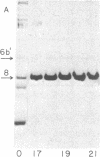
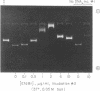
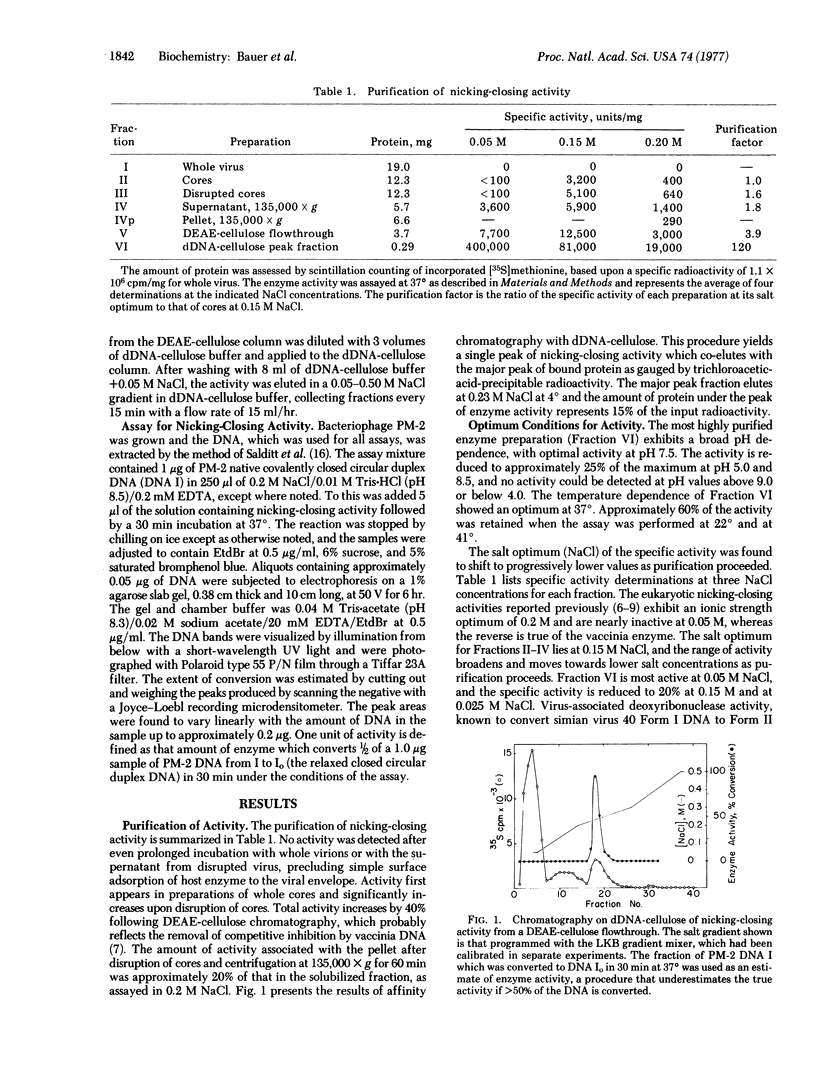
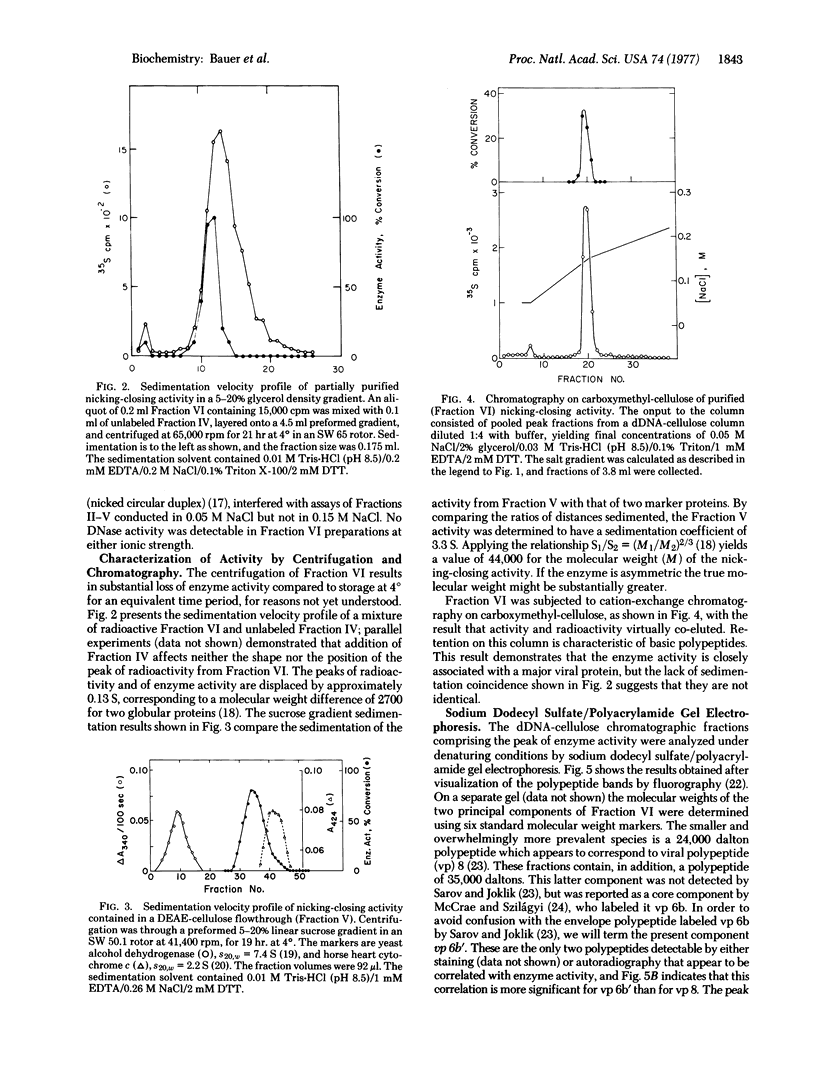
Abstract
Vaccinia virus cores contain an activity which is able to relax both left-and right-handed superhelical DNA. This virus-specific nicking closing enzyme has been highly purified and differs from the corresponding host enzyme in salt optimum, in sedimentation coefficient, and in polypeptide composition as determined on sodium dodecyl sulfate/polyacrylamide gels. The enzyme is probably newly synthesized after the cessation of host protein synthesis which follows virus infection. The most highly purified preparation contains two polypeptides, one of molecular weight 24,000 and the other 35,000. The former polypeptide is a major constituent of the virus (7% of total protein by weight), whereas the latter is present in a much smaller amount (0.2%). Chromatography with denatured DNA-cellulose reveals that the activity is predominately associated with those fractions enriched in the polypeptide of greater molecular weight.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baase W. A., Wang J. C. An omega protein from Drosophila melanogaster. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 8;13(21):4299–4303. doi: 10.1021/bi00718a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer W., Vinograd J. Interaction of closed circular DNA with intercalative dyes. II. The free energy of superhelix formation in SV40 DNA. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):419–435. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrington M. G., Morgan A. R. The purification from Escherichia coli of a protein relaxing superhelical DNA. Can J Biochem. 1976 Apr;54(4):301–306. doi: 10.1139/o76-045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Champoux J. J., Dulbecco R. An activity from mammalian cells that untwists superhelical DNA--a possible swivel for DNA replication (polyoma-ethidium bromide-mouse-embryo cells-dye binding assay). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jan;69(1):143–146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.1.143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geshelin P., Berns K. I. Characterization and localization of the naturally occurring cross-links in vaccinia virus DNA. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 5;88(4):785–796. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90399-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOKLIK W. K. The preparation and characteristics of highly purified radioactively labelled poxvirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1962 Aug 20;61:290–301. doi: 10.1016/0926-6550(62)90091-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. I. The mechanism of synthesis and release of RNA in vaccinia cores. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):1–18. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90100-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kates J., Beeson J. Ribonucleic acid synthesis in vaccinia virus. II. Synthesis of polyriboadenylic acid. J Mol Biol. 1970 May 28;50(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90101-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller W. Characterization of purified DNA-relaxing enzyme from human tissue culture cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2550–2554. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Szilágyi J. F. Preparation and characterisation of a subviral particle of vaccinia virus containing the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase activity. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):234–244. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90164-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B. Inhibition of HeLa cell protein synthesis by the vaccinia virion. J Virol. 1968 Oct;2(10):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.10.1028-1037.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Gershowitz A. Characterization of a polyriboadenylate polymerase from vaccinia virions. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jun 25;250(12):4722–4729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N., Paoletti E. Polyadenylate polymerase from vaccinia virions. Nat New Biol. 1973 Sep 12;245(141):59–63. doi: 10.1038/newbio245059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munyon W., Paoletti E., Grace J. T., Jr RNA polymerase activity in purified infectious vaccinia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1967 Dec;58(6):2280–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.58.6.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulleyblank D. E., Morgan A. R. Partial purification of "omega" protein from calf thymus. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5205–5209. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosemond-Hornbeak H., Moss B. Single-stranded deoxyribonucleic acid-specific nuclease from vaccinia virus. Endonucleolytic and exonucleolytic activities. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3292–3296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt M., Braunstein S. N., Camerini-Otero R. D., Franklin R. M. Structure and synthesis of a lipid-containing bacteriophage. X. Improved techniques for the purification of bacteriophage PM2. Virology. 1972 Apr;48(1):259–262. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90133-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarov I., Joklik W. K. Studies on the nature and location of the capsid polypeptides of vaccinia virions. Virology. 1972 Nov;50(2):579–592. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinograd J., Lebowitz J. Physical and topological properties of circular DNA. J Gen Physiol. 1966 Jul;49(6):103–125. doi: 10.1085/jgp.49.6.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Grossman L. I., Vinograd J. Isolation and partial characterisation of the relaxation protein from nuclei of cultured mouse and human cells. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Jun 16;55(1):79–93. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P., Vinograd J. Purification and demonstration of the enzymatic character of the nicking-closing protein from mouse L cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jan 26;68(2):456–464. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)91167-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang J. C. Interaction between DNA and an Escherichia coli protein omega. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):523–533. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90334-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei C. M., Moss B. Methylated nucleotides block 5'-terminus of vaccinia virus messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):318–322. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worcel A., Burgi E. On the structure of the folded chromosome of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1972 Nov 14;71(2):127–147. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90342-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]