Abstract
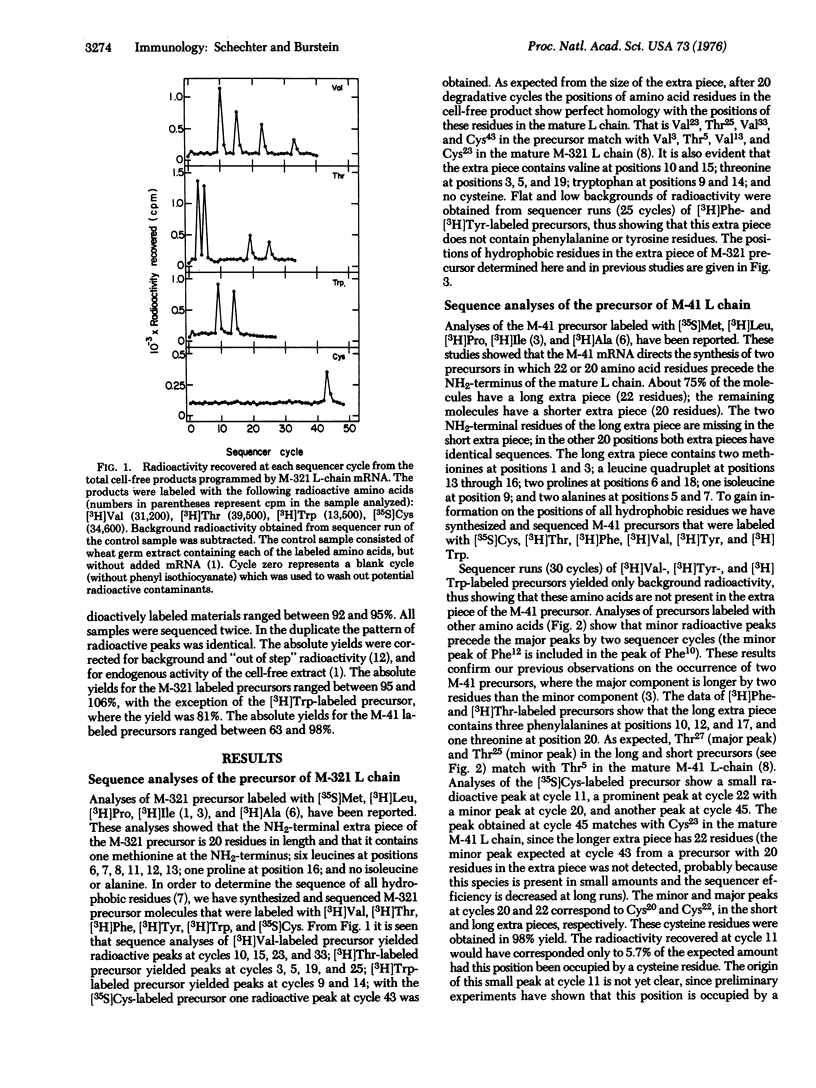
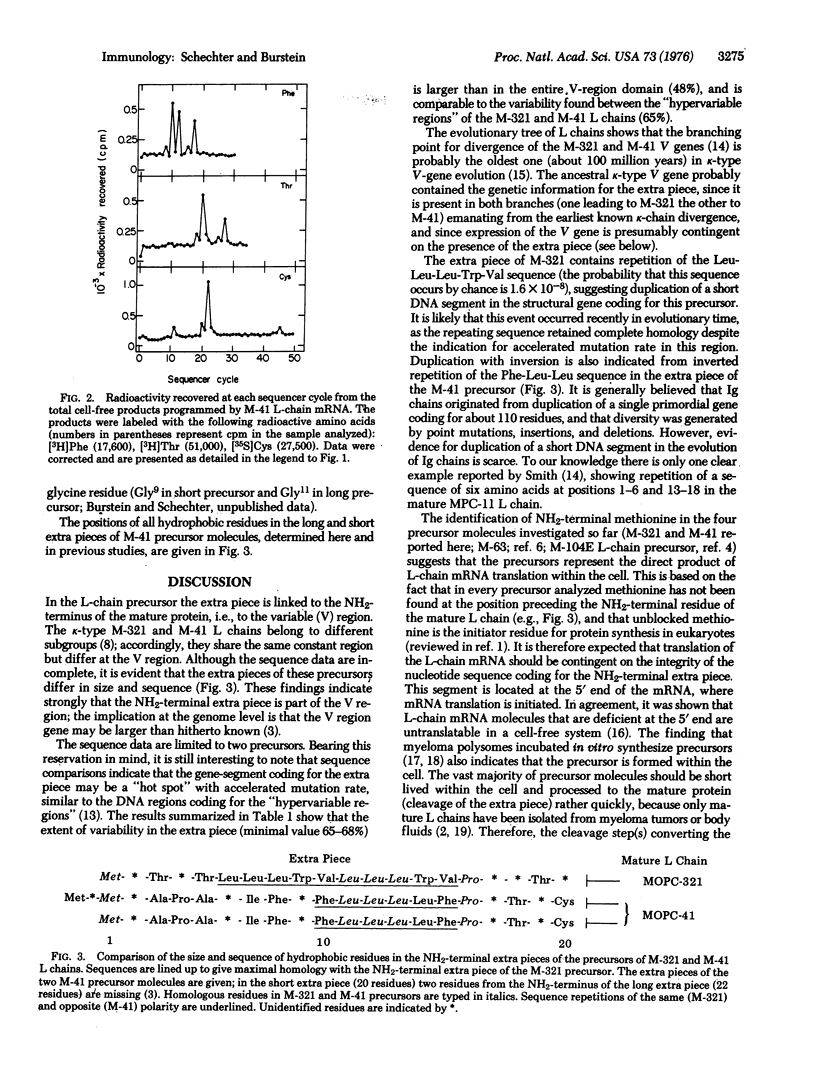
mRNAs coding for mouse immunoglobulin light chains direct the cell-free synthesis of precursors in which extra peptide segments precede the NH2-termini of the mature proteins. The abundance (18-30%) of leucine residues in the extra piece indicates that it is quite hydrophobic [Schechter and Burstein (1976) Biochem. Biophys, Res. Commun. 68, 489]. Accordingly, we have determined the positions of all hydrophobic residues by sequencing two k-type light (L)-chain precursors that were labeled with: [3H]Ala, [3H]Val, [3H]Leu, [3H]Ile, [3H]Thr, [3H]Pro, [3H]Phe, [3H]Tyr, [3H]Trp, [35S]Met, and [35S]Cys. The partial sequences (and sizes) of the extra pieces obtained are: in MOPC-321 precursor, Met-X-Thr-X-Thr-Leu-Leu-Leu-Trp-Val-Leu-Leu-Leu-Trp-Val-Pro-X-X-Thr-X-(20 residues; X is unknown); in MOPC-41 precursor, Met-X-Met-X-Ala-Pro-Ala-X-Ile-Phe-X-Phe-Leu-Leu-Leu-Leu-Phe-Pro-X-Thr-X-Cys- (22 residues). Despite the fact that these extra pieces differ extensively in sequence (68%), both of them are highly enriched with hydrophobic residues (75% in MOPC-321, 73% in MOPC-41). This marked hydrophobicity suggests that the extra piece favors interaction of the precursor with cell membranes, in a manner similar to the function of the "hydrophobic domain" of membrane-bound proteins (e.g., glycophorin). We propse that the hydrophobic extra piece directs most precursor molecules to the endoplasmic reticulum, where they are cleaved to yield mature L chain destined for scretion; a few precursor molecules escape cleavage and are embedded in the cell surface to serve as the antigen-recognizing receptor. The probability that the Leu-Leu-Leu-Trp-Val sequence occurs by change is 1.6 X 10(-8). Therefore, the data provide evidnece for duplication of a short DNA segment in the structural gene coding for the MOPC-321 precurosr. Duplication with inversion is also indicated from inverted repetition of the Phe-Lue-Leu sequence in the extra piece of the MPOC-41 precursor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson J., Buxbaum J., Citronbaum R., Douglas S., Forni L., Melchers F., Pernis B., Stott D. IgM-producing tumors in the BALB-c mouse: a model for B-cell maturation. J Exp Med. 1974 Sep 1;140(3):742–763. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.3.742. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. I. Presence of proteolytically processed and unprocessed nascent immunoglobulin light chains on membrane-bound ribosomes of murine myeloma. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):835–851. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G., Dobberstein B. Transfer of proteins across membranes. II. Reconstitution of functional rough microsomes from heterologous components. J Cell Biol. 1975 Dec;67(3):852–862. doi: 10.1083/jcb.67.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Kantour F., Schechter I. Partial amino-acid sequence of the precursor of an immunoglobulin light chain containing NH2-terminal pyroglutamic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2604–2608. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burstein Y., Schechter I. Amino acid-sequence variability at the N-terminal extra piece of mouse immunoglobulin light-chain precursors of the same and different subgroups. Biochem J. 1976 Jul 1;157(1):145–151. doi: 10.1042/bj1570145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devillers-Thiery A., Kindt T., Scheele G., Blobel G. Homology in amino-terminal sequence of precursors to pancreatic secretory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5016–5020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannestad K., Kao M. S., Eisen H. N. Cell-bound myeloma proteins on the surface of myeloma cells: potential targets for the immune system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2295–2299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKean D., Potter M., Hood L. Mouse immunoglobulin chains. Pattern of sequence variation among kappa chains with limited sequence differences. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb;12(4):760–771. doi: 10.1021/bi00728a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C., Brownlee G. G., Harrison T. M., Mathews M. B. A possible precursor of immunoglobulin light chains. Nat New Biol. 1972 Sep 27;239(91):117–120. doi: 10.1038/newbio239117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preud'homme J. L., Scharff M. D. The capping of surface immunoglobulin on mouse myeloma cells. J Immunol. 1974 Aug;113(2):702–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. E., Paterson B. M. Efficient translation of tobacco mosaic virus RNA and rabbit globin 9S RNA in a cell-free system from commercial wheat germ. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2330–2334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Biologically and chemically pure mRNA coding for a mouse immunoglobulin L-chain prepared with the aid of antibodies and immobilized oligothymidine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2256–2260. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Identification of N-terminal methionine in the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain. Initiation of translation of messenger ribonucleic acid in plants and animals. Biochem J. 1976 Mar 1;153(3):543–550. doi: 10.1042/bj1530543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I., Burstein Y. Partial sequence of the precursors of immunoglobulin light-chains of different subgroups: evidence that the immunoglobulin variable-region gene is larger than hitherto known. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):489–496. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91172-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Further characterization of the mRNA coding for immunoglobulin light-chain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Nov 3;67(1):228–235. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(75)90306-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Partial amino acid sequence of the precursor of immunoglobulin light chain programmed by messenger RNA in vitro. Science. 1975 Apr 11;188(4184):160–162. doi: 10.1126/science.803715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter I. Use of antibodies for the isolation of biologically pure messenger ribonucleic acid from fully functional eukaryotic cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Apr 23;13(9):1875–1885. doi: 10.1021/bi00706a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T., Guyer R. B., Terry W. Red cell membrane glycoprotein: amino acid sequence of an intramembranous region. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1972 Nov 15;49(4):964–969. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(72)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segrest J. P., Kahane I., Jackson R. L., Marchesi V. T. Major glycoprotein of the human erythrocyte membrane: evidence for an amphipathic molecular structure. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Mar;155(1):167–183. doi: 10.1016/s0003-9861(73)80019-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. P. Mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain MPC 11: extra amino-terminal residues. Science. 1973 Sep 7;181(4103):941–943. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4103.941. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smithies O., Gibson D., Fanning E. M., Goodfliesh R. M., Gilman J. G., Ballantyne D. L. Quantitative procedures for use with the Edman-Begg sequenator. Partial sequences of two unusual immunoglobulin light chains, Rzf and Sac. Biochemistry. 1971 Dec 21;10(26):4912–4921. doi: 10.1021/bi00802a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spatz L., Strittmatter P. A form of cytochrome b5 that contains an additional hydrophobic sequence of 40 amino acid residues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 May;68(5):1042–1046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.5.1042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svasti J., Milstein C. The disulphide bridges of a mouse immunoglobulin G1 protein. Biochem J. 1972 Feb;126(4):837–850. doi: 10.1042/bj1260837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu T. T., Kabat E. A. An analysis of the sequences of the variable regions of Bence Jones proteins and myeloma light chains and their implications for antibody complementarity. J Exp Med. 1970 Aug 1;132(2):211–250. doi: 10.1084/jem.132.2.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto S., Lampen J. O. Membrane penicillinase of Bacillus licheniformis 749/C, a phospholipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):3212–3213. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



