Abstract
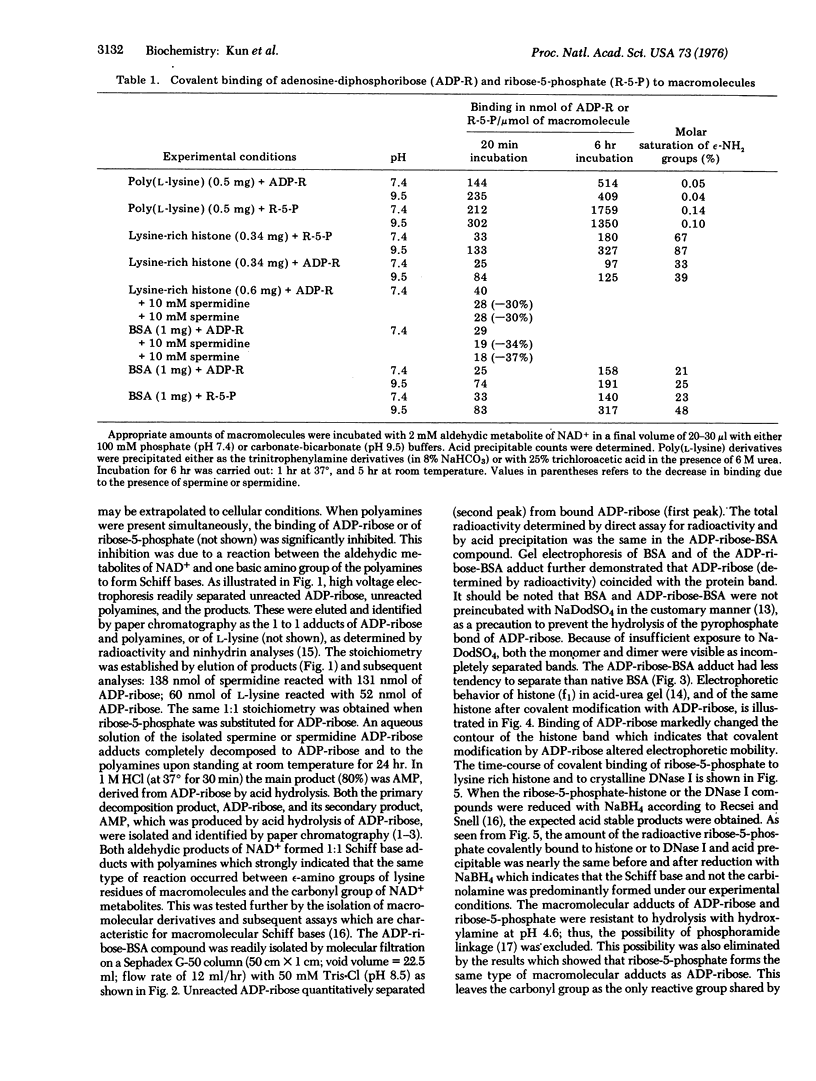
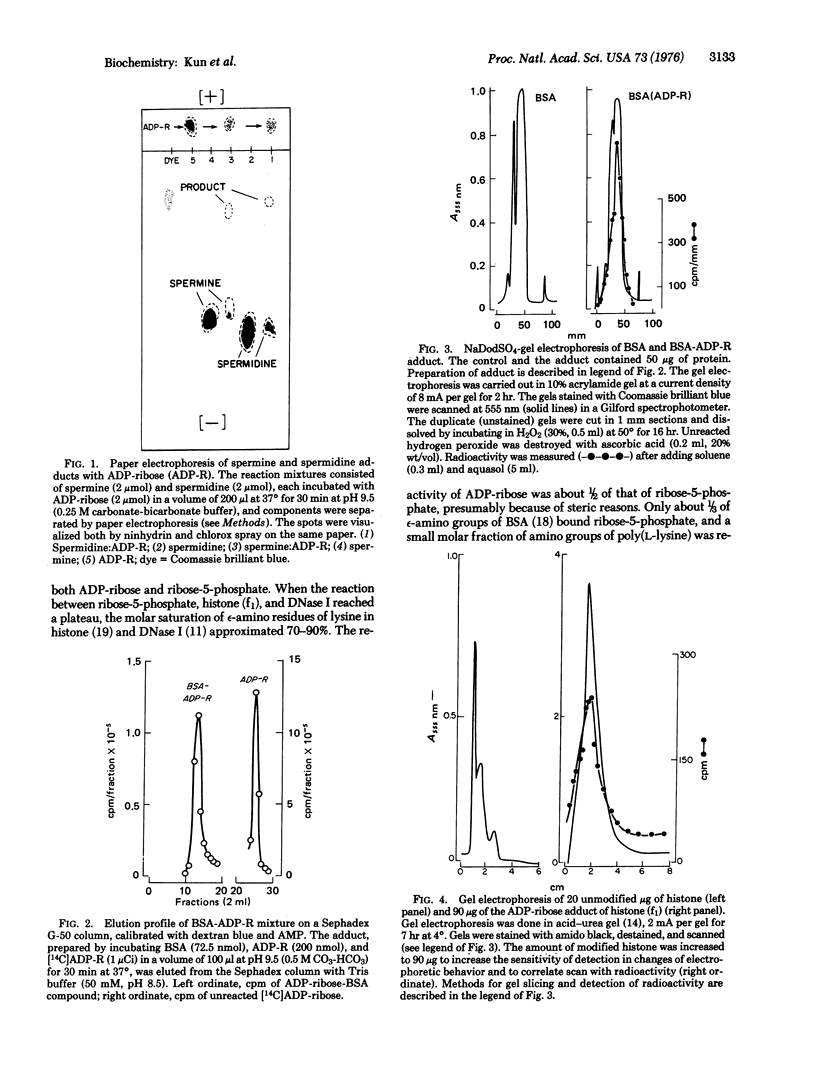
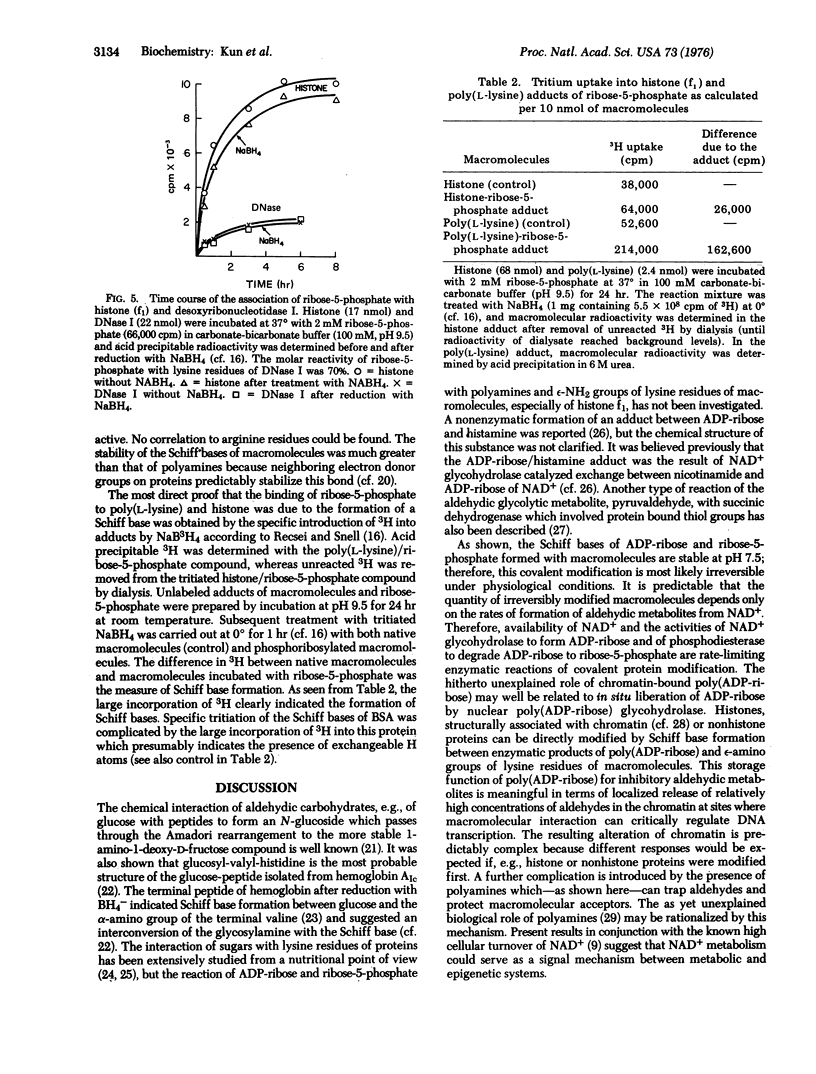
Covalently bound adducts of ply(L-lysine), bovine serum albumin, lysine rich histone (f1) and deoxyribonucleotidase I (DNase, EC 3.1.4.5) with adenosine diphosphoribose and ribose-5-phosphate were prepared at pH 7.4 and 9.5. Macromolecular adducts of bovine serum albumin and histone (f1) were isolated by gel filtration and electrophoresis. Reduction of products by NaBH4 did not dissociate the ribose-5-phosphate moiety from macromolecules. Specific introduction of 3H into the adducts also indicated Schiff base formation. The reaction of ribose-5-phosphate with epsilon-amino groups of histone (f1) approached 70-90% saturation. Spermine and spermidine also react with adenosine diphosphoribose and ribose-5-phosphate to form 1:1 Schiff bases. It is proposed that high turnover of cellular NAD+ is the source of aldehydic metabolites which may regulate macromolecular metabolism by covalent modification of nuclear proteins, whereas polyamines serve as modulators of this control cycle.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson B. M., Anderson C. D., Vercellotti S. V. Bull semen nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide nucleosidase. VII. Nonenzymatic basis of apparent transglycosidation with histamine. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Aug;157(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90660-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bookchin R. M., Gallop P. M. Structure of hemoglobin AIc: nature of the N-terminal beta chain blocking group. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1968 Jul 11;32(1):86–93. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(68)90430-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon H. B. A reaction of glucose with peptides. Biochem J. 1972 Aug;129(1):203–208. doi: 10.1042/bj1290203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ELLIS G. P. The Maillard reaction. Adv Carbohydr Chem. 1959;14:63–134. doi: 10.1016/s0096-5332(08)60223-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferro A. M., Kun E. Macromolecular derivatives of NAD+ in heart nuclei: poly adenosine diphosphoribose and adenosine diphosphoribose proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jul 12;71(1):150–154. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90261-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumport R. I., Lehman I. R. Structure of the DNA ligase-adenylate intermediate: lysine (epsilon-amino)-linked adenosine monophosphoramidate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Oct;68(10):2559–2563. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.10.2559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUN E. Inhibition of succinic dehydrogenase by methylglyoxal. J Biol Chem. 1950 Nov;187(1):289–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinkade J. M., Jr, Cole R. D. The resolution of four lysine-rich histones derived from calf thymus. J Biol Chem. 1966 Dec 25;241(24):5790–5797. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kun E., Zimber P. H., Chang A. C., Puschendorf B., Grunicke H. Macromolecular enzymatic product of NAD+ in liver mitochondria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1436–1440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa M., Sugimura T. Splitting of the ribose-ribose linkage of poly(adenosine diphosphate-robose) by a calf thymus extract. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6362–6364. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa M., Tanaka M., Matsushima T., Sugimura T. Purification and properties of glycohydrolase from calf thymus splitting ribose-ribose linkages of poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose). J Biol Chem. 1974 Jun 10;249(11):3475–3482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyakawa N., Ueda K., Hayaishi O. Association of poly ADP-ribose glycohydrolase with liver chromatin. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Oct 6;49(1):239–245. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90035-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panyim S., Chalkley R. High resolution acrylamide gel electrophoresis of histones. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Mar;130(1):337–346. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90042-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROSEN H. A modified ninhydrin colorimetric analysis for amino acids. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1957 Mar;67(1):10–15. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(57)90241-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechsteiner M., Hillyard D., Olivera B. M. Magnitude and significance of NAD turnover in human cell line D98/AH2. Nature. 1976 Feb 26;259(5545):695–696. doi: 10.1038/259695a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Recsei P. A., Snell E. E. Histidine decarboxylase of Lactobacillus 30a. VI. Mechanism of action and kinetic properties. Biochemistry. 1970 Mar 31;9(7):1492–1497. doi: 10.1021/bi00809a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shima T., Hasegawa S., Fujimura S., Matsubara H., Sugimura T. Studies on poly adenosine diphosphate-ribose. VII. Methods of separation and identification of 2'-(5"-phosphoribosyl)-5'-adenosine monophosphate, ribosyladenosine monophosphate, and phosphoribosyladenosine. J Biol Chem. 1969 Dec 25;244(24):6632–6635. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Fukushima M., Okayama H., Hayaishi O. Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide glycohydrolase from rat liver nuclei. Isolation and characterization of a new enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1975 Oct 10;250(19):7541–7546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda K., Oka J., Naruniya S., Miyakawa N., Hayaishi O. Poly ADP-ribose glycohydrolase from rat liver nuclei, a novel enzyme degrading the polymer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Jan 31;46(2):516–523. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(72)80169-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



