Abstract
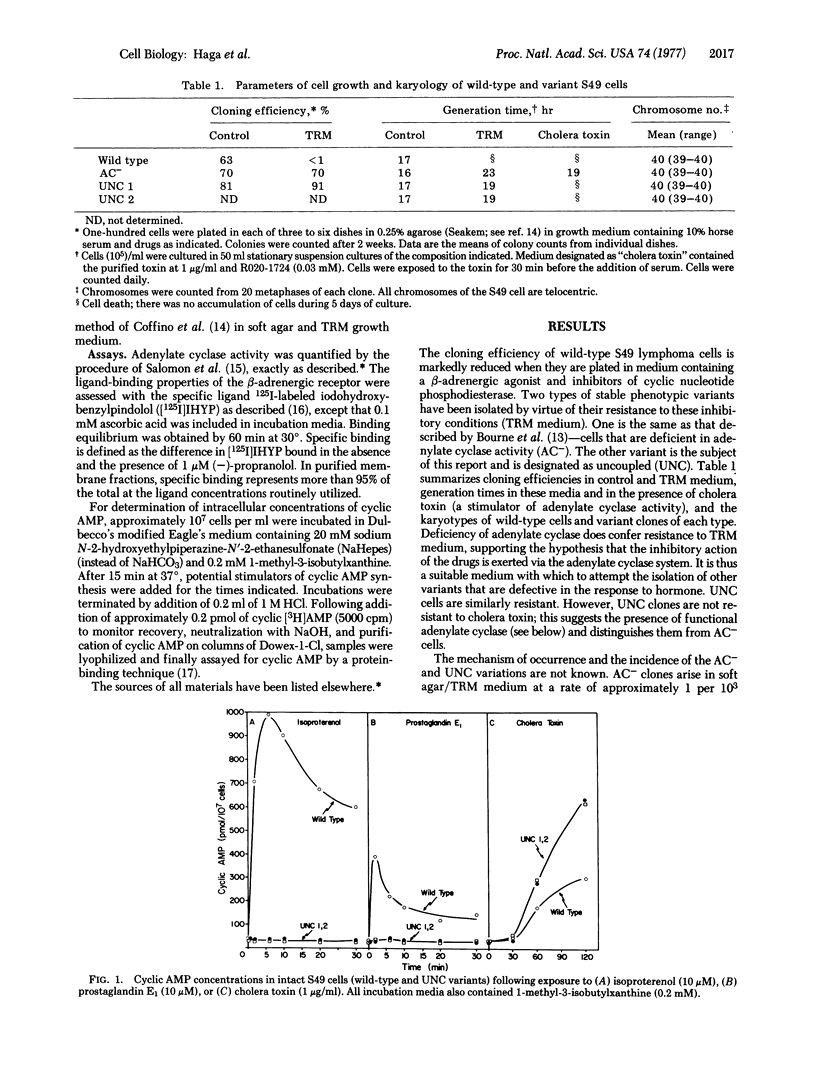
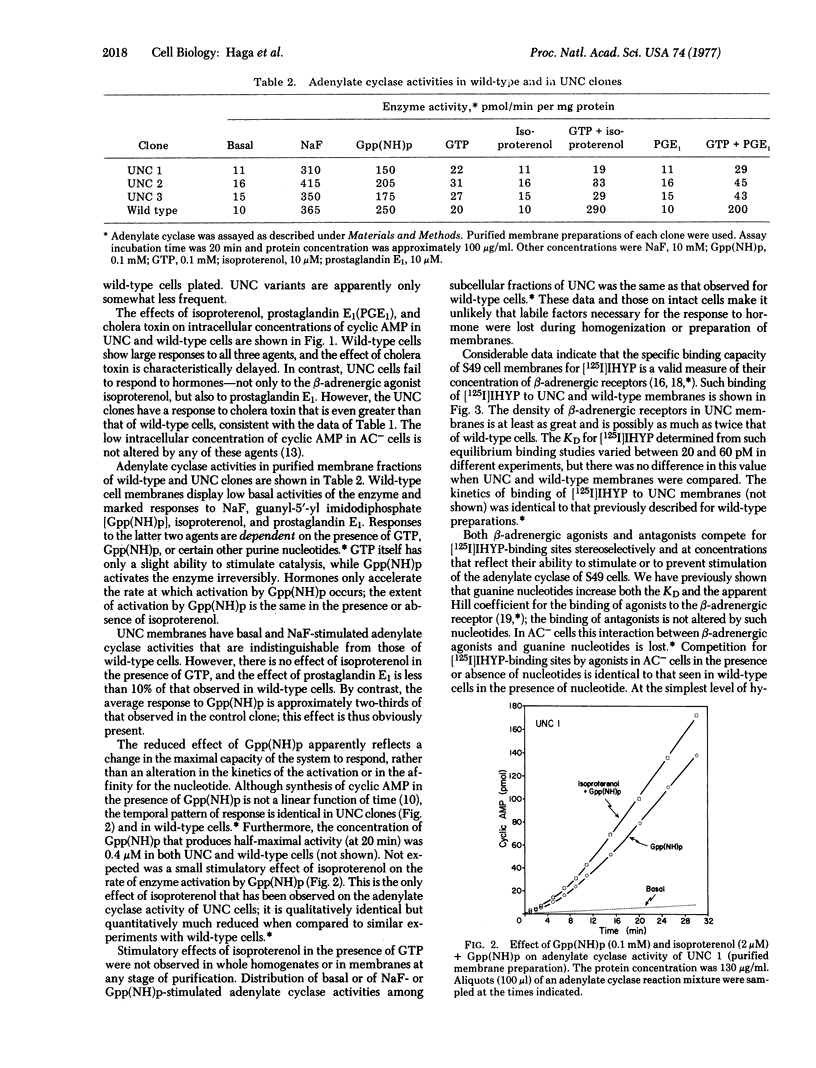
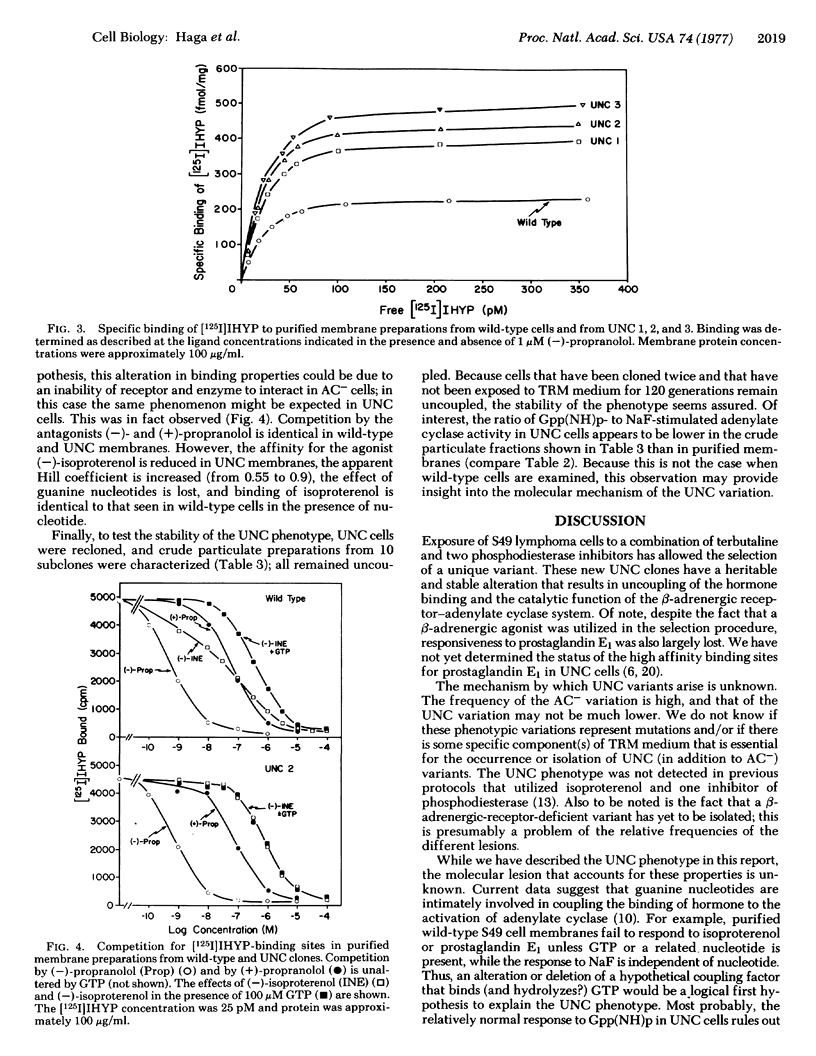
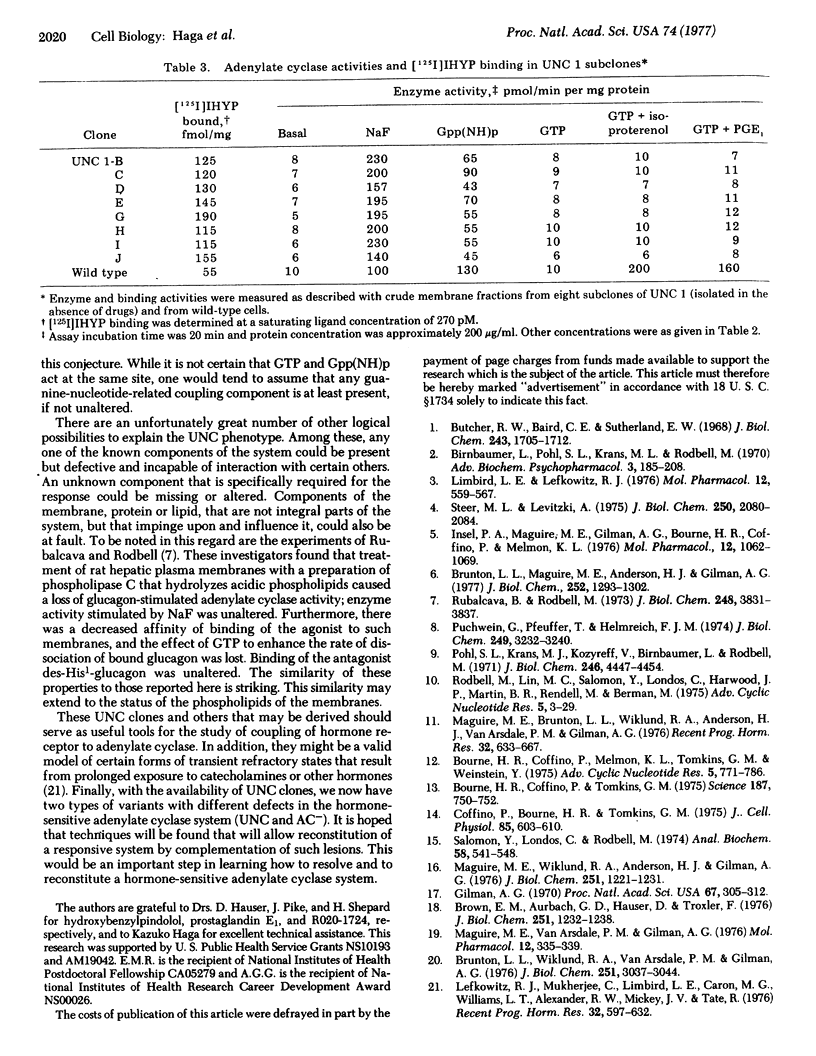
A novel variant of the S49 mouse lymphoma has been selected from wild-type cells by growth in medium containing the beta-adrenergic agonist terbutaline and inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase. In contrast to the situation in the wild-type clone, synthesis of adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate (cyclic AMP) is not stimulated by beta-adrenergic agonists or by prostaglandin E1 either in intact variant cells or in membrane preparations of such clones. However, basal and NaF-stimulated activities of adenylate cyclase [ATP pyrophosphate-lyase (cyclizine), EC 4.6.1.1] are normal, enzyme activity is stimulated by guanyl-5'-yl imidodiphosphate [Gpp(NH)p], and intact cells accumulate cyclic AMP when exposed to cholera toxin. Furthermore, variant cell membranes possess ligand-binding activity consistent with the conclusion that a normal or an excessive number of beta-adrenergic receptors is present. Thus, interaction between the hormone-binding and the catalytic moieties of the adenylate cyclase system is lost. This variant phenotype, designated as uncoupled (UNC), has been stable for more than 100 generations without exposure to the drugs used for selection. Such cells should be useful for the elucidation of methanisms of transmission of information from hormone receptors to adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnbaumer L., Pohl S. L., Michiel H., Krans M. J., Rodbell M. The actions of hormones on the adenyl cyclase system. Adv Biochem Psychopharmacol. 1970;3:185–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Melmon K. L., Tomkins G. M., Weinstein Y. Genetic analysis of cyclic AMP in a mammalian cell. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:771–786. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Tomkins G. M. Selection of a variant lymphoma cell deficient in adenylate cyclase. Science. 1975 Feb 28;187(4178):750–752. doi: 10.1126/science.163487. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. M., Aurbach G. D. Beta-Adrenergic receptor interactions. Characterization of iodohydroxybenzylpindolol as a specific ligand. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1232–1238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton L. L., Maguire M. E., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Expression of genes for metabolism of cyclic adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate in somatic cells. beta-Adrenergic and PGE1 receptors in parental and hybrid cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 25;252(4):1293–1302. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunton L. L., Wiklund R. A., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. Binding of (3H)prostaglandin E1 to putative receptors linked to adenylate cyclase of cultured cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1976 May 25;251(10):3037–3044. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butcher R. W., Baird C. E., Sutherland E. W. Effects of lipolytic and antilipolytic substances on adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate levels in isolated fat cells. J Biol Chem. 1968 Apr 25;243(8):1705–1712. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffino P., Bourne H. R., Tomkins G. M. Somatic genetic analysis of cyclic AMP action: selection of unresponsive mutants. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Jun;85(3):603–610. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. A protein binding assay for adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Sep;67(1):305–312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.67.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Maguire M. E., Gilman A. G., Bourne H. R., Coffino P., Melmon K. L. Beta adrenergic receptors and adenylate cyclase: products of separate genes? Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Nov;12(6):1062–1069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefkowitz R. J., Mukherjee C., Limbird L. E., Caron M. G., Williams L. T., Alexander R. W., Mickey J. V., Tate R. Regulation of adenylate cyclase coupled beta-adrenergic receptors. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:597–632. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50033-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Limbird L. E., Lefkowitz R. J. Adenylate cyclase-coupled beta adrenergic receptors effect of membrane lipid-perturbing agents on receptor binding and enzyme stimulation by catecholamines. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Jul;12(4):559–567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Brunton L. L., Wiklund R. A., Anderson H. I., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. Hormone receptors and the control of cyclic AMP metabolism in parental and hybrid somatic cells. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1976;32:633–667. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571132-6.50035-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Van Arsdale P. M., Gilman A. G. An agonist-specific effect of guanine nucleotides on binding to the beta adrenergic receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1976 Mar;12(2):335–339. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maguire M. E., Wiklund R. A., Anderson H. J., Gilman A. G. Binding of (125I)iodohydroxybenzylpindolol to putative beta-adrenergic receptors of rat glioma cells and other cell clones. J Biol Chem. 1976 Mar 10;251(5):1221–1231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pohl S. L., Krans H. M., Kozyreff V., Birnbaumer L., Rodbell M. The glucagon-sensitive adenyl cyclase system in plasma membranes of rat liver. VI. Evidence for a role of membrane lipids. J Biol Chem. 1971 Jul 25;246(14):4447–4454. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puchwein G., Pfeuffer T., Helmreich E. J. Uncoupling of catecholamine activation of pigeon erythrocyte membrane adenylate cyclase by filipin. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3232–3240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Lin M. C., Salomon Y., Londos C., Harwood J. P., Martin B. R., Rendell M., Berman M. Role of adenine and guanine nucleotides in the activity and response of adenylate cyclase systems to hormones: evidence for multisite transition states. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1975;5:3–29. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubalcava B., Rodbell M. The role of acidic phospholipids in glucagon action on rat liver adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jun 10;248(11):3831–3837. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salomon Y., Londos C., Rodbell M. A highly sensitive adenylate cyclase assay. Anal Biochem. 1974 Apr;58(2):541–548. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steer M. L., Levitzki A. The control of adenylate cyclase by calcium in turkey erythrocyte ghosts. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 25;250(6):2080–2084. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



