Abstract
Aldosterone-independent mechanisms may contribute to K+ homeostasis. We studied aldosterone synthase knockout (AS−/−) mice to define renal control mechanisms of K+ homeostasis in complete aldosterone deficiency. AS−/− mice were normokalemic and tolerated a physiologic dietary K+ load (2% K+, 2 days) without signs of illness, except some degree of polyuria. With supraphysiologic K+ intake (5% K+), AS−/− mice decompensated and became hyperkalemic. High-K+ diets induced upregulation of the renal outer medullary K+ channel in AS−/− mice, whereas upregulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) sufficient to increase the electrochemical driving force for K+ excretion was detected only with a 2% K+ diet. Phosphorylation of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter was consistently lower in AS−/− mice than in AS+/+ mice and was downregulated in mice of both genotypes in response to increased K+ intake. Inhibition of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor reduced renal creatinine clearance and apical ENaC localization, and caused severe hyperkalemia in AS−/− mice. In contrast with the kidney, the distal colon of AS−/− mice did not respond to dietary K+ loading, as indicated by Ussing-type chamber experiments. Thus, renal adaptation to a physiologic, but not supraphysiologic, K+ load can be achieved in aldosterone deficiency by aldosterone-independent activation of the renal outer medullary K+ channel and ENaC, to which angiotensin II may contribute. Enhanced urinary flow and reduced activity of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter may support renal adaptation by activation of flow-dependent K+ secretion and increased intratubular availability of Na+ that can be reabsorbed in exchange for K+ secreted.
Keywords: membranous nephropathy, immunology, pathology, pathophysiology renal disease, progression
Aldosterone is thought to be critical for potassium (K+) homeostasis. According to common knowledge, increased plasma K+ concentrations, as they occur after a K+-rich meal, directly stimulate adrenal aldosterone secretion, which then is thought to stimulate K+ excretion by the kidney and the colon until the excessive K+ load is excreted. Consistent with a dominant role of aldosterone, the epithelial sites for regulated K+ excretion correspond to the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron (ASDN) (i.e., the late distal convoluted tubule [DCT2], the connecting tubule [CNT], and the collecting duct [CD])1,2 and the aldosterone-sensitive distal colon (ASDC).3,4 The ASDN contributes to >90% and the ASDC to <10% to whole-body K+ excretion.5 Both the ASDN and the ASDC are characterized by high abundance of the mineralocorticoid receptor (MR) and the enzyme 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2.1,6 The latter rapidly metabolizes cortisol (in humans) or corticosterone (in rodents) to protect the MR from activation by these glucocorticoids.1 Although the molecular mechanisms of K+ secretion between kidney and colon differ, K+ secretion follows in both organs the pump leak model and depends on active K+ uptake across the basolateral plasma membrane and passive K+ excretion across the apical plasma membrane. In the ASDN, K+ is taken up by basolateral Na+/K+-ATPases and is excreted by luminal renal outer medullary K+ (ROMK) and large conductance Ca2+-activated K+ (BK) channels.2,7–9 The electrochemical driving force for K+ secretion is provided by activation of apical epithelial Na+ channels (ENaCs).1,10 In the ASDC, K+ is taken up across the basolateral plasma membrane by the Na+/K+-ATPase and the Na+-K+-2Cl−-cotransporter type 1. The sole luminal exit pathway is the BK channel.11 ENaC is also expressed in the colon, but there is no clear dependence of colonic K+ secretion on ENaC activity.12,13 Aldosterone regulates the function of the transport and channel proteins mentioned above by direct stimulation of their expression and/or by modulation of their activity due to an altered expression of regulatory proteins.1 The relevance of aldosterone for K+ homeostasis is underlined by the observation that hypoaldosteronism and hyperaldosteronism as in Addison’s disease and Conn syndrome, respectively, cause severe disturbances in K+ balance.14–16 Likewise, pharmacologic inhibition of the MR may cause hyperkalemia.17 Nevertheless, despite these clinical observations and numerous experimental studies confirming the relevance of aldosterone, it becomes increasingly clear that regulation of K+ homeostasis is at least in part also independent from aldosterone.18–20 Indeed, the kaliuretic response to a dietary K+ load occurs very rapidly and often before plasma aldosterone is elevated.18 Moreover, even in adrenalectomized animals, increased K+ intake augments K+ excretion in kidney and colon.3,21 Likewise, dietary K+ increases apical Na+ and K+ channel conductances in the CD not only of intact but also of adrenalectomized rats19,21 and rabbits.22,23 However, adrenalectomy is not always complete and residual plasma aldosterone levels may persist.24 Moreover, local aldosterone producing systems may exist in many organs including the kidney.25 Hence, we used mice with targeted inactivation of the aldosterone synthase (AS)26 to analyze in detail the cellular and molecular mechanisms involved in the regulation of K+ homeostasis under conditions of complete aldosterone deficiency.
Results
AS−/− Mice Tolerate 2% and 3% K+, But Not 5% K+ Diets
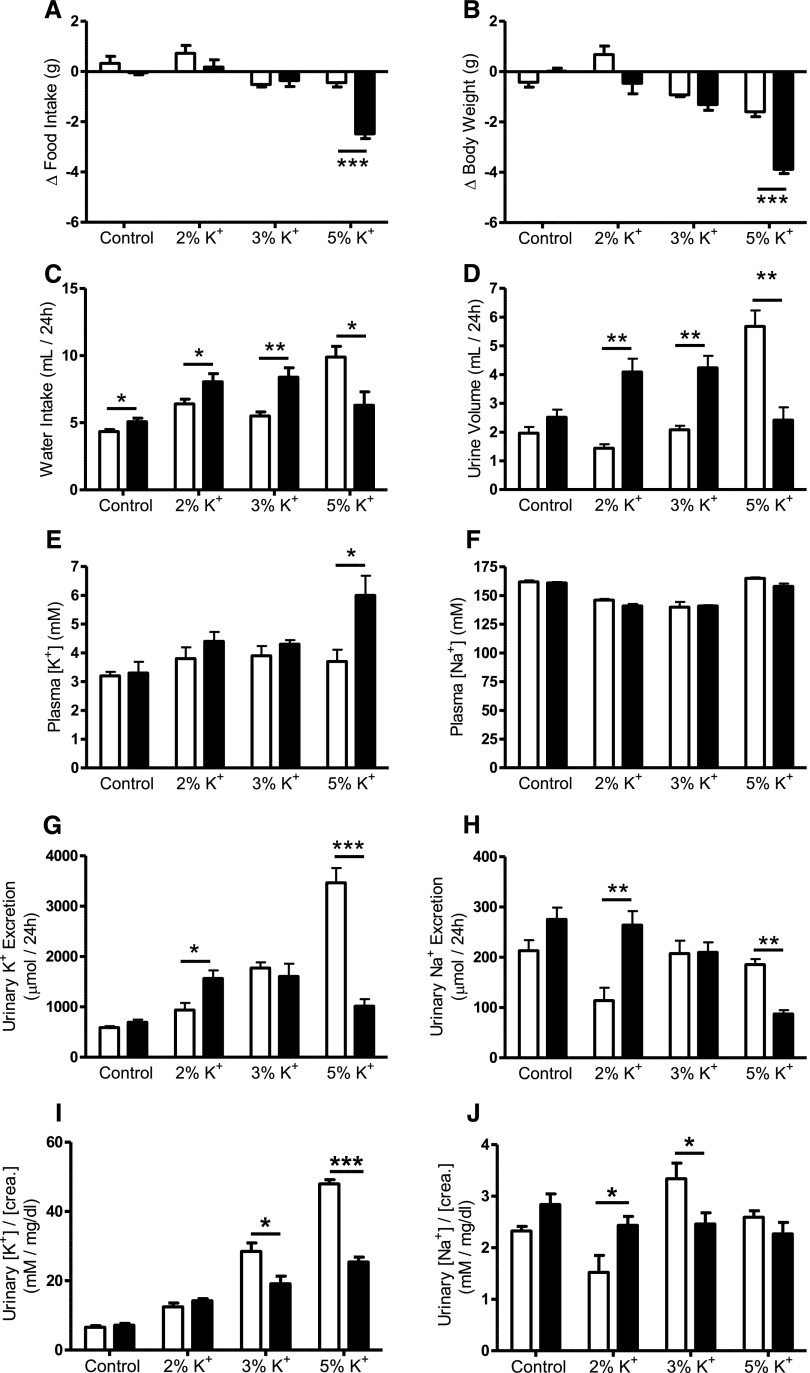
On the control diet, food intake was 4.7±0.2 g in AS+/+ mice and 5.1±0.2 g in AS−/− mice (n=5 for each genotype; P=0.17), whereas the body weights were 26.7±0.3 g for AS+/+ mice and 23.7±0.8 g for AS−/− mice (n=5 for each genotype; P=0.01). Plasma levels and urinary excretion of K+ and Na+ did not differ significantly between genotypes, although urinary K+ and Na+ excretion tended to be slightly higher in AS−/− mice consistent with the slightly higher food intake (Figure 1, A–H). AS+/+ and AS−/− mice tolerated a K+ load of up to 3% K+ in the food without any signs of illness and significant changes in food intake, body weight, plasma K+, or plasma Na+. However, with increased K+ intake, the increase in water consumption and the urinary flow rate was more pronounced in AS−/− mice than in AS+/+ mice. When dietary K+ was raised to 5%, AS−/− mice but not AS+/+ mice became hyperkalemic, showed food avoidance, and lost body weight (Figure 1, A, B, and E). In AS+/+ mice, urinary K+ excretion rose progressively with increasing dietary K+ intake, whereas urinary Na+ excretion dropped with 2% K+ diet, remaining unchanged with the 3% and 5% K+ diets. AS−/− mice adapted their urinary K+ excretion to increased dietary K+ intake. On 2% K+ diet, urinary K+ excretion was even higher in AS−/− than in AS+/+ mice. With the 3% K+ diet, urinary K+ excretion did not further increase. With 5% K+ intake, AS−/− mice decompensated and showed a lowered urinary K+ and Na+ excretion possibly owing to the reduced food intake and perhaps also to impaired renal function due to the sickness of the mice. When the 24-hour urinary K+ and Na+ excretion was normalized to creatinine excretion, it became obvious that the 24-hour urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratio progressively rose with K+ intake in mice of both genotypes. However, with the 3% and 5% K+ diets, the [K+]/[creatinine] ratio was significantly lower in AS−/− than in AS+/+ mice. The 24-hour urine [Na+]/[creatinine] ratio remained rather stable in AS−/− mice, but decreased with the 2% K+ diet and increased with 3% K+ diet in AS+/+ mice compared with the control diet (Figure 1, I and J).
Figure 1.
Physiological parameters of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice. Response of AS+/+ (open bars) and AS−/−mice (filled bars) to 48-hour feeding of control (0.8% K+), 2% K+, 3% K+, and 5% K+ diets. Mice are kept in metabolic cages to record food intake (A), body weight (B), water intake (C), urine volume (D), plasma [K+] (E), plasma [Na+] (F), urinary K+ excretion (G), urinary Na+ excretion (H), 24-hour urine [K+]/[creatinine] (I), and 24-hour urine [Na+]/[creatinine] (J) ratios. Changes in food intake and body weight are recorded over the entire 48-hour feeding period and are expressed as the difference (Δ) in the food and body weight of the mice in the last 48 hours before the experiment. Urinary fluid and ion excretion are reported for the last 24 hours. Blood ion concentrations are measured at the end of the feeding experiment. n=5–7 mice per group. Values are the mean±SEM. *P≤0.05; **P≤0.01; ***P≤0.001.
ENaC But Not ROMK Regulation Is Impaired in Kidneys of AS−/− Mice on a 5% K+ Diet
Dietary K+ loading increases the abundance and activity of ROMK and ENaC along the ASDN.27–29 Activation of ENaC is usually accompanied by a proteolytic cleavage of its α- and γ-subunits.30 On the control diet, AS−/− mice showed less full-length (approximately 90 kDa) α-ENaC and more nonmature (approximately 42 kDa) and mature (approximately 55 kDa) glycosylated ROMK abundances compared with AS+/+ mice. By contrast, the abundances of proteolytically cleaved ENaC subunits were not different between the genotypes (Supplemental Figure 1). With excessive dietary K+ loading (i.e., 5% K+), the abundance of ROMK was similar between genotypes, but the proteolytic cleavage of α-ENaC and γ-ENaC was less in AS−/− than in AS+/+ mice. Likewise, the apical localization of ENaC, but not of ROMK, was less pronounced in the ASDN of AS−/− than of AS+/+ mice (Supplemental Figure 2). Because the AS−/− mice have low BP31 that may reduce GFR and delivery of Na+ to the ASDN, we tested whether a high-Na+ diet (2% Na+), which should correct extracellular volume contraction and enhance Na+ delivery to the distal tubule, is able to overcome the detrimental effect of 5% K+ intake in the AS−/− mice. However, AS−/− mice on a 5% K+ + 2% Na+ diet also showed food avoidance, loss of body weight, and severe hyperkalemia (Supplemental Figure 3) similar to AS−/− mice on a 5% K+ diet with a control Na+ content (Figure 1).
Upregulation of ROMK and ENaC in Early ASDN of AS−/− Mice in Response to a 2% K+ Diet
AS−/− mice were apparently able to adapt to a 2% K+ load, which is in the range of the maximum K+ concentrations reached in natural diets such as in dried vegetables and fruits.32 Under this condition, the AS−/− mice are also in whole-body K+ balance as indicated by the fact that on a 2% K+ diet, muscle K+ content is similar in mice of both genotypes (Supplemental Figure 4). Therefore, we focused in the following experiments on the effects of a 2% K+ diet. First, we analyzed by immunoblotting and immunohistochemistry the abundance and subcellular localization of ROMK and ENaC subunits in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice on a control diet and a 2% K+ diet (Supplemental Figures 5–7). One consistent change in response to a 2% K+ diet in mice of both genotypes was an increase in the abundance of the proteolytically cleaved α-ENaC subunit (approximately 35 kDa) (Supplemental Figures 5 and 6). Moreover, the 2% K+ diet induced an apical translocation of ROMK in the late DCT (DCT2) and CNT in the kidneys of both AS+/+ and AS−/− mice (Supplemental Figure 7). By contrast, an apical translocation of β-ENaC was seen in DCT2 and CNT of AS+/+ mice, only. In AS−/− mice, the apical translocation of β-ENaC appeared to be restricted to the DCT2. Neither in AS+/+ nor in AS−/− mice, any detectable apical translocation of ROMK and β-ENaC was visible in cortical CDs (Supplemental Figure 7). To analyze further a possible differential ROMK and ENaC regulation between genotypes, we also directly compared AS+/+ and AS−/− mice. After 2 days on a 2% K+ diet, AS+/+ and AS−/− mice showed the same abundance of ROMK in kidney (Figure 2A). ROMK was located at the luminal cell side of the late DCT (DCT2) and CNT of both AS+/+ and AS−/− mice (Figure 2B). Consistent with previous studies on wild-type mice,29 the apical localization of ROMK was more prominent in DCT2 than CNT in mice of both genotypes, whereby the apical immunostaining for ROMK appeared to be slightly stronger in AS−/− than AS+/+ mice (Figure 2B). AS−/− mice on a 2% K+ diet had an enhanced abundance of full-length β-ENaC and γ-ENaC compared with AS+/+ mice (Figure 3A). However, the abundance of the cleaved forms of α-ENaC (approximately 35 kDa) and γ-ENaC (approximately 70 kDa) was not different between genotypes. Consistent with previous results in mice on a standard diet,31 quantitative RT-PCR revealed slightly higher γ-ENaC mRNA levels in AS−/− than in AS+/+ mice on a 2% K+ diet (Supplemental Figure 8), suggesting that at least part of the upregulation of γ-ENaC at the protein level is caused by a transcriptional effect. Immunohistochemistry showed that the 2% K+ diet caused an apical translocation of all three ENaC subunits in the CNTs of AS+/+ mice, whereas only few CNTs showed a faint apical localization of α-ENaC, in AS−/− mice. β-ENaC and γ-ENaC were distributed over the entire cytoplasm in CNTs and CDs of AS−/− mice (Figure 3B and Supplemental Figure 7). Although we observed a predominant intracellular localization of ENaC in the CNT and CD of AS−/− mice, the very early ASDN (i.e., the late DCT or DCT2) of these mice showed a prominent apical localization for all ENaC subunits (Figure 4A). The intact apical translocation of ENaC in the early ASDN was functionally confirmed by patch-clamp studies on early ASDN segments isolated from mice on a 2% K+ diet (Figure 4B). Moreover, AS+/+ and AS−/− mice on a 2% K+ diet showed a similar amiloride-induced natriuresis and kaliuresis (Figure 4C).
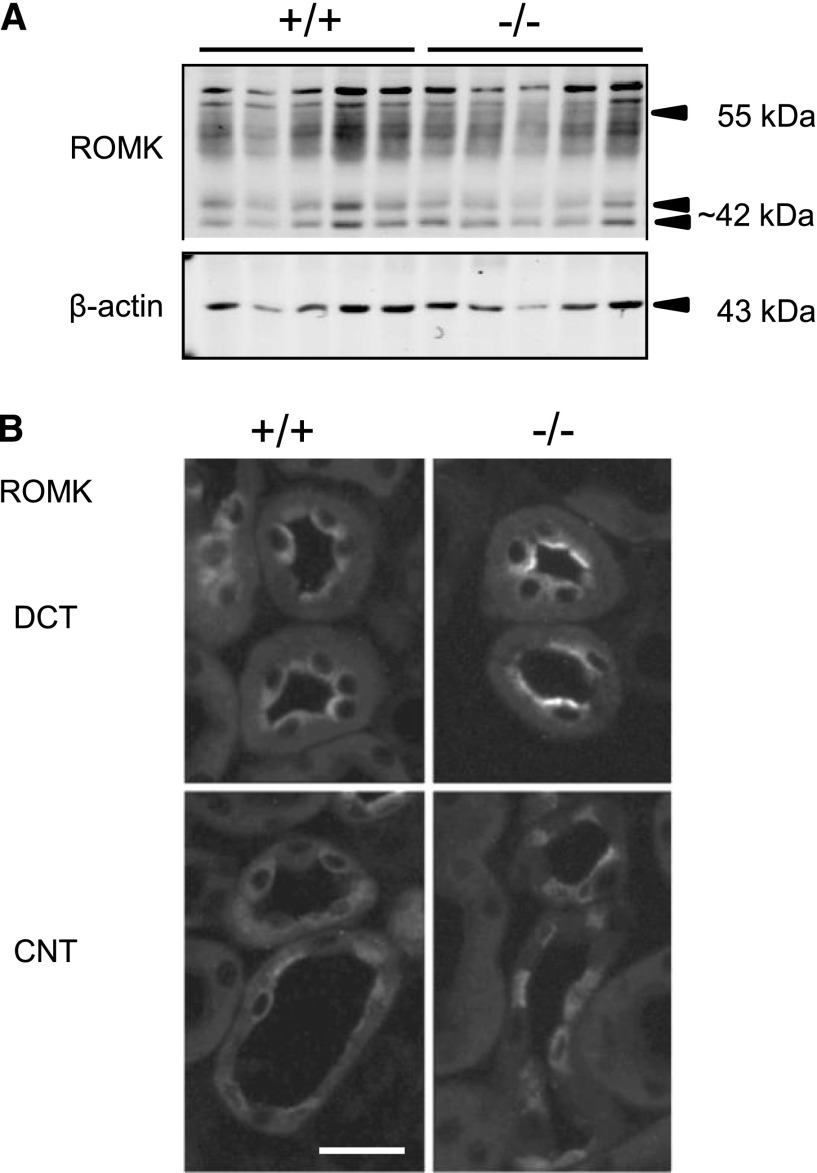
Figure 2.
Expression and subcellular distribution of the ROMK in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) Detection of fully and nonmature-glycosylated ROMK channels (55 kDa and approximately 42 kDa bands, respectively) by immunoblotting using total membrane fractions of whole kidney homogenates. The membrane is reprobed for β-actin. n=5 mice per group. (B) Detection of ROMK channels in DCTs and CNTs by immunofluorescence on kidney cryosections. Tubules are identified by costaining for calbindin D28K (not shown) as described in the Concise Methods. Bar, approximately 25 μm.
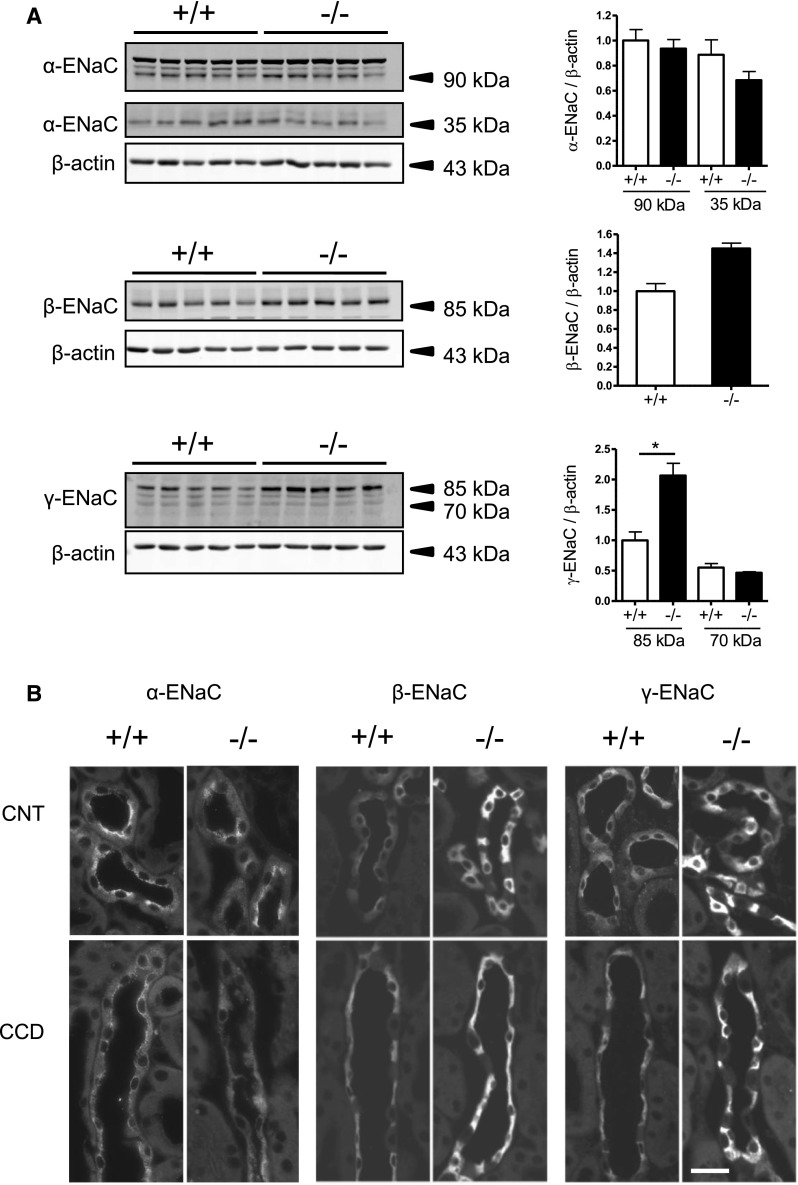
Figure 3.
Expression and subcellular localization of the ENaC subunits in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) Detection of α-ENaC, β-ENaC, and γ-ENaC subunits by immunoblotting using total membrane fractions of whole kidney homogenates. All membranes are reprobed for β-actin and data are normalized against β-actin. Bar graphs represent densitometric data. n=5 mice per group. Values are the mean±SEM. *P≤0.05. (B) Detection of α-ENaC, β-ENaC, and γ-ENaC subunits in CNTs and cortical CDs by immunofluorescence on kidney cryosections. Tubules are identified by costaining for calbindin D28K (not shown) as described in the Concise Methods. Bar, approximately 25 μm.
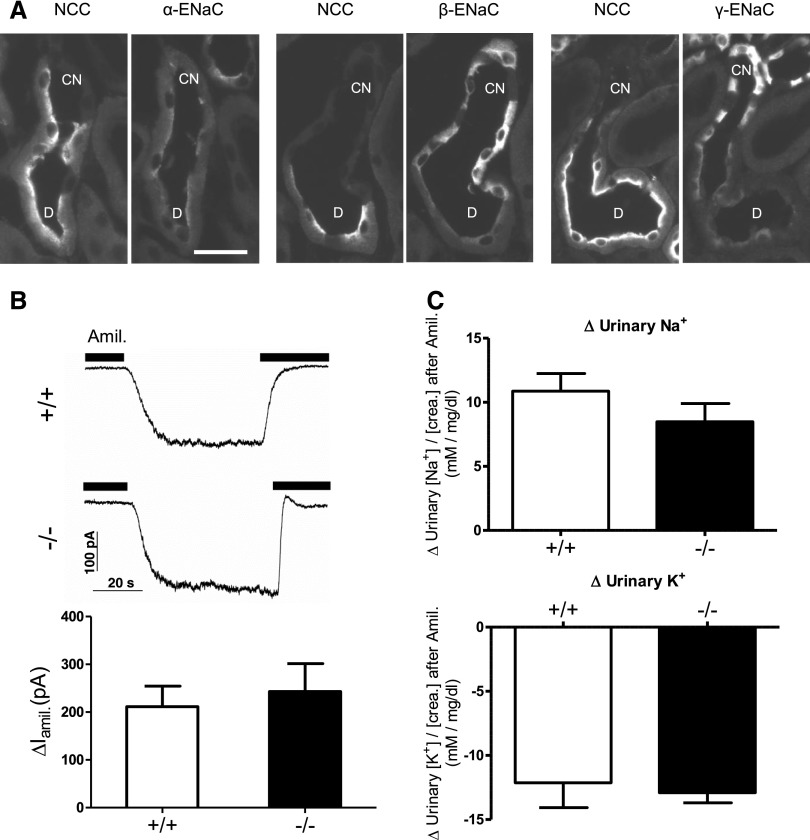
Figure 4.
Subcellular distribution and electrophysiologic activity of ENaC and amiloride response in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) Detection of α-ENaC, β-ENaC, and γ-ENaC subunits and NCC in the late DCT (D) and CNT of AS-deficient (AS−/−) mice by immunofluorescence on kidney cryosections. Pairs of consecutive cryosections stained either for NCC or for one of the ENaC subunits are always shown. Tubules are identified by costaining for calbindin D28K (not shown) as described in the Concise Methods. (B) Amiloride-sensitive whole-cell currents (∆Iami) reflecting ENaC activity are measured by patch-clamp recordings on isolated early ASDN segments (DCT2/CNT) from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. Representative whole-cell current traces are shown for AS−/− and AS+/+ mice. Currents are recorded using a pipette holding potential of −60 mV. Amiloride (Amil; 2 μM) is present as indicated by the black bars above the traces. The bar diagram summarizes results from similar experiments. n=7–9 measurements per group. (C) Difference (Δ) in urine [Na+]/[creatinine] and urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratios between vehicle (0.9% saline) and amiloride-injected mice. Amiloride or vehicle is injected intraperitoneally 48 hours after starting the feeding experiment. Urine is collected for the following 4 hours. n=8–11 mice per group. Values are the mean±SEM. Bar, approximately 25 μm.
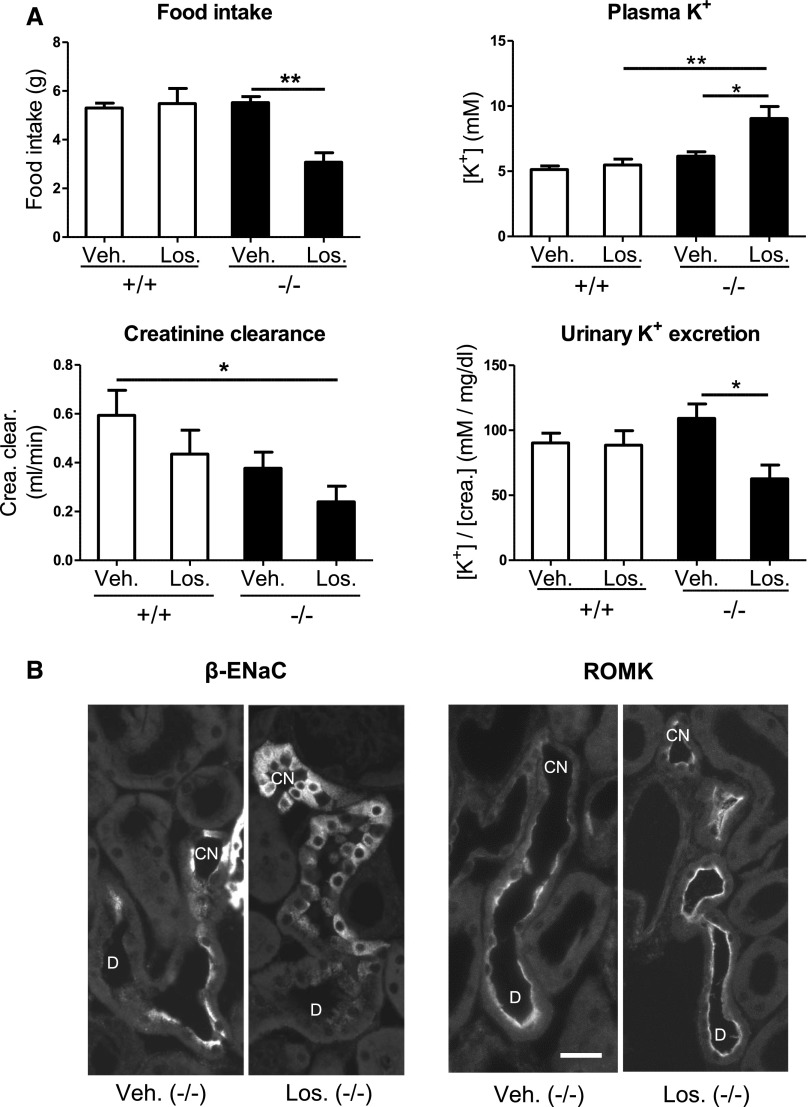
Loss of Aldosterone in AS−/− Mice Is Compensated by Angiotensin II
AS−/− mice have a profound upregulation of the renin-angiotensin II system,33 which may help to maintain sufficient BP, glomerular filtration, and ENaC activity to keep mice in homeostatic balance even in the absence of any aldosterone. Consistent with this hypothesis, injection of the angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) antagonist losartan caused a decompensation of AS−/− mice with reduced renal creatinine clearance, diminished urinary K+ excretion, severe hyperkalemia, and food avoidance (Figure 5A). ENaC was no longer detectable at the apical cell side, but predominantly showed an intracellular localization, which was most evident at the transition from the DCT2 to the CNT (Figure 5B). By contrast, the apical localization of ROMK was not diminished by AT1R inhibition, but appeared to be even slightly increased compared with vehicle-treated mice (Figure 5B). The lack of any detectable apical ENaC localization in losartan-treated AS−/− mice is consistent with the fact that both aldosterone and angiotensin II are potent stimuli for renal ENaC activity.1,34
Figure 5.
Effect of AT1R inhibition by losartan on food intake, plasma K+, urinary K+ excretion, creatinine clearance, and subcellular distribution of β-ENaC and ROMK in AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) Food intake, urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratio, blood K+ concentrations, creatinine clearance in the mice at 13 hours after vehicle (Veh) or losartan (Los) treatment. Vehicle and losartan are injected subcutaneously at 36 hours after starting the feeding experiment. Food intake and urinary ion excretion are recorded for the following 13 hours. n=5 in the losartan group; n=4 in the vehicle group. Values are the mean±SEM. *P≤0.05; **P≤0.01. (B) Detection of β-ENaC and ROMK in the late DCT and CNT of vehicle- and losartan-treated AS-deficient mice by immunofluorescence on kidney cryosections. Tubules are identified by costaining for calbindin D28K (not shown) as described in the Concise Methods. Bar, approximately 25 μm.
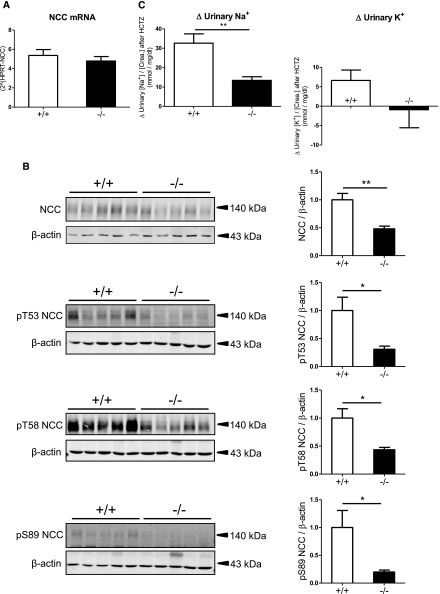
Decreased NaCl Cotransporter Protein Expression and Activity in AS−/− Mice on a 2% K+ Diet
A K+ diet–induced downregulation of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter (NCC) in the DCT may participate in the control of urinary K+ excretion.28,35–37 NCC mRNA levels did not differ between AS−/− and AS+/+ mice on a 2% K+ diet (Figure 6A). However, the total abundance of NCC and the phosphorylation of NCC at three phospho-sites (pT53, pT58, and pS89) were >50% lower in AS−/− mice compared with AS+/+ mice (Figure 6B). Consistently, AS−/− mice revealed a >50% lower thiazide-sensitive Na+ excretion than AS+/+ mice (Figure 6C). Interestingly, AS−/− mice did not show any thiazide-induced kaliuresis, suggesting that NCC downregulation is already maximized for K+ excretion and a further decrease of its activity does not augment kaliuresis. The more profound downregulation of NCC activity in AS−/− than AS+/+ mice may explain why AS−/− mice on a 2% K+ diet excrete more Na+ in the urine than AS+/+ mice on the same diet (Figure 1). That both genotypes of mice do not show an enhanced urinary Na+ excretion in response to the 2% K+ diet despite NCC downregulation could be explained at least in part by the concomitant K+ diet–induced ENaC activation, which is similar in both genotypes (Figures 3 and 4). The ENaC upregulation may outreach and hence overcompensate the slight NCC downregulation in AS+/+ mice, but may just be sufficient to compensate for the prominent NCC downregulation in AS−/− mice (Figure 6, Supplemental Figure 9).
Figure 6.
Transcription, expression, phosphorylation, and activity of the thiazide-sensitive NCC in kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept on a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (A) NCC mRNA levels are assessed by real-time RT-PCR. n=7 mice per group. (B) Detection of total NCC and NCC phosphorylated at threonine 53 (pT53 NCC), threonine 58 (pT58 NCC), and serine 89 (pS89 NCC) by immunoblotting using total membrane fractions of whole kidney homogenates. Data are normalized against β-actin. Bar graphs represent densitometric data. n=5 mice per group. (C) Difference (Δ) in urine [Na+]/[creatinine] and [K+]/[creatinine] ratios between vehicle-injected (DMSO) mice and hydrochlorothiazide-injected (HCTZ) mice. Vehicle and HCTZ are injected intraperitoneally at 48 hours after starting the feeding experiment. Urine is collected for the following 4 hours. n=8–9 for in each group. Values are the mean±SEM. *P≤0.05; **P≤0.01.
Regulation of Electrolyte Transport in the late Distal Colon Is Aldosterone Dependent
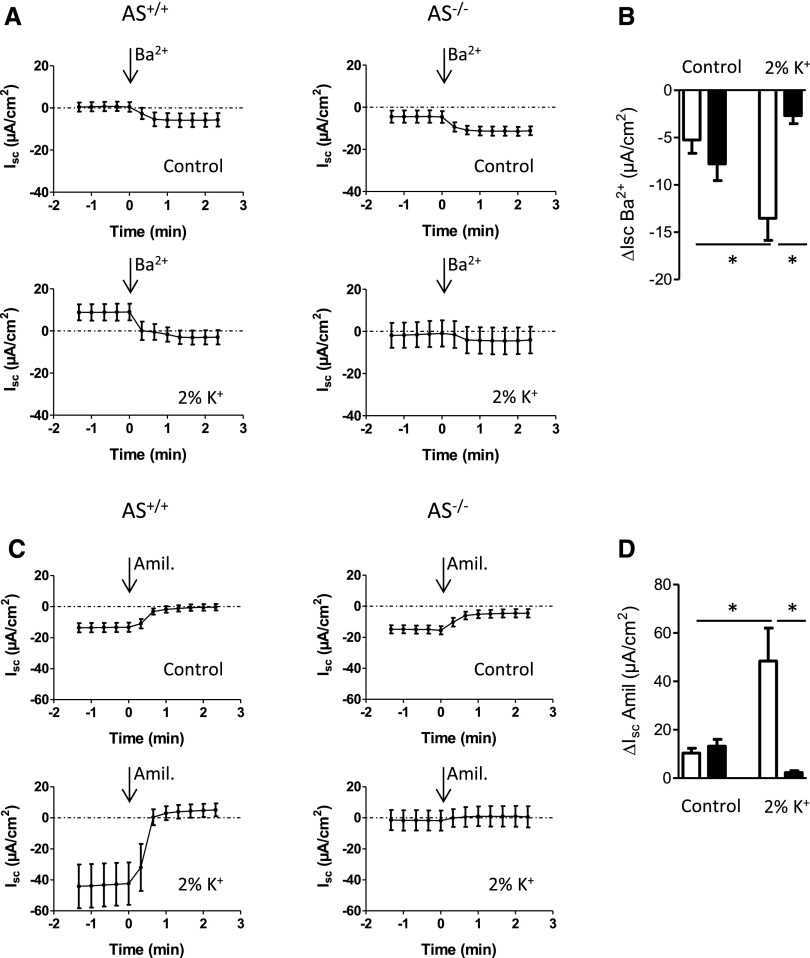
The distal colon is another site for K+ secretion in the body and both colonic BK channels and ENaC are regulated by aldosterone.6,11,12 We placed colonic mucosa from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice in Ussing-type chambers and recorded barium-sensitive [Isc(Ba2+)] and amiloride-sensitive [Isc(amil)] short circuit currents as read-outs for BK channels and ENaC activity, respectively. On the control diet, the barium-sensitive Isc(Ba2+) and amiloride-sensitive Isc(amil) currents were small and did not differ between AS+/+ and AS−/− mice (Figure 7, A and C). However, in response to the 2% K+ diet, K+ and Na+ channel activities rose significantly in the colonic mucosa of the AS+/+ mice only (Figure 7).
Figure 7.
Na+ and K+ channel activity in the distal colon. (A) Ussing-type chamber experiments are used to record barium (Ba+)–sensitive K+ channel currents in the colonic mucosae isolated from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice after feeding either a control or a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (B) The barium-sensitive difference of ion currents are calculated and plotted as bar graphs. (C) Recording of amiloride (Amil) –sensitive Na+ channel currents on distal colon mucosae from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice kept either on a control diet or a 2% K+ diet for 48 hours. (D) The amiloride-sensitive differences of ion currents are calculated and plotted as bar graphs. n=5–6 mice per diet and genotype. Luminal concentrations are 5 mM for BaCl2 and 100 µM for amiloride. Values are the mean±SEM. *P≤0.05.
Discussion
The traditional view of the control of K+ homeostasis assumes that increases in plasma K+ concentrations (e.g., in response to a K+-rich diet) directly stimulate aldosterone secretion by the adrenal glands. Enhanced plasma aldosterone levels stimulate renal K+ secretion restoring plasma K+. This classic feed-back model was challenged by studies of Rabinowitz and others18–20 showing that a K+-rich meal provokes a kaliuretic response before plasma K+ and aldosterone levels were increased.18 Moreover, aldosterone has a rather weak kaliuretic effect at normal physiologic levels.18 This study on aldosterone-deficient mice strongly supports the concept that control of K+ homeostasis can be achieved independent from aldosterone at least as long as dietary K+ intake is modulated in the physiologic range. Only when dietary K+ concentrations exceed a certain limit (3% K+ in the case of the AS−/− mice), aldosterone-independent mechanisms are no longer sufficient to maintain K+ homeostasis.
Our data are in line with observations in humans with type 1 aldosterone deficiency, who are usually still able to adapt renal K+ excretion and to stay more or less in K+ balance.38 Likewise, adrenalectomized animals23,24,39 were shown to augment renal K+ excretion in response to an increased dietary K+ intake, although usually at the expense of more or less elevated plasma K+ levels. Previous studies on adrenalectomized rats and rabbits indicated that a high-K+ diet increases renal Na+ and K+ channel activities independent from aldosterone.19,21–23 However, because adrenalectomies in rodents are often incomplete and the existence of local aldosterone producing systems in kidney and other organs have been suggested,25 these previous studies could not exclude that minute amounts of remaining aldosterone production could have contributed to the observed activation of Na+ and K+ channels in the ASDN. In AS−/− mice, any aldosterone production is prevented because of the systemic disruption of the AS gene. Thus, our experiments now conclusively demonstrate that high K+ intake increases urinary Na+ and K+ excretion and renal Na+ and K+ channel activity even in animals not producing any aldosterone. Nevertheless, our data should not be interpreted to indicate that aldosterone is dispensable for the renal control of K+ homeostasis. In fact, although the 24-hour urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratio increases in parallel with the amount of dietary K+ intake in mice of both genotypes (Figure 1), this increase is clearly less in AS−/− mice than in AS+/+ mice with the 3% and 5% K+ diets. Even with the 2% K+ intake, when the 24-hour urine [K+]/[creatinine] ratio tended to be higher in AS−/− than in AS+/+ mice, the AS−/− mice appear to have higher plasma K+ levels than the AS+/+ mice. Thus, the data are in good agreement with previous studies in adrenalectomized dogs, which indicated that with low aldosterone replacement doses, higher plasma K+ concentrations are needed to excrete similar amounts of K+ as with high aldosterone replacement doses.39 This is in line with transport and renal clearance studies on adrenalectomized laboratory animals, which suggested that aldosterone is not absolutely necessary, but plays at least a permissive role and is important to achieve maximal K+ secretion.22,40 Likewise, inhibition of aldosterone action by the MR-inhibitor spironolactone increases plasma K+ levels in mice on a combined high-K+ (5%) and high-Na+ (3%) diet.41
Interestingly, the apical translocation of ROMK and ENaC occurred predominately in the early ASDN in mice of both genotypes (AS−/− and AS+/+). This supports the crucial role of this tubule segment for Na+ and K+ homeostasis27 and is consistent with previous immunohistochemical and electrophysiologic data indicating that apical ROMK and ENaC localization and activity in the early ASDN are several times higher than in the late ASDN.29,42,43 Our immunofluorescence and functional data are also in good agreement with patch-clamp studies on isolated early and late ASDN segments from AS+/+ and AS−/− mice that indicated that ENaC regulation in the early ASDN is largely aldosterone independent.44 Here, we provide a possible explanation for the aldosterone-independent activity of ENaC in the early ASDN of AS−/− mice. AS−/− mice have very high levels of angiotensin II.26 This probably does not directly contribute to the regulation of K+ homeostasis, but may compensate for the loss of aldosterone at least in part by ensuring a residual ENaC activity in the kidney of AS−/− mice. Consistent with this interpretation, we demonstrated that inhibition of AT1 receptors caused removal of ENaC, but not ROMK, from the luminal cell side of the ASDN. This loss of ENaC activity together with a reduced GFR due to the hemodynamic effects of losartan likely explains the severe hyperkalemia in losartan-treated AS−/− mice. Interestingly, losartan caused hyperkalemia and K+ food avoidance only in AS−/− mice, but not in AS+/+ mice, indicating that AT1R inhibition disturbs renal K+ handling only in the absence of aldosterone and that the action of both hormones may compensate for each other. Consistently, a recent meta-analysis revealed that patients with a combined inhibition of aldosterone and angiotensin II action develop much more frequent episodes of severe hyperkalemia than patients with inhibition of either MR or AT1-dependent signaling.45
Consistent with previous studies on adrenalectomized rats,3,21,46 aldosterone-independent mechanisms cannot fully compensate for the loss of aldosterone. On a 5% K+ diet, AS−/− mice but not AS+/+ mice decompensated, became hyperkalemic, and showed food avoidance. Our data suggest that the decompensation of the animals is likely the result of an impaired regulation of ENaC rather than of ROMK. Apparently, in response to a dietary K+ load, maximum apical translocation of ENaC but not of ROMK requires aldosterone. Our finding that the activation of renal secretory K+ channels in response to K+ intake does not require aldosterone is consistent with previous ion transport and electrophysiologic studies on isolated CDs from adrenalectomized animals.19,21 Although previous studies did not show a reduced creatinine clearance in AS−/− mice at baseline,33 we saw a slight, although not statistically different, trend for a lowered creatinine clearance in AS−/− mice on a 2% K+ diet (Figure 5). To what extent a possibly reduced GFR may have contributed to the decompensation of the AS−/− mice on the 5% K+ diet is open.
AS−/− mice are polyuric.33 Polyuria, seen on standard diet, became even more prominent under dietary K+ loading. K+ secretion in renal distal tubules as well as the activity of renal potassium channels such as the BK channel are flow-dependent47,48 and changes in BK channel activity were suggested to add to the adaptation of urinary K+ excretion in response to an altered dietary K+ intake.49 Unfortunately, we could not analyze the expression and subcellular localization of BK channels in the kidneys of AS+/+ and AS−/− mice as none of the BK channel antibodies available to us allowed a convincing detection of renal BK channels. However, on the basis of the previous observation that AS−/− do not tolerate any water restriction,31 we speculate that the high urinary flow rate does also contribute to an efficient renal K+ elimination.
NCC was reported to be an aldosterone-induced protein.50 Consistently, we found a lowered thiazide response and a reduced total NCC and pNCC abundance in AS−/− mice on a standard diet (not shown) and on a 2% K+ diet. NCC mRNA expression was similar in both genotypes, supporting that the aldosterone-dependent regulation of NCC occurs at the post-transcriptional level.51 Similar to previous data on wild-type rats37 and mice,35,36 the high-K+ diet also decreased NCC phosphorylation in AS−/− mice (Supplemental Figure 9). Although the underlying mechanism for the K+-induced downregulation of NCC is unclear, it likely contributes to the maintenance of K+ balance because it augments Na+ delivery to the ENaC-expressing ASDN in which then more luminal Na+ is available for electrogenic Na+ reabsorption in exchange for K+ secretion.5,52 Nevertheless, a recent renal clearance study with thiazide-treated mice pointed out that lowered NCC activity per se is not sufficient to activate electrogenic Na+ reabsorption in the ASDN and to induce a significant kaliuresis.53 Other renal adaptation mechanisms, including an activation of ROMK and ENaC, might be needed as well.
The distal colon is aldosterone sensitive and both electrogenic Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion are regulated by aldosterone.6,11,12 Previous studies revealed the importance of aldosterone for colonic K+ adaptation,3,54 and showed an upregulation of electrogenic Na+ and K+ transport and mRNA expression of BK channels and ENaC in the distal colon of mice on a high-K+ diet.11,13 Here, we confirmed that a K+ diet induced activation of Na+ reabsorption and K+ secretion in the colon of AS+/+ mice. However, this adaptation of Na+ and K+ channel activity was completely absent in the colon of AS−/− mice. Thus, it appears that K+ adaptation in the colon, even in physiologic ranges, strictly depends on the presence of aldosterone. This is in sharp contrast with the kidney. The significantly higher urinary K+ excretion rate in AS−/− mice on a 2% K+ diet indicates that the colonic defect of K+ excretion might be even partly compensated by an aldosterone-independent stimulation of renal K+ excretion.
The underlying mechanism for the aldosterone-independent activation of ENaC and ROMK, as well as the downregulation of NCC in the kidney, remains elusive. The existence of yet undefined kaliuretic factors18 has been proposed and indeed there is experimental evidence for such factors to be present in plasma55 and urine.56 Increased plasma K+ levels may also directly affect the kidney. Young and Paulsen stressed the powerful effect of increased plasma K+ levels on renal K+ excretion>25 years ago.39 However, although elevation of plasma K+ concentrations by intravenous K+ infusions increases apical K+ conductances in distal tubules,23,57 reduces NCC phosphorylation, and drives kaliuresis,58 ex vivo studies on mouse CD cells and isolated renal tubules failed to detect any significant direct effects of increased extracellular K+ concentrations on ENaC and ROMK channel activities59 and NCC phosphorylation.35
In summary, AS−/− mice adapt to physiologically relevant challenges in dietary K+ intake without major signs of illnesses and hyperkalemia. Apparently, K+ balance in these mice is mainly achieved by an aldosterone-independent ROMK and ENaC activity in the early ASDN. In addition, an increased urinary flow and a profound downregulation of the thiazide-sensitive NaCl cotransporter NCC in the distal convoluted tubule likely contribute to the renal K+ adaptation in AS−/− mice. With supraphysiologic K+ intake, AS−/− mice decompensate probably because of an inefficient upregulation of ENaC. To what extent other factors, including a possibly reduced GFR, may contribute to the decompensation of the AS−/− mice remains elusive. In contrast with the kidney, aldosterone deficiency completely diminishes the colonic regulation of K+ excretion. The aldosterone-independent capacity of the kidney to eliminate an increased dietary K+ load highlights the redundancy and complexity of renal mechanisms to upregulate renal K+ excretion.
Concise Methods
Animal Model
Experiments were performed in AS wild-type (AS+/+) and AS-deficient (AS−/−) mice, which were bred in a 129 SvEv genetic background.26 All breeding was done in our in-house animal breeding facility. Age-matched male AS+/+ and AS−/− mice were used for all experiments. Experiments were performed according to Swiss Animal Welfare laws and were approved by the local veterinary authorities. All animals received standard rodent chow GLP 3433 (Provimi Kliba, Kaiseraugst, Switzerland).
Experimental Protocol for Dietary Potassium Load
Four different potassium (K+) diets were used: a control K+ diet (0.8% K+ in standard powder food), a 2% K+ diet (2.2 g of KCl+97.8 g standard powder food), a 3% K+ diet (4.2 g KCl+95.8 g standard powder food), and a 5% K+ diet (8 g of KCl+92 g standard chow powder food). The food was mixed with milliQ water in 1:1 proportion (50 g food+50 ml water) to ensure homogeneous soaking with K+. Sodium content of diets was identical in all conditions (0.2% Na+).
Metabolic Cages
Mice were kept individually in metabolic cages. Before the experiments, mice were adapted to the metabolic cages for 2 days. The diets were then changed to the experimental diets for an additional 2 days. Daily food, water intake, and body weights were measured, and 24-hour urine was collected under mineral oil. At the end of the experiment, mice were anesthetized and heparinized venous blood was collected and analyzed immediately for pH, blood gases, and electrolytes on a Radiometer ABL 505 (Radiometer, Copenhagen, Denmark) blood gas analyzer. Plasma was prepared and frozen until further analysis. Both kidneys were harvested, immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen, and stored at −80°C for mRNA or protein extraction. Urinary electrolytes (Na+, K+) were measured by ion chromatography (Metrohm, Herisau, Switzerland). Urine creatinine was measured by the Jaffe method.60
Amiloride and Thiazide Tests
Mice were kept in metabolic cages on a control or a 2% K+ diet. After 2 days on these diets, urinary bladder was emptied by abdominal massage and mice were injected intraperitoneally with either amiloride (5 µg/g body wt in 0.9% saline) or hydrochlorothiazide (50 µg/g body wt in DMSO), respectively. Control mice were injected intraperitoneally with vehicle (saline or DMSO) only. Four hours after injection, urinary bladder was emptied again and urine was combined with the urine sampled in the urine collector of the metabolic cage. The 4-hour urine collection was analyzed for Na+, K+, and creatinine as described above.
Losartan Treatment
Mice were kept in metabolic cages on either a control diet or a 2% K+ diet. After 36 hours on these diets, urinary bladder of mice was emptied by abdominal massage and mice received a single subcutaneous injection of either losartan (10 mg/kg body wt in deionized water) or vehicle (deionized water) and urine was collected for the next 12 hours for analyses of Na+, K+, and creatinine. Urine and plasma creatinine were measured by the UniCel DxC 800 Synchron system (Beckman Coulter International, Nyon, Switzerland) to calculate renal creatinine clearance.
RNA Extraction from the Kidney
Snap-frozen kidneys (five kidneys per group) were homogenized in RLT buffer (Qiagen) supplemented with 2-mercaptoethanol to a final concentration of 1%. Total RNA was extracted from 200 µl of homogenized samples using the RNeasy Mini Kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and concentration of the isolated RNA preparations were measured by an ND-1000 spectrophotometer (NanoDrop Technologies).
Quantitative Real-Time PCR
We used 300 ng of total RNA as a template for RT using the TaqMan Reverse Transcription Kit (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA). Quantitative real-time PCR was performed on the ABI Prism 7500 Sequence Detection System (Applied Biosystem). The following primers for the sodium chloride cotransporter (NCC) and the hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase (HPRT) were used: NCC, forward 5′-TAG ACC CCA TCA ATG ACA TCC-3′ and reverse 5′-AGG TAG TTG GCA AAG GAG ACC-3′ (accession number NM_001205311); and HPRT, forward 5′-TTA TCA GAC TGA AGA GCT ACT GTA AGA TC-3′ and reverse 5′-TTA CCA GTG TCA ATT ATA TCT TCA ACA ATC-3′ (accession number NM_013556). Specificity of the primers was first tested in a standard PCR with subsequent separation of PCR products in a 2% agarose gel. Real-time PCR reactions were performed using the iQ SYBR Green Supermix (Bio-Rad). ROX Passive Reference Dye (Bio-Rad) 3.3 µl/1.25 ml of iQ SYBR Green Supermix was added. Briefly, 3 µl cDNA, 0.8 µl of each primer (10 µM), 5.4 µl RNase free water, 10 µl iQ SYBR Green Supermix reached 20 µl final reaction volume. Reaction conditions were as follows: denaturation at 95°C for 10 minutes followed by 40 cycles of denaturation at 95°C for 15 seconds and annealing/elongation at 60°C for 60 seconds followed by dissociation stage (95°C for 15 seconds and 60°C for 15 seconds, followed by slow ramp to 95°C). All reactions were run in duplicate. The expression of the gene of interest was calculated in relation to HPRT.
Membrane Preparation and Western Blot Analyses
Mice were anesthetized with a combination of ketamine (65 mg/kg body wt [Vétoquinol, Switzerland]) and xylazine (13 mg/kg body wt [Streuli, Switzerland]) intraperitoneally. Kidneys were removed and immediately frozen in liquid nitrogen. Total membrane proteins were prepared as previously described,61 separated (50 µg per lane) by SDS-PAGE (8% polyacrylamide), and blotted to nitrocellulose membranes (PROTRAN 0.2 µM; Whatman GmbH, Dassel, Germany). After preincubation with Odyssey blocking buffer (LI-COR Biosciences, Lincoln, NE), blots were incubated with primary antibodies (Table 1) diluted in Odyssey blocking buffer overnight at 4°C. After repeated washing with PBS containing 0.1% Tween-20, membranes were incubated for 1 hour at room temperature with fluorescence secondary antibodies (goat anti-rabbit IRDye 800, 1:10,000; goat anti-mouse IRDye 680, 1:20,000; Li-COR Biosciences or Rockland Immunochemicals Inc., Gilbertsville, PA) and processed for signal detection and densitometric analysis by the Odyssey Infrared Imaging System (Li-COR Biosciences).
Table 1.
Antibodies used for Western blotting and immunofluorescence
| Antibody | Host | Dilution | Source | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Western Blotting | Immunofluorescence | ||||
| ROMK | Rabbit | 1:800 | 1:4000 | Alomone | — |
| αENAC | Rabbit | 1:5000 | 1:5000 | J. Loffing | 35 |
| βENaC | Rabbit | 1:10,000 | 1:40,000 | J. Loffing | 61 |
| γENaC | Rabbit | 1:10,000 | 1:40,000 | J. Loffing | 61 |
| NCC | Rabbit | 1:800035 | 1:10,00064 | J. Loffing | 35,64 |
| pNCC-T53 | Rabbit | 1:1000 | R. Fenton | 65 | |
| pNCC-T58 | Rabbit | 1:2000 | R. Fenton | 65 | |
| pNCC-S89 | Rabbit | 1:4000 | J. Loffing | 35 | |
| Calbindin D28k | Mouse | 1:10,000 | Swant (Switzerland) | — | |
| β-actin | Rabbit | 1:10,000 | Sigma | — | |
Immunohistochemistry
Kidneys of anesthetized mice were fixed by vascular perfusion with 3% paraformaldehyde/0.1 M phosphate buffer and processed for immunohistochemistry as previously described.62 Cryosections (4–5 µm) were incubated with primary antibodies (Table 1) at 4°C overnight and with fluorescent dye–conjugated secondary antibodies (Jackson Immunoresearch Laboratories) at room temperature for 1 hour. Sections were analyzed using a Leica DM 6000 fluorescence microscope (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany). Sections stained with one of the rabbit antibodies were always costained with the mouse anti-calbindin D28K antibody for unequivocal identification of distal tubule segments and CDs, as established in previous studies.63 Images were captured with a charge-coupled device camera (Leica) and were processed with Photoshop and PowerPoint software.
Ussing Chamber Experiments
Mice kept on the respective diets were euthanized by cervical dislocation. The distal part of the colon was isolated and rinsed in ice-cold Ringer solution. Only the distal 1.5 cm of the intact mouse colon was then mounted in an Ussing chamber (Physiologic Instruments). The two halves of the chamber were perfused with identical solutions: 120 mM NaCl, 25 mM NaHCO3, 1.6 mM K2HPO4, 0.4 mM KH2PO4, 1.3 mM Ca-gluconate, 1 mM MgCl2, 5 mM D-glucose, and 5 µM indomethacine kept at 37°C by water jackets and continuously bubbled with carbogen (5% CO2 and 95% O2). Initially, tetrodotoxin (1 µM) was added to the serosal side to inhibit possible autonomous nerve activity. Experiments were performed with the transepithelial voltage clamped to zero. After mounting of the tissues and an equilibration period of 30 minutes, amiloride (100 µM) was added to the mucosal side to measure amiloride-sensitive short circuit currents [ΔIsc(amil)] as a readout for ENaC activity. After an additional 5 minutes, BaCl2 (5 mM) was also added to the mucosal side to measure Ba2+-sensitive short circuit currents [Isc(Ba2+)] as a readout for BK channel activity.
Patch-Clamp Experiments
Microdissection of DCT2/CNT tubular fragments and conventional whole-cell patch-clamp recordings were performed as recently described.44
Statistical Analyses
Results are expressed as the mean±SEM. All data were tested for significance using one-way ANOVA followed by the Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and unpaired and paired t tests where appropriate. Only values with P<0.05 were considered significant.
Disclosures
None.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Monique Carrel and Udo Schnitzbauer for expert technical assistance, Jan Czogalla for reading of the manuscript, and Dr. Lawrence Rabinowitz for a fruitful exchange of ideas on mechanisms of K+ homeostasis. The authors also thank Dr. Oliver Smithies for kindly providing the AS−/− mice. The authors gratefully acknowledge the technical support by the Zurich Integrative Rodent Physiology facility and the Centre for Microscopy and Image Analysis.
This study was supported by a collaborative project grant from the Zurich Center for Integrative Human Physiology (to J.L. and C.A.W.), as well as project grants from the Swiss National Centre for Competence in Research Kidney Control of Homeostasis and the Swiss National Science Foundation (310030_143929/1 to J.L. and 31003A_138143/1 to C.A.W.).
Footnotes
Published online ahead of print. Publication date available at www.jasn.org.
This article contains supplemental material online at http://jasn.asnjournals.org/lookup/suppl/doi:10.1681/ASN.2013111156/-/DCSupplemental.
References
- 1.Staub O, Loffing J: Mineralocorticoid action in the aldosterone sensitive distal nephron. In: Seldin and Giebisch's The Kidney, 5th Ed., London, Academic Press, 2013, pp 1181–1211 [Google Scholar]
- 2.Welling PA: Regulation of renal potassium secretion: Molecular mechanisms. Semin Nephrol 33: 215–228, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Foster ES, Jones WJ, Hayslett JP, Binder HJ: Role of aldosterone and dietary potassium in potassium adaptation in the distal colon of the rat. Gastroenterology 88: 41–46, 1985 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Pácha J, Miksík I: Distribution of 11 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase along the rat intestine. Life Sci 54: 745–749, 1994 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Giebisch G: Renal potassium transport: Mechanisms and regulation. Am J Physiol 274: F817–F833, 1998 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Kunzelmann K, Mall M: Electrolyte transport in the mammalian colon: Mechanisms and implications for disease. Physiol Rev 82: 245–289, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Wang WH, Giebisch G: Regulation of potassium (K) handling in the renal collecting duct. Pflugers Arch 458: 157–168, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Rieg T, Vallon V, Sausbier M, Sausbier U, Kaissling B, Ruth P, Osswald H: The role of the BK channel in potassium homeostasis and flow-induced renal potassium excretion. Kidney Int 72: 566–573, 2007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pluznick JL, Sansom SC: BK channels in the kidney: Role in K(+) secretion and localization of molecular components. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 291: F517–F529, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Palmer LG: Potassium secretion and the regulation of distal nephron K channels. Am J Physiol 277: F821–F825, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Sorensen MV, Matos JE, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J: Colonic potassium handling. Pflugers Arch 459: 645–656, 2010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Sweiry JH, Binder HJ: Characterization of aldosterone-induced potassium secretion in rat distal colon. J Clin Invest 83: 844–851, 1989 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sorensen MV, Strandsby AB, Larsen CK, Praetorius HA, Leipziger J: The secretory KCa1.1 channel localises to crypts of distal mouse colon: Functional and molecular evidence. Pflugers Arch 462: 745–752, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Conn JW, Louis LH: Primary aldosteronism: A new clinical entity. Trans Assoc Am Physicians 68: 215–231, 1955 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Ten S, New M, Maclaren N: Clinical review 130: Addison’s disease 2001. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 2909–2922, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Torpy DJ, Stratakis CA, Chrousos GP: Hyper- and hypoaldosteronism. Vitam Horm 57: 177–216, 1999 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Tamirisa KP, Aaronson KD, Koelling TM: Spironolactone-induced renal insufficiency and hyperkalemia in patients with heart failure. Am Heart J 148: 971–978, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Rabinowitz L: Aldosterone and potassium homeostasis. Kidney Int 49: 1738–1742, 1996 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Palmer LG, Antonian L, Frindt G: Regulation of apical K and Na channels and Na/K pumps in rat cortical collecting tubule by dietary K. J Gen Physiol 104: 693–710, 1994 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Youn JH, McDonough AA: Recent advances in understanding integrative control of potassium homeostasis. Annu Rev Physiol 71: 381–401, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Stanton B, Pan L, Deetjen H, Guckian V, Giebisch G: Independent effects of aldosterone and potassium on induction of potassium adaptation in rat kidney. J Clin Invest 79: 198–206, 1987 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Muto S, Sansom S, Giebisch G: Effects of a high potassium diet on electrical properties of cortical collecting ducts from adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest 81: 376–380, 1988 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wingo CS, Seldin DW, Kokko JP, Jacobson HR: Dietary modulation of active potassium secretion in the cortical collecting tubule of adrenalectomized rabbits. J Clin Invest 70: 579–586, 1982 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Kobayashi M, Yasuoka Y, Sato Y, Zhou M, Abe H, Kawahara K, Okamoto H: Upregulation of calbindin D28k in the late distal tubules in the potassium-loaded adrenalectomized mouse kidney. Clin Exp Nephrol 15: 355–362, 2011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Xue C, Siragy HM: Local renal aldosterone system and its regulation by salt, diabetes, and angiotensin II type 1 receptor. Hypertension 46: 584–590, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Lee G, Makhanova N, Caron K, Lopez ML, Gomez RA, Smithies O, Kim HS: Homeostatic responses in the adrenal cortex to the absence of aldosterone in mice. Endocrinology 146: 2650–2656, 2005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Meneton P, Loffing J, Warnock DG: Sodium and potassium handling by the aldosterone-sensitive distal nephron: The pivotal role of the distal and connecting tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F593–F601, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Frindt G, Palmer LG: Effects of dietary K on cell-surface expression of renal ion channels and transporters. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 299: F890–F897, 2010 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Wade JB, Fang L, Coleman RA, Liu J, Grimm PR, Wang T, Welling PA: Differential regulation of ROMK (Kir1.1) in distal nephron segments by dietary potassium. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 300: F1385–F1393, 2011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kleyman TR, Myerburg MM, Hughey RP: Regulation of ENaCs by proteases: An increasingly complex story. Kidney Int 70: 1391–1392, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Makhanova N, Sequeira-Lopez ML, Gomez RA, Kim HS, Smithies O: Disturbed homeostasis in sodium-restricted mice heterozygous and homozygous for aldosterone synthase gene disruption. Hypertension 48: 1151–1159, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.USDA National Nutrient Database for Standard Reference: Release 26, 2013. Available at: http://ndb.nal.usda.gov. Accessed November 1, 2013
- 33.Makhanova N, Lee G, Takahashi N, Sequeira Lopez ML, Gomez RA, Kim HS, Smithies O: Kidney function in mice lacking aldosterone. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 290: F61–F69, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Peti-Peterdi J, Warnock DG, Bell PD: Angiotensin II directly stimulates ENaC activity in the cortical collecting duct via AT(1) receptors. J Am Soc Nephrol 13: 1131–1135, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Sorensen MV, Grossmann S, Roesinger M, Gresko N, Todkar AP, Barmettler G, Ziegler U, Odermatt A, Loffing-Cueni D, Loffing J: Rapid dephosphorylation of the renal sodium chloride cotransporter in response to oral potassium intake in mice. Kidney Int 83: 811–824, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Vallon V, Schroth J, Lang F, Kuhl D, Uchida S: Expression and phosphorylation of the Na+-Cl- cotransporter NCC in vivo is regulated by dietary salt, potassium, and SGK1. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 297: F704–F712, 2009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.van der Lubbe N, Moes AD, Rosenbaek LL, Schoep S, Meima ME, Danser AH, Fenton RA, Zietse R, Hoorn EJ: K+-induced natriuresis is preserved during Na+ depletion and accompanied by inhibition of the Na+-Cl- cotransporter. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 305: F1177–F1188, 2013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kayes-Wandover KM, Schindler RE, Taylor HC, White PC: Type 1 aldosterone synthase deficiency presenting in a middle-aged man. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86: 1008–1012, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Young DB, Paulsen AW: Interrelated effects of aldosterone and plasma potassium on potassium excretion. Am J Physiol 244: F28–F34, 1983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Martin RS, Hayslett JP: Role of aldosterone in the mechanism of renal potassium adaptation. Pflugers Arch 407: 76–81, 1986 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Vitzthum H, Seniuk A, Schulte LH, Müller ML, Hetz H, Ehmke H: Functional coupling of renal K+ and Na+ handling causes high blood pressure in Na+ replete mice. J Physiol 592: 1139–1157, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Loffing J, Zecevic M, Féraille E, Kaissling B, Asher C, Rossier BC, Firestone GL, Pearce D, Verrey F: Aldosterone induces rapid apical translocation of ENaC in early portion of renal collecting system: Possible role of SGK. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280: F675–F682, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Frindt G, Palmer LG: Apical potassium channels in the rat connecting tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 287: F1030–F1037, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nesterov V, Dahlmann A, Krueger B, Bertog M, Loffing J, Korbmacher C: Aldosterone-dependent and -independent regulation of the epithelial sodium channel (ENaC) in mouse distal nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 303: F1289–F1299, 2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Weir MR, Rolfe M: Potassium homeostasis and renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibitors. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5: 531–548, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Rabinowitz L, Castonguay TW, Rutledge JC: Aldosterone reverses potassium-induced food aversions in adrenalectomized rats. Physiol Behav 42: 137–140, 1988 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Woda CB, Bragin A, Kleyman TR, Satlin LM: Flow-dependent K+ secretion in the cortical collecting duct is mediated by a maxi-K channel. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 280: F786–F793, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Malnic G, Berliner RW, Giebisch G: Flow dependence of K+ secretion in cortical distal tubules of the rat. Am J Physiol 256: F932–F941, 1989 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Bailey MA, Cantone A, Yan Q, MacGregor GG, Leng Q, Amorim JB, Wang T, Hebert SC, Giebisch G, Malnic G: Maxi-K channels contribute to urinary potassium excretion in the ROMK-deficient mouse model of Type II Bartter’s syndrome and in adaptation to a high-K diet. Kidney Int 70: 51–59, 2006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kim GH, Masilamani S, Turner R, Mitchell C, Wade JB, Knepper MA: The thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter is an aldosterone-induced protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95: 14552–14557, 1998 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Masilamani S, Wang X, Kim GH, Brooks H, Nielsen J, Nielsen S, Nakamura K, Stokes JB, Knepper MA: Time course of renal Na-K-ATPase, NHE3, NKCC2, NCC, and ENaC abundance changes with dietary NaCl restriction. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 283: F648–F657, 2002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Weinstein AM: Potassium excretion during antinatriuresis: Perspective from a distal nephron model. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302: F658–F673, 2012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Hunter RW, Craigie E, Homer NZ, Mullins JJ, Bailey MA: Acute inhibition of NCC does not activate distal electrogenic Na+ reabsorption or kaliuresis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306: F457–F467, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Martin RS, Oszi P, Brocca S, Arrizurieta E, Hayslett JP: Failure of potassium adaptation in vivo in the colon of aldosterone-deficient rats. J Lab Clin Med 108: 241–245, 1986 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Dekel B, Nakhoul F, Abassi Z, Aviv R, Winaver J, Szylman P: Complete adaptation to chronic potassium loading after adrenalectomy: Possible humoral mechanisms. J Lab Clin Med 129: 453–461, 1997 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Malnic G, Berliner RW, Giebisch G: Distal perfusion studies: Transport stimulation by native tubule fluid. Am J Physiol 258: F1523–F1527, 1990 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Field MJ, Stanton BA, Giebisch GH: Differential acute effects of aldosterone, dexamethasone, and hyperkalemia on distal tubular potassium secretion in the rat kidney. J Clin Invest 74: 1792–1802, 1984 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rengarajan S, Lee DH, Oh YT, Delpire E, Youn JH, McDonough AA: Increasing plasma [K+] by intravenous potassium infusion reduces NCC phosphorylation and drives kaliuresis and natriuresis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 306: F1059–F1068, 2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Fodstad H, Gonzalez-Rodriguez E, Bron S, Gaeggeler H, Guisan B, Rossier BC, Horisberger JD: Effects of mineralocorticoid and K+ concentration on K+ secretion and ROMK channel expression in a mouse cortical collecting duct cell line. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 296: F966–F975, 2009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Seaton B, Ali A: Simplified manual high performance clinical chemistry methods for developing countries. Med Lab Sci 41: 327–336, 1984 [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Wagner CA, Loffing-Cueni D, Yan Q, Schulz N, Fakitsas P, Carrel M, Wang T, Verrey F, Geibel JP, Giebisch G, Hebert SC, Loffing J: Mouse model of type II Bartter’s syndrome. II. Altered expression of renal sodium- and water-transporting proteins. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 294: F1373–F1380, 2008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Loffing J, Pietri L, Aregger F, Bloch-Faure M, Ziegler U, Meneton P, Rossier BC, Kaissling B: Differential subcellular localization of ENaC subunits in mouse kidney in response to high- and low-Na diets. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 279: F252–F258, 2000 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Loffing J, Loffing-Cueni D, Valderrabano V, Kläusli L, Hebert SC, Rossier BC, Hoenderop JG, Bindels RJ, Kaissling B: Distribution of transcellular calcium and sodium transport pathways along mouse distal nephron. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 281: F1021–F1027, 2001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Loffing J, Vallon V, Loffing-Cueni D, Aregger F, Richter K, Pietri L, Bloch-Faure M, Hoenderop JG, Shull GE, Meneton P, Kaissling B: Altered renal distal tubule structure and renal Na(+) and Ca(2+) handling in a mouse model for Gitelman’s syndrome. J Am Soc Nephrol 15: 2276–2288, 2004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Pedersen NB, Hofmeister MV, Rosenbaek LL, Nielsen J, Fenton RA: Vasopressin induces phosphorylation of the thiazide-sensitive sodium chloride cotransporter in the distal convoluted tubule. Kidney Int 78: 160–169, 2010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.