations for beta-thalassemia using size-fractionated cell-free DNA in maternal plasma. Jama. 2005;293:843–9. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.7.843. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI Y, HOLZGREVE WE, DIN, VITUCCI A, HAHN S. Cell-free DNA in maternal plasma: is it all a question of size? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2006;1075:81–7. doi: 10.1196/annals.1368.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LI Y, PAGE-CHRISTIAENS GC, GILLE JJ, HOLZGREVE W, HAHN S. Non-invasive prenatal detection of achondroplasia in size-fractionated cell-free DNA by MALDI-TOF MS assay. Prenat Diagn. 2007;27:11–7. doi: 10.1002/pd.1608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LO YM. Fetal RhD genotyping from maternal plasma. Ann Med. 1999;31:308–12. doi: 10.3109/07853899908995896. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LO YM. Fetal DNA in maternal plasma: biology and diagnostic applications. Clin Chem. 2000;46:1903–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LO YM. Noninvasive prenatal detection of fetal chromosomal aneuploidies by maternal plasma nucleic acid analysis: a review of the current state of the art. BJOG. 2009;116:152–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-0528.2008.02010.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LO YM, TSUI NB, CHIU RW, LAU TK, LEUNG TN, HEUNG MM, GEROVASSILI A, JIN Y, NICOLAIDES KH, CANTOR CR, DING C. Plasma placental RNA allelic ratio permits noninvasive prenatal chromosomal aneuploidy detection. Nat Med. 2007;13:218–23. doi: 10.1038/nm1530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALONE FD, CANICK JA, BALL RH, NYBERG DA, COMSTOCK CH, BUKOWSKI R, BERKOWITZ RL, GROSS SJ, DUGOFF L, CRAIGO SD, TIMOR-TRITSCH IE, CARR SR, WOLFE HM, DUKES K, BIANCHI DW, RUDNICKA AR, HACKSHAW AK, LAMBERT-MESSERLIAN G, WALD NJ, D’ALTON ME. First-trimester or second-trimester screening, or both, for Down’s syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2005;353:2001–11. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa043693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MUJEZINOVIC F, ALFIREVIC Z. Procedure-related complications of amniocentesis and chorionic villous sampling: a systematic review. Obstet Gynecol. 2007;110:687–94. doi: 10.1097/01.AOG.0000278820.54029.e3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ODIBO AO, GRAY DL, DICKE JM, STAMILIO DM, MACONES GA, CRANE JP. Revisiting the fetal loss rate after second-trimester genetic amniocentesis: a single center’s 16-year experience. Obstet Gynecol. 2008;111:589–95. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e318162eb53. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLD RW, CREA F, PUSZYK W, HULTEN MA. Candidate epigenetic biomarkers for non-invasive prenatal diagnosis of Down syndrome. Reprod Biomed Online. 2007;15:227–35. doi: 10.1016/s1472-6483(10)60713-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAGEORGIOU EA, FIEGLER H, RAKYAN V, BECK S, HULTEN M, LAMNISSOU K, CARTER NP, PATSALIS PC. Sites of differential DNA methylation between placenta and peripheral blood: molecular markers for noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of aneuploidies. Am J Pathol. 2009;174:1609–18. doi: 10.2353/ajpath.2009.081038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PAPAGEORGIOU EA, KARAGRIGORIOU A, TSALIKI E, VELISSARIOU V, CARTER NP, PATSALIS PC. Fetal-specific DNA methylation ratio permits noninvasive prenatal diagnosis of trisomy 21. Nat Med. 2011;17:510–3. doi: 10.1038/nm.2312. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAITO H, SEKIZAWA A, MORIMOTO T, SUZUKI M, YANAIHARA T. Prenatal DNA diagnosis of a single-gene disorder from maternal plasma. Lancet. 2000;356:1170. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)02767-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR A, ALFIREVIC Z. Update on procedure-related risks for prenatal diagnosis techniques. Fetal Diagn Ther. 27:1–7. doi: 10.1159/000271995. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TABOR A, PHILIP J, MADSEN M, BANG J, OBEL EB, NORGAARD-PEDERSEN B. Randomised controlled trial of genetic amniocentesis in 4606 low-risk women. Lancet. 1986;1:1287–93. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(86)91218-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONG YK, CHIU RW, AKOLEKAR R, LEUNG TY, LAU TK, NICOLAIDES KH, LO YM. Epigenetic-genetic chromosome dosage approach for fetal trisomy 21 detection using an autosomal genetic reference marker. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONG YK, DING C, CHIU RW, GEROVASSILI A, CHIM SS, LEUNG TY, LEUNG TN, LAU TK, NICOLAIDES KH, LO YM. Noninvasive prenatal detection of fetal trisomy 18 by epigenetic allelic ratio analysis in maternal plasma: Theoretical and empirical considerations. Clin Chem. 2006;52:2194–202. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2006.076851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TONG YK, JIN S, CHIU RW, DING C, CHAN KC, LEUNG TY, YU L, LAU TK, LO YM. Noninvasive prenatal detection of trisomy 21 by an epigenetic-genetic chromosome-dosage approach. Clin Chem. 2009;56:90–8. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.134114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUI DW, CHIU RW, LO YD. Epigenetic approaches for the detection of fetal DNA in maternal plasma. Chimerism. 2011;1:30–35. doi: 10.4161/chim.1.1.12439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUI DW, LAM YM, LEE WS, LEUNG TY, LAU TK, LAU ET, TANG MH, AKOLEKAR R, NICOLAIDES KH, CHIU RW, LO YM, CHIM SS. Systematic identification of placental epigenetic signatures for the noninvasive prenatal detection of Edwards syndrome. PLoS One. 2010;5:e15069. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015069. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TSUI NB, AKOLEKAR R, CHIU RW, CHOW KC, LEUNG TY, LAU TK, NICOLAIDES KH, LO YM. Synergy of total PLAC4 RNA concentration and measurement of the RNA single-nucleotide polymorphism allelic ratio for the noninvasive prenatal detection of trisomy 21. Clin Chem. 2009;56:73–81. doi: 10.1373/clinchem.2009.132662. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.