Abstract
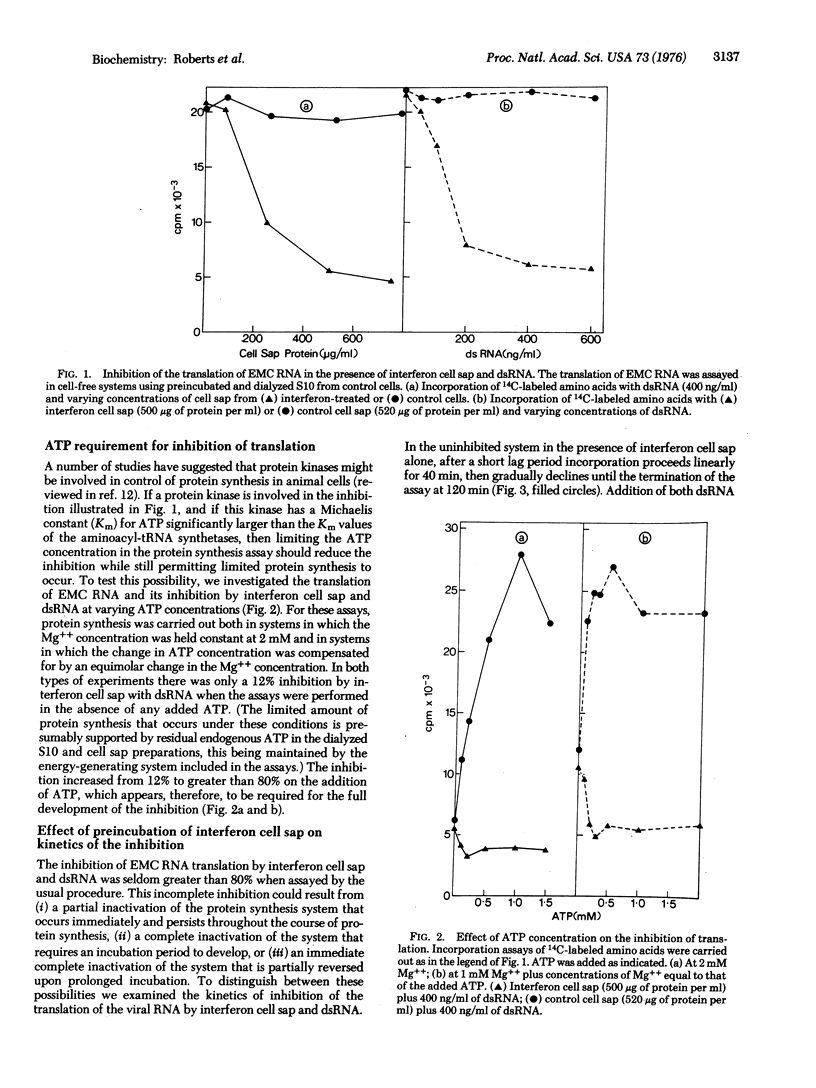
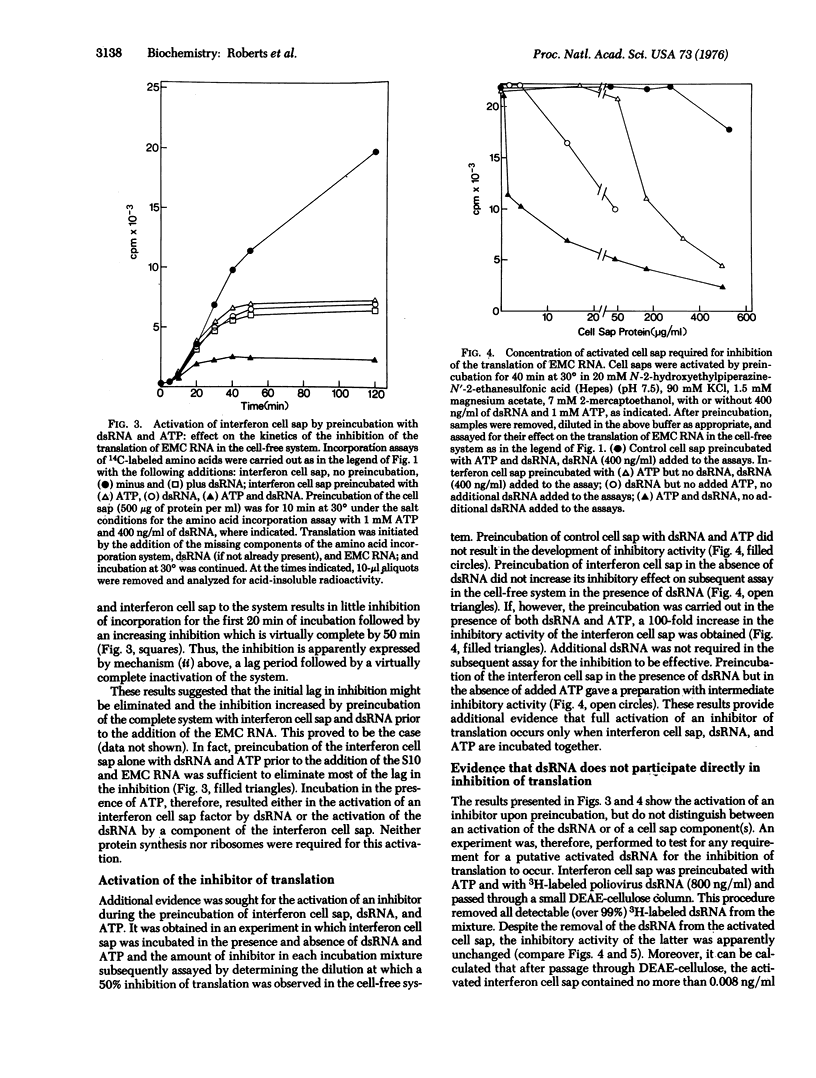
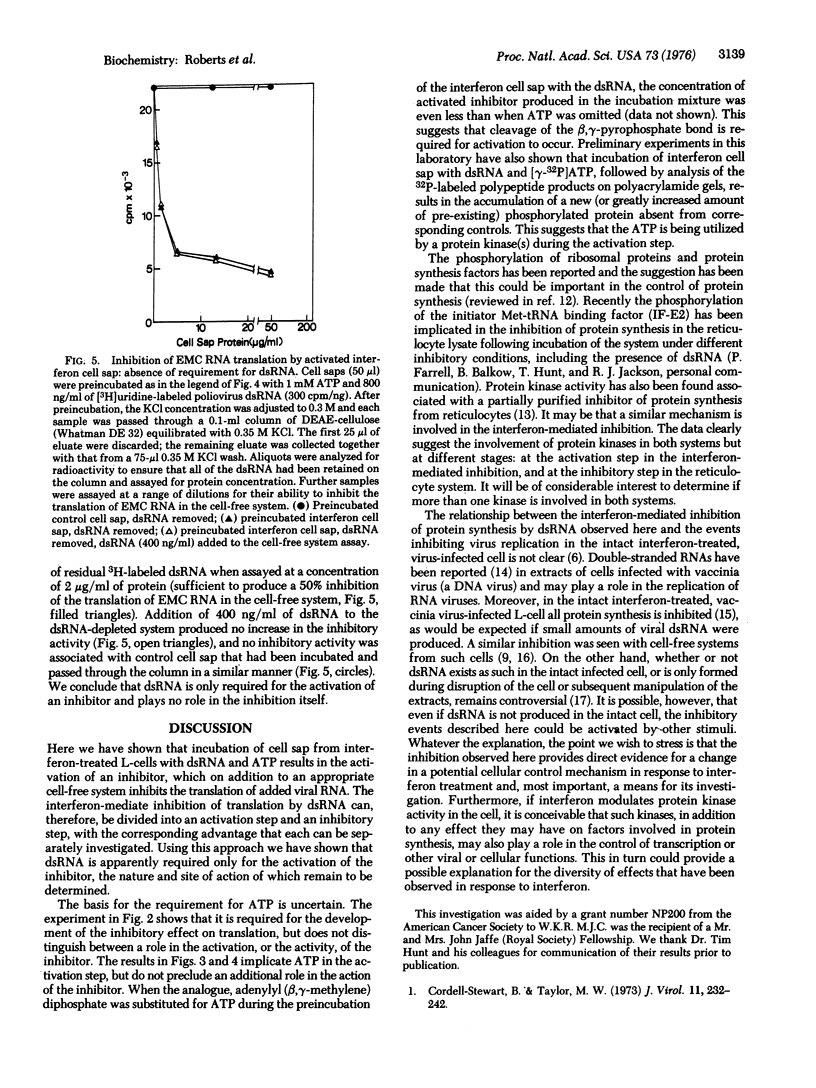
The translation of encephalomyocarditis virion RNA in extracts from interferon-treated L-cells is inhibited by the addition of double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) at 400 ng/ml. A similar inhibition in response to dsRNA is seen in control cell extracts supplemented with small amounts of a postribosomal supernatant fraction from interferon-treated cells (interferon cell sap): Neither interferon cell sap nor dsRNA alone is inhibitory in control systems. The inhibition is much reduced if translation is carried out at low ATP concentrations.Conversely, the inhibitory capacity of the interferon cell sap is increased 100-fold if it is preincubated with dsRNA and ATP prior to its addition to the protein-synthesizing system. After this preincubation all detectable dsRNA can be removed without any diminution of the inhibitory activity of the cell sap. These results are compatible with a two-step model for the inhibition in which a pre-inhibitor is activated by dsRNA, the activated inhibitor then interacting with the protein synthesis system to inhibit translation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cordell-Stewart B., Taylor M. W. Effect of viral double-stranded RNA on protein synthesis in intact cells. J Virol. 1973 Feb;11(2):232–237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.2.232-237.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Colby C. On the biosynthesis and structure of double-stranded RNA in vaccinia virus-infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Sep;64(1):396–403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.64.1.396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Hunt T. Double-stranded poliovirus RNA inhibits initiation of protein synthesis by reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1075–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1075. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Metz D. H., Esteban R. M., Tovell D. R., Ball L. A., Kerr I. M. Mechanism of interferon action: inhibition of viral messenger ribonucleic acid translation in L-cell extracts. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1184–1198. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1184-1198.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaempfer R., Kaufman J. Inhibition of cellular protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA: inactivation of an initiation factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Apr;70(4):1222–1226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.4.1222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Brown R. E., Ball L. A. Increased sensitivity of cell-free protein synthesis to double-stranded RNA after interferon treatment. Nature. 1974 Jul 5;250(461):57–59. doi: 10.1038/250057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Cohen N., Work T. S. Factors controlling amino acid incorporation by ribosomes from krebs II mouse ascites-tumour cells. Biochem J. 1966 Mar;98(3):826–835. doi: 10.1042/bj0980826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Friedman R. M., Brown R. E., Ball L. A., Brown J. C. Inhibition of Protein Synthesis in Cell-Free Systems from Interferon-Treated, Infected Cells: Further Characterization and Effect of Formylmethionyl-tRNA(F). J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):9–21. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.9-21.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr I. M., Olshevsky U., Lodish H. F., Baltimore D. Translation of murine leukemia virus RNA in cell-free systems from animal cells. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):627–635. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.627-635.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Ranu R. S., Ernst V., Fifer M. A., London L. M. Association of a cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase with a purified translational inhibitor isolated from hemin-deficient rabbit reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):4849–4853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.4849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz D. H., Esteban M. Interferon inhibits viral protein synthesis in L cells infected with vaccinia virus. Nature. 1972 Aug 18;238(5364):385–388. doi: 10.1038/238385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogburn C. A., Berg K., Paucker K. Purification of mouse interferon by affinity chromatography on anti-interferon globulin-sepharose. J Immunol. 1973 Oct;111(4):1206–1218. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Double-stranded RNA as an inhibitor of protein synthesis and as a substrate for a nuclease in extracts of Krebs II ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):225–229. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin C. S., Rosen O. M. Protein phosphorylation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:831–887. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.004151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spector D. H., Baltimore D. Polyadenylic acid on poliovirus RNA. II. poly(A) on intracellular RNAs. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1418–1431. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1418-1431.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart W. E., 2nd, De Clercq E., De Somer P. Specificity of interferon-induced enhancement of toxicity for double-stranded ribonucleic acids. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):237–246. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thach S. S., Thach R. E. Mechanism of viral replication. I. Structure of replication complexes of R17 bacteriophage. J Mol Biol. 1973 Dec 15;81(3):367–380. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


