Abstract
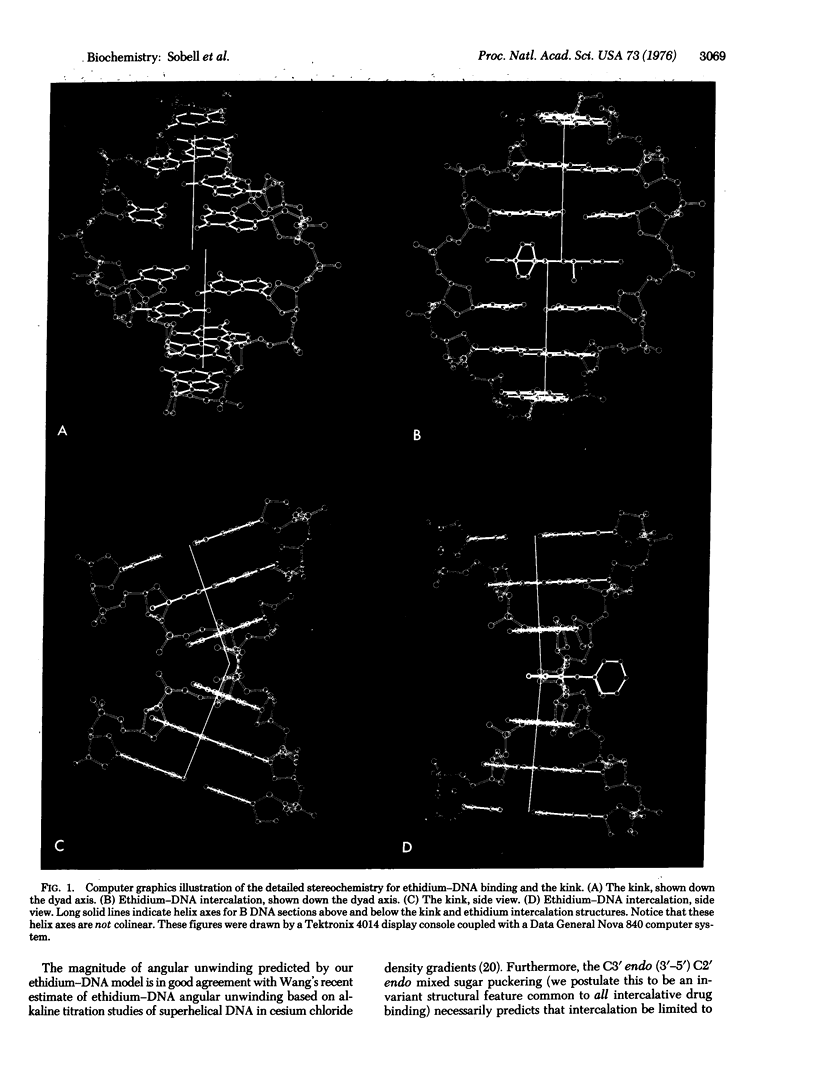
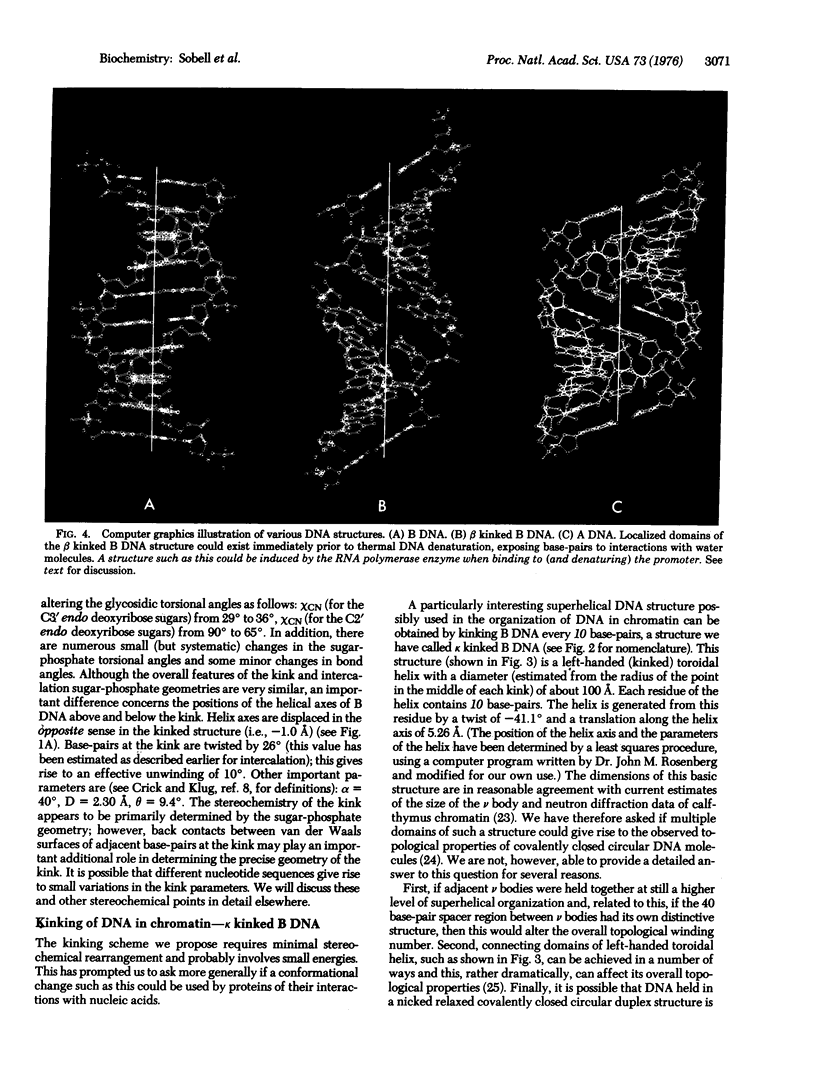
Conformational changes in DNA that accompany drug intercalation have led us to ask if DNA first bends or "kinks" to accept an intercalative drug or dye. Kinking is made possible by altering the normal C2' endo deoxyribose sugar ring puckering in B DNA to a mixed sugar puckering pattern of the type C3' and partially unstacking base-pairs. A kinking scheme such as this would require minimal stereochemical rearrangement and would also involve small energies. This has prompted us to ask more generally if a conformational change such as this could be used by proteins in their interactions with nucleic acids. In this papter we describe an interesting superhelical DNA structure formed by kinking DNA every 10 base-pairs. The structure may be used in the organization of DNA in chromatin.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alden C. J., Arnott S. Visualization of planar drug intercalations in B-DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1975 Oct;2(10):1701–1717. doi: 10.1093/nar/2.10.1701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnott S., Hukins D. W. Conservation of conformation in mono and poly-nucleotides. Nature. 1969 Nov 29;224(5222):886–888. doi: 10.1038/224886a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. P., Boseley P. G., Bradbury E. M., Ibel K. The subunit structure of the eukaryotic chromosome. Nature. 1975 Jan 24;253(5489):245–249. doi: 10.1038/253245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. The interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. I. The superhelix density of SV40 DNA in the presence and absence of dye. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 14;33(1):141–171. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90286-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond P. J., Langridge R., Jennette K. W., Lippard S. J. X-ray fiber diffraction evidence for neighbor exclusion binding of a platinum metallointercalation reagent to DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4825–4829. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H., Klug A. Kinky helix. Nature. 1975 Jun 12;255(5509):530–533. doi: 10.1038/255530a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crick F. H. Linking numbers and nucleosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2639–2643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crothers D. M. Calculation of binding isotherms for heterogenous polymers. Biopolymers. 1968 Apr;6(4):575–584. doi: 10.1002/bip.1968.360060411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson R. C., Abelson J., Barnes W. M., Reznikoff W. S. Genetic regulation: the Lac control region. Science. 1975 Jan 10;187(4171):27–35. doi: 10.1126/science.1088926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elgin S. C., Weintraub H. Chromosomal proteins and chromatin structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:725–774. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.003453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffith J. D. Chromatin structure: deduced from a minichromosome. Science. 1975 Mar 28;187(4182):1202–1203. doi: 10.1126/science.187.4182.1202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Determination of the number of superhelical turns in simian virus 40 DNA by gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4876–4880. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornberg R. D. Chromatin structure: a repeating unit of histones and DNA. Science. 1974 May 24;184(4139):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4139.868. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll M. Internal structure of the chromatin subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1974 Nov;1(11):1573–1578. doi: 10.1093/nar/1.11.1573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olins A. L., Olins D. E. Spheroid chromatin units (v bodies). Science. 1974 Jan 25;183(4122):330–332. doi: 10.1126/science.183.4122.330. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oudet P., Gross-Bellard M., Chambon P. Electron microscopic and biochemical evidence that chromatin structure is a repeating unit. Cell. 1975 Apr;4(4):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90149-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saucier J. M., Wang J. C. Angular alteration of the DNA helix by E. coli RNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1972 Oct 11;239(93):167–170. doi: 10.1038/newbio239167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Kornberg R. D. An octamer of histones in chromatin and free in solution. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2626–2630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. Drug-nucleic acid interaction: X-ray crystallographic determination of an ethidium-dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, ethidium: 5-iodouridylyl(3'-5')adenosine. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1975 Nov 6;272(915):137–146. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1975.0076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai C. C., Jain S. C., Sobell H. M. X-ray crystallographic visualization of drug-nucleic acid intercalative binding: structure of an ethidium-dinucleoside monophosphate crystalline complex, Ethidium: 5-iodouridylyl (3'-5') adenosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):628–632. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walz A., Pirrotta V. Sequence of the PR promoter of phage lambda. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):118–121. doi: 10.1038/254118a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. The degree of unwinding of the DNA helix by ethidium. I. Titration of twisted PM2 DNA molecules in alkaline cesium chloride density gradients. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):783–801. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90053-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]