Abstract
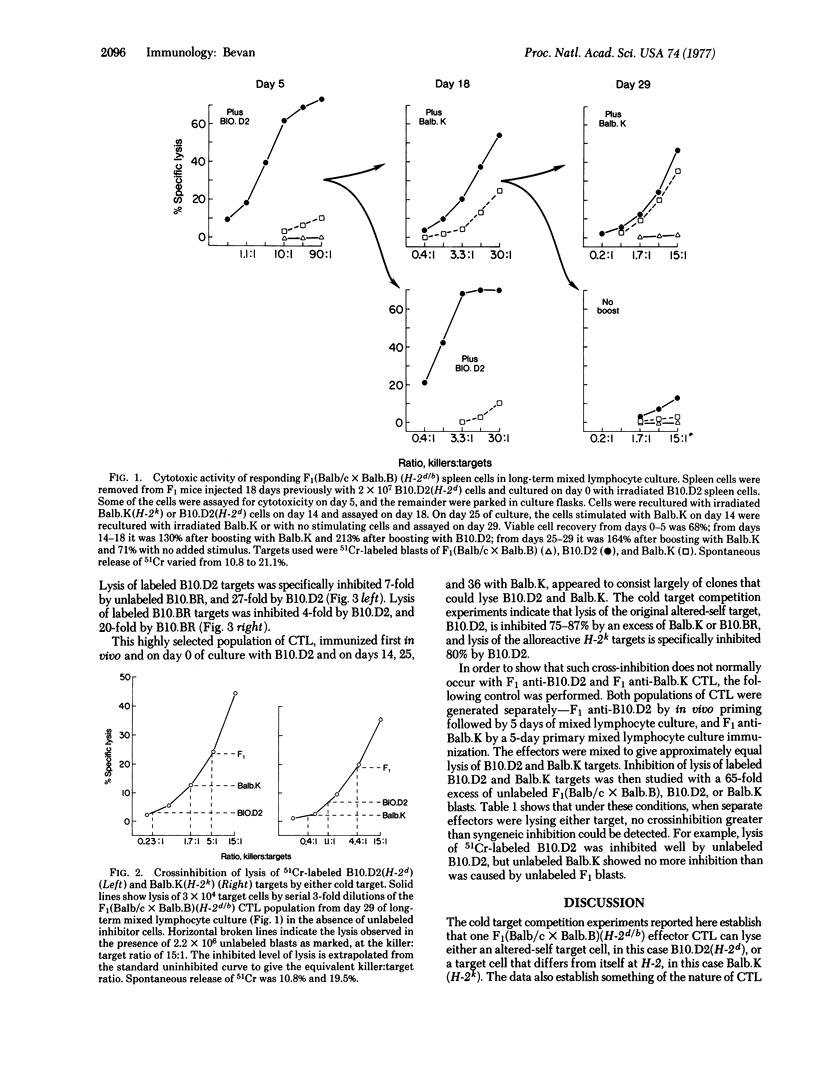
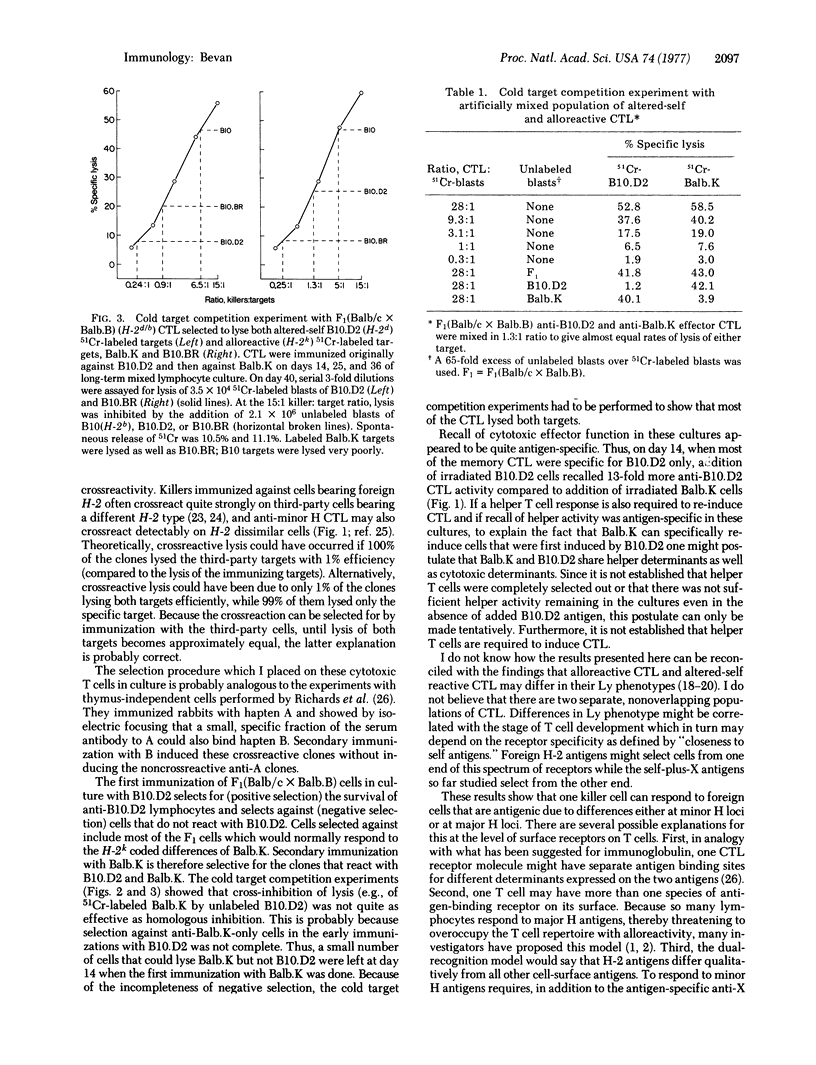
Murine cytotoxic thymus-derived lymphocytes immunized against cells bearing foreign minor histocompatibility antigens are specific for the immunizing minor antigens and for their own major H-2 antigens; they do not lyse target cells that bear the correct minor antigens plus a different H-2 haplotype. These are referred to as "altered-self" or "self-plus-X" killer cells. Alloreactive killer cells are those which respond to allogeneic cells expressing a foreign (non-self) H-2 haplotype. In this study, cytotoxic lymphocytes were immunized against minor histocompatibility differences in vivo and in vitro. These effector cells killed the immunizing altered-self target very well and showed about 1% cross-reactive lysis of an allogeneic target differing from themselves only at H-2. These cross-reactive clones were then selected for by repeated in vitro stimulation with the cells bearing foreign H-2 such that an effector population was obtained which lysed both the altered-self and the alloreactive target with the same efficiency. Cold target competition experiments established that the same killer cell could lyse either target; however, it was not determined if a killer cell uses the same receptor to respond to altered-self antigens as it does respond to foreign H-2 antigens.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bevan M. J. Alloimmune cytotoxic T cells: Evidence that they recognize serologically defined antigens and bear clonally restricted receptors. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 2):316–319. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. Cytotoxic t-cell response to histocompatibility antigens: the role of H-2. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 2):519–527. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J., Langman R. E., Cohn M. H-2 antigen-specific cytotoxic T cells induced by concanavalin A: estimation of their relative frequency. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Mar;6(3):150–156. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bevan M. J. The major histocompatibility complex determines susceptibility to cytotoxic T cells directed against minor histocompatibility antigens. J Exp Med. 1975 Dec 1;142(6):1349–1364. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.6.1349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binz H., Wigzell H. Shared idiotypic determinants on B and T lymphocytes reactive against the same antigenic determinants. II. Determination of frequency and characteristics of idiotypic T and B lymphocytes in normal rats using direct visualization. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1218–1230. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Functional subclasses of T-lymphocytes bearing different Ly antigens. I. The generation of functionally distinct T-cell subclasses is a differentiative process independent of antigen. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1376–1389. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1376. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor H., Boyse E. A. Regulation of cellular and humoral immune responses by T-cell subclasses. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1977;41(Pt 1):23–32. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1977.041.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Blanden R. V., Zinkernagel R. M. Specificity of virus-immune effector T cells for H-2K or H-2D compatible interactions: implications for H-antigen diversity. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:89–124. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00198.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ford W. L., Simmonds S. J., Atkins R. C. Early cellular events in a systemic graft-vs.-host reaction. II. Autoradiographic estimates of the frequency of donor lymphocytes which respond to each Ag-B-determined antigenic complex. J Exp Med. 1975 Mar 1;141(3):681–696. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.3.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Kelly F., Avner P., Gachelin G. Sensitivity of H-2-less target cells and role of H-2 in T-cell-mediated cytolysis. Nature. 1976 Aug 19;262(5570):693–695. doi: 10.1038/262693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon R. D., Simpson E., Samelson L. E. In vitro cell-mediated immune responses to the male specific(H-Y) antigen in mice. J Exp Med. 1975 Nov 1;142(5):1108–1120. doi: 10.1084/jem.142.5.1108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heber-Katz E., Wilson D. B. Sheep red blood cell-specific helper activity in rat thoracic duct lymphocyte populations positively selected for reactivity to specific strong histocompatibility alloantigens. J Exp Med. 1976 Mar 1;143(3):701–706. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.3.701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz D. H., Benacerraf B. The function and interrelationships of T-cell receptors, Ir genes and other histocompatibility gene products. Transplant Rev. 1975;22:175–195. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1975.tb01559.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kisielow P., Hirst J. A., Shiku H., Beverley P. C., Hoffman M. K., Boyse E. A., Oettgen H. F. Ly antigens as markers for functionally distinct subpopulations of thymus-derived lymphocytes of the mouse. Nature. 1975 Jan 17;253(5488):219–220. doi: 10.1038/253219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl F., Peck A. B., Bach F. H. Specificity of cell-mediated lympholysis for public and private H-2 determinants. Scand J Immunol. 1975 Sep;4(5-6):541–553. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1975.tb02660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl K. F., Wilson D. B. Histocompatibility antigen-activated cytotoxic T lymphocytes. II. Estimates of the frequency and specificity of precursors. J Exp Med. 1977 Mar 1;145(3):508–522. doi: 10.1084/jem.145.3.508. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pang T., McKenzie I. F., Blanden R. V. Cooperation between mouse T-cell subpopulations in the cell-mediated response to a natural poxvirus pathogen. Cell Immunol. 1976 Oct;26(2):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(76)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peavy D. L., Pierce C. W. Cell-mediated immune responses in vitro. II. Simultaneous generation of cytotoxic lymphocyte responses to two sets of alloantigens of limited cross-reactivity. J Immunol. 1975 Dec;115(6):1515–1520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. F., Konigsberg W. H., Rosenstein R. W., Varga J. M. On the specificity of antibodies. Science. 1975 Jan 17;187(4172):130–137. doi: 10.1126/science.46122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shearer G. M., Rehn T. G., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M. Role of the murine major histocompatibility complex in the specificity of in vitro T-cell-mediated lympholysis against chemically-modified autologous lymphocytes. Transplant Rev. 1976;29:222–246. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1976.tb00203.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Rosenthal A. S. Function of macrophages in antigen recognition by guinea pig T lymphocytes. II. Role of the macrophage in the regulation of genetic control of the immune response. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1213–1229. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiku H., Takahashi T., Bean M. A., Old L. J., Oettgen H. F. Ly phenotype of cytotoxic T cells for syngeneic tumor. J Exp Med. 1976 Oct 1;144(4):1116–1120. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.4.1116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skinner M. A., Marbrook J. An estimation of the frequency of precursor cells which generate cytotoxic lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1976 Jun 1;143(6):1562–1567. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.6.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


