Abstract
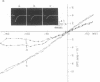
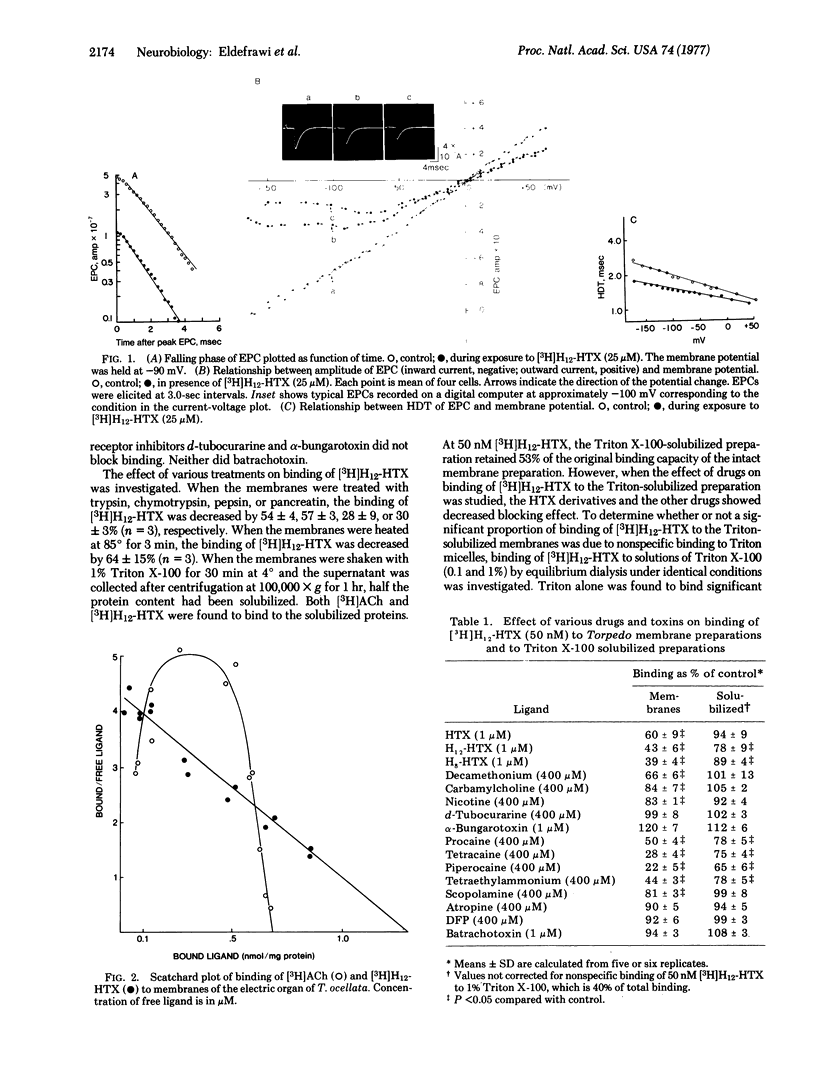
Histrionicotoxin from the Colombian frog Dendrobates histrionicus and its perhydro derivative reversibly block the acetylcholine-sensitive ion conductance system in frog neuromuscular preparations. The perhydro derivative and [3H]perhydrohistrionicotoxin, like histrionicotoxin, caused a significant decrease in the peak amplitude of the end-plate current and shortened its rise time and half-decay time. In membrane preparations from Torpedo electroplax, [3H]perhydrohistrionicotoxin bound reversibly to a limited number of high-affinity sites [dissociation constant, (KD) = 0.4 micronM]. The ratio of perhydrohistrionicotoxin to acetylcholine binding sites in these membrane preparations approached 2. Histrionicotoxins, local anesthetics, and certain cholinergic agonists inhibited binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin. Binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin to membranes was decreased by heat or treatment with proteases. Treatment of membranes with Triton X-100 solubilized acetylcholine binding proteins and apparently also perhydrohistrionicotoxin-binding proteins. However, the detergent Triton X-100 also bound [3H]perhydrohistrionicotoxin. This nonspecific binding was not saturable and complicated studies on the antagonism by drugs of binding of [3H]perhydrohistrionicotoxin. In solubilized preparations the binding protein for acetylcholine could be removed by affinity chromatography or immunoprecipitation without affecting binding of perhydrohistrionicotoxin. Sephadex chromatography also separated acetylcholine- from perhydrohistrionicotoxin-binding proteins. Perhydrohistrionicotoxin did not bind significantly to purified acetylcholine-receptor protein but presumably bound to an ion conductance modulator protein that was associated with the acetylcholine-receptor in intact membrane and readily separable from the receptor protein after solubilization.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adler M., Albuquerque E. X. An analysis of the action of atropine and scopolamine on the end-plate current of frog sartorius muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1976 Feb;196(2):360–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Barnard E. A., Chiu T. H., Lapa A. J., Dolly J. O., Jansson S. E., Daly J., Witkop B. Acetylcholine receptor and ion conductance modulator sites at the murine neuromuscular junction: evidence from specific toxin reactions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):949–953. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albuquerque E. X., Kuba K., Daly J. Effect of histrionicotoxin on the ionic conductance modulator of the cholinergic receptor: a quantitative analysis of the end-plate current. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 May;189(2):513–524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Karle I., Myers C. W., Tokuyama T., Waters J. A., Witkop B. Histrionicotoxins: roentgen-ray analysis of the novel allenic and acetylenie spiroalkaloids isolated from a Colombian frog, Dendrobates histrionicus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Aug;68(8):1870–1875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.8.1870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolly J. O., Albuquerque E. X., Sarvey J., Mallick B., Barnard E. A. Binding of perhydro-histrionicotoxin to the postsynaptic membrane of skeletal muscle in relation to its blockage of acetylcholine-induced depolarization. Mol Pharmacol. 1977 Jan;13(1):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J., Beyer W. B., Elderfrawi A. T., Elderfrawi M. E. Molecular weight of the acetylcholine receptors of electric organs and the effect of Triton X-100. J Biol Chem. 1975 Aug 10;250(15):6101–6106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Purification and molecular properties of the acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo electroplax. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):362–373. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90462-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T., Wilson D. B. Tryptophan and cystein residues of the acetylcholine receptors of Torpedo species. Relationship to binding of cholinergic ligands. Biochemistry. 1975 Sep 23;14(19):4304–4310. doi: 10.1021/bi00690a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eldefrawi M. E., Fertuck H. C. A rapid method for the preparation of (125I)alpha-bungarotoxin. Anal Biochem. 1974 Mar;58(1):63–70. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90441-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grünhagen H. H., Changeux J. P. Studies on the electrogenic action of acetylcholine with Torpedo marmorata electric organ. IV. Quinacrine: a fluorescent probe for the conformational transitions of the cholinergic receptor protein in its membrane-bound state. J Mol Biol. 1976 Sep 25;106(3):497–516. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90249-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz B., Miledi R. The effect of procaine on the action of acetylcholine at the neuromuscular junction. J Physiol. 1975 Jul;249(2):269–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1975.sp011015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klett R. P., Fulpius B. W., Cooper D., Smith M., Reich E., Possani L. D. The acetylcholine receptor. I. Purification and characterization of a macromolecule isolated from Electrophorus electricus. J Biol Chem. 1973 Oct 10;248(19):6841–6853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuba K., Albuquerque E. X., Daly J., Barnard E. A. A study of the irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor, diisopropylfluorophosphate, on time course of end-plate currents in frog sartorius muscle. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1974 May;189(2):499–512. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapa A. J., Albuquerque E. X., Sarvey J. M., Daly J., Witkop B. Effects of histrionicotoxin on the chemosensitive and electrical properties of skeletal muscle. Exp Neurol. 1975 Jun;47(3):558–580. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(75)90088-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeno T. Analysis of sodium and potassium conductances in the procaine end-plate potential. J Physiol. 1966 Apr;183(3):592–606. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1966.sp007886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamee M. G., Weill C. L., Karlin A. Purification of acetylcholine receptor from Torpedo californica and its incorporation into phospholipid vesicles. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1975 Dec 30;264:175–182. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1975.tb31482.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelson D. M., Raftery M. A. Purified acetylcholine receptor: its reconstitution to a chemically excitable membrane. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Dec;71(12):4768–4772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.12.4768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. D., Eldefrawi M. E., Eldefrawi A. T. Isolation of acetylcholine receptors. Annu Rev Pharmacol. 1972;12:19–34. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.12.040172.000315. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsen R. W., Meunier J. C., Changeux J. P. Progress in the purification of the cholinergic receptor protein from Electrophorus electricus by affinity chromatography. FEBS Lett. 1972 Nov 15;28(1):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(72)80686-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders D. B., Schleifer L. S., Eldefrawi M. E., Norcross N. L., Cobb E. E. An immunologically induced defect of neuromuscular transmission in rats and rabbits. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1976;274:319–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1976.tb47695.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Raftery M. A. Purification of acetylcholine receptors from Torpedo californica electroplax by affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1973 Feb 27;12(5):852–856. doi: 10.1021/bi00729a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shamoo A. E., Eldefrawi M. E. Carbamylcholine and acetylcholine-sensitive, cation-selective ionophore as part of the purified acetylcholine receptor. J Membr Biol. 1975 Dec 4;25(1-2):47–63. doi: 10.1007/BF01868567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinbach A. B. Alteration by xylocaine (lidocaine) and its derivatives of the time course of the end plate potential. J Gen Physiol. 1968 Jul;52(1):144–161. doi: 10.1085/jgp.52.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M., Changeux J. P. Binding of Naja nigricollis (3H)alpha-toxin to membrane fragments from Electrophorus and Torpedo electric organs. 3. Effects of local anaesthetics on the binding of the tritiated alpha-neurotoxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1974 Jan;10(1):35–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]