Abstract
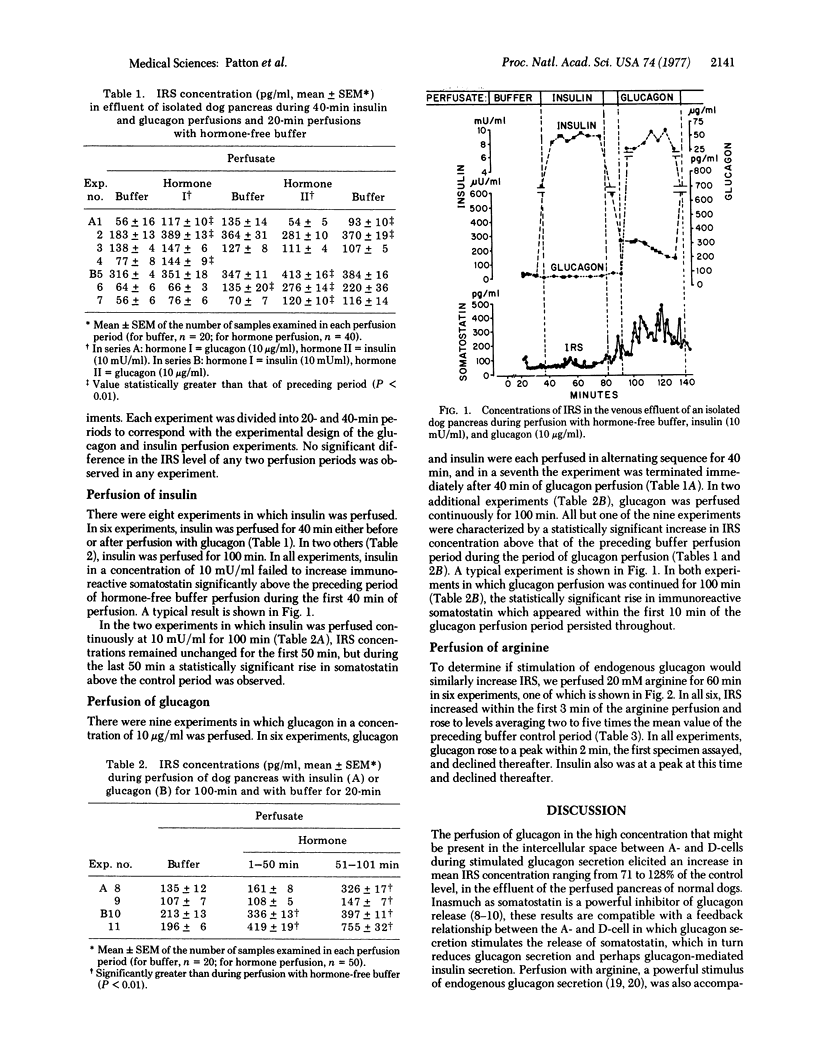
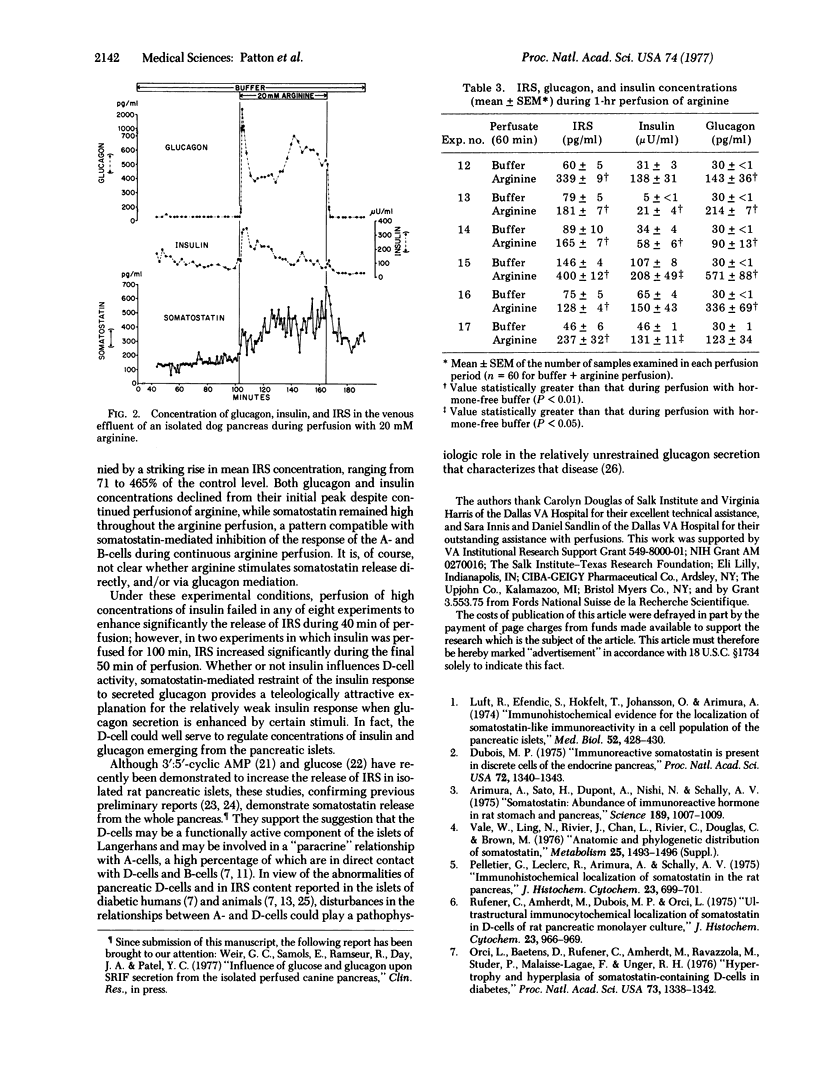
The location of the somatostatin-containing D-cells of the pancreatic islets between the A- and B-cells suggests that their function might be to inhibit insulin and/or glucagon secretion by these neighboring cells. To determine if insulin and/or glucagon, in concentrations that might be present in the extracellular space surrounding the D-cells, stimulate immunoreactive somatostatin (IRS) release, we perfused 10 microng of glucagon or 10 milliunits of insulin per ml in 11 isolated dog pancreases, for 40 min in seven experiments and for 100 min in four experiments. In eight of the nine experiments in which glucagon was perfused, a prompt and significant rise in mean IRS release, ranging from 71 to 128% above the control level, was observed. In the eight experiments in which insulin was perfused. IRS did not increase during the first 40 min; in the two 100-min insulin experiments, it did rise during the final 50 min, however. To determine the effect of an A- and B-cell secretogogue on IRS release, we perfused 20 mM arginine for 60 min in six experiments. In all, IRS rose within 3 min and reached a level 71-465% above the control, remaining significantly elevated throughout the perfusion, while glucagon and insulin rose to peak levels at 2 min and then declined somewhat despite continuing arginine perfusion. The results indicate that perfusion of the normal dog pancreas with high doses of glucagon or arginine is accompanied by a prompt increase in IRS release and are compatible with a local feedback circuit involving A- and D-cells. Insulin appears not to augment IRS release, at least not promptly, but IRS stimulated by local endogenous glucagon could inhibit the B-cell response to locally secreted glucagon and thereby influence the composition of the insulin/glucagon secretion mixture.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alberti K. G., Christensen N. J., Christensen S. E., Hansen A. P., Iversen J., Lundbaek K., Seyer-Hansen K., Orskov H. Inhibition of insulin secretion by somatostatin. Lancet. 1973 Dec 8;2(7841):1299–1301. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(73)92873-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arimura A., Sato H., Dupont A., Nishi N., Schally A. V. Somatostatin: abundance of immunoreactive hormone in rat stomach and pancreas. Science. 1975 Sep 19;189(4207):1007–1009. doi: 10.1126/science.56779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assan R., Rosselin G., Dolais J. Effets sur la glucagonémie des perfusions et ingestions d'acides aminés. Journ Annu Diabetol Hotel Dieu. 1967;7:25–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barden N., Alvarado-Urbina G., Côté J. P., Dupont A. Cyclic AMP-dependent stimulation of somatostatin secretion by isolated rat islets of Langerhans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Aug 9;71(3):840–844. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90907-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. P. Immunoreactive somatostatin is present in discrete cells of the endocrine pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1340–1343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbert V., Lau K. S., Gottlieb C. W., Bleicher S. J. Coated charcoal immunoassay of insulin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1965 Oct;25(10):1375–1384. doi: 10.1210/jcem-25-10-1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iversen J., Miles D. W. Evidence for a feedback inhibition of insulin on insulin secretion in the isolated, perfused canine pancreas. Diabetes. 1971 Jan;20(1):1–9. doi: 10.2337/diab.20.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koerker D. J., Ruch W., Chideckel E., Palmer J., Goodner C. J., Ensinck J., Gale C. C. Somatostatin: hypothalamic inhibitor of the endocrine pancreas. Science. 1974 Apr 26;184(4135):482–484. doi: 10.1126/science.184.4135.482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luft R., Efendic S., Hökfelt T., Johansson O., Arimura A. Immunohistochemical evidence for the localization of somatostatin--like immunoreactivity in a cell population of the pancreatic islets. Med Biol. 1974 Dec;52(6):428–430. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer C. H., Tunbridge W. M., Carr D., Yeomans L., Lind T., Coy D. H., Bloom S. R., Kastin A., Mallinson C. N., Besser G. M. Effects of growth-hormone release-inhibiting hormone on circulating glucagon, insulin, and growth hormone in normal, diabetic, acromegalic, and hypopituitary patients. Lancet. 1974 Apr 20;1(7860):697–701. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(74)92903-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Baetens D., Rufener C., Amherdt M., Ravazzola M., Studer P., Malaisse-Lagae F., Unger R. H. Hypertrophy and hyperplasia of somatostatin-containing D-cells in diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1338–1342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H. Functional subdivision of islets of Langerhans and possible role of D cells. Lancet. 1975 Dec 20;2(7947):1243–1244. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(75)92078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel Y. C., Weir G. C. Increased somatostatin content of islets from streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1976 Mar;5(2):191–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1976.tb02832.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton G. S., Dobbs R., Orci L., Vale W., Unger R. H. Stimulation of pancreatic immunoreactive somatostatin (IRS) release by glucagon [proceedings]. Metabolism. 1976 Nov;25(11 Suppl 1):1499–1499. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(76)80177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patton G. S., Ipp E., Dobbs R. E., Orci L., Vale W., Unger R. H. Response of pancreatic immunoreactive somatostatin to arginine. Life Sci. 1976 Dec 15;19(12):1957–1959. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(76)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier G., Leclerc R., Arimura A., Schally A. V. Letter: Immunohistochemical localization of somatostatin in the rat pancreas. J Histochem Cytochem. 1975 Sep;23(9):699–702. doi: 10.1177/23.9.1100709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauder P., McIntosh C., Arends J., Arnold R., Frerichs H., Creutzfeldt W. Somatostatin and insulin release from isolated rat pancreatic islets stimulated by glucose. FEBS Lett. 1976 Oct 1;68(2):225–227. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(76)80441-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Aguilar-Parada E., Müller W. A., Eisentraut A. M. Studies of pancreatic alpha cell function in normal and diabetic subjects. J Clin Invest. 1970 Apr;49(4):837–848. doi: 10.1172/JCI106297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unger R. H., Orci L. Possible roles of the pancreatic D-cell in the normal and diabetic states. Diabetes. 1977 Mar;26(3):241–244. doi: 10.2337/diab.26.3.241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YALOW R. S., BERSON S. A. Immunoassay of endogenous plasma insulin in man. J Clin Invest. 1960 Jul;39:1157–1175. doi: 10.1172/JCI104130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



