Abstract
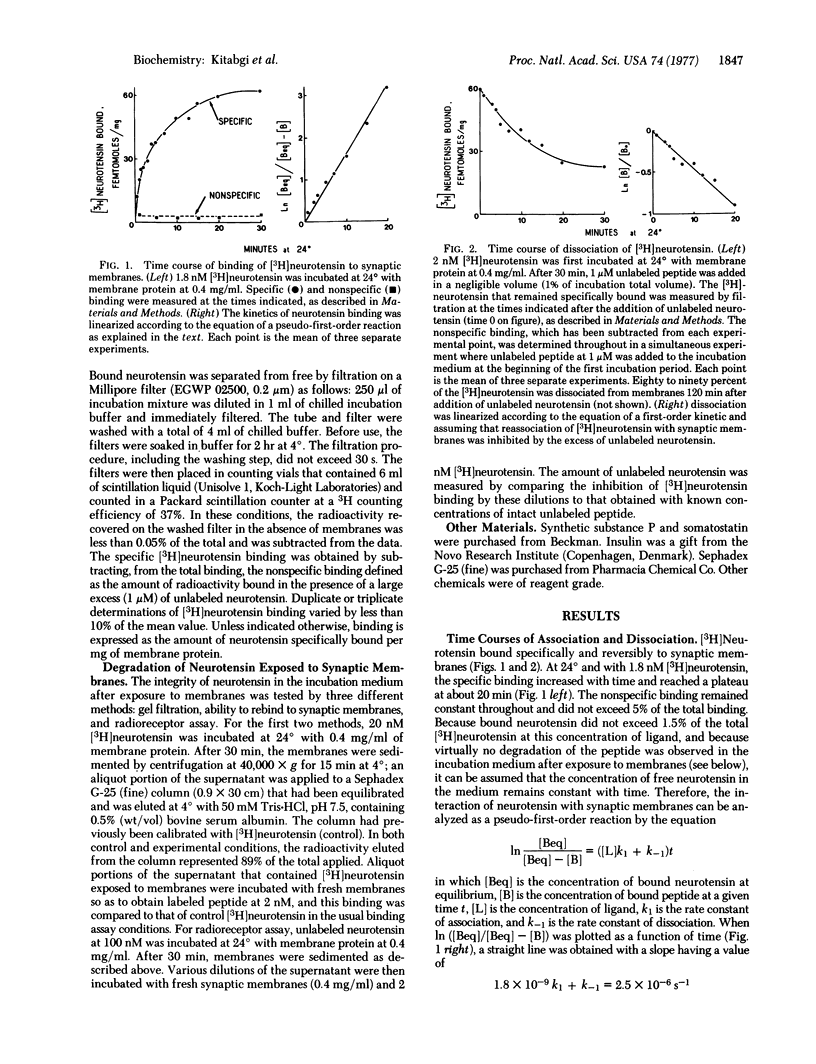
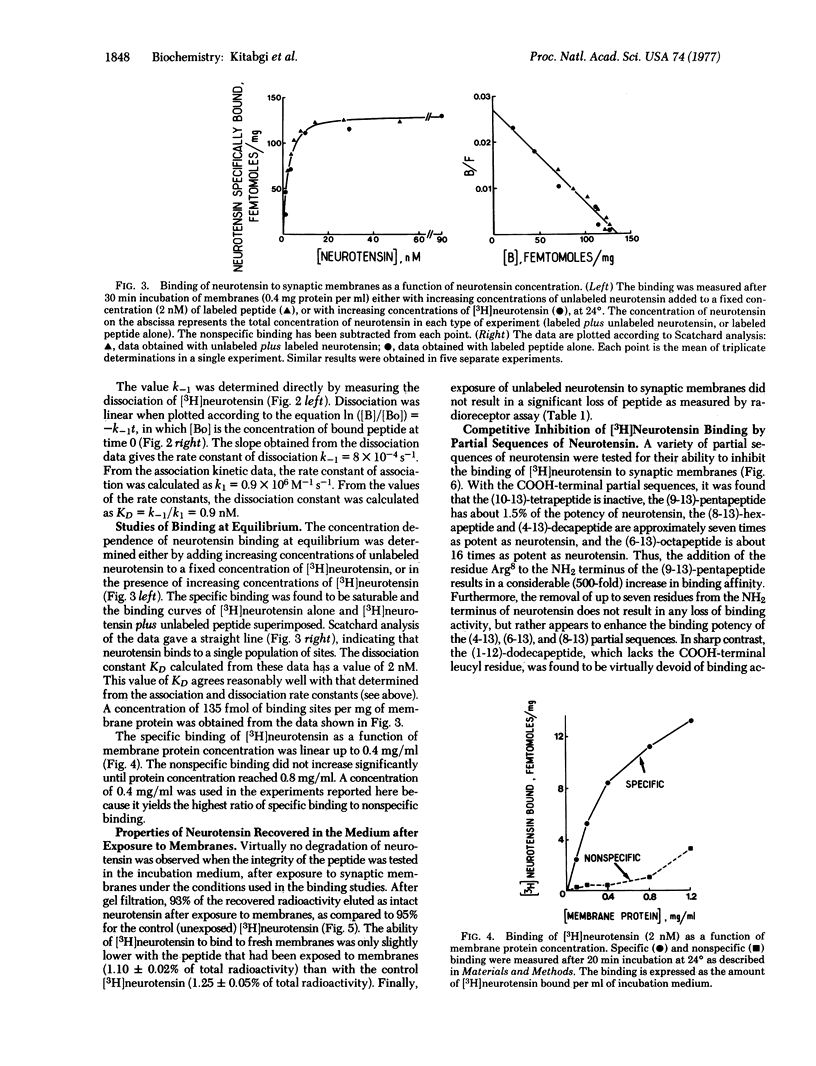
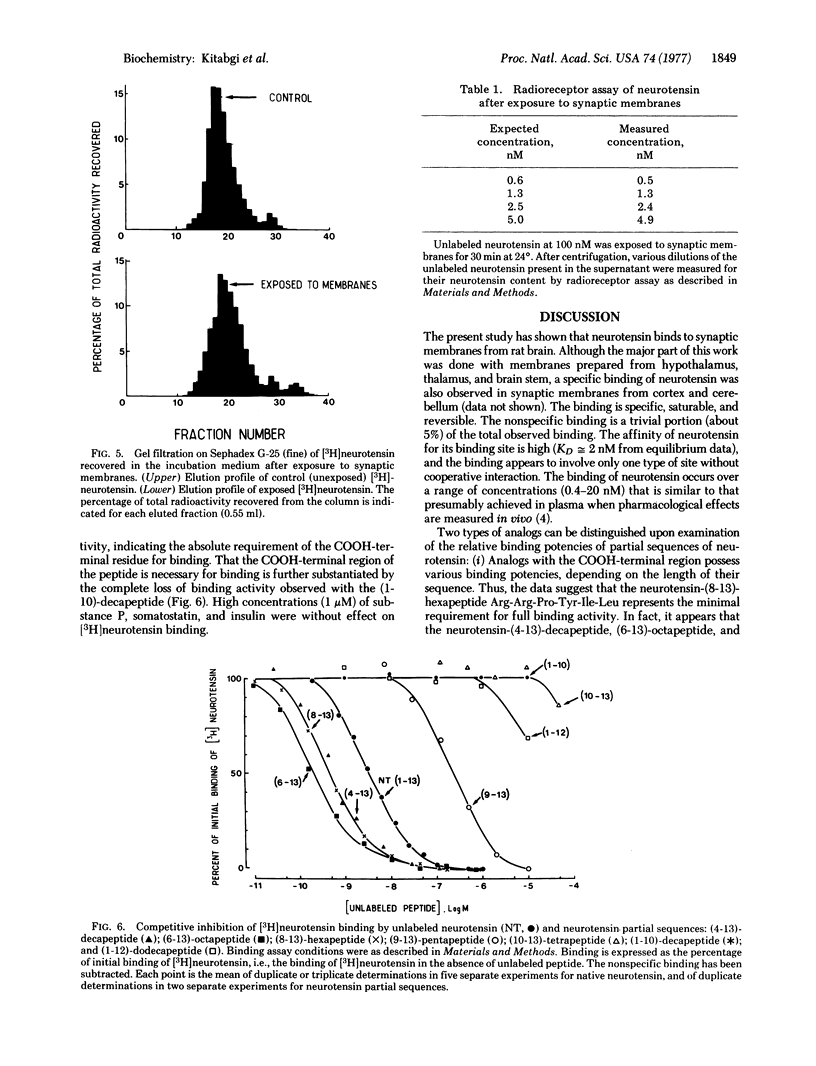
The binding of neurotensin to synaptic membranes from rat brain was studied at 24 degrees with the use of [3H]neurotensin. The binding was found to be highly specific, saturable, and reversible. Values for KD of 2 nM and 0.9 nM were derived from equilibrium and kinetic experiments, respectively. Virtually no degradation of neurotensin was observed in the incubation medium after exposure to synaptic membranes under the conditions of the binding studies. Competitive inhibition of [3H]neurotensin binding by partial sequences of neurotensin revealed that the addition of the residue arginine-8 to the neurotensin-(9-13)-pentapeptide increases about 500-fold the relative binding potency, whereas the remaining portion of the NH2-terminal region is mainly responsible for full pharmacological potency; the COOH-terminal leucyl residue is essential for binding.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arimura A., Sato H., Dupont A., Nishi N., Schally A. V. Somatostatin: abundance of immunoreactive hormone in rat stomach and pancreas. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):1007–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.56779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Characterization of radioimmunoassayable neurotensin in the rat. Its differential distribution in the central nervous system, small intestine, and stomach. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7045–7052. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The amino acid sequence of a hypothalamic peptide, neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1907–1911. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carraway R., Leeman S. E. The isolation of a new hypotensive peptide, neurotensin, from bovine hypothalami. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6854–6861. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang M. M., Leeman S. E. Isolation of a sialogogic peptide from bovine hypothalamic tissue and its characterization as substance P. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4784–4790. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. H., Matus A. I. Isolation of synaptic plasma membrane from brain by combined flotation-sedimentation density gradient centrifugation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 Aug 9;356(3):276–287. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(74)90268-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitabgi P., Carraway R., Leeman S. E. Isolation of a tridecapeptide from bovine intestinal tissue and its partial characterization as neurotensin. J Biol Chem. 1976 Nov 25;251(22):7053–7058. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. B. Solid-phase peptide synthesis. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1969;32:221–296. doi: 10.1002/9780470122778.ch6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgat J. L., Hung L. T., Fromageot P. Preparation of highly labelled (3H)angiotensin II. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 26;207(2):374–376. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(70)90032-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Said S. I., Rosenberg R. N. Vasoactive intestinal polypeptide: abundant immunoreactivity in neural cell lines and normal nervous tissue. Science. 1976 May 28;192(4242):907–908. doi: 10.1126/science.1273576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Rietschoten J., Granier C., Rochat H., Lissitzky S., Miranda F. Synthesis of apamin, a neurotoxic peptide from bee venom. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 1;56(1):35–40. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02204.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


