Abstract
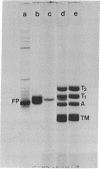
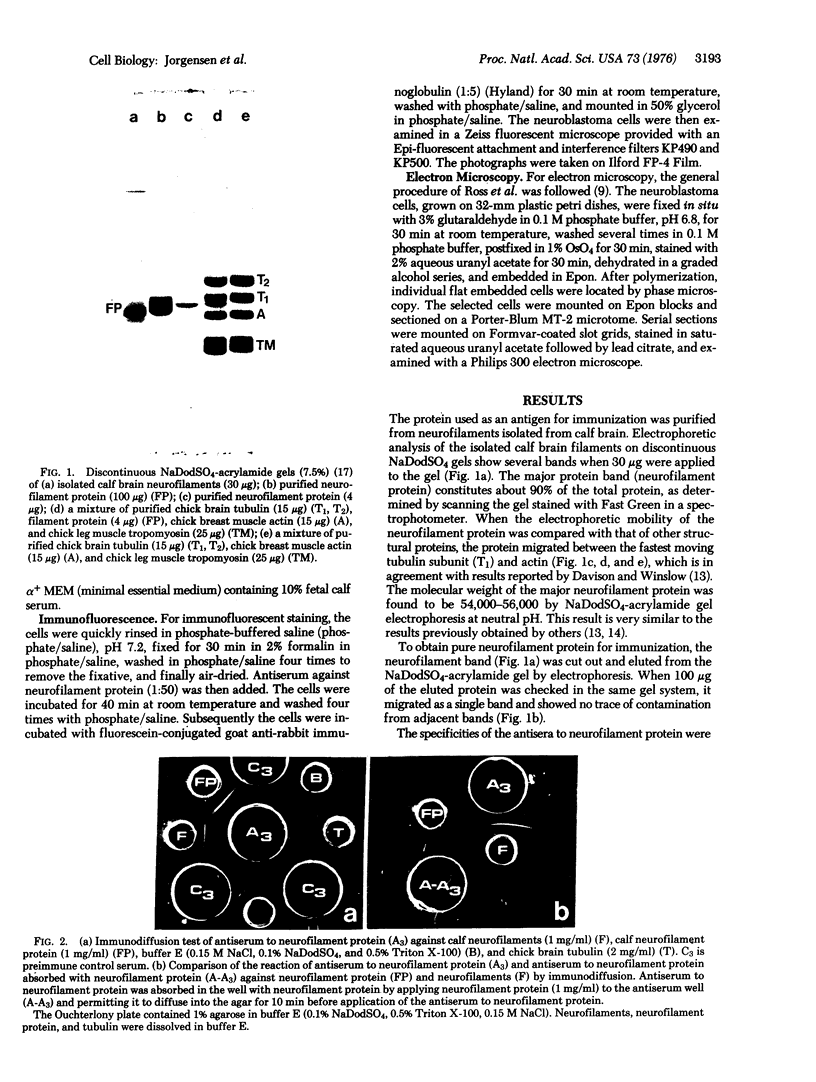
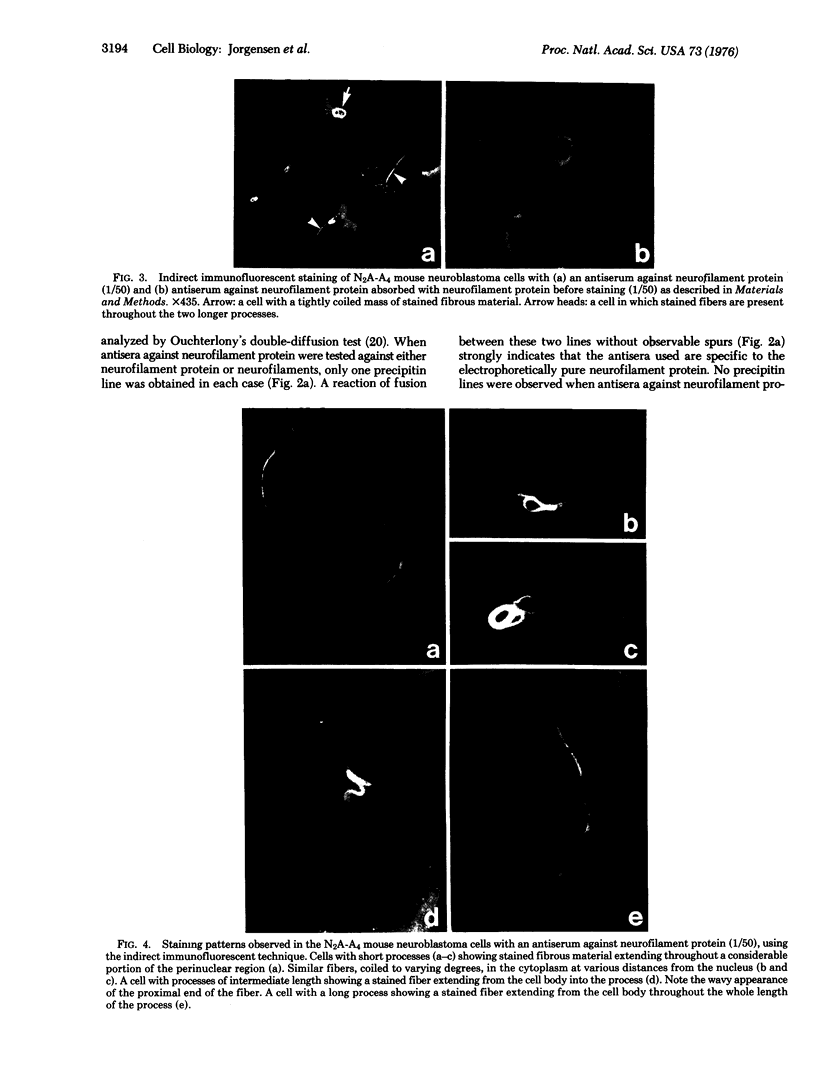
Neurofilament protein (54,000-56,000 daltons) has been localized in murine neuroblastoma cells by indirect immunofluorescent staining with antisera to purified calf brain neurofilament protein. In some cells with only short processes, specific staining of fibrous material was present in the perinuclear region while in other cells similar fibers, coiled to varying degrees, were present in other regions of the cytoplasm. In cells with longer processes a stained fiber extended throughout each process. The staining pattern observed followed the distribution of bundles of 100 A filaments as determined by electron microscopy. The fibers did not stain with antisera to tubulin or tropomyosin. The observations reported strongly indicate (i) that neurofilament protein isolated from calf brain is antigenically related to a component of the bundles of 100 A filaments in neuroblastoma cells, and (ii) that the neurofilament protein is an integral part of bundles of 100 A filaments in neuroblastoma cells, while neither tubulin nor tropomyosin is present in these bundles.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubin J. E., Subrahmanyan L., Kalnins V. I., Ling V. Antisera against electrophoretically purified tubulin stimulate colchicine-binding activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1246–1249. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckley I. K. Subcellular motility: a correlated light and electron microscopic study using cultured cells. Tissue Cell. 1974;6(1):1–20. doi: 10.1016/0040-8166(74)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. H., Chase R. H. Potassium chloride-insoluble myofilaments in vertebrate smooth muscle cells. Exp Cell Res. 1971 Jun;66(2):417–425. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(71)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke P. A filamentous cytoskeleton in vertebrate smooth muscle fibers. J Cell Biol. 1976 Mar;68(3):539–556. doi: 10.1083/jcb.68.3.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crapper D. R., Dalton A. J. Aluminum induced neurofibrillary degeneration, brain electrical activity and alterations in acquisition and retention. Physiol Behav. 1973 May;10(5):935–945. doi: 10.1016/0031-9384(73)90064-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison P. F., Winslow B. The protein subunit of calf brain neurofilament. J Neurobiol. 1974;5(2):119–133. doi: 10.1002/neu.480050204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham D. I., Gonatas N. K., Charalampous F. C. The undifferentiated and extended forms of C1300 murine neuroblastoma. An ultrastructural study and detection of concanavalin A binding sites on the plasma membrane. Am J Pathol. 1974 Aug;76(2):285–312. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray E. G., Guillery R. W. Synaptic morphology in the normal and degenerating nervous system. Int Rev Cytol. 1966;19:111–182. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)60566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtrop M. E., Raisz L. G., Simmons H. A. The effects of parathyroid hormone, colchicine, and calcitonin on the ultrastructure and the activity of osteoclasts in organ culture. J Cell Biol. 1974 Feb;60(2):346–355. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.2.346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzer H., Croop J., Dienstman S., Ishikawa H., Somlyo A. P. Effects of cytochaslasin B and colcemide on myogenic cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):513–517. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huneeus F. C., Davison P. F. Fibrillar proteins from squid axons. I. Neurofilament protein. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 28;52(3):415–428. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90410-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa H., Bischoff R., Holtzer H. Mitosis and intermediate-sized filaments in developing skeletal muscle. J Cell Biol. 1968 Sep;38(3):538–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.3.538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen A. O., Subrahmanyan L., Kalnins V. I. Localization of tropomyosin in mouse embryo fibroblasts. Am J Anat. 1975 Apr;142(4):519–525. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001420409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirpatrick J. B. Chromatolysis in the hypoglossal nucleus of the rat: an electron microscopic analysis. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Jan;132(1):189–212. doi: 10.1002/cne.901320110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Vaughn J. E. Microtubules and filaments in the axons and astrocytes of early postnatal rat optic nerves. J Cell Biol. 1967 Jan;32(1):113–119. doi: 10.1083/jcb.32.1.113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rewcastle N. B., Ball M. J. Electron microscopic structure of the "inclusion bodies" in Pick's disease. Neurology. 1968 Dec;18(12):1205–1213. doi: 10.1212/wnl.18.12.1205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J., Olmsted J. B., Rosenbaum J. L. The ultrastructure of mouse neuroblastoma cells in tissue culture. Tissue Cell. 1975;7(1):107–135. doi: 10.1016/s0040-8166(75)80010-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochet S. S., Jr, Lampert P. W., Earle K. M. Neuronal changes induced by intrathecal vincristine sulfate. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1968 Oct;27(4):645–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Albert S., DeVries G. H., Norton W. T. Isolation of filaments from brain. Science. 1971 Dec 17;174(4015):1242–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.174.4015.1242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shelanski M. L., Wiśniewski H. Neurofibrillary degeneration induced by vincristine therapy. Arch Neurol. 1969 Feb;20(2):199–206. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1969.00480080099012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKANO I. ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDIES ON RETROGRADE CHROMATOLYSIS IN THE HYPOGLOSSAL NUCLEUS AND CHANGES IN THE HYPOGLOSSAL NERVE, FOLLOWING ITS SEVERANCE AND LIGATION. Okajimas Folia Anat Jpn. 1964 Apr;40:1–69. doi: 10.2535/ofaj1936.40.1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D. Neuronal fibrous protein in human pathology. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1971 Jan;30(1):8–19. doi: 10.1097/00005072-197101000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uehara Y., Campbell G. R., Burnstock G. Cytoplasmic filaments in developing and adult vertebrate smooth muscle. J Cell Biol. 1971 Aug;50(2):484–497. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.2.484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss P. A., Mayr R. Organelles in neuroplasmic ("axonal") flow: neurofilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Apr;68(4):846–850. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.4.846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H., Shelanski M. L., Terry R. D. Effects of mitotic spindle inhibitors on neurotubules and neurofilaments in anterior horn cells. J Cell Biol. 1968 Jul;38(1):224–229. doi: 10.1083/jcb.38.1.224. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wuerker R. B., Kirkpatrick J. B. Neuronal microtubules, neurofilaments, and microfilaments. Int Rev Cytol. 1972;33:45–75. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61448-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Dahl D., Schachner M., Shelanski M. L. Biochemistry of the filaments of brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Feb;73(2):529–533. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.2.529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogeeswaran G., Murray R. K., Pearson M. L., Sanwal B. D., McMorris F. A., Ruddle F. H. Glycosphingolipids of clonal lines of mouse neuroblastoma and neuroblastoma X L cell hybrids. J Biol Chem. 1973 Feb 25;248(4):1231–1239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]