Abstract
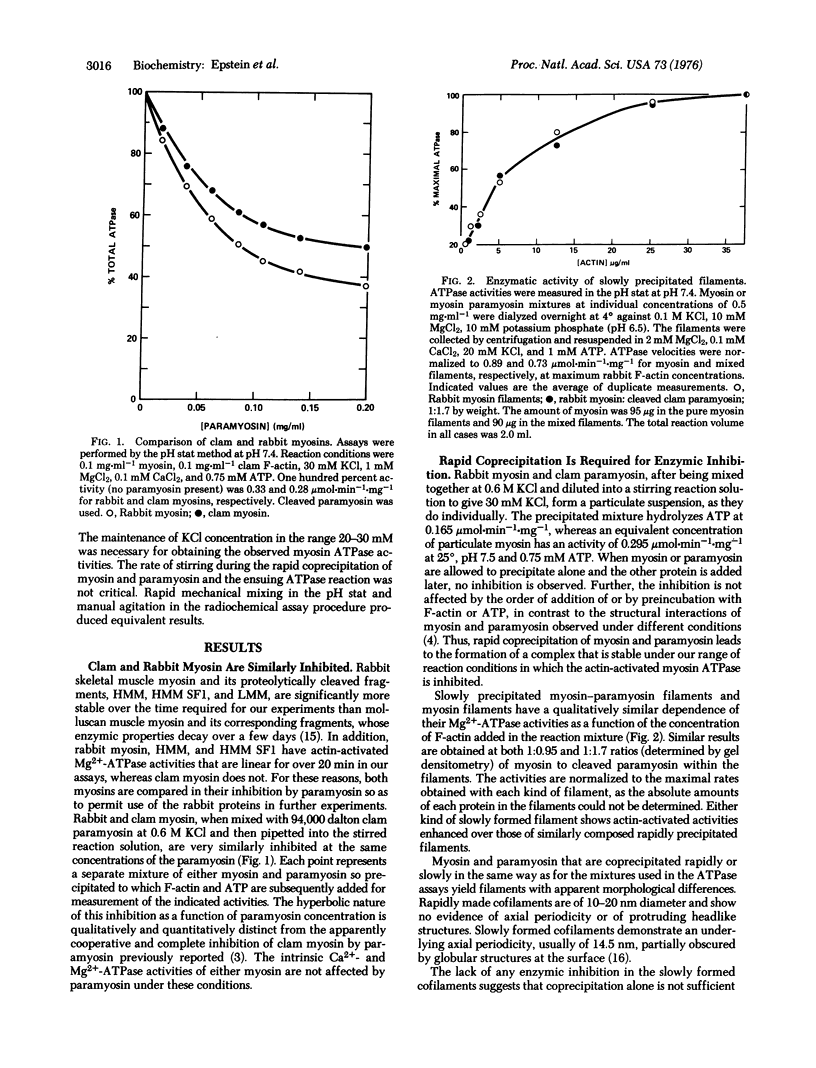
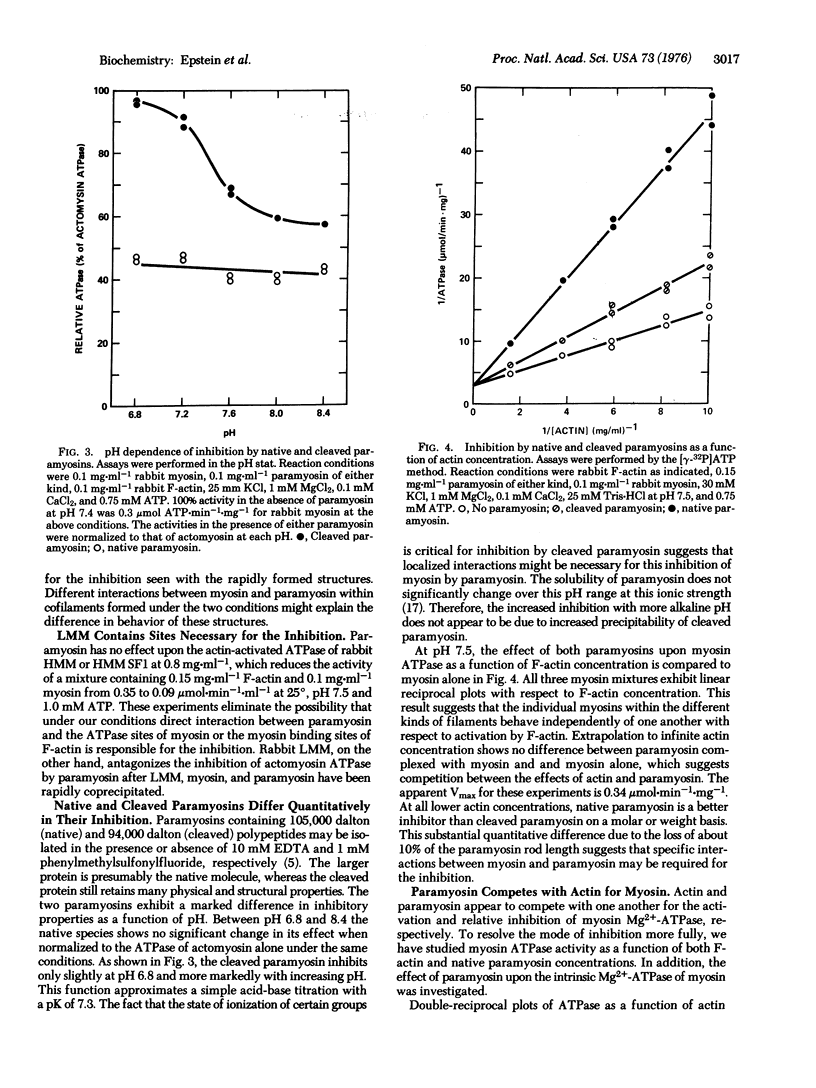
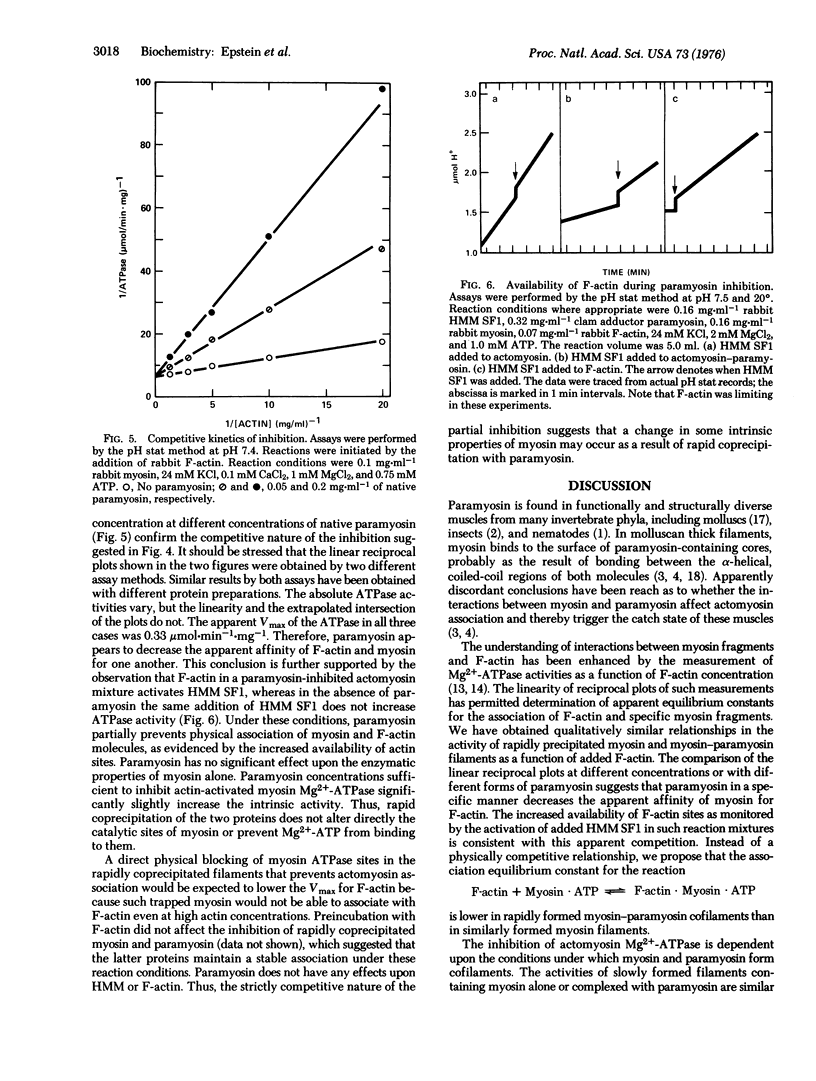
The interaction between paramyosin and myosin has been studied by enzymological methods. Clam adductor paramyosin inhibits the actin-activated, Mg2+-requiring ATPase of both clam adductor and rabbit skeletal muscle myosins. Myosin and paramyosin must be rapidly coprecipitated for this inhibition. Incubation with F-actin in the absence of ATP does not alter this effect. This inhibition follows a hyperbolic function with respect to paramyosin concentration. Slow precipitation by dialysis of myosin and paramyosin together leads to copolymers with actin-activated ATPase equivalent to that of slowly formed myosin filaments. Both kinds of slowly formed filaments have enzymatic properties distinct from those of the rapidly precipitated proteins. Paramyosin is competitive with F-actin for their effects upon myosin. The apparent affinity of myosin for F-actin is markedly reduced by association with paramyosin, but the extrapolated maximal velocity of actomyosin is unaffected. The specificity of this inhibition is strongly suggested by marked quantitative differences between native and cleaved paramyosins. No inhibition of intrinsic myosin ATPase by paramyosin is seen. These studies suggest that at least two types of condition-dependent association between myosin and paramyosin are possible. One class of interactions is associated with enzymic inhibition in rapidly coprecipitated filaments, whereas slowly formed cofilaments exhibit catalytic activity similar to that of identically treat-d myosin and have a characteristic 14.5 nm axial repeat.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bullard B., Luke B., Winkelman L. The paramyosin of insect flight muscle. J Mol Biol. 1973 Apr 5;75(2):359–367. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90026-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen C., Szent-Györgyi A. G., Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. I. Paramyosin: structure and assembly. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):223–227. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90461-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg E., Moos C. The interaction of actin with myosin and heavy meromyosin in solution at low ionic strength. J Biol Chem. 1967 Jun 25;242(12):2945–2951. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Aronow B. J., Harris H. E. Interaction of myosin and paramyosin. J Supramol Struct. 1975;3(4):354–360. doi: 10.1002/jss.400030407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein H. F., Waterston R. H., Brenner S. A mutant affecting the heavy chain of myosin in Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON W. H., KAHN J. S., SZENTGYORGYI A. G. Paramyosin and contraction of catch muscles. Science. 1959 Jul 17;130(3368):160–161. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3368.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIELLEY W. W., BRADLEY L. B. The relationship between sulfhydryl groups and the activation of myosin adenosinetriphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):653–659. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowey S., Slayter H. S., Weeds A. G., Baker H. Substructure of the myosin molecule. I. Subfragments of myosin by enzymic degradation. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 28;42(1):1–29. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90483-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margossian S. S., Lowey S. Substructure of the myosin molecule. IV. Interactions of myosin and its subfragments with adenosine triphosphate and F-actin. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 5;74(3):313–330. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90376-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonomura Y. Fine structure of the thick filament in molluscan catch muscle. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):445–455. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90494-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A. Biochemical and structural studies of actomyosin-like proteins from non-muscle cells. II. Purification, properties, and membrane association of actin from amoebae of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Biol Chem. 1974 Sep 25;249(18):6013–6020. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spudich J. A., Watt S. The regulation of rabbit skeletal muscle contraction. I. Biochemical studies of the interaction of the tropomyosin-troponin complex with actin and the proteolytic fragments of myosin. J Biol Chem. 1971 Aug 10;246(15):4866–4871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stafford W. F., 3rd, Yphantis D. A. Existence and inhibition of hydrolytic enzymes attacking paramyosin in myofibrillar extracts of Mercenaria mercenaria. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 1;49(3):848–854. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90488-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Cohen C., Kendrick-Jones J. Paramyosin and the filaments of molluscan "catch" muscles. II. Native filaments: isolation and characterization. J Mol Biol. 1971 Mar 14;56(2):239–258. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szent-Györgyi A. G., Szentkiralyi E. M., Kendrick-Jonas J. The light chains of scallop myosin as regulatory subunits. J Mol Biol. 1973 Feb 25;74(2):179–203. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90106-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterston R. H., Epstein H. F., Brenner S. Paramyosin of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1974 Dec 5;90(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90373-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


