Abstract
Background
Heat shock transcription factors (Hsfs), which act as important transcriptional regulatory proteins in eukaryotes, play a central role in controlling the expression of heat-responsive genes. At present, the genomes of Chinese white pear (‘Dangshansuli’) and five other Rosaceae fruit crops have been fully sequenced. However, information about the Hsfs gene family in these Rosaceae species is limited, and the evolutionary history of the Hsfs gene family also remains unresolved.
Results
In this study, 137 Hsf genes were identified from six Rosaceae species (Pyrus bretschneideri, Malus × domestica, Prunus persica, Fragaria vesca, Prunus mume, and Pyrus communis), 29 of which came from Chinese white pear, designated as PbHsf. Based on the structural characteristics and phylogenetic analysis of these sequences, the Hsf family genes could be classified into three main groups (classes A, B, and C). Segmental and dispersed duplications were the primary forces underlying Hsf gene family expansion in the Rosaceae. Most of the PbHsf duplicated gene pairs were dated back to the recent whole-genome duplication (WGD, 30–45 million years ago (MYA)). Purifying selection also played a critical role in the evolution of Hsf genes. Transcriptome data demonstrated that the expression levels of the PbHsf genes were widely different. Six PbHsf genes were upregulated in fruit under naturally increased temperature.
Conclusion
A comprehensive analysis of Hsf genes was performed in six Rosaceae species, and 137 full length Hsf genes were identified. The results presented here will undoubtedly be useful for better understanding the complexity of the Hsf gene family and will facilitate functional characterization in future studies.
Electronic supplementary material
The online version of this article (doi:10.1186/s12870-014-0401-5) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Keywords: Hsf, Stress-response, Evolution, Transcriptome sequencing, Pear, Rosaceae
Background
Plant development and agricultural production are seriously disturbed by adverse environmental conditions such as cold, drought, and excess heat. Heat stress due to increases in temperature beyond a threshold level cause significant damage to plant morphology, physiology, and biochemistry and may drastically reduce plant biomass production and economic yield in many areas worldwide [1,2]. In response, plants have developed numerous sophisticated adaptations over the long course of evolution [3]. Plant survival is dependent upon a network of interconnected cellular stress response systems that involve the activation of a wide range of transcriptional factors; this network is challenged by global climate changes such as global warming, which makes heat stress a significant concern [4–7]. As important gene regulators, transcription factors are involved in an array of plant protective mechanisms and cellular stress-response pathways and play an essential role in enhancing the stress tolerance of crop plants [8–13]. Hsfs are particularly involved in the heat stress response, and these products are important regulators in the sensing and signaling of heat stress [13]. Recent studies have also shown that Hsfs are involved in plant growth and development, as well as in responses to other abiotic stresses such as cold, salt, and drought [12–21]. For example, HsfA1a acts as the master regulator of the heat stress response in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) [22]; HsfA2 is the dominant Hsf in tomato and Arabidopsis and is also associated with oxidative and drought stress responses [12,19,23]; HsfA4a is related to cadmium tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa) [21]; and HsfA9 is involved in embryogenesis and seed maturation in sunflowers and Arabidopsis [16–18].
As do many other transcription factors, Hsfs possess a modular structure composed of several structurally and functionally conserved domains. Hsfs share a common core structure composed of an N-terminal DNA binding domain (DBD) and an adjacent bipartite oligomerization domain (HR-A/B) [24,25]. Some Hsfs also include other well-defined domains: a nuclear localization signal (NLS) domain essential for nuclear import, nuclear export signal (NES) domain rich in leucine, and C-terminal activator domain (CTAD) characterized by aromatic (W, F, Y), large hydrophobic (L, I, V), and acidic (E, D) amino acid residues, known as AHA motifs [13,24,26]. Close to the N-terminus, the DBD is the most conserved region of the Hsfs and is composed of an antiparallel four-stranded β-sheet (β1-β2-β3-β4) and a three-helical bundle (H1, H2, and H3). A central helix-turn-helix motif (H2-T-H3) located in the hydrophobic core of this domain specifically binds to the heat shock promoter elements [27]. The HR-A/B domain is characterized by hydrophobic heptad repeats that form a helical coiled-coil structure, which is a prerequisite for high affinity DNA binding and, subsequently, for transcriptional activity. Furthermore, a flexible linker exists between the DBD domain and HR-A/B domain [28].
Differences in the numbers of Hsf genes have been widely determined in angiosperms. In contrast to those of other eukaryotes, which possess one to three heat stress Hsf genes, the plant Hsf gene family contains a striking number of genes, with more than 20 and up to 52 members in any given species [12,29,30]. According to the structural characteristics of their HR-A/B domain and phylogenetic comparisons, plant Hsf genes may be divided into three classes: A, B, and C [24,25]. Hsf genes of class B are comparatively compact, not containing any insertions, while those of classes A and C have insertions of 21 (class A) and seven (class C) amino acid residues between the A and B components of the HR-A/B domain. This classification is also supported by the flexible linker between the DBD domain and HR-A/B domain (9 to 39, 50 to 78, and 14 to 49 amino acid residues for class A, B, and C Hsf genes, respectively) [13,24]. In addition, many plant class A Hsf genes have a particular signature domain comprising a combination of an AHA motif with an adjacent NES [13,25].
Because of the vital regulatory functions of Hsf genes in plant responses to different stresses and developmental processes [18–20], Hsf gene family have been extensively studied in the model plant Arabidopsis thaliana, as well as in nonmodel plants such as rice (Oryza sativa), poplar (Populus trichocarpa), maize (Zea mays), apple (Malus domestica), etc. [9,13,24,31–33]. In comparison with that in other species, the Hsf gene family in the Rosaceae has not been widely examined. Pear is a member of the Rosaceae family and is also the third-most important temperate fruit species [34]. Recently, the genome of the domesticated Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd. cv. ‘Dangshansuli’) [34] has been fully sequenced. Genome sequences are also available for five other Rosaceae species (apple, peach, strawberry, Chinese plum, and European pear). This information provides an opportunity to further analyze the Hsf gene family in Rosaceae species. Therefore, our present study aims to annotate the full-length Hsf genes in Chinese white pear and other Rosaceae fruit species, infer their expansion and evolutionary history, explore their heat stress responses as elicited by naturally increased temperature, and provide a relatively complete profile of the Hsf gene family in Rosaceae. The results of this work will be useful for revealing the mechanisms of thermotolerance in fruit trees and for improving the tolerance of fruit trees to high-temperature stress, which is becoming more prevalent due to global warming.
Results
Identification and classification of Hsf genes in the Rosaceae
Two strategies were used to search for members of the Hsfs family in Pyrus bretschneideri and five other Rosaceae species: Hidden Markov Model search (HMMsearch) with the Hsf domain HMM profile (PF00447) and BLASTP using Hsf protein sequences from Arabidopsis thaliana and Populus trichocarpa as queries. A total of 185 candidate Hsf genes were identified. We removed six and one Hsf genes located in unanchored scaffolds of Chinese white pear and Chinese plum, respectively. A further 40 candidates were removed due to an incomplete DBD domain and loss of the functional HR–A/B domain. One abnormal pear Hsf (Pbr013854.1) containing a Really Interesting New Gene (RING) finger domain and a tryptophan-aspartic acid 40 (WD40) domain was also removed. The selection of apple Hsf genes was based on recent research results [32]. Consequently, 137 nonredundant and complete Hsf genes were surveyed in our study. A total of 29 Hsf genes were identified in Chinese white pear(PbHsf), 33 in European pear (PcHsf), 25 in apple (MdHsf), 17 in peach (PpHsf), 16 in strawberry (FvHsf), and 17 in Chinese plum (PmHsf) (Table 1).
Table 1.
Genome information and Hsf genes number identified in Rosaceae species
| Common name | Scientific name | Chromosome number | Release version | Genome gene number | Identified | Gene name prefix |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hsf genes | ||||||
| Chinese white pear | Pyrus bretschneideri | 34 | NJAU, v1.0 | 42341 | 29 (38) | Pbr |
| Apple | Malus domestica | 34 | GDR, v1.0 | 63541 | 25 (49) | MDP |
| Peach | Prunus persica | 16 | JGI, v1.0 | 27864 | 17 (21) | ppa |
| Strawberry | Fragaria vesca | 14 | GDR, v1.0 | 32831 | 16(16) | gene |
| Chinese plum | Prunus mume | 16 | BFU, v1.0 | 31390 | 17 (20) | Pm |
| European pear | Pyrus communis | 34 | GDR, v1.0 | 43419 | 33 (41) | PCP |
In this study we totally investigated six Rosaceae species genomes. NJAU, Nanjing Agricultural Univerisity (http://peargenome.njau.edu.cn/); GDR, Genome Database for Rosaceae (http://www.rosaceae.org/); JGI, Joint Genome Institude (http://www.jgi.doe.gov/); BFU, Beijing Forestry University (http://prunusmumegenome.bjfu.edu.cn/index.jsp). The numbers in parenthesis show gene count before filtering the unanchored and incomplete genes.
The phylogenetic tree of the six Rosaceae species was reconstructed, and the WGD events over the course of genome evolution were inferred from recent studies [34] (Figure 1). Chinese white pear, European pear, and apple belong to the Maloideae, strawberry belongs to Rosoideae, and peach and Chinese plum belong to the Prunoideae [35]. Nearly twice as many Hsf genes were present in pear and apple than in peach, strawberry, and Chinese plum. A recent WGD event occurred in the Maloideae but not in the Rosoideae and Prunoideae. We can therefore infer that the recent WGD led to the specific expansion of the Hsf gene family in the Maloideae.
Figure 1.
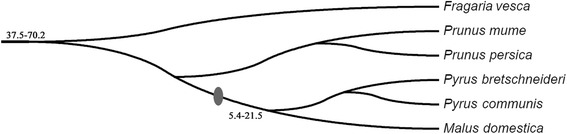
Species tree of six Rosaceae species. Solid oval indicates the occurrence of WGD. Numbers in the figure indicate species divergence time. Unit: MYA. The data were downloaded from NCBI Taxonomy common tree (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/CommonTree/wwwcmt.cgi) and the tree was constructed by MEGA6.
The PbHsf genes are distributed on 14 of the 17 pear chromosomes, with five Hsf genes detected on chromosome 15 (Figure 2). Similarly to that in PbHsf genes, the distribution of the Hsf genes in the other five Rosaceae genomes is random (Figure 2 and Additional file 1).
Figure 2.
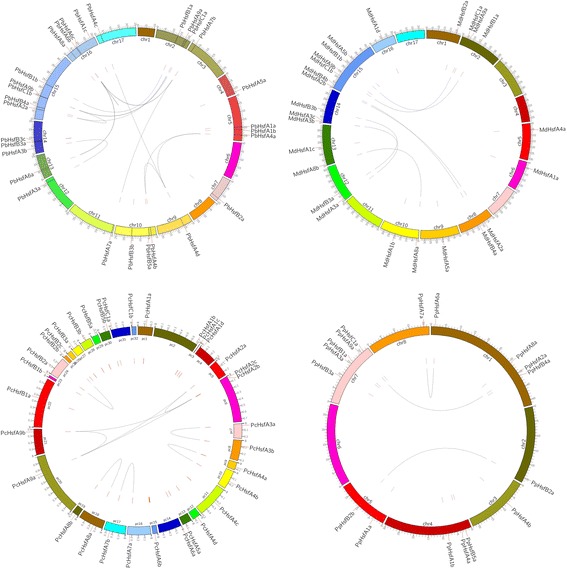
Localization and synteny of the Hsf genes in Rosaceae genomes. Hsf genes in Chinese white pear (PbHsf), apple (MdHsf) and peach (PpHsf) were mapped on the different chromosomes, while in European pear (PcHsf) were anchored to the scaffolds. Chromosome or scaffold number is indicated on the inner side and highlighted red short lines in the inner circle correspond to different Hsf genes. Gene pair with a syntenic relationship was joined by the line.
According to the multiple sequence alignment of the functional domains and the phylogenetic analysis, the members of the Rosaceae Hsf family genes were divided into three subfamilies (A, B, and C) (Table 2 and Additional file 2). These results were consistent with the classification of the genes in other plants [24,33]. In contrast with class B, classes A and C possess insertions of amino acid residues in the HR-A/B region. The protein sequences of class A contain more specific domains than do those of class C. Furthermore, a phylogenetic tree was generated using the protein sequences of Pyrus bretschneideri (PbHsf), Populus trichocarpa (PtHsf), and Arabidopsis thaliana (AtHsf) (Figure 3). The tree was constructed using the neighbor joining (NJ) method, and a maximum likelihood (ML) tree confirmed the result. The Hsf genes from the three species were clearly grouped into three different clades corresponding to the main Hsf classes A, B, and C. In the PbHsf genes family, 19, 8, and 2 genes were assigned to Classes A, B, and C, respectively. Within the A clade, nine distinct subclades (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, and A9) were resolved and contained all of the PbHsf genes. The C-type Hsf genes from the three plant species also constituted one distinct clade, which appeared to be more closely related to the Hsf A-group. Correspondingly, the B-type Hsf genes were grouped into a separate clade subdivided into five groups (B1, B2, B3, B4, and B5); notably, the B5 sub-clade was obviously distinct from the other four subclades.
Table 2.
Classification of Hsf genes in six Rosaceae species
| Hsfs | Chinese white pear(29) | Apple(25) | Peach(17) | Strawberry(16) | Chinese plum(17) | European pear(33) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HsfA1a | Pbr025227.1 | MDP0000517644 | ppa004782m | gene13904 | Pm023178 | PCP005520.1 |
| b | Pbr041026.1 | MDP0000156337 | ppa004559m | gene10474 | Pm011227 | PCP027354.1 |
| c | Pbr031411.1 | MDP0000232623 | PCP027124.1 | |||
| d | MDP0000259645 | PCP011761.1 | ||||
| HsfA2a | Pbr019856.1 | MDP0000489886 | ppa007300m | gene02705 | Pm005519 | PCP044449.1 |
| b | MDP0000243895 | PCP016141.1 | ||||
| c | PCP034937.1 | |||||
| HsfA3a | Pbr005496.1 | MDP0000131346 | ppa015602m | gene30146 | Pm026236 | PCP016675.1 |
| b | Pbr016805.1 | MDP0000606400 | PCP026047.1 | |||
| c | MDP0000174161 | |||||
| HsfA4a | Pbr000538.1 | MDP0000155849 | ppa006534m | gene23802 | Pm010169 | PCP025026.1 |
| b | Pbr016090.1 | ppa015468m | gene15872 | Pm013905 | PCP026169.1 | |
| c | Pbr022463.1 | PCP024177.1 | ||||
| d | Pbr005379.1 | PCP015400.1 | ||||
| HsfA5a | Pbr016487.1 | MDP0000301101 | gene06570 | Pm007815 | PCP002437.1 | |
| b | MDP0000613011 | |||||
| HsfA6a | Pbr036788.1 | ppa1027143m | gene29004 | Pm009237 | PCP030606.1 | |
| b | Pbr014670.1 | PCP018714.1 | ||||
| c | Pbr018847.1 | |||||
| HsfA7a | Pbr009953.1 | ppa010224m | gene20347 | Pm020253 | PCP019575.1 | |
| b | Pbr012908.1 | PCP022776.1 | ||||
| HsfA8a | Pbr012136.1 | MDP0000191541 | ppa006514m | Pm005887 | PCP006787.1 | |
| b | MDP0000172376 | PCP031284.1 | ||||
| HsfA9a | Pbr041474.1 | MDP0000194672 | ppa016533m | gene12667 | Pm027197 | PCP005035.1 |
| b | Pbr015630.1 | MDP0000319456 | PCP027517.1 | |||
| HsfB1a | Pbr025141.1 | MDP0000527802 | ppa009274m | gene24036 | Pm026366 | PCP024136.1 |
| b | Pbr030422.1 | MDP0000578396 | PCP030007.1 | |||
| HsfB2a | Pbr013953.1 | MDP0000155667 | ppa009180m | gene13301 | Pm019357 | PCP030684.1 |
| b | ppa008441m | gene32416 | Pm023788 | PCP033244.1 | ||
| c | PCP007662.1 | |||||
| HsfB3a | Pbr002020.1 | MDP0000622590 | ppa014675m | gene02464 | PCP029678.1 | |
| b | Pbr030436.1 | MDP0000202716 | PCP024839.1 | |||
| c | Pbr002038.1 | |||||
| HsfB4a | Pbr019653.1 | MDP0000209135 | ppa026635m | Pm005297 | ||
| b | MDP0000129357 | |||||
| HsfB5a | Pbr016270.1 | ppa011804m | gene02408 | Pm010031 | PCP044895.1 | |
| b | PCP016888.1 | |||||
| HsfC1a | Pbr014107.1 | MDP0000230456 | ppa008830m | gene30881 | Pm027421 | PCP000545.1 |
| b | Pbr016948.1 | MDP0000320827 | PCP022060.1 |
Figure 3.
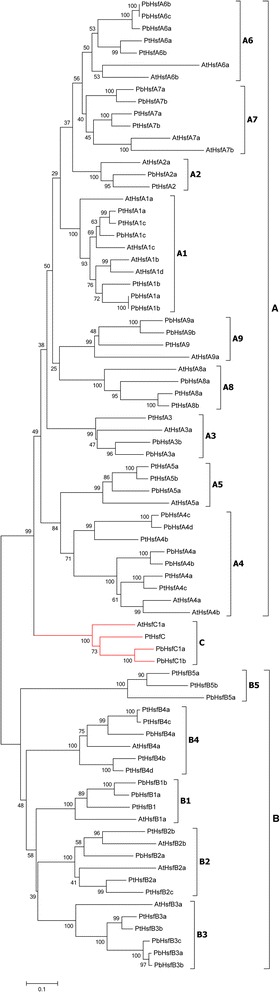
Neighbor-joining phylogeny of Hsfs from P. bretschneideri , P. trichocarpa and A. thaliana . The phylogenetic tree was obtained using the MEGA 6.0 software on the basis of amino-acid sequences of the N-terminal domains of Hsfs including the DNA-binding domain, the HR-A/B domain and the linker between these two domains. Bootstrap analysis was conducted with 1000 replicates. The abbreviations of species names are as follows: Pb, Pyrus bretschneideri; Pt, Populus trichocarpa; At, Arabidopsis thaliana.
Gene features of Hsf genes
Gene features such as structural complexity and GC3 content have intense impacts on gene retention and evolution after WGD [36]. Hence, we investigated the features of Hsf genes in the Rosaceae, including gene length, intron length, GC content, and GC3 content (Additional file 3). The average GC and GC3 contents of the Hsf gene family were higher than the average levels for the whole genome in most of the six Rosaceae species. Additionally, the average intron lengths of these genes in each of the Rosaceae genomes, except that of European pear, were shorter than those at the whole genome level. Especially in peach and Chinese plum, the average gene lengths and intron lengths of Hsf genes were significantly shorter than the whole genome averages. These results may be related to the intron losses that occurred during the expansion and divergence of the Hsf gene family [37].
Furthermore, the exon–intron structures of the Hsf genes in Chinese white pear and the other Rosaceae species were resolved (Additional files 4 and 5). The structures of the genes in the different subfamilies were extremely similar; this observation further verified the precision of the classification. However, the location and number of introns and exons varied among the Hsf genes. Most members of the Hsf gene family in the Rosaceae contained one intron. Strikingly, Hsf genes comprised of multiple introns were found in all six Rosaceae species and were especially prevalent in apple, strawberry, and European pear (Additional file 5). Notably, PcHsfA6b contained 13 introns; this gene was extremely different from the other Hsf genes because of its large size (16595 bp) and the presence of TIFY and CCT_2 domains.
Conserved protein domains in PbHsfs
Prediction of the typical signature domains of the PbHsfs protein sequences was conducted by comparing the identified PbHsfs with their well-characterized homologs from tomato, Arabidopsis, and apple [13,24,25,32]. Five conserved domains were identified by sequence alignment, and their positions in the protein sequences were determined (Table 3). All of the PbHsfs protein sequences contained the highly conserved DBD domain, consisting of a three helical bundle (H1, H2, and H3) and a four-stranded antiparallel β-sheet, in the N-terminal region. However, the length of the DBD domain was quite variable within the Hsf family. The presence of the coiled-coil structure characteristic of leucine zipper–type protein interaction domains, which is a property of the HR-A/B region, was instead predicted in all PbHsfs protein sequences using the MARCOIL tool. Furthermore, the majority of the PbHsfs protein sequences contained NES and NLS domains, which are essential for shuttling Hsfs between the nucleus and cytoplasm [13]. Additional sequence comparison identified AHA domains in the center of the C-terminal activation domains, as was expected in the A-type PbHsfs. By contrast, these domains were not identified in the B- and C-type PbHsfs.
Table 3.
Functional domains of PbHsfs
| Gene name | DBD | HR-A/B | NLS | NES | AHA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PbHsfA1a | 16-109 | 126-196 | (222) NKKRRLPR | (486) MNYITEQMQ | AHA(439) DIFWEQFLTAS |
| PbHsfA1b | 16-109 | 126-196 | (222) NKKRRLPR | (486) MNYITEQMQ | AHA(439) DIFWEQFLTAS |
| PbHsfA1c | 39-132 | 153-220 | (243) NKKRRLKQ | (499) MDNLTEKMG | AHA(452) DIEAFLKDWDD |
| PbHsfA2a | 38-131 | 145-212 | (227) KNR-X6-RKRR | (365) LVDQMGYL | AHA1(315) ETIWEELWSD |
| AHA2(355) DWGEDLQD | |||||
| PbHsfA3a | 99-216 | 237-296 | (308) KT-X10-RRKFVK | nd | AHA1(472) EDIWSMGFGV |
| AHA2(491) ELWGNPVNY | |||||
| AHA3(511) LDVWDIGPLQ | |||||
| AHA4(527) IDKSPAHDS | |||||
| AHA1(471) EDIWSMDFDI | |||||
| PbHsfA3b | 103-215 | 237-295 | (311) KDRGSSRVRRKFVK | nd | AHA2(489) NELLGNPVNY |
| AHA3(510) LDVWDIDPLQ | |||||
| AHA4(526) INKWPAHES | |||||
| PbHsfA4a | 11-94 | 113-190 | (208) RKRRLPR | (407) LTEQMGHL | AHA1(252) LTFWEDTIHD |
| AHA2(356) DGFWEQFLTE | |||||
| PbHsfA4b | 11-94 | 113-188 | (206) RKRRLPR | (410) LTEQMGHL | AHA1(250) LTFWEDTIHD |
| AHA2(359) DVFWEQFLTE | |||||
| PbHsfA4c | 12-106 | 137-186 | (204) KKRR | (429) FTNQIGRL | AHA1(252) LNFWEDFVHGI |
| AHA2(378) DVFWEQCLTE | |||||
| PbHsfA4d | 12-106 | 137-187 | (205) KKRR | (425) FRNQIGRP | AHA1(247) LNFWEDFLHGV |
| AHA2(372) DVFWEQCLTE | |||||
| PbHsfA5a | 12-105 | 116-183 | (194) RK-X10-KKRR | (477) AETLTL | AHA (431) DVFWEQFLTE |
| PbHsfA6a | 31-125 | 154-204 | (229) KKRRR | (344) LIEELGFL | AHA(312) DKGFWQDLFNE |
| (271) EVSELNQFAM | |||||
| PbHsfA6b | 21-115 | 144-194 | (210) RKELEKAVTKKRRR | (334) LIEELGFL | AHA(302) DKGYWQELFNE |
| PbHsfA6c | 21-115 | 144-194 | (210) RKELEKAVTKKRRR | (334) LIEELGFL | AHA(302) DKGYWQDLFNE |
| PbHsfA7a | 44-138 | 167-217 | (232) KKKELEEAMTKKRRR | (351) LADRLGYV | AHA(319) DEGFWEELFSE |
| PbHsfA7b | 44-138 | 167-217 | (232) KKKELEEAMTKKRRR | (344) LADRLGYF | AHA(312) DEGFWEELLSE |
| PbHsfA8a | 18-111 | 129-198 | (177) RNRLR | (389) TEQMGHL | AHA (308) DGAWEQFLLA |
| PbHsfA9a | 95-182 | 247-315 | (268) KR-X12-KRRR | (401) FYQELEDL | AHA(467) PCDWSAYVSHS |
| PbHsfA9b | 139-239 | 241-308 | (324) KR-X8-KRRR | (258) LKKDQD | AHA(460) PCDWSAYVSNS |
| PbHsfB1a | 6-99 | 142-191 | (246) KGDEKMKGKK | nd | nd |
| PbHsfB1b | 66-99 | 42-191 | (246) KGEEKMKGKK | (223) LDMEGG | nd |
| PbHsfB2a | 42-135 | 174-217 | (187) RLRK | nd | nd |
| PbHsfB3a | 19-112 | 149-194 | (223) RKRKR | (208) PKLFGVRLE | nd |
| PbHsfB3b | 19-112 | 149-194 | (223) RKRKR | (208) PKLFGVRLE | nd |
| PbHsfB3c | 22-116 | 149-194 | (180) KRKCK (223) RKRKR | (208) LKLFGVRLE | nd |
| PbHsfB4a | 21-114 | 179-239 | (326) KNTK-X9-KKR | (367) LEKDDLGLHLM | nd |
| PbHsfB5a | 11-111 | 151-188 | nd | (151) LRKQKLELQV | nd |
| PbHsfC1a | 9-102 | 121-173 | (197) KKRR | nd | nd |
| PbHsfC1b | 9-102 | 126-178 | (225) KKRR | nd | nd |
nd: no motifs detectable by sequence similarity search.
The Multiple EM for Motif Elicitation (MEME) motif search tool was used to predict and verify domains in the PbHsf protein sequences. Thirty corresponding consensus motifs were detected (Figure 4; Additional file 6). The number of motifs contained in the PbHsf protein sequences was quite variable. The members of class A contained the most conserved motifs, with the largest number (12) detected in PbHsfA1a and PbHsfA1b. Class C members possessed the fewest motifs, while class B PbHsfs contained an intermediate number. Regarding the DBD domain, motifs 1, 2, and 4 were found in 29 members of the PbHsfs family. The coiled-coil structure motifs 3, 5, 6 were detected in all members of the PbHsfs family. All class B proteins exhibited the coiled-coil region motifs 5 or 6, whereas motifs 3 and 6 were detected in classes A and C. The conserved motifs 3, 5, 6, 12, 16, 18, and 20 were identified as NLS. Motifs 3, 5, 16, and 20 were representative NLS domains in class A, while NLS domains were represented by motifs 6, 12, and 18 in class B. Furthermore, motifs 9, 12, 17, 18, and 23 represented NES domains; motifs 9, 17, and 23 were only observed in class A, while motifs 12 and 18 were seen only in class B. Motifs 7, 8, 10, 15, 17, and 27 was identified as characteristic AHA domains. Despite the variability in size and sequence, predicted DBD domain, HR-A/B domain and NLS domain were observed in each PbHsfs through the combination of the two methods.
Figure 4.
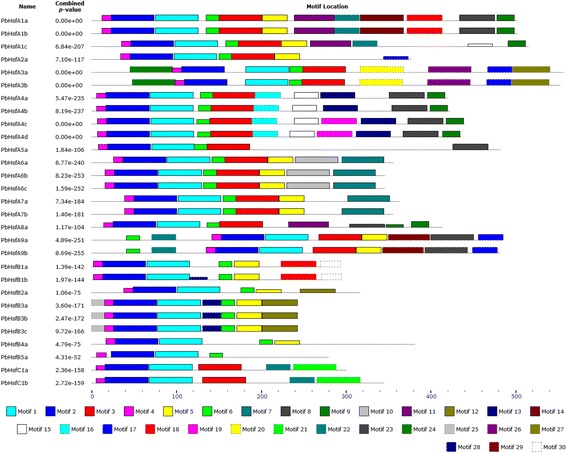
Motifs identified by MEME tools in Chinese white pear Hsfs. Thirty motifs (1 to 30) were identified and indicated by different colors. Motif location and combined p-value were showed.
Synteny analyses reveal the origin and expansion of the Hsf gene family
Several gene duplication modes drive the evolution of protein-coding gene families, including WGD or segmental duplication, tandem duplication, and rearrangements at the gene and chromosomal level [38]. We detected the origins of duplicate genes for the Hsf genes family in five Rosaceae genomes using the MCScanX package. Each member of Hsf gene family was assigned to one of five different categories: singleton, WGD, tandem, proximal or dispersed. Different patterns of gene duplication contributed differentially to the expansion of the Hsf gene family in the investigated taxa (Table 4). Remarkably, 75.9% (22) of the Hsf genes in Chinese white pear and 68% (17) of those in apple were duplicated and retained from WGD events, compared to only 35.3% (6) in peach, 25% (4) in strawberry, and 23.5% (4) in Chinese plum. The recent lineage-specific WGD events (30–45 MYA) in pear and apple likely resulted in the higher proportions of WGD-type Hsf gene duplications observed in these species. However, the proportions of dispersed Hsf gene duplication in peach (64.7%), strawberry (75%), and Chinese plum (76.5%) were considerably higher than in pear (17.2%) and apple (20%). Peach, strawberry, and Chinese plum have not experienced a WGD since their divergence from apple and pear. Therefore, genome rearrangements, gene losses, and RNA- and DNA-based transposed gene duplications may account for the larger proportions of dispersed duplicates in these species. These results showed that WGD or segmental duplication and dispersed gene duplication played critical roles in the expansion of the Hsf gene family in the Rosaceae.
Table 4.
Numbers of Hsf genes from different origins in five Roseceae genomes
| Species | No. of Hsf genes | No. of Hsf genes from different origins (percentage) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Singleton | WGD | Tandem | Proximal | Dispersed | ||
| Chinese white pear | 29 | 0 | 22(75.9) | 0 | 2(6.9) | 5(17.2) |
| Apple | 25 | 0 | 17(68.0) | 0 | 3(12.0) | 5(20.0) |
| Peach | 17 | 0 | 6(35.3) | 0 | 0 | 11(64.7) |
| Strawberry | 16 | 0 | 4(25) | 0 | 0 | 12(75) |
| Chinese plum | 17 | 0 | 4(23.5) | 0 | 0 | 13(76.5) |
Collinearity and synteny are traditionally identified by looking for both intra- and intergenomic pairwise conservation blocks. To further investigate the potential evolutionary mechanisms of the PbHsf gene family, we performed all-vs.-all local BLASTP to identify synteny blocks, using a method similar to that used for the Plant Genome Duplication Database (PGDD), across the entire Chinese white pear genome. The dates of segmental duplications can be inferred through this method; if two or more syntenic regions exist in one species, these regions are considered to be segmental duplications.
Conserved synteny was observed in 22 regions containing Hsf genes across the Chinese white pear genome (Figure 5), and these syntenic blocks included most of the Hsf genes (Table 5). We observed strongly conserved synteny in some of these blocks, several of which contained over 100 syntenic gene pairs (data not shown). These results support the occurrence of chromosome segment duplication or WGD in Chinese white pear [34]. A total of 13 segmentally duplicated gene pairs were found in the PbHsf gene family. Chromosomes 4 and 7 were not involved in any duplication events.
Figure 5.
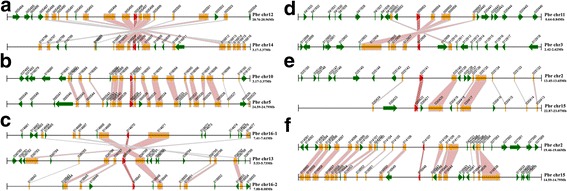
Segmental duplication between members of the Hsf family in Chinese white pear. (a) PbHsfA3a(Pbr005496) and PbHsfA3b(Pbr016805), (b) PbHsfA4a(Pbr000538) and PbHsfA4b(Pbr016090), (c) PbHsfA6a(Pbr036788) and PbHsfA6b(Pbr014670) and PbHsfA6a(Pbr036788) and PbHsfA6c(Pbr018847), (d) PbHsfA7a(Pbr009953) and PbHsfA7b(Pbr012908), (e) PbHsfB1a(Pbr025141) and PbHsfB1c(Pbr030422), (f) PbHsfC1a(Pbr014107) and PbHsfC1b(Pbr016948). The figure shows a region of 100 kb on each side flanking the Hsf genes. Homologous gene pairs are connected with bands. The chromosome segment is indicated by black horizontal line, and the broad line with arrowhead represents gene and its transcriptional orientation. The text besides the gene is the gene locus identifier suffix. The Hsf genes are shown in red, homologous genes are shown in yellow, and other genes shown in green.
Table 5.
Synteny analysis of Hsf gene regions in Chinese white pear genome
| Duplicated Hsf gene 1 | Duplicated Hsf gene 2 | Mean Ks | Homologous gene pairs in 200 kb | Genes in 200 kb |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PbHsfA2a | PbHsfA9a | 2.13 | 6 | 30 |
| PbHsfA2a | PbHsfA9b | 1.60 | 2 | 30 |
| PbHsfA3a | PbHsfA3b | 0.25 | 14 | 21 |
| PbHsfA4a | PbHsfA4b | 0.25 | 17 | 25 |
| PbHsfA4a | PbHsfA4d | 2.35 | 1 | 12 |
| PbHsfA4c | PbHsfA4d | 0.31 | 5 | 12 |
| PbHsfA6a | PbHsfA6b | 0.21 | 7 | 17 |
| PbHsfA6a | PbHsfA6c | 0.20 | 8 | 14 |
| PbHsfA7a | PbHsfA7b | 0.24 | 6 | 20 |
| PbHsfA7b | PbHsfA6b | 1.51 | 2 | 17 |
| PbHsfA7b | PbHsfA6c | 1.79 | 2 | 14 |
| PbHsfB1a | PbHsfB1b | 0.32 | 8 | 12 |
| PbHsfC1a | PbHsfC1b | 0.24 | 17 | 28 |
We chose six consecutive homologous gene pairs on each side flanking the Hsf genes to calculate the mean Ks, and calculated the number of genes in 200 kb according to the segment with less genes in 200 kb.
Ks value and Ka/Ks ratio reveal dates and driving forces of evolution
The Ks value (synonymous substitutions per site) is widely used to estimate the evolutionary dates of WGD or segmental duplication events. Based on Ks values, two genome-wide duplication events were observed in the apple genome: the paleoduplication event corresponding to the γ triplication (Ks ~1.6) and a recent WGD (Ks ~0.2) [39]. Similarly to that in apple, the ancient WGD (Ks ~1.5–1.8) in pear resulted from a paleohexaploidization (γ) event that took place ~140 MYA [40], while the recent WGD (Ks ~0.15–0.3) in pear was inferred to have occurred at 30–45 MYA [34,39]. All members of the rosid clade have undergone paleohexaploidization (γ) [39,41–43]. Therefore, we used Ks values to estimate the evolutionary dates of the segmental duplication events among the PbHsf gene family. The mean Ks of the Hsf duplicated gene pairs in the syntenic region are shown in Table 5. The Ks values for the PbHsf gene pairs ranged from 0.20 to 2.35. We further inferred that the segmental duplications PbHsfA2a and PbHsfA9b (Ks ~1.60), PbHsfA7b and PbHsfA6b (Ks ~1.51), and PbHsfA7b and PbHsfA6c (Ks ~1.79) may have arisen from the γ triplication (~140 MYA). Furthermore, many duplicated gene pairs had similar Ks values (0.21–0.32), suggesting that these duplications may have been derived from the same recent WGD (30~45 MYA). Surprisingly, two duplicated gene pairs (PbHsfA2a and PbHsfA9a, PbHsfA4a and PbHsfA4d) possessed higher Ks values (2.13-2.15), suggesting that they might have stemmed from a more ancient duplication event.
The determination of orthology is an essential part of comparative genomics. Identification of orthology using synteny analysis has been employed in many studies [44–46]. According to the identified synteny relationships, we identified orthologous pairs of Hsf genes among five Rosaceae species (Table 6 and Additional file 7). A total of 29 PbHsf genes were found in orthologous blocks within five Rosaceae species, while 18 in apple, 17 in peach, 15 in strawberry, and 16 in Chinese plum. The numbers of orthologous pairs between Chinese white pear and other four Rosaceae species (apple, peach, strawberry and Chinese plum) are 30, 32, 26 and 29, respectively. The average Ks values of the Hsf orthologs between Chinese white pear and apple, peach, strawberry, or Chinese plum ranged from 0.21 to 0.75 (Additional file 8). The Hsf orthologs between Chinese white pear and apple possessed the lowest average Ks value (0.21), suggesting that the evolutionary distance was closest between these species. The average Ks values of the Hsf orthologs between Chinese white pear and peach, Chinese plum, and strawberry were 0.55, 0.53, and 0.75, respectively.
Table 6.
The orthology of Hsf genes in five Rosaceae species
| Chinese pear | Apple | Peach | Strawberry | Chinese plum | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HsfA1 | PbHsfA1a | MdHsfA1b | PpHsfA1b | FvHsfA1b | PmHsfA1b |
| PbHsfA1b | MdHsfA1b | PpHsfA1b | FvHsfA1b | PmHsfA1b | |
| PbHsfA1c | PpHsfA1a | PmHsfA1a | |||
| HsfA2 | PbHsfA2a | MdHsfA2a,2b,9b | PpHsfA2a,9a | FvHsfA2a,9a | PmHsfA2a,9a |
| HsfA3 | PbHsfA3a | MdHsfA3a,b | PpHsfA3a | FvHsfA3a | PmHsfA3a |
| PbHsfA3b | MdHsfA3a,b | PpHsfA3a | FvHsfA3a | PmHsfA3a | |
| HsfA4 | PbHsfA4a | PpHsfA4a | FvHsfA4a,b | PmHsfA4a | |
| PbHsfA4b | PpHsfA4a | FvHsfA4a,b | PmHsfA4a | ||
| PbHsfA4c | PpHsfA4b | FvHsfA4b | PmHsfA4b | ||
| PbHsfA4d | PpHsfA4a,4b | FvHsfA4b | PmHsfA4b | ||
| HsfA5 | PbHsfA5a | MdHsfA5a | FvHsfA5a | PmHsfA5a | |
| HsfA6 | PbHsfA6a | PpHsfA6a | FvHsfA6a | PmHsfA6a | |
| PbHsfA6b | PpHsfA6a,7a | FvHsfA6a,7a | PmHsfA6a,7a | ||
| PbHsfA6c | PpHsfA6a,7a | FvHsfA6a,7a | PmHsfA6a,7a | ||
| HsfA7 | PbHsfA7a | PpHsfA7a | PmHsfA7a | ||
| PbHsfA7b | PpHsfA6a,7a | FvHsfA7a | PmHsfA6a,7a | ||
| HsfA8 | PbHsfA8a | MdHsfA8a,8b | PpHsfA8a | PmHsfA8a | |
| HsfA9 | PbHsfA9a | MdHsfA9a,9b | PpHsfA9a | FvHsfA9a | PmHsfA9a |
| PbHsfA9b | MdHsfA9a,9b | PpHsfA9a | FvHsfA9a | PmHsfA9a | |
| HsfB1 | PbHsfB1a | MdHsfB1a | PpHsfB1a | FvHsfB1a | PmHsfB1a |
| PbHsfB1b | MdHsfB1a | PpHsfB1a | FvHsfB1a | ||
| HsfB2 | PbHsfB2a | MdHsfB2a | PpHsfB2a,2b | FvHsfB2a,2b | PmHsfB2a |
| HsfB3 | PbHsfB3a | MdHsfB3a | PpHsfB3a | ||
| PbHsfB3b | MdHsfB3a,3b | PpHsfB3a | |||
| PbHsfB3c | MdHsfB3a,3b | PpHsfB3a | |||
| HsfB4 | PbHsfB4a | MdHsfB4a,4b | PpHsfB4a | PmHsfB4a | |
| HsfB5 | PbHsfB5a | PpHsfB5a | FvHsfB5a | PmHsfB5a | |
| HsfC1 | PbHsfC1a | MdHsfC1a,1b | PpHsfC1a | FvHsfC1a | PmHsfC1a |
| PbHsfC1b | MdHsfC1a,1b | PpHsfC1a | FvHsfC1a | PmHsfC1a |
Genes in the same row are putative orthologs within five species. Note that one PbHsf gene may anchor to multiple Hsf genes in another Rosaceae species, each of those Hsf genes was identified as the ortholog for this PbHsf gene.
Negative selection (purifying selection) is the process by which deleterious mutations are removed. Conversely, positive selection (Darwinian selection) accumulates new advantageous mutations and spreads them through the population [47]. To further detect which selection process drove the evolution of the Hsf gene family, we also analyzed the Ka value (nonsynonymous substitutions per site), Ka/Ks ratio of paralogs in the Rosaceae Hsf gene family using coding sequences (CDS) (Additional file 9). The Ka/Ks ratio measures the direction and magnitude of selection: a value greater than one indicates positive selection, a value of one indicates neutral evolution, and a value less than one indicates purifying selection [48]. All Ka/Ks ratios of the paralogous genes were less than one, implying that purifying selection was the primary influence on the Hsf family genes.
Expression of Hsf family genes in pear fruit
The expression of PbHsf genes was investigated at the transcriptional level. At first, the Chinese white pear expressed sequence tags (ESTs) database was searched for the Hsf genes to verify the accuracy of the previous genomic predictions. These results provided reliable transcriptional evidence for most of these PbHsf genes (Additional file 10). Of the 29 predicted PbHsf genes, 22 were found to have EST hits with highest score. A total of 44 EST hits were found for all PbHsf genes, with the greatest number (four each) for PbHsfA1a and PbHsfB2a. These results provide credible support for the identification of PbHsf family genes. However, no EST hits were identified for PbHsfA6a, PbHsfA6b, PbHsfA6c, PbHsfA9b, PbHsfB3a, PbHsfB3b, and PbHsfB5a against the EST database. The functional roles of these genes will require further investigation.
To further explore the expression patterns of Hsf family genes in Chinese white pear, transcriptome sequencing analysis was conducted using fruit samples harvested from pear trees under field conditions and naturally increased temperatures. We took fruit samples from spring to summer 2012 at four different developmental stages (S1-S4) corresponding to different temperature ranges. The first sampling, used as a reference, was conducted on April 22 (S1) at 26°C/15°C (day/night; max/min), corresponding to 15 days after flowering (DAF). Subsequent samples were taken on May 13 at 26°C/19°C (S2, 36 DAF), June 27 at 27°C/21°C (S3, 80 DAF), and July 28 at of 36°C/28°C (S4, 110 DAF).
The results of transcriptome sequencing analysis are shown in Figure 6 (Additional file 11), and the PbHsf genes were responsive to the increased temperatures. RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) values were used to measure the expression level of the PbHsf genes. The expression patterns of the 29 PbHsf genes were very diverse, and most PbHsf genes exhibited some degree of stage specificity. Only PbHsfA6c exhibited no expression. Twenty-four genes were detected across the four fruit developmental stages. Five genes (PbHsfA4a, PbHsfA5a, PbHsfA8a, PbHsfB1a, and PbHsfB3c) presented high expression in all four stages. Moreover, six PbHsf genes (PbHsfA3a, PbHsfA4b, PbHsfA4d, PbHsfA6a, PbHsfB1b, and PbHsfC1a) showed increasing transcript expression with rising temperature, while PbHsfA9a, PbHsfA9b, and PbHsfB4a expression decreased with the increased temperatures. However, PbHsfB3a and PbHsfB3b showed only relatively little expression in stage S4, and PbHsfA6b was expressed only in S3. Additionally, the transcriptional changes of PbHsfA1a, PbHsfA1b, and PbHsfA1c were not obviously associated with temperature.
Figure 6.
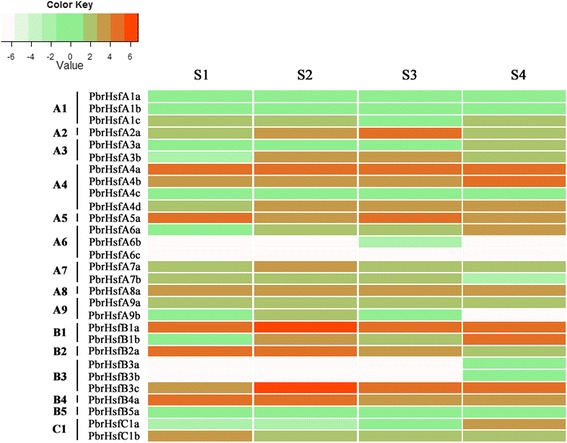
Heatmap of expression level of Hsf genes in Chinese white pear fruit. Transcriptome data were used to measure the expression level of Hsf genes. The groups A1-C1 on the left correspond to different subfamilies. S1-S4 correspond to four different developmental stages: on 22nd April (S1), 13rd May (S2), 27th June (S3), and 28th July (S4). Color scale at the top represents log2 transformed RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) values. Light green indicates low expression and red indicates high expression. Heatmap was generated using R.
Discussion
Members of the Hsf gene family have been identified and analyzed in different land plant species [13]. The number and composition of Hsf family members differ in various plants. Ancient polyploidy events (also known as WGDs) and additional recent lineage-specific WGDs have presumably resulted in varying numbers of Hsf genes within flowering plants. In this study, the sizes of the Hsf gene families identified from the six Rosaceae genomes are diverse. The number of Hsf genes in Chinese white pear (29), European pear (33), and apple (25) are greater than those in peach (17), strawberry (16), and Chinese plum (17). Pear and apple were inferred to have undergone a recent lineage-specific WGD, while peach, strawberry, and Chinese plum did not experience this event [49]. Therefore, this recent WGD event likely led to the different numbers of Hsf genes in the investigated Rosaceae species.
Different patterns of gene duplication, such as genome-wide, tandem, and dispersed duplications, contribute differentially to the expansion of specific gene families in plant genomes [50–52]. Some large gene families, including the APETALA 2/ethylene-responsive element binding factor (AP2/ERF) and WRKY, are more likely to expand by segmental and tandem duplications [53,54]. Conversely, gene families such as MADS (MINICHROMOSOME MAINTENANCE1, AGAMOUS, DEFICIENS and SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR)-box, and NBS-LRR (nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat) expand primarily through transposed duplications [50]. It has been estimated that more than 90% of the increase in regulatory genes in the Arabidopsis lineage has been caused by genome duplications [55]. Recent genome-wide studies have revealed that the pear and apple genomes experienced at least two genome duplications, one ancient and one before the pear-apple divergence [34]. Indeed, in this study, the results of the synteny analysis verified that the expansion of the Hsf gene family in Chinese white pear and apple was derived primarily from WGD or segmental duplications. This situation, in which segmental Hsf gene duplications were more frequent than tandem duplications, also occurred in Arabidopsis, maize, and poplar [32,33,56]. However, dispersed duplications were the major drivers of Hsf gene family expansion in peach, strawberry, and Chinese plum. The genomes of these three species have not experienced recent WGD. The genome rearrangements, gene losses, and gene transposition and retrotransposition after the ancient polyploidy event may have had a comparatively stronger impact on the evolution of the Hsf gene family in peach, strawberry, and Chinese plum.
Polyploidy through WGD is often followed by rapid gene loss, and genome rearrangements have been widely recognized as important in the evolution of plant genomes [57]. The retention of genes duplicated through WGD is biased in plant genomes and has been shown to be nonrandom across gene families [36,50]. For example, in Arabidopsis, genes encoding transcription factors, protein kinases, and ribosomal proteins have been preferentially retained after WGD [55,58,59]. In recent years, several models have been applied to elucidate the evolutionary fates and biased retention of duplicated genes, such as subfunctionalization, neofunctionalization, and dosage balance [60]. Recent studies have strongly supported the hypothesis that the overretention of duplicated genes derived from WGD is intensely correlated with greater structural complexity, highly conserved domains, lower evolutionary rates, and higher GC3 content in the plant genome, suggesting that multiple models may together drive the evolution of genes duplicated after WGDs [36]. Our present study showed that the Hsf gene family has undergone specific expansion and been preferentially retained. Rosaceae Hsf family genes possess shorter intron lengths and higher GC and GC3 contents than the genome average, contain several highly conserved functional domain, and present lower ka/ks ratios, corresponding to a slower evolutionary rate. These results were consistent with previously obtained results [36], implying that Hsf genes have been functionally stable over recent years and may serve as good targets for dosage balance selection [50].
Pear and apple belong to the Maloideae, peach and Chinese plum belong to the Prunoideae, and strawberry belongs to the Rosoideae. The divergence of the Rosoideae occurred prior to that of the Maloideae and Prunoideae. Therefore, the Maloideae and Prunoideae have a closer evolutionary relationship. Phylogenetic analysis of the Hsf genes in the six Rosaceae species showed that PbHsfs, MdHsfs, and PcHsfs were clustered together in the phylogenetic tree, while PpHsfs and PmHsfs had a closer relationship, as was consistent with the evolutionary history among the three subfamilies. These observations suggest that the expansion of these Hsf genes occurred before the divergence of the Rosaceae species. Furthermore, the majority of the PbHsf genes were related more closely to PtHsfs than to AtHsfs. This result may be explained by the fact that both Pyrus and Populus belong to the Fabids clade [61] and are both trees subjected to prolonged environmental stress. All three Hsf classes (A, B, and C) identified in Populus, Arabidopsis, and pear imply that the Hsf genes originated prior to the divergence of the three species. Additionally, Hsf members of the three classes have been detected in different lineages of monocots and dicots. In light of the present results, we inferred that the expansion of the Hsf gene family may have occurred in the common ancestor of angiosperms.
The functional diversification of Hsf genes has been observed in several plant species. HsfA1a has been reported as a single master regulator gene in tomato [22]. AtHsfA1a and AtHsfA1b are known to be involved in the early response to heat stress (HS) in Arabidopsis [62,63]. AtHsfA2 enhances and maintains the HS response when plants are subjected to long-term or repeated cycles of HS [64,65]. Previous data regarding Hsf expression in apple trees exposed to naturally increased temperatures are also available. For example, the A1-type MdHsf genes are expressed at the same level regardless of temperature in apple leaves, while MdHsfA2a-b, MdHsfA3b-c are strongly induced by high temperature [32]. Similarly to those of MdHsf genes, the transcriptional expression levels of A1-type PbHsf genes showed no significant changes as plants were exposed to naturally increasing temperatures. PbHsfA4a, PbHsfA5a, and PbHsfA8a were all strongly induced across the four stages of fruit development, indicating that the subclasses PbHsfA4, PbHsfA5, and PbHsfA8 were closely related with maintaining the heat shock response of pear trees subjected to high-temperature conditions. PbHsfA3a, PbHsfA4b, PbHsfA4d, and PbHsfA6a were upregulated under naturally increased temperatures, implying that these genes play a critical role during heat stress response.
The members of the B class Hsf genes may act as transcription repressors or coactivators regulating acquired thermotolerance during HS regimes [66–68]. The function of class C Hsf genes has not yet been fully identified. Notably, PbHsfB1a and PbHsfB3c were highly expressed in all four of the studied stages (S1, S2, S3, S4). PbHsfB1b and PbHsfC1a were upregulated under rising temperature, suggesting that these genes may play important roles in the response to high temperatures in pear. However, further investigations will be required to determine the functions of class B and C Hsf genes in pear. Some PbHsf genes showed unaltered or downregulated expression under increased temperatures, suggesting that these genes may operate at other signal transduction pathways in the complex regulatory network of plant stress response [69,70]. We also compared the expression levels of 13 duplicated gene pairs in pear Hsf gene family; differences were detected between the two members of each gene pair. This result suggested that the duplicated genes exhibited significant functional divergence regarding the response to heat stress.
Conclusions
A total of 137 full-length Hsf genes were identified in the six Rosaceae genomes, and the Chinese white pear genome contained 29 Hsf genes. According to the structural characteristics of the proteins, phylogenetic analysis, and comparison with homologues from Populus and Arabidopsis, the Hsf genes were grouped into three classes (A, B, and C). Collinearity analysis suggested that the recent WGD (30–45 MYA) may have driven the large scale expansion of the Hsf gene family in Chinese white pear and apple. Purifying selection is the major force acting upon Hsf family genes. EST and transcriptome sequencing analysis provided evidence of the identified PbHsf genes and revealed that they play an important role in heat stress response and fruit development. Considered together, these results constitute a foundation for further studies examining the functioning and complexity of the Hsf gene family in the Rosaceae.
Methods
Identification and classification of Hsfs
The Chinese white pear (Pyrus bretschneideri) genome sequence was downloaded from the pear genome project (http://peargenome.njau.edu.cn/) [34]. The genome sequences of apple, peach, and strawberry were downloaded from Phytozome (http://phytozome.jgi.doe.gov/pz/portal.html#), and the European pear genome sequence was download from the Genome Database for Rosaceae (GDR) (http://www.rosaceae.org/). The Chinese plum genome sequence was downloaded from the Prunus mume Genome Project (http://prunusmumegenome.bjfu.edu.cn/index.jsp). Initially, the Arabidopsis Hsf protein sequences At4g17750 (class A), At4g36990 (class B), and AT3g24520 (class C) downloaded from The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) [71] (http://www.arabidopsis.org/) were used as queries to perform BLAST against the six Rosaceae genome databases. Additionally, the seed alignment file for the Hsf domain (PF00447) obtained from the Pfam database [72] was used to build a HMM file using the HMMER3 software package [73]. HMM searches were then performed against the local protein databases of the six Rosaceae species using HMMER3. A total of 185 candidate Hsf genes were identified from the six Rosaceae species. Moreover, we checked the physical localizations of all candidate Hsf genes and rejected redundant sequences with the same chromosome location. Furthermore, all obtained Hsf protein sequences were again analyzed in the Pfam database to verify the presence of DBD domains. DBD domains and coiled-coil structures were also detected by the SMART and MARCOIL programs (SMART: http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/, MARCOIL: http://toolkit.tuebingen.mpg.de/marcoil). Those protein sequences lacking the DBD domain or a coiled-coil structure were removed.
To identify signature domains, the PbHsf protein sequences were compared to the Hsf proteins of Arabidopsis thaliana, Solanum lycopersicum, Populus trichocarpa, and Malus domestica by amino acid sequence alignment using ClustalW2 (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/Tools/msa/clustalw2/). The protein sequences of those four species were downloaded from Heatster (http://www.cibiv.at/services/hsf/). PredictNLS [74] and NetNES 1.1 [75] were also used to predict NLS and NES domains, respectively. All full-length amino acid sequences of the PbHsfs were also used by the MEME tool [76] to identify conserved domain motifs. The parameters were set as follows: maximum numbers of different motifs, 30; minimum motif width, 6; maximum motif width, 50. Hsf names were assigned based on the original nomenclature established for the Arabidopsis thaliana Hsf family [13,24]. Classification of the three different groups A, B, and C was based on observations of the oligomerization domains [24].
Chromosomal location and gene structure of Hsfs
The chromosomal location information of the Hsf genes was obtained from genome annotation documents. The data were then plotted using Circos software [77]. The gene structures of the Hsf genes were drawn using Gene Structure Display Server [78].
Phylogenetic analysis
First, a neighbor joining phylogenetic tree was created using the full-length protein sequences of Hsf from six Rosaceae species. Second, another phylogenetic tree was constructed using the N-terminal Hsf protein sequences containing the DBD and HR-A/B regions and parts of the linker between these two regions from Pyrus bretschneideri, Arabidopsis thaliana, and Populus trichocarpa [24,33] using the NJ method in MEGA (version 6.0) [79]. NJ analysis was performed with the Poisson model. Bootstrap analysis was conducted with 1000 replicates to assess the statistical support for each node.
Synteny analysis
The analysis of synteny among the six Rosaceae genomes was conducted locally using a method similar to that developed for the PGDD (http://chibba.agtec.uga.edu/duplication/) [80]. First, BLASTP was performed to search for potential homologous gene pairs (E < 1 e−5, top 5 matches) across multiple genomes. Then, these homologous pairs were used as the input for MCScanX to identify syntenic chains [81,82]. MCScanX was further used to identify WGD/segmental, tandem, proximal and dispersed duplications in the Hsf gene family.
Calculating Ka and Ks of the Hsf gene family
MCScanX downstream analysis tools were used to annotate the Ka and Ks substitution rates of syntenic gene pairs. The mean Ks values of orthologous Hsf gene pairs between Chinese white pear and the other Rosaceae species were calculated using all homologous gene pairs located in the same synteny block. KaKs_Calculator 2.0 was used to determine Ka and Ks [83]. To date segmental duplication events, six consecutive homologous gene pairs on each side flanking the Hsf genes were chosen to calculate the mean Ks. For those segments with fewer than 12 homologous genes, all available anchor pairs were used [46].
Expression analysis by ESTs
We conducted a local BLASTN against Chinese white pear EST libraries to find the corresponding record for each putative PbHsf genes using the following parameters: maximum identity > 95%, length > 200 bp, and E-value <10−10.
Plant material and transcriptome sequencing
We conducted this experiment in 2012 on pear trees (cultivar ‘Dangshansuli’) planted in the experimental orchard of the College of Horticulture at Nanjing Agricultural University. Fruit samples were taken from homogeneous trees, and three biological replicates were collected. Pear fruit were harvested between April and July 2012 from trees grown under the natural variability of weather and climate. Total RNA was extracted for RNA sequencing, and RNA sequencing libraries were constructed using an Illumina standard mRNASeq Prep Kit (TruSeq RNA and DNA Sample Preparation Kits version 2). Transcriptome sequencing and assembly were performed on an Illumina Hi-seq 2000 Sequencer.
Availability of supporting data
The data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article and its additional files. The phylogenetic data including data matrices, phylogenetic trees, and analysis steps have been submitted to TreeBASE database under accession number 16806 (http://purl.org/phylo/treebase/phylows/study/TB2:S16806). The raw RNA-seq reads are available from the National Center for Biotechnology Information repository under accession PRJNA185970 (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioproject/PRJNA185970). The EST datasets are available from the pear genome project (http://peargenome.njau.edu.cn/).
Acknowledgements
The Project was supported by the Independent Innovation of Agricultural Sciences in Jiangsu Province (CX(14)2020, CX(12)5079, CX(13)3010), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31301748), the National High-tech R&D Program of China (2013AA102606-02), the National Key Technology R&D Program of the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (2014BAD16B03-4), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31301748), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities: Science and Young scholar Technology Innovation Fund of Nanjing Agricultural University (KJ2013014), and the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2014M551607).
Abbreviations
- WGD
Whole-genome duplication
- MYA
Million years ago
- DBD
N-terminal DNA binding domain
- HR-A/B
Bipartite oligomerization domain
- NLS
Nuclear localization signal
- NES
Nuclear export signal
- CTAD
C-terminal activator domain
- HMM
Hidden Markov Model
- NJ
Neighbor-joining
- ML
Maximum likelihood
- RING
Really Interesting New Gene
- WD40
Tryptophan-aspartic acid 40
- MEME
Multiple EM for Motif Elicitation
- PGDD
Plant genome duplication database
- ESTs
Expressed sequence tags
- GDR
Genome database for Rosaceae
- AP2/ERF
APETALA 2/ethylene-responsive element binding factor
- MADS
MINICHROMOSOME MAINTENANCE1, AGAMOUS, DEFICIENS and SERUM RESPONSE FACTOR
- NBS-LRR
Nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat
Additional files
Location of Hsf genes in strawberry and Chinese plum. Hsf genes in strawberry(FvHsf), and Chinese plum (PmHsf) were mapped on the different chromosomes. Chromosome number is indicated on the inner side and highlighted red short lines in the inner circle correspond to different Hsf genes. Two genes with a syntenic relationship were joined by the lines.
Phylogenetic tree for Hsf genes of six Roseceae species. 137 Hsf protein sequences were used, including 29 PbHsfs, 25 MdHsfs, 33 PcHsfs, 17 PpHsfs, 16 FvHsfs, 17 PmHsfs. A, B and C stands for the three major groups of Hsf genes. Hsf genes were further classified into 15 subgroups (A1, A2, A3, A4, A5, A6, A7, A8, A9, B1, B2, B3, B4, B5, C). The abbreviations of species names are as follows: Pb, Chinese white pear; Md, apple; Pp, peach; Fv, strawberry; Pm, Chinese plum; Pc, European pear.
Gene features of Hsf genes in five Rosaceae species.
Exon-intron structure of Hsfs genes in Chinese white pear, peach, Chinese plum. Exons are indicated by the yellow boxes. Introns are represented by black lines, and blue boxes represent Untranslated Regions (UTR). Intron phase was showed by 0, 1, 2. The capital letter (A, B, and C) and number after each gene name indicate the subfamily to which it belongs.
Exon-intron structures of Hsf genes in strawberry, apple and European pear. Exons are indicated by the yellow boxes. Introns are represented by black lines, and blue boxes represent Untranslated Regions (UTR). Intron phase was showed by 0, 1, 2.
Motif sequences identified by MEME tools in pear Hsfs.
Orthologous pairs of Hsf genes between any two Rosaceae species.
Synteny analysis of Hsf genes regions between Chinese white pear and other Roseceae species.
Ka/Ks ratios of paralogous genes among Hsf gene family in Roseceae.
The ESTs for putative PbHsf genes.
The RPKM (reads per kilobase per million) value of Hsf genes expression in Chinese white pear.
Footnotes
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Authors’ contributions
QX carried out the experimental design and data analysis. LM designed the experiment and revising the manuscript. LLT contributed to collinearity analysis, perl script and some figures configuration. WJY and YH participated in revising the final manuscript. ZSL managed the experiments. All authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Contributor Information
Xin Qiao, Email: 2014204010@njau.edu.cn.
Meng Li, Email: mli@njau.edu.cn.
Leiting Li, Email: lileiting@gmail.com.
Hao Yin, Email: yinhao85@gmail.com.
Juyou Wu, Email: juyouwu@njau.edu.cn.
Shaoling Zhang, Email: slzhang@njau.edu.cn.
References
- 1.Wahid A, Gelani S, Ashraf M, Foolad M. Heat tolerance in plants: an overview. Environ Exp Bot. 2007;61(3):199–223. doi: 10.1016/j.envexpbot.2007.05.011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Allakhverdiev SI, Kreslavski VD, Klimov VV, Los DA, Carpentier R, Mohanty P. Heat stress: an overview of molecular responses in photosynthesis. Photosynth Res. 2008;98(1–3):541–50. doi: 10.1007/s11120-008-9331-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Boyer JS. Plant productivity and environment. Science. 1982;218(4571):443–8. doi: 10.1126/science.218.4571.443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Mittler R. Abiotic stress, the field environment and stress combination. Trends Plant Sci. 2006;11(1):15–9. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2005.11.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hua J. From freezing to scorching, transcriptional responses to temperature variations in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2009;12(5):568–73. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2009.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ahuja I, de Vos RC, Bones AM, Hall RD. Plant molecular stress responses face climate change. Trends Plant Sci. 2010;15(12):664–74. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2010.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Huang GT, Ma SL, Bai LP, Zhang L, Ma H, Jia P, et al. Signal transduction during cold, salt, and drought stresses in plants. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(2):969–87. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0823-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Century K, Reuber TL, Ratcliffe OJ. Regulating the regulators: the future prospects for transcription-factor-based agricultural biotechnology products. Plant Physiol. 2008;147(1):20–9. doi: 10.1104/pp.108.117887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chauhan H, Khurana N, Agarwal P, Khurana P. Heat shock factors in rice (Oryza sativa L.): genome-wide expression analysis during reproductive development and abiotic stress. Mol Genet Genomics. 2011;286(2):171–87. doi: 10.1007/s00438-011-0638-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Chung E, Kim KM, Lee JH. Genome-wide analysis and molecular characterization of heat shock transcription factor family in Glycine max. J Genet Genomics. 2013;40(3):127–35. doi: 10.1016/j.jgg.2012.12.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Jin GH, Gho HJ, Jung KH. A systematic view of rice heat shock transcription factor family using phylogenomic analysis. J Plant Physiol. 2013;170(3):321–9. doi: 10.1016/j.jplph.2012.09.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.von Koskull-Döring P, Scharf K-D, Nover L. The diversity of plant heat stress transcription factors. Trends Plant Sci. 2007;12(10):452–7. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2007.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Scharf K-D, Berberich T, Ebersberger I, Nover L. The plant heat stress transcription factor (Hsf) family: structure, function and evolution. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2012;1819(2):104–19. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagrm.2011.10.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kotak S, Larkindale J, Lee U, von Koskull-Döring P, Vierling E, Scharf K-D. Complexity of the heat stress response in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007;10(3):310–6. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2007.04.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Swindell WR, Huebner M, Weber AP. Transcriptional profiling of Arabidopsis heat shock proteins and transcription factors reveals extensive overlap between heat and non-heat stress response pathways. BMC Genomics. 2007;8(1):125. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-8-125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Almoguera C, Rojas A, Diaz-Martin J, Prieto-Dapena P, Carranco R, Jordano J. A seed-specific heat-shock transcription factor involved in developmental regulation during embryogenesis in sunflower. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(46):43866–72. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M207330200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Díaz-Martín J, Almoguera C, Prieto-Dapena P, Espinosa JM, Jordano J. Functional interaction between two transcription factors involved in the developmental regulation of a small heat stress protein gene promoter. Plant Physiol. 2005;139(3):1483–94. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.069963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Kotak S, Vierling E, Bäumlein H, von Koskull-Döring P. A novel transcriptional cascade regulating expression of heat stress proteins during seed development of Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 2007;19(1):182–95. doi: 10.1105/tpc.106.048165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nishizawa A, Yabuta Y, Yoshida E, Maruta T, Yoshimura K, Shigeoka S. Arabidopsis heat shock transcription factor A2 as a key regulator in response to several types of environmental stress. Plant J. 2006;48(4):535–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02889.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Miller G, Mittler R. Could heat shock transcription factors function as hydrogen peroxide sensors in plants? Ann Bot. 2006;98(2):279–88. doi: 10.1093/aob/mcl107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Shim D, Hwang J-U, Lee J, Lee S, Choi Y, An G, et al. Orthologs of the class A4 heat shock transcription factor HsfA4a confer cadmium tolerance in wheat and rice. Plant Cell. 2009;21(12):4031–43. doi: 10.1105/tpc.109.066902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mishra SK, Tripp J, Winkelhaus S, Tschiersch B, Theres K, Nover L, et al. In the complex family of heat stress transcription factors, HsfA1 has a unique role as master regulator of thermotolerance in tomato. Genes Dev. 2002;16(12):1555–67. doi: 10.1101/gad.228802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Qin F, Kakimoto M, Sakuma Y, Maruyama K, Osakabe Y, Tran LS, et al. Regulation and functional analysis of ZmDREB2A in response to drought and heat stresses in Zea mays L. Plant J. 2007;50(1):54–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03034.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Nover L, Bharti K, Döring P, Mishra SK, Ganguli A, Scharf K-D. Arabidopsis and the heat stress transcription factor world: how many heat stress transcription factors do we need? Cell Stress Chaperones. 2001;6(3):177. doi: 10.1379/1466-1268(2001)006<0177:AATHST>2.0.CO;2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Baniwal SK, Bharti K, Chan KY, Fauth M, Ganguli A, Kotak S, et al. Heat stress response in plants: a complex game with chaperones and more than twenty heat stress transcription factors. J Biosci. 2004;29(4):471–87. doi: 10.1007/BF02712120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Döring P, Treuter E, Kistner C, Lyck R, Chen A, Nover L. The role of AHA motifs in the activator function of tomato heat stress transcription factors HsfA1 and HsfA2. Plant Cell. 2000;12(2):265–78. doi: 10.1105/tpc.12.2.265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Harrison CJ, Bohm AA, Nelson H. Crystal structure of the DNA binding domain of the heat shock transcription factor. Science. 1994;263(5144):224–7. doi: 10.1126/science.8284672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Peteranderl R, Rabenstein M, Shin Y-K, Liu CW, Wemmer DE, King DS, et al. Biochemical and biophysical characterization of the trimerization domain from the heat shock transcription factor. Biochemistry. 1999;38(12):3559–69. doi: 10.1021/bi981774j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Morimoto RI. Regulation of the heat shock transcriptional response: cross talk between a family of heat shock factors, molecular chaperones, and negative regulators. Genes Dev. 1998;12(24):3788–96. doi: 10.1101/gad.12.24.3788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Pirkkala L, Nykänen P, Sistonen L. Roles of the heat shock transcription factors in regulation of the heat shock response and beyond. FASEB J. 2001;15(7):1118–31. doi: 10.1096/fj00-0294rev. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Guo J, Wu J, Ji Q, Wang C, Luo L, Yuan Y, et al. Genome-wide analysis of heat shock transcription factor families in rice and Arabidopsis. J Genet Genomics. 2008;35(2):105. doi: 10.1016/S1673-8527(08)60016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Giorno F, Guerriero G, Baric S, Mariani C. Heat shock transcriptional factors in Malus domestica: identification, classification and expression analysis. BMC Genomics. 2012;13(1):1–13. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Wang F, Dong Q, Jiang H, Zhu S, Chen B, Xiang Y. Genome-wide analysis of the heat shock transcription factors in Populus trichocarpa and Medicago truncatula. Mol Biol Rep. 2012;39(2):1877–86. doi: 10.1007/s11033-011-0933-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Wu J, Wang Z, Shi Z, Zhang S, Ming R, Zhu S, et al. The genome of the pear (Pyrus bretschneideri Rehd.) Genome Res. 2013;23(2):396–408. doi: 10.1101/gr.144311.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Potter D, Eriksson T, Evans RC, Oh S, Smedmark J, Morgan DR, et al. Phylogeny and classification of Rosaceae. Plant Syst Evol. 2007;266(1):5–43. doi: 10.1007/s00606-007-0539-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Wk J, Yl L, Xia E, Lz G. Prevalent role of gene features in determining evolutionary fates of whole-genome duplication duplicated genes in flowering plants. Plant Physiol. 2013;161(4):1844–61. doi: 10.1104/pp.112.200147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Wang Y, You FM, Lazo GR, Luo M-C, Thilmony R, Gordon S, et al. PIECE: a database for plant gene structure comparison and evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(D1):D1159–66. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Maher C, Stein L, Ware D. Evolution of Arabidopsis microRNA families through duplication events. Genome Res. 2006;16(4):510–9. doi: 10.1101/gr.4680506. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Velasco R, Zharkikh A, Affourtit J, Dhingra A, Cestaro A, Kalyanaraman A, et al. The genome of the domesticated apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) Nat Genet. 2010;42(10):833–9. doi: 10.1038/ng.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Fawcett JA, Maere S, Van de Peer Y. Plants with double genomes might have had a better chance to survive the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction event. Proc Natl Acad Sci. 2009;106(14):5737–42. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0900906106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jaillon O, Aury JM, Noel B, Policriti A, Clepet C, Casagrande A, et al. The grapevine genome sequence suggests ancestral hexaploidization in major angiosperm phyla. Nature. 2007;449(7161):463–7. doi: 10.1038/nature06148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Shulaev V, Sargent DJ, Crowhurst RN, Mockler TC, Folkerts O, Delcher AL, et al. The genome of woodland strawberry (Fragaria vesca) Nat Genet. 2010;43(2):109–16. doi: 10.1038/ng.740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Verde I, Abbott AG, Scalabrin S, Jung S, Shu SQ, Marroni F, et al. The high-quality draft genome of peach (Prunus persica) identifies unique patterns of genetic diversity, domestication and genome evolution. Nat Genet. 2013;45(5):487–U447. doi: 10.1038/ng.2586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Lemoine F, Lespinet O, Labedan B. Assessing the evolutionary rate of positional orthologous genes in prokaryotes using synteny data. BMC Evol Biol. 2007;7(1):237. doi: 10.1186/1471-2148-7-237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jun J, Mandoiu II, Nelson CE. Identification of mammalian orthologs using local synteny. BMC Genomics. 2009;10(1):630. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-10-630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Du D, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Wang J, Zhang Q. Genome-wide identification, molecular evolution and expression analyses of the phospholipase D gene family in three Rosaceae species. Sci Hortic. 2013;153:13–21. doi: 10.1016/j.scienta.2013.01.002. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Starr TK, Jameson SC, Hogquist KA. Positive and negative selection of T cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 2003;21(1):139–76. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.21.120601.141107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Yang Z. PAML 4: phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24(8):1586–91. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msm088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Zhang Q, Chen W, Sun L, Zhao F, Huang B, Yang W, et al. The genome of Prunus mume. Nat Commun. 2012;3:1318. doi: 10.1038/ncomms2290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Freeling M. Bias in plant gene content following different sorts of duplication: tandem, whole-genome, segmental, or by transposition. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:433–53. doi: 10.1146/annurev.arplant.043008.092122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wang YP, Wang XY, Tang HB, Tan X, Ficklin SP, Feltus FA, Paterson AH. Modes of gene duplication contribute differently to genetic novelty and redundancy, but show parallels across divergent angiosperms. PLoS One. 2011;6(12):e28150. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0028150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Wang N, Xiang Y, Fang L, Wang Y, Xin H, Li S. Patterns of gene duplication and their contribution to expansion of gene families in grapevine. Mol Biol Rep. 2013;31(4):852–61. doi: 10.1007/s11105-013-0556-5. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Guo C, Guo R, Xu X, Gao M, Li X, Song J, et al. Evolution and expression analysis of the grape (Vitis vinifera L.) WRKY gene family. J Exp Bot. 2014;65(6):1513–28. doi: 10.1093/jxb/eru007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Du D, Hao R, Cheng T, Pan H, Yang W, Wang J, Zhang Q. Genome-wide analysis of the AP2/ERF gene family in Prunus mume. Plant Mol Biol Rep. 2012;31(3):741–50. doi: 10.1007/s11105-012-0531-6. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Maere S, De Bodt S, Raes J, Casneuf T, Van Montagu M, Kuiper M, et al. Modeling gene and genome duplications in eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(15):5454–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0501102102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Lin Y-X, Jiang H-Y, Chu Z-X, Tang X-L, Zhu S-W, Cheng B-J. Genome-wide identification, classification and analysis of heat shock transcription factor family in maize. BMC Genomics. 2011;12(1):76. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-12-76. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Sémon M, Wolfe KH. Consequences of genome duplication. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2007;17(6):505–12. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2007.09.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Blanc G, Wolfe KH. Functional divergence of duplicated genes formed by polyploidy during Arabidopsis evolution. Plant Cell. 2004;16(7):1679–91. doi: 10.1105/tpc.021410. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Seoighe C, Gehring C. Genome duplication led to highly selective expansion of the Arabidopsis thaliana proteome. Trends Genet. 2004;20(10):461–4. doi: 10.1016/j.tig.2004.07.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Innan H, Kondrashov F. The evolution of gene duplications: classifying and distinguishing between models. Nat Rev Genet. 2010;11(2):97–108. doi: 10.1038/nrg2689. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Judd WS, Olmstead RG. A survey of tricolpate (eudicot) phylogenetic relationships. Am J Bot. 2004;91(10):1627–44. doi: 10.3732/ajb.91.10.1627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Busch W, Wunderlich M, Schöffl F. Identification of novel heat shock factor‐dependent genes and biochemical pathways in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J. 2005;41(1):1–14. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2004.02272.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Lohmann C, Eggers-Schumacher G, Wunderlich M, Schöffl F. Two different heat shock transcription factors regulate immediate early expression of stress genes in Arabidopsis. Mol Gen Genomics. 2004;271(1):11–21. doi: 10.1007/s00438-003-0954-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Y-y C, H-c L, N-y L, W-t C, C-n W, S-h C, et al. A heat-inducible transcription factor, HsfA2, is required for extension of acquired thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol. 2007;143(1):251–62. doi: 10.1104/pp.106.091322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Meiri D, Breiman A. Arabidopsis ROF1 (FKBP62) modulates thermotolerance by interacting with HSP90. 1 and affecting the accumulation of HsfA2‐regulated sHSPs. Plant J. 2009;59(3):387–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2009.03878.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Czarnecka-Verner E, Yuan C-X, Scharf K-D, Englich G, Gurley WB. Plants contain a novel multi-member class of heat shock factors without transcriptional activator potential. Plant Mol Biol. 2000;43(4):459–71. doi: 10.1023/A:1006448607740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Ikeda M, Mitsuda N, Ohme-Takagi M. Arabidopsis HsfB1 and HsfB2b act as repressors of the expression of heat-inducible Hsfs but positively regulate the acquired thermotolerance. Plant Physiol. 2011;157(3):1243–54. doi: 10.1104/pp.111.179036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Bharti K, von Koskull-Döring P, Bharti S, Kumar P, Tintschl-Körbitzer A, Treuter E, et al. Tomato heat stress transcription factor HsfB1 represents a novel type of general transcription coactivator with a histone-like motif interacting with the plant CREB binding protein ortholog HAC1. Plant Cell. 2004;16(6):1521–35. doi: 10.1105/tpc.019927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Mittal D, Chakrabarti S, Sarkar A, Singh A, Grover A. Heat shock factor gene family in rice: genomic organization and transcript expression profiling in response to high temperature, low temperature and oxidative stresses. Plant Physiol Biochem. 2009;47(9):785–95. doi: 10.1016/j.plaphy.2009.05.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Victor M, Benecke B-J. Expression levels of heat shock factors are not functionally coupled to the rate of expression of heat shock genes. Mol Biol Rep. 1998;25(3):135–41. doi: 10.1023/A:1006801205904. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Swarbreck D, Wilks C, Lamesch P, Berardini TZ, Garcia-Hernandez M, Foerster H, et al. The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR): gene structure and function annotation. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008;36(suppl 1):D1009–14. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkm965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Finn RD, Mistry J, Tate J, Coggill P, Heger A, Pollington JE, et al. The Pfam protein families database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;38(suppl 1):D211–22. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Eddy SR. Accelerated Profile HMM Searches. PLoS Comput Biol. 2011;7(10):e1002195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Cokol M, Nair R, Rost B. Finding nuclear localization signals. EMBO Rep. 2000;1(5):411–5. doi: 10.1093/embo-reports/kvd092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.La Cour T, Kiemer L, Mølgaard A, Gupta R, Skriver K, Brunak S. Analysis and prediction of leucine-rich nuclear export signals. Protein Eng Des Sel. 2004;17(6):527–36. doi: 10.1093/protein/gzh062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Bailey TL, Williams N, Misleh C, Li WW. MEME: discovering and analyzing DNA and protein sequence motifs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2006;34(suppl 2):W369–73. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkl198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol İ, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, et al. Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res. 2009;19(9):1639–45. doi: 10.1101/gr.092759.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Guo A-Y, Zhu Q-H, Chen X, Luo J-C. GSDS: a gene structure display server. Yi Chuan. 2007;29(8):1023. doi: 10.1360/yc-007-1023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S. MEGA6: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2013;30(12):2725–9. doi: 10.1093/molbev/mst197. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Lee TH, Tang HB, Wang XY, Paterson AH. PGDD: a database of gene and genome duplication in plants. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013;41(D1):D1152–8. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Tang HB, Wang XY, Bowers JE, Ming R, Alam M, Paterson AH. Unraveling ancient hexaploidy through multiply-aligned angiosperm gene maps. Genome Res. 2008;18(12):1944–54. doi: 10.1101/gr.080978.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Wang YP, Tang HB, DeBarry JD, Tan X, Li JP, Wang XY, Lee TH, Jin HZ, Marler B, Guo H, et al. MCScanX: a toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012;40(7):e49. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Wang D, Zhang Y, Zhang Z, Zhu J, Yu J. KaKs_Calculator 2.0: a toolkit incorporating gamma-series methods and sliding window strategies. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2010;8(1):77–80. doi: 10.1016/S1672-0229(10)60008-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


